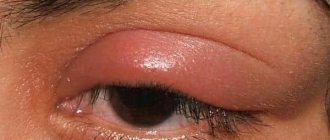
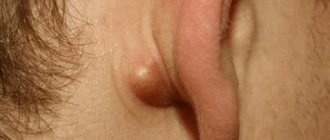
For some, the formation of swelling is painless and unnoticeable. But there are situations in which swelling under the armpit is the first symptom of dangerous infections or the development of diseases.
In any case, an armpit with various pathological changes is a good reason to consult a doctor. Regardless of the pain, you should not hesitate to undergo a medical examination.
Liposarcoma - what is it?
The content of the article
Liposarcoma (eng. Liposarcoma) is a cancer of soft tissue. Of all soft tissue sarcomas that occur in adults, liposarcoma accounts for about 20%.
The change can develop at different ages. Pediatric liposarcoma is very rare, but possible. These types of tumors most often occur in people between 50 and 60 years of age.
Both men and women can suffer from liposarcoma, however, the disease is more common in women.
Liposarcoma
Causes of swelling under the armpit
Such processes can occur in every person, regardless of gender and age. The most common reasons for change may be:
- Wearing uncomfortable, tight clothing,
- Neglect of personal hygiene rules,
- Swelling of the skin in the armpit area as a result of injury,
- Increased physical activity and sweating
- Allergy to personal hygiene products (gels, creams),
- Constant use of antiperspirants
- Allergy to drug treatment.
Among the more dangerous reasons are the following:
- Inflammatory processes of the sweat gland, occurring as a result of blockage of the hair follicles and the formation of purulent abscesses.
- An enlarged lymph node, which causes the appearance of benign and malignant neoplasms.
- Proliferation of axillary lymph nodes as a signal of a malignant tumor of internal organs.
- Benign tumors near nerve nodes.
A caring attitude towards yourself will help you identify health problems in time and receive qualified, effective help.
Liposarcoma - causes and types
Liposarcoma develops when certain mutations cause fat cells to grow uncontrollably. However, what the exact causes of this type of genetic disorder are has not yet been established.
- Local sarcoma.
The most common tumor type is well-differentiated liposarcoma, which is characterized by local malignancy. This means that the tumor can invade adjacent healthy tissue, but overall it has a very low propensity for distant metastasis. Among its most characteristic features is the fact that it has an extremely high tendency to relapse. - Liposarcoma of the mucous membrane.
Another type of liposarcoma is mucosal liposarcoma, which is now associated with round cell liposarcoma tumor. This soft tissue sarcoma, in turn, is known for the fact that it often leads to distant metastases.
In addition to those listed, there is also multiform liposarcoma, also called polymorphic. This is a fairly rare type of sarcoma and is known to be extremely metastatic. And undetermined liposarcoma, since it has the characteristics of all the previously mentioned types of liposarcoma.
Symptoms of axillary lymphadenitis
The inflammatory process in the regional axillary lymph nodes is isolated and, as a rule, is characterized by a catarrhal or purulent course. Below are the most common clinical pictures of inflammation of the axillary lymph nodes.
- Acute catarrhal form. This inflammatory process is more common than others and often occurs in a mild form. It is characterized by severe pain, enlarged lymph nodes and their hardening. With catarrh, the lymph nodes are easily separated and do not lose their mobility. In the axillary area, hyperemia and mild swelling may develop. The patient may notice worsening of the condition, discomfort during shoulder abduction, and mild low-grade fever.
- Purulent form. This type of inflammatory process poses the greatest danger due to the formation of a purulent focus, which can be represented by single or multiple abscesses. The lymph node itself loses its mobility and becomes painful and swollen. Nearby tissues are sharply hyperemic and may be subject to alteration or melting. Possible fusion of lymph nodes with the skin.
- Chronic course of lymphadenitis. Sluggish inflammatory processes occur quite often, in which the lymph node under the arm becomes inflamed when the immune system is weakened and the body’s resistance to various infectious agents is reduced. Symptoms in this form are mild, the lymph nodes are mobile, but there is slight pain.
Liposarcoma - symptoms
With liposarcoma, symptoms depend both on the type and where exactly the lesion develops. It is possible—especially if the patient's tumor is growing very slowly—that symptoms of liposarcoma will not be present at all for a very long time.
However, possible signs of liposarcoma include:
- Pain. Whether liposarcoma hurts depends on the location and size of the lesion. Pain may occur, for example, in people who develop abdominal liposarcoma - when the tumor reaches a significant size, it can press on nearby organs and cause discomfort or pain.
- Thickening under the skin. Most often, liposarcoma is found in the extremities; for example, a tumor may develop on the thigh under the skin; in addition, liposarcoma is also possible on the back.
- Gastrointestinal disorders - constipation, which can occur, among other things, in patients who develop a retroperitoneal tumor.
- General symptoms of cancer. Among which, weight loss or a feeling of general, significant weakness are especially common.
Causes of inflammation of the lymph nodes
The most common cause of lymphadenitis is staphylococcal, streptococcal infection, as well as E. coli. If the body is weakened by a large number of pathogenic bacteria, then the lymphatic system simply cannot cope with them. Therefore, there is an accumulation of microorganisms in the lymph nodes, as a result of which they give an inflammatory reaction. Factors contributing to inflammation of the lymph nodes can be considered pathologies of the mammary glands, colds and respiratory diseases, cancer, furunculosis, excessive work of the sweat glands, allergies, intoxications and infections.
It happens that only one node becomes inflamed, and sometimes the inflammation affects several lymph nodes throughout the body. The enlargement of the nodes can be quite strong, as a result of which they become sensitive and painful. The nodes located in the armpit begin to ache, swell, and turn red. Inflammation may be accompanied by general weakness, drowsiness, headache, nausea, and vomiting.
Liposarcoma - diagnosis
Patients with different types of tumors under the skin often wonder how to recognize liposarcoma? To make a diagnosis, just one examination is not enough, since the tumor is very similar to a harmless lipoma. Therefore, first of all, in order to distinguish the quality of the tumor, the dermatologist prescribes magnetic resonance imaging.
Magnetic resonance imaging
This study allows, among other things, to suspect liposarcoma, however, the diagnosis requires clarification using a histopathological examination that reveals cancer cells. First of all, histopathology allows us to accurately determine whether the change described in the studies is liposarcoma or lipoma. In addition, microscopic tests allow you to diagnose a specific type of tumor, identifying, for example, liposarcoma, myxoids.
Knowing the type of change is important to determine the patient's prognosis for cure. Material for histopathological examination is obtained by biopsy.
Infection as a cause of swelling under the armpit
Damage to the body by infections often provokes the appearance of edema and swelling. Among the most common infections are:
- Measles,
- Flu,
- Sore throat, ARVI,
- Tularemia,
- Brucellosis,
- Lupus erythematosus,
- Fungal microorganisms.
Often, diseases that cause swelling under the armpit are caused by low immunity and endocrine system disorders. The lack of vitamins and beneficial microelements in the body is the impetus for the development of various types of edema and hormonal imbalances.
Liposarcoma - treatment
Surgery plays a fundamental role in the treatment of liposarcoma. Patients who develop a tumor, for example, on the hip, often fear having to amputate the entire limb. Unfortunately, this risk exists, but in general, amputations are only carried out when this is the final possible solution. If possible, conservative procedures are considered first.
The most important thing in the treatment of these changes is their complete removal with a supply of healthy tissue.
In addition to surgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy are used. They are especially useful when a patient's existing tumor has invaded important structures, such as major blood vessels, and the tumor cannot be completely removed. In this case, radiation therapy is effective. Then, when the patient develops multiple metastases, chemotherapy becomes the main treatment option.
Chemotherapy for the treatment of liposarcoma
Treatment of lymphadenitis
The main thing that the patient should know and take into account is the inadmissibility of self-treatment. Under no circumstances should you try to stop the disease yourself. Only a doctor prescribes the necessary treatment tactics, and it consists of conducting the correct etiotropic and pathogenetic therapy. As a rule, all efforts of the doctor and the patient are directed toward eliminating the source of inflammation that provoked the development of axillary lymphadenitis. Most often, the doctor prescribes anti-inflammatory drugs and prescribes antibacterial therapy. It is also advisable to use compresses with Dimexide, physiotherapeutic treatment, and immunomodulators. All this helps the body to get stronger and cope with the disease that has arisen. If a malignant process arises and develops and is accompanied by axillary lymphadenitis, then the patient must undergo a course of chemotherapy or surgery will be indicated.
Liposarcoma - prognosis
The prognosis for liposarcoma depends primarily on the type of lesion. For example, people with well-differentiated liposarcoma can have a 5-year survival rate of up to 90-100% after appropriate treatment. Patients with liposarcoma multiforme, which is more likely to metastasize, have a much worse chance.
Another aspect to consider is the propensity for recurrence, which also varies depending on the type of tumor. Relapse of liposarcoma can occur after different times; it happens that the tumor recurs even several years after the end of treatment. This is due to the fact that lipomas grow very slowly.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
Diseases that cause swelling
The armpit is an area where a large number of lymph nodes and nerve nodes accumulate.
Any changes in the armpit may occur with the development of the following diseases:
- The most likely cause is hidradenitis. The inflammatory process affecting the sweat glands is more common in men. This can occur due to excessive sweating, lack of proper hygiene, excess weight and diabetes. Without appropriate treatment, hidradenitis becomes chronic.
- Dermatitis, eczema or other skin diseases contribute to the development of armpit tumors in men.
- Wounds and injuries caused by careless shaving can cause swelling.
- Boils and purulent inflammations are accompanied by the appearance of swelling in the armpit area.
- The development of viral bacteria, infections such as syphilis, chickenpox, tuberculosis.
- The appearance of a benign tumor (lipoma) is also one of the common reasons why a lymph node can become swollen in both women and men.
Read also: Swelling of the legs during pregnancy