Sebaceous glands
(
glandulae sebaceae
) - skin glands, the secretion of which serves as a fatty lubricant for the hair and skin surface.
Sebaceous glands are found only in the skin of mammals. In birds, amphibians and other animals, the glands of the skin only resemble the Sebaceous glands, without being such in essence. Being fundamentally similar in histological structure, the Sebaceous glands can have significant differences in size, location and structural complexity not only in different animal species, but also in different areas of the skin of an individual.
Where is increased fat content possible?
The content of the article
Problem areas:
- upper back;
- facial part, especially the chin, forehead and cheeks;
- cervical and thoracic parts of the body;
- genitals in both sexes;
- peripapillary zone.
These are the most common and most common, but there may be others. The only places on the body where acne cannot appear are the palms and feet. Due to the too thick and rough layer of the epidermis, incapable of this kind of inflammation.
Embryology
There are conflicting opinions regarding the timing of the formation of the Sebaceous glands. Thus, according to I.I. Podvysotskaya (1971), their formation occurs both in the early postnatal period and during puberty. According to other data, the bookmark of the S. zh. in humans it occurs within 3-6 months. embryonic development in the upper third of the outer root sheath of the hair in the form of a flask-shaped accumulation of epithelial cells growing into the surrounding dermis. The secretory section is formed from the expanded part of this accumulation of cells, the excretory duct is formed from the cord connecting to the external root sheath, and the capsule of the genus is formed from the surrounding connective tissue. The simple gland formed in this way, growing, turns into a branched, and sometimes complex, lobed one.
Causes
- Dry skin;
- Hormonal changes in the whole body;
- Infection;
- Too much sebum production.
In addition to these reasons, there is another factor that was recently established by scientists - heredity.
Let's look at each reason in more detail.
Dry skin
One of the most common reasons. Due to dryness, the skin exfoliates and its particles clog the pores, which causes inflammation. It is very important to consider several points that cause excessive dry skin:
- Age. Over the years, the skin gradually loses many of its important properties, which include moisture retention.
- Environment. Dry and cold air, low humidity, and so on.
- Shower with hot water. Leads to the destruction of the protective layer of the skin.
- Allergic diseases.
- Hygiene products. Using regular soap on sensitive areas of the skin: facial skin, intimate areas, can cause dryness and cause acne.
Hormonal background
The reason lies in the incorrect proportion of sex hormones in the blood. Androgens (male hormones) play a very important role here. If their level is exceeded, then excess secretion begins from the sebaceous and sweat glands, which is the reason for the appearance of acne. You can also isolate progesterone, a hormone secreted in pregnant women. Leads to clogging of pores and, as a result, sebaceous inflammation appears.
Lack of estrogen can also cause excessive oily skin.
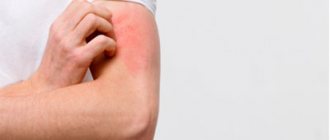
What do people with oily skin suffer from?
If you have oily skin, it means that the sebaceous glands on your face produce too much sebum. In addition, they can expand and become clogged with comedones. Such skin appears to be covered with mini-craters and looks unaesthetic. At the same time, the oiliness of the skin surface itself does not indicate that you will definitely have acne.
In some cases, after washing, a feeling of tightness may occur, this indicates a violation of the lipid barrier of the epidermis - a lack of ceramides in it, which are responsible for creating a protective film on the skin.
The lipid barrier could be damaged as a result of improper care, for example, frequent use of aggressive lotions containing alcohol.
Sebum production
There are 3 factors that can affect the amount of sebum production. Androgen, or rather its excess in the blood, is one of the reasons. Rarely, but still there is a special disease called “seborrhea”. And of course, a very common cause in the 21st century is poor nutrition.
Here is a list of products that promote the active secretion of sebum:
- carbonated drinks;
- alcoholic drinks;
- products in the production of which dyes were used;
- caffeinated drinks (black tea, coffee;
- sweet and flour;
- spicy, smoked food.
Pathology
Pathology S. includes developmental defects, functional disorders, dystrophic changes, inflammatory processes, and tumors.
To malformations of S. zh. include congenital asteatosis (lack of sebaceous secretion or its sharp decrease as a result of insufficient development of the gland), as well as heterotopia of the gland. in the mucous membrane of the mouth and the red border of the lips - Fordyce's disease. The appearance of S. in the oral cavity with this disease is not accompanied by subjective sensations; they are detected by chance during examination in the form of small translucent pale yellow nodules on the oral mucosa. No treatment is required for Fordyce disease.
Functional disorders
The activities of the sebaceous glands are caused by damage to the autonomic, central or peripheral nervous system, disruption of hormonal regulation, metabolism, etc. Increased activity of the sebaceous glands. noted in patients with epidemic viral encephalitis as a result of damage to the autonomic centers, with mental illnesses accompanied by symptoms of vagotonia (psychosis, etc.), with lesions of the anterior pituitary gland, adrenal cortex, gonads associated with increased function, for example, with Itsenko’s disease - Cushing's (see Itsenko - Cushing's disease), seminoma (see), etc. A decrease in the function of these endocrine glands as a result of their damage leads to a decrease in the functional activity of the glands, which is noted, for example, during orchiectomy (see Castration , Post-castration syndrome).
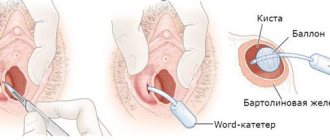
A common pathological condition, which is based on a violation of the secretory function of the stomach. with a change in the chemical composition of the sebaceous secretion, seborrhea occurs (see). At the same time, seborrheic skin changes often lead to the formation of seborrhea in the excretory ducts. sebaceous-horny plugs - comedones, as well as atheromas (steatomas) - deep retention cysts of the stomach. (see Epidermoid cyst). Multiple cysts of the stomach, resulting from nevoid dysplasia of the epidermis, can be observed in pilosebocystomatosis (see).
Dystrophic changes
The sebaceous glands can be observed as age-related changes (in old age) or in a number of acquired diseases - scleroderma (see), skin atrophy (see), etc. However, often degenerative changes in the sebaceous glands. are associated with hereditary characteristics of their morphology and functional activity, in particular, thinning of the epithelium lining the excretory ducts of the stomach and the secretory epithelium of the sacs, a decrease in secretory function and the formation of superficial epidermal cysts - milia (see), for example, in dystrophic forms of bullous epidermolysis (see Epidermolysis bullosa).
Inflammatory processes
in S. zh. are often observed, especially during puberty against the background of seborrhea. Characterized by the formation of acne (see), in which the inflammatory process can develop both in the walls of the stomach. and the surrounding tissue (pustular acne), and spread into the deep layers of the skin (indurative acne) around the skin. and hair follicles, often involving subcutaneous tissue (phlegmonous acne).
Benign tumor
S. - true sebaceous gland adenoma - is rarely observed in adults and elderly people in the form of a dense, round, often single nodule on the face or back; it is an encapsulated organoid tumor of a lobular structure. Incorrectly called adenomas of the Pringle, Allopo-Leredda-Darier type (see Adenoma of the sebaceous glands) and Balser-Menetrier type (see Epithelioma adenoid cystic) nevi of the gland. (see Nevus).
To malignant tumors
The sebaceous glands include basalioma (see), characterized by locally destructive growth and being an intraepidermal cancer. Cancer S. g. - a rare type of cancer that develops from the gland, often from the glands of the cartilage of the eyelids, the so-called. meibomian glands (see Skin, tumors).
Bibliography:
Kalantaevskaya K. A. Histomorphology of human sebaceous glands in ontogenesis, Scientific. Izv. Kazakh honey. Institute, vol. 16, p. 174, Alma-Ata, 1960; Korolev Yu. Seborrhea and acne, Minsk, 1972; Podvysotskaya I. I. Age-related evolution of the sebaceous glands, in the book: Theory and practice of dermal-venereolitis, ed. E. V. Maistrakha et al., p. 346, L., 1971; Sokolov V. E., Shabadash S. A. and Zelikina T. I. On the question of the innervation of the sebaceous glands, Izv. USSR Academy of Sciences, ser. biol., no. 6, p. 805, 1980, bibliogr.; The sebaceous glands, ed. by W. Montagna, Oxford, 1963.
S. S. Kryazheva; Yu. K. Eletsky (an., hist., embr.).
Treatment and prevention
It would be best and safest to contact a competent doctor - an endocrinologist, so that further treatment takes place under his strict supervision. You will have to start with a healthy diet that limits the consumption of foods that are harmful to good skin condition. And it won’t hurt to start special cosmetic skin care.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
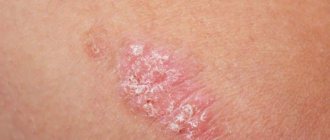
Clinical picture of acne
Acne rashes are divided into non-inflammatory (open or closed comedones), inflammatory (papules, pustules, nodes) and post-inflammatory (scars, hypo- and hyperpigmentation).
Comedones are non-inflammatory elements resulting from blockage of the mouths of hair follicles. Slightly expressed comedones are a physiological phenomenon. At the beginning of the development of acne, microcomedones transform into so-called “closed” comedones, that is, those that do not have free communication with the surface of the skin. They are non-inflammatory nodules with a dense consistency, up to 2 mm in diameter, consisting of sebum, horny scales and bacterial bodies. “Open” comedones look like yellowish-black dots. The black-colored tip of an open comedone is made of melanin, not debris.
Papules are a red inflammatory element, rising above the surface of the skin, of a hard consistency with a diameter of up to 0.5 cm.
Pustules are an inflammatory element with purulent contents, having a hemispherical shape. Typically resolve without scar formation, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation may occur.
Nodes are convex, painful formations of a red-violet color, filled with contents of pus and sebum. They often leave scars.
Most patients have comedonal and papulopustular forms of acne. All others are relatively rare, but also deserve attention.
Conglobate acne is a severe form of acne, most common in men aged 20 to 30 years. They are localized mainly on the back, less often on the face and chest. It is characterized by the gradual appearance of multiple extensive, deeply located nodular cystic elements. They can merge. Some of them retain a dense consistency, others soften during development and open with the release of purulent exudate. After healing, stagnant bluish-colored spots persist for quite a long time and scars remain.
Excoriated acne - this form occurs mainly in patients against the background of constant attempts to remove any, even minimal, manifestations of acne. It is characterized by a small number of typical acne formations on the skin and a large number of wounds covered with crusts.
Is R. acnes good or bad for health?
We previously mentioned P. acnes and promised to look into it in more detail. In this part of the article we will talk about beneficial and harmful traits, various interactions of this bacterium, as well as the possibility of determining it on yourself.
Useful features
P. acnes shares properties with dairy propionibacteria, which are considered harmless - and even beneficial [12]. Organisms like it have many positive properties: synthesis of vitamin B12, riboflavin, folic acid. P. acnes is also able to regulate the number of other bacteria by producing SCFAs (short chain fatty acids). Fermentation of glycerol by P. acnes and S. epidermidis can inhibit the growth of the most common skin pathogen, Staphylococcus aureus. This prevents the dangerous bacterium from colonizing skin wounds [15].
Opportunistic traits
The pathogenesis of acne is the mechanism of disease development in which P. acnes plays a significant role. It secretes enzymes that destroy human tissue components and can aggravate a number of other diseases [16], [17].
A clogged sebaceous gland creates an anaerobic environment. It is beneficial to P. acnes and promotes overgrowth. But during the development of acne, not only this bacterium was found there, but also other microorganisms, including S. epidermis. That is, more than just P. acnes is involved in the process.
The relationships between bacteria are ambiguous. S. epidermidis breaks down fatty acids into shorter SCFAs. It turns out that it can curb the excessive growth of P. acnes and indirectly improve the situation with acne [18]. Although not so long ago we talked about how S. epidermidis and P. acnes together “protect” us from Staphylococcus aureus (Staphylococcus aureus).
Competition “Bio/Mol/Text”-2021/2022
This work was published in the “School” category of the “Bio/Mol/Text” competition - 2021/2022.
The nomination partner is the non-profit boarding school “Letovo”.
The general partner of the competition is the international innovative biotechnology company BIOCAD.
The general partner of the competition is: the largest supplier of equipment, reagents and consumables for biological research and production.
"Book" sponsor of the competition - "Alpina Non-Fiction"