The article was prepared by a specialist for informational purposes only. We urge you not to self-medicate. When the first symptoms appear, consult a doctor.
A benign fatty tumor (lipoma), popularly called a wen, can form in almost any part of the human body, but its favorite places are areas with relatively thin subcutaneous fatty tissue, which, of course, includes the neck. A fatty tissue is a connective tissue capsule containing fat cells.
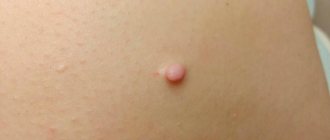
Lipoma looks like a round tumor that rises above the surface of the skin and sometimes reaches the size of an orange or a tennis ball. The formation is painless until it begins to compress the nerve endings, or its surface is subject to friction with clothing or other irritation. The risk of malignancy of the wen is minimal, but such a danger cannot be completely excluded.
Classification of wen on the neck
Lipid formations that occur on the neck are divided into several categories:
- Soft wen - is a connective tissue capsule filled exclusively with fat;
- Diffuse, or spilled variety - wen without a shell;
- Fibrous wen is a dense formation, the connective tissue capsule of which has grown and hardened;
- Petrified wen is a formation saturated with calcium salts;
- Angiolipoma is a wen that has blood vessels in its structure;
- Perineural wen is a formation affecting nerve fibers;
- Myolipoma is a wen that contains muscle tissue;
- Adenolipoma is a wen that has invaded the sweat glands;
- Dercum's disease, or lipomatosis, is a disease that forms multiple fatty formations, including on the neck and head;
- Madelung syndrome, or ring lipoma of the neck, is a disease that forms a collar of fatty tissue around the neck, making speech and breathing difficult;
- Bisha's hump, or widow's hump, is a massive wen in the projection of the seventh cervical vertebra, impeding the flow of blood through the vertebral artery.
Wen can be located in any part of the neck - under the lower jaw, behind, on the side, on the front surface.
Surgical method for removing wen
If a child’s wen is too large, what to do? Usually in this case surgery is needed.
Surgical intervention may be prescribed in several cases:
- if the tumor is larger than 5 or 7 centimeters;
- if the lipoma grows very quickly;
- if the tumor develops rapidly in an infant in the first year of life;
- if there are white wen on the child's face.
During surgery, when it is performed on a small child, only general anesthesia is used. If the child is an older child or a teenager, then a local anesthetic is injected subcutaneously. General anesthesia is also used when operating on a lipoma on the face of a child.
The operation is performed on an outpatient basis if the lipoma is small. For newborns and children of the first year of life, surgery is performed only inpatiently. Surgery is also performed in a hospital if a tumor of significant size needs to be removed.
Before the lipoma removal procedure, certain types of tests are performed. This is a general blood and urine test. The blood is also tested for clotting and its group is determined. In addition, sometimes a test is prescribed to check for syphilis and/or HIV, etc.
Reasons for the appearance of wen
One of the main reasons for the appearance of wen on the neck is pathological heredity, leading to a deficiency of the enzyme responsible for extracting energy and water from lipids. It is this genetically determined mutation of chromosome 12 that is the basis for the formation of lipomas from undigested fat.
Other reasons for the formation of wen on the neck:
- Monotonous muscle load of the neck muscles;
- Inactivity leading to disruption of blood microcirculation in blood vessels;
- Mechanical injuries to the skin of the neck due to rubbing with clothing;
- Poor diet, predominance of fats in the menu;
- Liver and kidney failure, gastrointestinal diseases;
- Cervical osteochondrosis;
- Age-related hormonal imbalance;
- Alcoholism.
Causes of atheroma in children
Atheromas in children occur due to a violation of the secretion of sebum by the corresponding glands.
When the excretory duct is blocked, the secretion of the gland has nowhere to go. It is secreted into the subcutaneous space, where a dense capsule is formed around it. Common causes of atheroma development in children are as follows:
- Using children's cosmetics (creams, ointments, moisturizing masks) in excessive quantities. Sometimes parents, in an effort to protect their child’s skin from harmful external factors, use cosmetic products uncontrollably. This leads to dysfunction of the sebaceous glands with blockage of their excretory ducts.
- Hormonal changes in the child's body. Infants and teenage children are traditionally at risk. It is during these periods that changes in the concentration of sex hormones occur. Against this background, acne appears, the function of the sebaceous glands is disrupted, and conditions are created for their blockage.
- Seborrhea. This is a dermatological disease that leads to dysfunction of the sebaceous glands in a certain area of the skin.
- Genetic predisposition or congenital structural features of the skin. Atheromas most often occur in children after 3 years of age. If neoplasms are detected in children immediately after birth, the doctor may assume the presence of problems with the sebaceous glands that developed in utero.
In addition, factors that increase the risk of developing atheromas are poor personal hygiene, metabolic disorders (obesity, diabetes) and frequent mechanical damage to the skin.
Symptoms of a wen on the neck
Wen can be detected with the naked eye. Upon visual examination, a tumor is visible, rising above the skin, the color of which does not differ from the surrounding areas. Upon palpation, a small formation easily moves without causing any discomfort. The growth of the wen does not stop over time, it is constantly increasing.
Negative symptoms as a reason for urgent consultation with a surgeon:
- Skin hyperemia is a sign of the onset of the inflammatory process;
- Reduced mobility of the wen - the transition of the wen to deep structures or its soldering to the epidermis;
- Pain on palpation - the growing wen touches the nerve fibers;
- Pallor of the skin - compression of the blood vessels by the wen;
- A rapid increase in wen is a dangerous sign of malignancy or a symptom of a serious metabolic disorder.
Questions
- Which doctor treats atheroma in children?
A pediatric surgeon is involved in identifying and treating atheroma in children. - Is it possible to cure atheroma without surgery?
Sometimes in the early stages of the disease the surgeon chooses a wait-and-see approach. In 20-35% of cases, atheroma can resolve on its own. However, if the capsule is formed and the tumor is large, it will not be possible to do without surgical intervention. - How dangerous is atheroma in childhood?
Atheroma is a relatively safe tumor. It does not become malignant, rarely becomes complicated and is not accompanied by the development of permanent defects. However, this does not eliminate the need to consult a pediatric surgeon. Only a doctor can establish the correct diagnosis and select treatment. In addition, atheroma can sometimes become inflamed due to the addition of bacterial flora and cause a deterioration in the child’s well-being. - Is it possible to play sports after surgery?
After surgical removal of atheroma, it is recommended to refrain from active activities for 2-3 weeks. This will allow the tissues to fully heal and recover.
Diagnostics
An accurate diagnosis can be made by visual examination and palpation of the wen.
It is characterized by such signs as:
- No pain;
- Softness and mobility;
- Clear contours.
The extent of the spread of the formation in the tissues of the neck and the condition of the wen capsule can be assessed by ultrasound or computed tomography. To determine the composition of the wen, a biopsy is performed, sending the material for cyto- and histology. This tactic will help differentiate cervical lipoma from tumors with similar external signs.
When to see a doctor
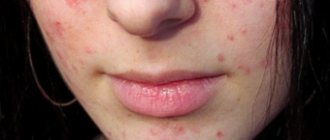
At first, the lipoma does not manifest itself in any way. In principle, this state of affairs can remain for quite a long time; perhaps, even throughout life, the tumor will not bother its owner. The formation in its usual state looks harmless and is painless. Where the wen is located, there is no itching, no burning and no suppuration. However, this happens until the lipoma becomes inflamed. This situation may arise if a wen on a child’s face or in another open place was exposed to drafts or other unfavorable factors, for example, injuries, blows, etc.
When should you contact a specialist? This must be done urgently if the formation on the skin has hardened or there is pain at the site of the tumor. Wen can be similar to other tumor formations. For example, with such as atheroma, hygroma or lymphadenitis. These tumors are benign. Only a professional can determine exactly what kind of tumor a child has. At the slightest suspicion of inflammation of lymphoma, you need to make an appointment with a dermatologist. The specialist will individually prescribe a treatment regimen for the pathology, taking into account the age of your child and the location of the tumor.
Treatment of wen on the neck
The dense capsule of the formation, which does not communicate with the surrounding tissues, prevents the penetration of drugs into it. Without opening the wen, it is impossible to transport active drugs inside it. The best treatment for wen on the neck is surgery.
Surgery
Treatment of a wen on the neck is carried out by a doctor in a surgical hospital. Any independent attempts to remove the formation by squeezing it out, puncturing it or opening the capsule can lead to tissue infection, the development of an abscess, phlegmon or sepsis. Intensive blood supply to this part of the body, saturation with blood vessels and nerve tissues, proximity to the brain make self-medication of a wen on the neck a deadly event.
Before surgery, the patient is sent to the laboratory for a blood test for coagulation and an allergy test for antibiotics and anesthetics.
Methods for removing wen:
- Excision with a scalpel - to treat a wen with this classical method, the surface of the skin over the formation is disinfected, an anesthetic is injected, and an incision is made to remove the capsule through it. During surgery on an inflamed wen, drainage is installed in the wound to remove pus and the inflammation is treated. The wound without pus is sutured immediately, the skin around it is treated with antiseptics. Possible complications include infection, rough scarring, granulation of the suture, allergic reactions to the suture material.
- Liposuction is a gentle method of removing the contents of a wen through a thin probe inserted directly into the capsule. The disadvantage of this method is that relapses are possible, since the capsule is not removed.
- Endoscopy is an effective and safe method of removing a lump, the procedure is performed through a tiny incision near the lump under the control of a miniature camera at the end of an endoscope.
- Laser surgery is a modern method of excision of a wen using a narrowly directed beam of a carbon laser. The risk of the wound becoming infected and the risk of bleeding is minimal, since coagulation of blood vessels is carried out directly during the operation.
- Radio wave surgery - using a special high-tech instrument - a radio knife - the wen is removed along with the capsule, almost no scars remain, relapses are excluded.
- Electrocoagulation and cryodestruction - cauterization of small wen under the influence of electric current or liquid nitrogen vapor. A pigment spot may appear at the intervention site.
After surgery to remove a wen on the neck, it is recommended to follow a gentle regime for a month - do not lift heavy objects, do not overexert yourself, and do not be exposed to high temperatures. These precautions will help prevent postoperative bleeding.
Treatment with drugs
In addition to surgical intervention, the patient is prescribed medications to correct the health condition:
- Stimulators of fat metabolism (Vitrum Cardio Omega-3, Atoris) – treatment of impaired metabolism that stimulates increased fat deposition;
- Hepatoprotectors (Phosphogliv, Essentiale Forte) – protection and restoration of liver cells;
- Relief of the inflammatory process with corticosteroids (Hydrocortisone, Dexamethasone);
- Taking calcium supplements (Calcimin) – treatment of osteochondrosis;
- Normalization of hormonal balance - synthetic analogues of estrogen or testosterone;
- Taking lipolytics (Aqualix, Aminomix, Phosphatidylcholine) – breakdown of fats.
Medication therapy can last from 2 to 5-6 months.
Physiotherapy and diet
To relieve the feeling of numbness in the neck, stimulate microcirculation, and stop tumor growth, physiotherapeutic methods such as micropulse exposure and high-frequency ultrasound are used. Electrophoresis with corticosteroids increases their effectiveness in the treatment of inflammatory processes around the capsule of the wen or postoperative wound.
It is impossible to cure fat with diet - it is not possible to extract the fat accumulated there through the capsule tissue. However, adjusting your diet will help improve your metabolism and stop excessive fat accumulation.
To do this, you should reduce the amount of carbohydrates and fats in the menu. It is advisable to include lean meats and fish, vegetables and fruits in any form, cereals with milk and water, and fermented milk products.
Cost of removing lipomas (fat) with laser
| Laser tumor removal | Prices, rub. |
| Laser removal of papillomas, single warts - Cat. I. difficulties | 1200 |
| Laser removal of papillomas, multiple warts - Cat. I. difficulties | 350 |
| Laser removal of moles, papillomas, warts - Cat. II. difficulties | 700 |
| Laser removal of moles, papillomas, warts - Cat. III. difficulties | 1500 |
| Laser removal of moles, papillomas, warts - IV category. difficulties | 3000 |
| Laser removal of moles, papillomas, warts - Cat. V. difficulties | 4500 |
| Laser removal of moles, papillomas, warts - Cat. VI. difficulties | 6100 |
| CO2 Laser callus removal (per unit) | 6100 |
| Removal of atheroma, lipoma, fibroma, xanthelasma with laser - Cat. I. difficulties | 6 900 |
| Removal of atheroma, basal cell carcinoma, lipoma, fibroma, xanthelasma with laser - Category II. difficulties | 9 400 |
| Removal of atheroma, basal cell carcinoma, lipoma, fibroma, xanthelasma with laser - Cat. III. difficulties | 16 900 |
| Removal of atheroma, basal cell carcinoma, lipoma, fibroma, xanthelasma with laser - IV category. difficulties | 22 400 |
| Removal of atheroma, basal cell carcinoma, lipoma, fibroma, xanthelasma with laser - Cat. V. difficulties | 33 400 |
Make an appointment for laser removal of lipoma on the neck
- Full name
- Telephone
How can a lipoma be removed?
There are three main methods for removing wen:
- Traditional surgery. Cutting out lipomas with a scalpel in an area such as the neck is extremely difficult and risky. If you do not trust modern methods, you will have to look for a very good doctor who will cut out the growth as carefully as possible.
- Radio wave removal method. Not as effective as laser, but safe and does not cause consequences. In general, it is suitable for fatty formations.
- Laser method. As a result of laser removal, there will be neither a lipoma nor a trace of it. Scars are excluded: the laser “melts” fat without damaging the skin and other tissues. The neck remains clean and beautiful.
A laser can remove any growth; it can replace both a surgical scalpel and radio wave equipment. The lipoma will disappear before your eyes. Interestingly, laser technology does not require anesthesia. The laser operates at low intensity.
Advantages of laser technique
The laser can be used in any area of the body. Even if the lipoma is very small and is located, for example, in an area such as the ear. Low frequencies and power make the treatment painless and harmless.
No rehabilitation is required. This distinguishes the technique from conventional surgery. If you decide to cut out the tumor, you will then have to regularly treat the incision site and take antibiotics against blood poisoning.
Photos before and after lipoma removal
Can a lipoma appear on the spine and its causes?
It can occur on the tailbone, in the lumbar and cervical region. Develops in the ventricles of the brain, spinal canal, and cauda equina region. There are risk factors that provoke the development of wen on parts of the spine, in particular on the cervical vertebra:
- Heredity. Occurs in young children. Such a formation is immediately removed; it may increase in size.
- Metabolism. It has a negative effect on adipose tissue and leads to tumors.
- Excess cholesterol. The fat becomes viscous and clogs the sebaceous glands.
- Hormonal background. The disorder is usually associated with a disease of the thyroid gland; an imbalance of hormones leads to the appearance of wen.
- Diseases of internal organs. Another cause of occurrence is in the neck or lower back. This is caused by disturbances in the functioning of the kidneys and liver.
- Poor nutrition. Poor quality nutrition affects the body and can lead to benign formations.
A tumor on the spine develops slowly, and at first it may not cause discomfort. If left untreated, it can lead to complications.
Causes and symptoms of vertebral lipoma
Doctors today do not have a clear answer to the question: “what is the reason for the appearance and development of vertebral hemangiolipoma?” This tumor is quite insidious. It may not make itself felt even for several years, developing slowly and without showing symptoms. But it happens that the lipoma begins its aggressive growth, accompanied by pain. At the same time, its volume reaches such dimensions that a break or fracture of the vertebra and compression of the brain in the spinal canal are possible. This leads to very dire consequences. Such anomalies are accompanied by pain in the back, numbness in the legs and arms, and disruption of the normal functioning of internal organs.
In most cases, the neoplasm grows in the thoracic and lumbar parts, less often in the sacral spine. As a rule, the formation does not tend to rapidly increase in size, but develops slowly and can, over time, reach an impressive volume, which not only causes inconvenience and pain, but also poses a serious threat to health. Thus, a wen on the spine can be described as a time bomb. The growth and development of education can be triggered by a number of factors:
- patient's age. The growth of hemangiolipoma directly depends on the aging of the human body;
- abnormal physical activity on the spine;
- oxygen starvation of vertebral tissue cells;
- predisposition to this disease (heredity);
- an increase in the level of a hormone (estrogen) in the patient’s blood. As a rule, this factor concerns women to a greater extent;
- change of place of residence and climate;
- spinal injuries that can cause the formation of vascular cavities;
- increased blood pressure in the vessels;
- diseases caused by external influences or internal disruption of organs/systems not related to mental activity.
Education mechanism
Sometimes the trigger for lipoma formation is considered to be skin damage. Lipoma is a neoplasm of fat cells. Its growth begins from a single cell, which grows and divides faster than the surrounding tissues. Under a microscope, a lipoma appears as a cluster of nodules of mature fat cells (adipocytes) separated by fibromuscular septa. The benign quality of the formation is established in the absence of atypia of the nuclei or the cells themselves.
Classification of lipoma according to ICD-10
According to the international classification of diseases, lipomas are classified in section D17, i.e. to benign formations of adipose tissue.
What does a lipoma look like?
Slow-growing soft growths under the skin - wen - are usually lipomas.
A lipoma looks like a “ball” or “lump” under the skin. The size of the formation varies; it can be from the size of a pea to several centimeters in diameter. When palpated (palpated), the lipoma is soft, resembles rubber in density, and is not fused to the underlying tissues.