Symptoms of warts
Warts look like nodules (papules) with a diameter of 0.2-0.8 cm, often located in groups.
The surface of the formation is covered with layers and cracks, the skin pattern on the wart disappears. The color of the papule varies from pink to brown, but may not differ from the color of healthy skin. The nodules do not hurt, but when squeezed, some patients report pain in this area. If warts are located on the periungual ridges, deformation of the nail plate may occur. When the formation is localized on the sole, pain is felt while walking; in the case of extensive growth of plantar warts, deformation of the foot may develop.
Recurrence of warts: what to do?
“The cause of warts is human papillomavirus type 1 or 2. For many patients, warts no longer appear after removal. This is possible if HPV is present in the body in small quantities and the immune system can easily cope with it. But if the virus continues to multiply, the warts will appear again. Therefore, an integrated approach is important in the fight against warts. An HPV test is necessary to determine the type of virus and its amount in the body. It is also important to determine the cause of decreased immunity. In some cases, during relapses, interferon drugs and antiviral drugs are prescribed. To avoid a relapse, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle, be sure to wear shoes in public places (in the bathhouse, sauna, swimming pool), and fight sweaty feet.”
Yuzup Irina Borisovna
expert
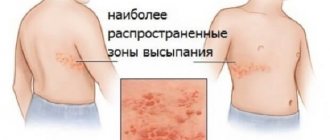
The most common localizations of warts:
- face;
- Hands;
- palms;
- fingers and toes;
- Feet;
- shins;
- knees.
Warts often appear on the face. Photo: kwanchaichaiudom / freepik.com
Factors contributing to infection
Whether a person becomes infected or not depends on his immune system. Most people are not susceptible to the influence of an infectious agent due to the presence of antiviral resistance due to intense cellular immunity. There are a number of factors that contribute to infection. These include:
- frequent visits to places with large crowds of people, high humidity (this applies to lovers of baths, saunas, swimming pools);
- indiscriminate change of sexual partners;
- microtraumas, abrasions due to wearing tight shoes or work (washing, cooking);
- some types of professions - this applies to workers in meat enterprises and poultry factories, the fish processing industry (high risk of becoming infected with HPV-7);
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules leads to autoinoculation, self-infection from the original source;
- violations of the body's immune defense: hereditary and acquired;
- If the expectant mother is infected, the newborn will become infected during childbirth.
If you notice symptoms of HPV, you should seek help from a doctor. Treatment is provided by a dermatologist, proctologist and oncologist.
Condylomas have an elongated shape, a thin base and stalk, and appear in the anorectal, genital, and pubic areas. They often have erosion. The wound may bleed blood, ichor, or pus with an unpleasant odor. The mucous membrane around the growths is healthy. The color may not differ from healthy tissue.
What can a wart be confused with?
Various strains of the human papillomavirus lead to the appearance of not only warts, but also other benign formations of the skin and mucous membranes: papillomas and condylomas.
How to distinguish a wart from a papilloma?
“Warts are often cone-shaped or round in shape, they are firm to the touch, and are usually flesh-colored.
Diameter - up to 10 mm, in rare cases - up to 1 cm. They are dry on top and have a root. Papillomas are characterized by the absence of a root, the presence of a stalk, their diameter is on average 5-10 mm, and their color ranges from flesh-colored to dirty brown. Papillomas appear most often on the face, neck, armpits and other natural folds. Warts are most often located on the face, hands, and soles of the feet and are considered benign. Papillomas can grow quickly, and in some cases they can become malignant.” Yuzup Irina Borisovna
expert
Papilloma is a small soft skin growth of flesh-colored or brownish color. Papillomas are often located in groups, and their number gradually increases. The outgrowths can be round or irregular in shape, sometimes resembling a head of cauliflower. Papillomas often grow on a thin stalk, due to which they can look like a hanging drop. The formation has the color of unchanged skin, sometimes brownish. Papillomas differ from warts by the presence of a thin stalk, a bumpy surface, and location in the armpits, genitals, chest, back, neck, and on the mucous membranes.
Condylomas are pointed pink formations of the skin and mucous membranes. They are located on the mucous membrane of the urethra, vagina, cervix, and on the skin in the genital area and anus. Condylomas are considered a sexually transmitted disease (STD) and can affect both men and women. Unlike warts and papillomas, condylomas can cause itching, burning, frequent urination, and discomfort during sexual intercourse. The danger of genital warts lies in the risk of their degeneration into a malignant tumor⁴.
A wart can also be easily confused with skin conditions not related to the human papillomavirus. Such diseases may be:
- Molluscum contagiosum. This is a viral infection that manifests itself as skin rashes in the form of multiple hemispherical nodules of pinkish-orange color. The rashes do not hurt, but are accompanied by intense itching. Inside the nodule there is a white pasty mass.
Molluscum contagiosum. It can be confused with a wart. Source: CC0 Public Domain
- Basalioma. This is one of the types of skin cancer. As a rule, it develops in older people. Basalioma is usually located on an open part of the body: on the face, neck, scalp. It can be presented as a nodule or plaque and is easily damaged and bleeds.
- Lichen planus. This disease is characterized by a confluent red rash. The rashes are flat, often have an irregular shape, and can occur on the mucous membranes.
Are toads to blame? Why do warts appear in children?
Anoint them with celandine... Or maybe garlic? Or take magnesium internally?... People go to great lengths to get rid of them. We are talking about the treatment of warts. Are the traditional medicine methods that the Internet is replete with justified, or is it still better to consult a specialist?
We talked about what warts are, why they occur, how to treat them correctly and prevent their appearance with Vladislav Leonidovich Sheinkman, candidate of medical sciences, dermatovenereologist at the Expert Tula Clinic.
— Vladislav Leonidovich, what are warts and what types of warts are they?
Warts are an infectious pathology caused by the human papillomavirus. There are several varieties of them. These are vulgar (or ordinary), flat, plantar warts, genital warts. Molluscum contagiosum can be included in this group.
Read the material on the topic: What is herpes? How to recognize it and cure it?
— What is the difference between warts and other neoplasms? For example, can a wart be confused with a mole?
They differ both in appearance and microscopically. The average person may confuse a wart and a mole, but a dermatologist cannot.
Therefore, when any formations appear on the skin, in order to avoid misdiagnosis, you should, firstly, always contact a dermatologist, and secondly, never self-medicate (which, unfortunately, often occurs in practice).
- What causes warts to appear?
The causes of warts are numerous. This is a weakening of the immune system; the presence of microtraumas, cuts, cracks in the skin; sweating of the hands (if warts are on the hands); failure to comply with personal hygiene rules; bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol); unbalanced diet, hypovitaminosis; non-compliance with sleep and rest schedules; some hormonal disorders; living in regions with unfavorable environmental conditions.
Warts are viral in nature and can be infected. This is possible through a handshake, using other people's things and personal hygiene products (for example, clothes, gloves, manicure accessories), in public places (transport, various institutions, swimming pools, beaches, etc.).
Genital warts are classified as sexually transmitted diseases. Therefore, transmission of the virus in this case occurs through sexual contact.
Read material on the topic: Cytomegalovirus, toxoplasmosis, syphilis, hepatitis B, rubella... What are the dangers of TORCH infections?
— How does the papilloma virus enter a child’s body?
Through microdamages on the skin (this is the “entry gate” for the virus). Children can have warts on their fingers and generally on their hands and feet. In adults, the same location, plus the genital area. Having appeared in one place, warts have a tendency to spread to other areas of the skin.
— Many people are carriers of the human papillomavirus, but not everyone develops warts. Why do some children and adults get warts and others do not?
Indeed, it happens that a person will never have warts in his entire life. As I said earlier, there is a connection between the state of immunity (both general and local) and the appearance of warts. The presence of concomitant diseases and environmental factors is important. For example, if a child often suffers from acute respiratory infections, his antiviral immunity is weakened, and the body “meets” the human papillomavirus, then the risk of infecting the child with it increases.
Read the material on the topic: Are unvaccinated children the healthiest?
— What is the incubation period for warts?
It ranges from several days to several months.
— Various forums on the Internet sometimes offer exotic methods of treating warts. For example, there are those who claim that you can get rid of warts with the help of celandine. Others say that an apple that needs to be buried in the ground will help. Are traditional methods of treating warts really effective?
The treatment of warts is based on destructive methods (i.e. methods aimed at destroying them).
Traditional methods based on destruction can help eliminate the wart. The problem is that, unlike standardized medical removal methods, when using traditional methods there is a possibility of both under-treating and “overdoing” when performing the removal procedure. In the first case, the infectious tissue of the wart will not be completely removed, and in the second there will be excessive tissue damage, excessive burns and the formation of rough scars at the site of exposure. And, most importantly, this does not always lead to results.
In my opinion, the use of such methods harms the patient, and does not relieve him of the problem.
— What can you say about the removal method when the wart is tied with thread?
This should not be done.
— Vladislav Leonidovich, is it true that warts can go away on their own?
This happens occasionally. This is due to the state of the immune system.
Read the material on the topic: What does immunity depend on?
— How are warts treated?
Treatment begins with destructive methods. There are several of them. Among them are cryodestruction with liquid nitrogen, laser removal using the Surgitron apparatus, and electrocoagulation. There is also a removal method using certain acids.
I prefer to use liquid nitrogen. One of its advantages is that you do not need to numb the wart first. A bubble forms at the site of exposure, which then dries up, and the “crust” subsequently disappears. If the wart is large, it is advisable to perform the procedure 2-3 times (layer-by-layer removal).
You can make an appointment with a dermatologist in your city here. Please note: the service is not available in all cities
During laser removal, anesthesia is first performed, and then the wart is “cauterized.” Removing it is painless.
If local treatment is ineffective, recurrence or multiple warts are also prescribed, immunomodulators and some antiviral drugs.
— Which wart removal is more effective: laser or liquid nitrogen?
Both methods are effective, but I start with liquid nitrogen. If this is not enough, then laser wart removal is used.
— Do any warts require mechanical removal?
No. For example, if there are 1-2 flat warts, they can be removed. If there are many of them, and they are located on the face and open parts of the body (for example, the back of the hands), then antiviral ointments are prescribed locally and systemic treatment.
— After removing warts, is there a scar left?
It depends on the individual characteristics of the skin. For example, some individuals have a tendency to form so-called keloid scars after any exposure. Therefore, before removal, we always interview our patients in detail.
The depth of the wart is important, as well as the method of removal (in particular, liquid nitrogen acts more superficially, laser - more deeply).
Read material on the topic: What is demodicosis: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Sometimes, when a wart was diagnosed in the initial stages of development, if it is properly removed, no traces remain on the skin.
— Why do new formations appear after wart removal? How to avoid this?
Since the incubation period can fluctuate greatly, new formations may in fact not be new: some warts appear earlier, others later.
Secondly, there could be microtraumas on the skin, where the virus from the “mother” wart could have penetrated, including after its incomplete removal.
— Why are warts dangerous? Can they develop into cancer?
This is a source of infection - both for the patient himself and for others. They do not turn into cancer.
— How to protect a child from viral warts? What is the prevention of warts?
It is simple and consists mainly of observing the rules of personal hygiene. After visiting public areas, try to wash your hands. Do not use other people's personal belongings, even within the family. Visit beauty salons with a good reputation. Handle personal care items (manicure sets, etc.).
More of our articles without advertising are on social networks: VKontakte, Facebook, Odnoklassniki
Carry out general strengthening procedures. Follow a daily routine, get plenty of rest, get enough sleep, and eat rationally. Get rid of bad habits.
Other questions:
How to treat chickenpox in children?
How to help your child not be afraid of injections?
What can you get infected on vacation? Watch out for malaria!
For reference:
Sheinkman Vladislav Leonidovich
Graduate of the Pediatric Faculty of Smolensk State Medical Institute in 1994
From 1994 to 1995, he completed an internship, and from 1996 to 1998, a clinical residency in the specialty “Dermatovenereology.”
Has an academic degree of Candidate of Medical Sciences
Currently working at Clinic Expert Tula LLC as a dermatovenerologist. Provides reception at the address: st. Boldina, 74
Treatment of warts
In most cases, warts disappear on their own within 2 years². Treatment is indicated if the wart does not disappear within the specified time, manifests itself clinically and causes great discomfort to the patient¹. The main direction of treatment is destruction (removal)².
Is it possible to treat warts using traditional methods?
“Treating warts with home methods is unacceptable.
Without examination, it is difficult to distinguish a wart from other diseases. The use of traditional methods can not only spoil a person’s appearance, but also harm his health. Self-medication often results in scars and burns remaining in place of the warts, which take a long time to heal. Traditional methods can cause dangerous complications. Only a doctor, based on the results of the examination, can correctly select the method of treating warts.” Yuzup Irina Borisovna
expert
The destruction method is selected by the doctor depending on the type and location of the wart. After removal of the formation, there is a fairly high risk of its reoccurrence, however, almost all methods of destruction can be performed in courses.
Multiple, periungual, and plantar warts are more likely to recur.
There are many ways to treat warts:
1. Physical methods of destruction.
- Electrocoagulation. The wart is removed under the influence of electric current using electrodes under local anesthesia. After the procedure, the patient must treat the wound surface with an antiseptic and healing ointment².
- Cryodestruction. This is the effect of cold on education. Freezing a wart is performed with liquid nitrogen, which is pressed onto the wart using a cotton swab or cryoprobe for 1-5 minutes. Repeated procedures are often required at intervals of 7-10 days. Treatment does not exceed 4 months. The main disadvantage of cryodestruction is the pain of this method.
- Laser destruction. Removal occurs using a laser under local anesthesia. After destruction, laser treatment of the wound surface is also carried out. Antiseptics and healing ointments are used to treat the wound.
Laser destruction of warts. Photo: bartekwardziak / Depositphotos
- Radiosurgical destruction. This is a modern and gentle way to remove warts. The method is based on the use of high power electromagnetic waves. The waves pass through the tissue of the wart and heat it, causing the actual evaporation of the tissue at the point of contact with the electrode, resulting in a cut. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. Afterwards you need to treat the wound until it heals. The method is safe, eliminates the formation of scars and scars, wounds usually heal quickly.
- Photodynamic therapy. A photosensitizer is applied to the wart - a special substance that increases the sensitivity of the tissue to light rays. After 3-5 hours, the wart is irradiated. After the photosensitizer, the wart tissue is oxidized under the influence of light and the formation is destroyed. A wound surface is formed that requires further treatment until healing.
2. Chemical methods of destruction.
- Removal with a solution of selenous acid in dichloropropionic acid. This procedure is performed on an outpatient basis and without pain relief. The drug is applied to the surface of the wart several times at intervals of 1-2 minutes. After 3-7 minutes, the wart tissue changes color to gray and thickens. There may be redness and swelling around the lesion, which will disappear within 24-48 hours. The next day after the procedure, the wart dries out, acquires a dark brown tint and sharply decreases in size. Then it disappears on its own within 2-3 weeks.
Important!
Under no circumstances should you tear off a dried wart! This will create a wound surface that will heal to form a scar².
- Application of a solution of zinc propionate in chloropropionic acid. Destruction is carried out by analogy with the previous method. A solution of zinc propionate can be used in courses with an interval of 24 hours between sessions.
- A combination of nitric, acetic, oxalic, lactic acids and copper nitrate trihydrate. Small warts can be treated this way. The solution is applied to the wart area for 3-5 minutes. After the skin color changes, the drug is removed. Subsequently, the wart dries out within a few days and disappears. 3-5 days after the procedure, the patient comes for a follow-up appointment with the doctor, and if necessary, he is prescribed repeated procedures. This treatment can be performed in courses with an interval of about 4 weeks.
Is it possible to remove warts yourself?
This is strictly not recommended! After such an attempt, inflammation often occurs at the site of the wart, and a scar may form. Also, when the formation is removed, the virus tends to spread throughout the skin, this will lead to the appearance of several new warts. It must be remembered that another skin disease may resemble a wart. A dermatologist will make the correct diagnosis and prescribe the necessary treatment.
How to understand that a wart goes away after celandine?
Often people try to remove a wart with celandine.
They usually suffer chemical burns to the skin.
In this case, the wart remains in its place and does not go anywhere.
But it’s hard for a person to believe that grandma’s “time-tested” method didn’t work.
So he searches the Internet for signs that the wart has begun to go away.
Among these signs he may encounter:
- redness
- peeling
- hardening, etc.
Encouraged by the presence of such signs, the person continues to wait for recovery.
But it usually doesn't happen.
Traditional methods are often dangerous and not very effective.
To remove warts, consult a dermatologist.
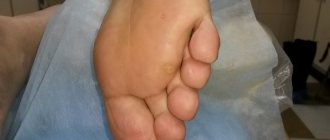
Plantar wart
These are formations in the form of dense plaques. They do not protrude above the surface of the skin, have a granular surface, and are often painful when pressed and walking³. The pattern of the skin over the wart is disturbed. Such formations tend to grow in width and merge (the size of individual elements can be from 2 mm to 3 cm³). The surface of the formation is easily injured and bleeds. Patients often confuse a plantar wart with a callus. Plantar warts are difficult to treat because they are prone to recurrence after removal.
Plantar wart. Photo: Magryt_Artur / Depositphotos
Reducing the risk of spread
Since the site of infection is most often public places with high humidity, you must be careful when visiting them. You should never touch the toilet rim with your skin when visiting a public toilet. Swimming masks must be used in the pool to prevent the virus from entering the body through the mucous membrane of the eyes. You should never wear someone else’s shoes, and you should also give even your close friends your towel, toothbrush, comb and other personal items.
It is important to carefully monitor the state of your immunity, avoid stress and eat properly so that the body has the strength to resist infection by both this virus and other diseases.
Causes of warts
The cause of warts is the human papillomavirus (HPV). It is due to the viral nature that warts spread across the skin and are also transmitted from another person. Currently, many types of HPV have been identified that can infect humans.
Different types of the virus infect specific areas of the body and affect the skin. The clinical features of the infection depend on the level of human immunity, the presence of injuries or microtraumas of the skin and mucous membranes, the type of HPV, and the place of penetration of the virus into the skin. The main causes of warts are HPV types 1, 2, 3 and 4. Other types may be detected less frequently¹.
The source of infection is a person infected with HPV. According to statistics, about 40% of people are carriers of this virus without manifestation of infection on the skin¹.
Diagnostics
Which doctor treats warts depends on the location of the growths and their nature. Initially, if growths are detected, you will need to visit a dermatologist. He will prescribe additional examinations that will confirm or refute the presence of papillomavirus in the body, and also determine the nature of the tumors.
Treatment of malignant papillomas will need to be carried out by an oncologist, treatment of benign formations is carried out by a dermatologist, and a surgeon will undertake the removal of growths.
Diagnosis of warts
The diagnosis is made by a dermatologist based on the patient’s complaints, the appearance of the formation and additional examinations. Your doctor may recommend the following laboratory tests:
- Dermatoscopy. The doctor examines the formation under magnification using a special device - a dermatoscope. This examination is especially relevant if you need to distinguish plantar warts from calluses¹.
- Biopsy. Performed after surgery to remove a wart. It is studied in the laboratory under a microscope¹.
In case of extensive skin damage by warts or their frequent occurrence, it is necessary to donate blood for antibodies of classes M and G (IgM, IgG) to the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Patients are also recommended to consult an allergist-immunologist².
Can the immune system fight infection?
Killer T lymphocytes recognize cells with damaged DNA and destroy them. This is natural antitumor immunity. This prevents the development of cancer. Antitumor immunity is relevant due to the fact that some strains are capable of inducing the synthesis of oncoproteins, leading to immortalization and proliferation of keratinocytes. As a result, it is possible to avoid consequences such as cancer.
After infection, the cells of the macroorganism begin to secrete interferon, which has a dual effect. It affects the genes of neighboring cells, reducing the rate of protein synthesis, which slows down the assembly of viral particles. Interferon increases the activity of macrophages and T-killers. The rate of antigen representation to T-lymphocytes and killer cells increases, which ensures rapid recognition and destruction of infected cells and warts.
Thanks to the coordinated work of the immune system, in some cases the disease goes away on its own. The prognosis for the disease is favorable. Timely treatment will help avoid complications.
Hardware methods are aimed at removing warts to prevent the appearance of new ones and reduce the concentration of the pathogen in the tissues of the body. Medication methods are aimed at strengthening the body’s strength to fight independently. This is achieved by using immunostimulants, antiviral agents and cytostatics.
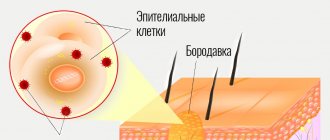
How do warts develop?
The human papillomavirus is transmitted through direct (for example, shaking hands) or indirect (through an object) contact. The virus penetrates the skin in the place where the epithelium is damaged: inflammation, trauma or microtrauma, which are not always noticeable to the naked eye¹. The virus may be latent on the skin.
Usually this period lasts from 1 to 6 months, but sometimes it can last up to 3 years or more³. When a person’s immunity decreases for some reason, the virus is activated and begins to actively multiply. This leads to disruption of the functioning of epithelial cells and the formation of benign formations on the skin.
Figure 1. Wart formation. Image: rob3000/Depositphotos
Methods of infection
The fact that many people on Earth have these growths suggests that warts are contagious. Since warts are transmitted exclusively through injured skin (cuts, abrasions, wounds, scratches), and microtraumas exist on the body of almost any person, everyone is at risk.
Since children's delicate skin is regularly injured, they encounter this problem more often than adults.
All family members may have warts on their hands, but this does not mean that the human papillomavirus is inherited. It’s just that contact with an infected person occurs more often and in a narrower circle. The virus can be transmitted in the following ways:
- when using a shared towel;
- through the doorknob and other common objects;
- through a damp rug on the bathroom floor;
- when shaking hands;
- even when using another person's office supplies.
Classification
We have prepared for you a detailed classification of warts. In modern clinical practice, the following types are distinguished:
- Vulgar warts. Multiple painless nodes up to 0.8 cm in diameter with keratinization on the surface. Such warts are often located on the dorsum of the hands and feet. They are caused by HPV types 1-4 and others³.
- Filiform warts. A type of vulgar warts that are located on the face². Most often appear in the area of the lips, nose, and eyes². They look like thin outgrowths. Occurs as a result of infection with HPV types 1-4.
- Periungual warts. These are thickenings with cracks that look like cauliflower. Located around the nail plate. Such formations occur in people with the habit of biting their nails or in those who work with their hands in water. Another name is “butcher’s” warts. They are caused by human papillomavirus type 7³.
- Palmoplantar warts. Round papules that can only appear on the thick skin of the palms and soles². Such warts cause pain to the patient when pressing and walking. Their appearance is promoted by HPV 1, 3 and other types.
- Mosaic plantar warts. They look like areas of excessive keratinization on the skin of the soles². Often such warts can be covered with cracks and cause discomfort to the patient. Mosaic plantar warts result from infection with HPV types 2 and 4.
- Cystic warts. Formations in the form of soft nodes with white-yellow curdled contents, as well as with cracks on the surface. They are localized in places of greatest pressure from the bone structures of the foot on the skin. Such warts are rare and are caused by HPV type 60³.
- Flat warts. Small papules with a diameter of 2-4 mm. The formations are flat, hyperpigmented or the color of healthy skin, always located in groups. Mostly appear on the face, back of the hands, and forearms. Flat warts are caused by HPV types 3, 10 and 28.
Which warts are most susceptible to transmission?
The body's susceptibility to the virus depends on the person's immunological status. Some groups of people are more prone to the disease. These include people taking immunosuppressants, congenital pathologies of the immune system, with cancer, and AIDS. Under such conditions, any types of warts are highly likely to appear.
Genital warts and simple warts are highly contagious. Genital warts rank second in prevalence after herpetic eruptions. In some countries, the proportion of women infected ranges from 3% to 28%. 9 out of 10 of their partners become infected after first contact. The danger of the disease is its chronic course. The infection persists throughout life with periodic periods of exacerbation. Virus carriers become most contagious when genital warts occur. At this time, it is worth tightening the rules of personal hygiene and excluding sexual activity. After entering the latent phase, condylomas disappear and a person can lead a full life.
Simple warts are found in most cases of HPV detection. Can be transmitted through a normal handshake or touch. Especially in conditions of minor damage. Formations appear on the fingers. When infected, this leads to the spread of the pathogen in the environment.
Sources
- Federal clinical guidelines. Dermatovenereology 2015: Skin diseases. Sexually transmitted infections. — 5th ed., revised. and additional - M.: Business Express, 2016. - 768 p.
- Viral warts / Clinical guidelines of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, 2022.
- Khlebnikova A., Selezneva E., Dorokhina O. Treatment of vulgar and plantar warts // Bulletin of Dermatovenerology. - 2015. - No. 1. - P. 122-128.
- World Health Organization. Human papillomavirus. — 2022.
How long does it take for a wart to heal after cauterization with nitrogen?
Warts are often removed with liquid nitrogen.
This is the simplest method of dealing with them.
It's also the cheapest.
But this method is also the most unpleasant and ineffective.
It often causes more suffering to the patient than the wart itself.
After cauterization with nitrogen, a focus of inflammation is formed.
With a short exposure time of the nitrogen swab, only small warts can be removed.
Medium and large ones do not pass.
To destroy them, it is necessary to increase the exposure time to nitrogen.
But increasing the exposure time leads to an increased risk of severe inflammation and scarring due to deep skin damage.
If you still have cauterization with nitrogen, you need to wait 1-2 weeks for healing.
After this, the doctor will examine the skin.
If the wart does not disappear, the procedure will have to be repeated.
Basic methods for removing warts
The two most commonly used methods for removing warts are cryotherapy and removal using a radio wave scalpel. If cryotherapy is performed, warts that appear on the patient's skin are treated with liquid nitrogen, a substance that allows objects to be cooled to very low temperatures. Namely, up to -187 degrees. After such a strong freezing of the wart, a characteristic bubble forms in its place after some time. Soon it opens, a wound forms in its place, which heals within 2-3 weeks, then a scar forms in this place. This method of removing warts is almost painless (there is only mild discomfort). The disadvantage of this method is that it is difficult to control the depth of removal, and therefore the remaining scar may be quite large or the wart may not be completely removed.
Removal using a “radio wave scalpel” involves exposing the wart to radio wave energy. This method is effective and safe. It allows you to accurately control the depth and size of the impact.
Prevention of warts
• Strict adherence to personal hygiene rules.
After visiting public places, wash your hands with soap. • If wounds or cuts occur on the skin, treat them with an alcohol solution, iodine or brilliant green. • When working with cleaning products or skin-damaging factors, use gloves. • Wear shoes made of genuine leather or fabric, avoid wearing synthetic shoes, especially for children and adolescents. • Normalize your diet, eat foods rich in vitamins. Avoid stress, organize your life. • When in contact with a person who already has warts, it is necessary to follow the rules of personal hygiene - wash your hands often with soap, limit the use of shared objects. [/td]
After wart removal
Immediately after removing the wart, I apply a sterile napkin or a special sterile gel to the wound, and the patient goes home. At home, the patient takes care of the wound independently. Since the wart is removed quite deeply, it may take quite a long time for the wound to heal. 6-10 days after the wart removal procedure, a crust usually forms at the site of the wound. After the crust comes off, a small pink scar usually remains. After 3-4 months, the scar will begin to turn white.
After the final formation of the scar, usually after 6-12 months, it becomes almost invisible.
There are other methods for removing warts - experienced doctors will select the right method for treating warts at our Center for Medical Cosmetology.