Euroonko is a Russian center of competence for the diagnosis, treatment of melanoma, and therapy of disseminated melanoma at the 4th stage. The knowledge and skills that Euroonco specialists have acquired over many years of practice are regularly presented at international conferences.
At one of them, INTERACTIVE WORKSHOP ON IMMUNOTHERAPY IN MELANOMA AND LUNG CANCER , held in Israel, Euroonco doctors presented their report on the topic of immunotherapy. Apart from Euroonco, there were no participants from Russia at the conference.
Treatment is carried out in cooperation with foreign partners. This allows Euroonco doctors, if necessary, to prescribe treatment with drugs that are available for use only in a few countries around the world and offer patients participation in clinical trials of the latest drugs.
Book a consultation around the clock +7+7+78
Depending on the appearance and growth pattern, there are several types of skin melanoma:
- Superficial spreading melanoma
occurs in approximately 60% of cases. Such tumors can remain in the radial growth phase for a long time, for several years, that is, grow in breadth without growing into the deeper layers of tissue. Metastasis occurs extremely rarely. But, sooner or later, the vertical growth phase will begin, and the tendency of melanoma to metastasize will increase sharply. - The nodular form
looks like a nodule that rises above the surface of the skin. Her growth is much more aggressive. - Lentigo maligna melanoma
appears as a spot on the skin with jagged, fuzzy edges. This is the most favorable type. Like superficial spreading melanoma, it can remain in the radial growth phase for a long time—up to 10–20 years—and only then begins to actively grow deeper and metastasize. - The acral-lentiginous form
most often appears as a spot on the palm or foot, in the area of the nail bed. It is similar to superficial spreading melanoma, but behaves more aggressively and metastasizes earlier. Due to the “inconvenient” location, a person may not notice this tumor for a long time and not see a doctor.
Melanoma statistics
Melanoma is the leading type of cancer, ranking third in prevalence in men and second in women. At the same time, the number of victims increases every year, and the disease becomes “younger.”
In most cases, tumors occur on exposed skin, with about 70% of cases on the face.
Modern medicine has a wide range of cancer treatment options. Oncologists have chemotherapy, hormonal treatment, immunotherapy, which allows them to block specific immune checkpoints, and targeted drugs, which specifically affect cancer target cells. Recovery is possible, the main thing is timely diagnosis!
MelanomaUnit oncologists recommend regular preventive examinations and medical examinations for early diagnosis of melanoma and other skin cancers.
Disease prognosis
Early detection of melanoma increases the likelihood of successful treatment and stable remission in more than 90% of patients. With timely diagnosis and a small thickness of the primary lesion, complete cure is likely in 90-95% of cases. Relapse with a tumor thickness of up to 1 mm and in the absence of metastases in regional lymph nodes occurs in approximately 8% of cases.
Overall survival of patients with cutaneous melanoma up to 5 years has increased due to early diagnosis and new treatment methods. Five-year survival data (if detected at the appropriate stage): I – up to 92%, II – 53-81%, III – 40-78%, IV – no more than 20%.
How does melanoma manifest?
Melanoma is one of the fastest growing types of cancer, which quickly “gives” metastases to the lymph nodes and internal organs.
At the initial stage of skin cancer, attention is drawn to the appearance of a new growth on the skin or a change in the color, size and shape of an existing mole.
The patient may also complain of itching, pain and burning sensation in the area of formation.
ABCDE method in diagnosing melanoma
There are criteria (ABCDE), thanks to which patients can independently suspect a problem and consult a doctor:
- A (asymmetry) – asymmetry . The mole grows unevenly to the side. Normally, if you draw an imaginary line through the middle of the mole, the halves will be symmetrical.
- B (border irregularity) – uneven, jagged, fuzzy edge.
- C (color) – color. Suspicion of melanoma is caused by changes or heterogeneity in color, the appearance of inclusions.
- D (diameter) – diameter. Increase in size of a common mole.
- E (evolving) – variability of any characteristic: color, shape, size is a reason for immediate consultation with an experienced dermato-oncologist.
IMPORTANT : there is a type of melanoma that contains virtually no pigment and in the initial stages resembles more of a pimple or an ingrown hair, this disease is called non-pigmented melanoma .
There are several successive stages in the development of melanoma:
- Stage O - characterized by damage to the upper layers of the epithelium, which responds well to treatment.
- Stage 1 - the pathological process penetrates into the deeper layers of the epithelium, but the size of the tumor does not exceed 2 cm.
- Stage 2 - the size of the tumor can increase up to 5 cm.
- Stage 3 - characterized by the appearance of the first metastases in sentinel and regional lymph nodes.
- Stage 4 is the terminal stage of the disease, which is characterized by multiple metastases to distant organs and tissues.
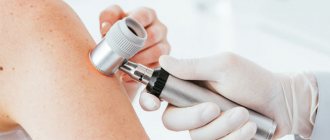
Dermatoscopy
Dermatoscopy is an examination in which a dermatologist uses a dermatoscope. This is an instrument that combines a magnifying glass 10 or 20 times, magnifying the fragment under study, equipped with a standardized light source. In such conditions, the doctor may initially assess skin changes.
Dermatoscopy
Videodermatoscopy is a study that, in addition to the techniques used in dermatoscopy, uses visualization on a computer monitor. This allows the clinician to store the displayed image in the device's memory, which can be useful for comparative purposes at a later stage in treatment. In practice, several dermoscopic methods are used to diagnose melanoma.
The doctor, based on the appearance of the lesion, will evaluate whether there is a reason to remove it along with a margin of healthy skin, and send the material after the procedure for histopathological examination.
The specialist studies the characteristic features of the mole, in particular:
- Color—uneven color, darker and lighter areas, or pink and red areas are abnormal;
- Ragged edges - moles with smooth edges are less dangerous to health;
- Asymmetrical shape;
- Size greater than 5 mm - smaller lesions are usually not a cause for concern, but if they are growing dynamically or show other abnormalities, they need to be removed;
- Bleeding, ulceration, presence of discharge.
Diagnosis that confirms or excludes a skin neoplasm, which is melanoma, is possible on the basis of a histopathological examination, which is carried out after removal of the entire lesion.
What types of melanoma are there?
There are several classifications of melanoma, the most common of which is the TNM system:
- Tumor
- LymphNode – lymph node
- Metastasis – metastases
T-category
This is the volume or thickness of the tumor, which is measured using the Breslow system. Also in this category the rate of development of metastases is taken into account.
N-category
Determines the presence of a tumor in the lymph nodes that are susceptible to metastasis in the first place.
M-category
This category determines the spread of the pathological process to internal organs.
Stages of melanoma
| Stages of melanoma | Characteristics of the stage |
| Melanoma 0 | Present only in the upper layer of the skin - the epidermis (in situ). This melanoma is non-invasive; it does not penetrate into the deeper layers of the skin and does not spread to other parts of the body. |
| Melanoma I | There are two subcategories here - A and B. The thickness of the tumor at an early stage does not exceed 1 mm. The neoplasm has no peeling or ulcers and does not bleed. The rate of cell division is quite low. Melanoma does not affect organs or lymph nodes. At this stage, surgery is recommended, i.e., surgical removal of the malignant neoplasm. |
| Melanoma II | There are three subcategories here - A, B and C. At this stage, the tumor penetrates deeper. The thickness of melanoma can reach 2.00 mm and sometimes 4.00 mm. The surface of the melanoma itself takes on a hypertrophied appearance. There is peeling, the presence of ulcers, and sometimes bleeding. Lymph nodes and other organs are not affected. |
| Melanoma III | There are also three subcategories here - A, B and C. At this stage, the tumor affects the lymph nodes. They can be increased, but not always. The malignant neoplasm thickens and penetrates even deeper into the tissue. Expressions can also either appear or not. At this stage, radiation and operable (surgical) methods are accepted as treatment. |
| Melanoma IV | This stage is the last stage of skin cancer. The malignant neoplasm is already metastasizing, affecting internal organs such as the liver, lungs, and brain. Penetrates to distant lymph nodes and affects individual areas of the skin. At this stage, long-term and complex treatment is necessary. It is also possible to resort to surgical methods, removing individual skin lesions affected by the tumor or cutting out metastases from internal organs. |
Diagnosis of melanoma
The prognosis for recovery largely depends on the timeliness of diagnosis and the prescription of adequate treatment.
Early accurate diagnosis of melanoma is carried out using an accurate modern examination - dermatoscopy .
The tumor can be diagnosed with high accuracy using special studies: dermatoscopy, drawing up a “mole map” using the Fotofinder system.
At the moment, no single cause of melanoma has been established, but doctors identify a number of predisposing factors :
- excessive inhalation or active exposure of the skin to the sun's rays
- heredity
- a certain phototype - freckles, light skin and eye color
- a large number of moles (nevi) on the body.
If you are at risk, it is recommended not to overuse ultraviolet rays (tanning, solarium). In people with dark hair and dark skin tone, melanomas may form on the surfaces of the palms and soles. Many clinical studies have proven that 50-75% of melanomas are formed from moles already on the body. Accidental damage can cause it to transform into a malignant tumor. Therefore, it is recommended to take special care to protect nevi from external trauma, rubbing, and to visit an oncologist at the first warning signs, which include:
- horizontal or vertical unnatural growth;
- identified asymmetry of the edges;
- growths on a mole;
- mole falling off;
- color changes;
- discomfort in the area of the nevus;
- the appearance of foreign formations on the mole, bleeding.
- sunburn, intense tanning both naturally and in a solarium
- congenital nevi
- genetic predisposition , that is, cases of cancer, especially skin cancer, in close relatives
- diseases of the endocrine system, especially damage to the thyroid gland
- trauma to the skin , birthmarks and moles
- increased sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation
- age factor – with age increases the risk of skin cancer
- Skin phenotypes 1 and 2 are people with fair skin, blond or red hair, blue or gray eyes and freckles.
Melanoma cancer cells spread throughout the body through the lymphatic system, and one of the earliest sites of spread for metastasis is nearby lymph nodes. Examination of the lymph nodes helps answer the question of whether melanoma has metastasized to other parts of the body.
Professor Chaim Gutman, doctor of the highest category
For more information about the causes and risk factors for melanoma, see the article “Risk Factors for Melanoma”
Risks of occurrence
Predisposing factors play one of the key roles in the development of skin cancer. Among them are:
- prolonged exposure to the sun and frequent sunburn;
- hereditary predisposition. If there have been cases of tumor formations on the skin in the family, this increases the risk of their development in subsequent generations;
- fair skin with a lot of moles and freckles, red hair color. This dermis is characterized by a low content of melanin in the cells;
- elderly age. It is believed that with age, the chance of developing skin tumors increases. Despite this, oncologists note an increase in the detection of pathology among young people;
- occupational hazards. Some professions involve constant contact with carcinogenic substances. Prolonged interaction of toxins with the skin increases the risk of tumor development.
The presence of at least one of the listed risk factors requires regular visits to the doctor for preventive examinations.
Melanoma staging
Staging of melanoma or, in other words, determining the stage of tumor development is based on its thickness, size, rate of spread of metastases, presentation of the tumor (how often and severely symptoms manifest itself), damage to the lymph nodes, as well as other organs.
To determine the stage, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination. It is carried out as follows:
- Examination by a dermato-oncologist
- Dermatoscopy
- Biopsy of the pathological formation followed by histology
- If necessary, computed tomography (CT), radiography, ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be prescribed.
Determining the stage of melanoma development is extremely important, as this helps to prescribe the most effective treatment and apply the right method in the fight against malignancy.
Pathogenesis
The pathogenesis of melanoma is a very complex process, characterized by significant metabolic and molecular abnormalities. Many aspects of pathogenesis still remain unclear to scientists.
Melanoma develops from melanocytes, pigment cells that produce melanin. In order for a tumor to appear and begin to develop, a certain effect on normal tissues or cells is necessary. Their damage provokes proliferative reactions. necrosis of cells or tissues occurs But if proliferation is delayed under the influence of certain carcinogenic factors, cell differentiation may be disrupted, as a result of which the change in the membrane antigenic structure is disrupted and hyporesponsiveness to the influences of regulatory factors of the body is noted.
As a result of these processes, undifferentiated proliferating cells can escape the body's control.
Speaking about the pathogenesis of melanoma, scientists do not exclude that changes in the DNA of the cell with disruption of its protein structure and differentiation in the future may occur due to primary damage.
More than half of primary skin melanomas develop against the background of previous pigmented nevi . Therefore, such nevi are regarded as optional precancer. The most important exogenous factors influencing the development of this tumor are trauma to nevi and UV radiation. The mechanism for the harmful effects of UV radiation may be the formation of highly active free chemical radicals in healthy cells. A tumor occurs when these radicals damage the cell's DNA and interfere with its normal repair.
If we describe the sequence of development of skin melanoma due to the influence of UV radiation, it is as follows: UV radiation affects melanoblasts, melanocytes or nevus cells, cell DNA is damaged, cell differentiation is disrupted, the protein structure changes and new membrane antigens appear. Hyporesponsiveness and tumor growth are noted. The possibility of this mechanism of carcinogenesis is confirmed by the fact that melanomas often develop after a single and strong influence of UV radiation (with a sunburn).
The essence of the mechanism of the carcinogenic effect of injury to pre-existing pigmented nevi is tissue proliferation in response to damage. However, trauma does not provoke tumor development. Cells in a state of proliferation are more sensitive to carcinogenic effects. They are especially vulnerable during the mitotic cycle. Consequently, proliferation (active reproduction) of cells can provoke their neoplastic transformation.
If we describe the sequence of development of skin melanoma due to trauma to pre-existing pigmented nevi, it is as follows: nevus cells are damaged, inflammation and proliferation of the damaged tissue occurs. Long-term proliferation is observed, and under the influence of endogenous carcinogenic factors, the structure of the cell's DNA is disrupted. As a result, cell differentiation is disrupted, its protein structure changes, and new membrane antigens . Hyporesponsiveness and tumor growth are noted.
How to determine the stage of melanoma
In general, there are two main methods for determining the stages of melanoma.
Clinical – based on an examination of the patient by a specialist and the results of a biopsy (morphological examination of a cell sample).
Histological – based on a microscopic method for studying tissues, organs and body systems, using biopsy and surgical methods. Histological analysis, as a rule, shows a higher stage of development of the malignant neoplasm. So, if a biopsy showed, for example, the 3rd stage of melanoma, then histological analysis may already show the 4th stage of skin cancer.
| Melanoma stage | Characteristics of the spread of melanoma |
| Stage 0 | Tis, N0, M0 – the earliest stage. This stage means that the tumor has not spread to the lower layer (dermis). Melanoma is found in the epidermis. |
| IA stage | T1a, N0, M0 – stage 1A melanoma, malignant neoplasm thinner than 1 mm. This stage means that melanoma has not been diagnosed. The rate of spread of metastases is less than 1/mm2. Melanoma has not yet invaded the lymph nodes or distal organs. |
| IB stage | T1b or T2a, N0, M0 – stage 1B melanoma, a malignant neoplasm thinner than 1 mm. Melanoma has been identified, the rate of spread of metastases is less than 1/mm2. Also at this stage, melanoma may not be detected, and its thickness can reach from 1.01 to 2.00 mm. At this stage, melanoma has not yet affected the lymph nodes or distal organs. |
| Stage IIA | T2b or T3a, N0, M0 – stage 2A melanoma. At this stage, the thickness of the melanoma can vary from 1.01 to 2.0 mm, and the neoplasm is identified. Also, the thickness of melanoma can be from 2.01 to 4.00 mm, but the neoplasm is not detected. Melanoma has not yet invaded the lymph nodes or distal organs. |
| IIB stage | T3b or T4a, N0, M0 – stage 2B melanoma. At this stage, the thickness of melanoma can be from 2.01 to 4.00, and the neoplasm is detected. Also, the thickness of the neoplasm may be more than 4.00 mm, but it is not pronounced. There is no melanoma in distal organs and lymph nodes. |
| IIC stage | T4b, N0, M0 - stage 2C melanoma. At this stage, the thickness of the melanoma is 4 mm, it is revealed. Melanoma has not yet invaded the lymph nodes or distal organs. |
| IIIA stage | T1a to T4a, N1a or N2a, M0 . At this stage, the thickness of the melanoma is any, it is not expressed. Melanoma has already spread to 1-3 lymph nodes located next to the area of skin that is affected. However, the nodes have not yet been enlarged. Melanoma is only visible when viewed carefully under a microscope. It has not yet spread to remote areas. |
| IIIB stage | T1a to T4a, N1b or N2b, M0. The thickness of melanoma is any, it is not expressed. Melanoma has already spread to 1-3 lymph nodes located next to the affected area of the skin. Lymph nodes are enlarged. The melanoma has not yet spread to distant areas. T1a to T4a, N2c, M0. The thickness of melanoma is any, it is not expressed. The melanoma has already spread to nearby small areas of skin or, possibly, to the lymphatic channels located next to the tumor. The nodes themselves, however, do not contain melanoma. The melanoma has not yet spread to distant areas. |
| IIIC stage | T1b to T4b, N1b or N2b, M0 . Melanoma is diagnosed at this stage; its thickness can be of any size. The zone of spread of melanoma in this case is 1-3 lymph nodes located next to the neoplasm that has affected the skin. There is an increase in lymph nodes. The melanoma has not spread to distant areas. T1b to T4b, N2c, M0. Melanoma was also detected, the thickness was any. In this case, it spreads to the lymphatic channels located next to the tumor and nearby areas of the skin. Lymph nodes are not affected by melanoma. The melanoma also did not spread to distant areas. Any T, N3, M0. In this case, melanoma may or may not be detected; its thickness can also be any. It has already spread to 4, and maybe more, clustered lymph nodes located near the site of the lesion. It can also spread to the lymphatic channels passing next to the tumor and nearby areas of the skin. Lymph nodes are enlarged. There is no spread to more distant areas. |
| IV stage | Any T, any N, M1(a, b, or c) . At this stage, melanoma has already spread far beyond the area on the skin where it appeared. It also spreads to other organs through nearby lymph nodes. Melanoma can spread to the brain, affecting the liver and lungs. It can affect distant lymph nodes, distant areas of the skin, and subcutaneous tissues. In this case, there is no need to consider the spread of melanoma to nearby lymph nodes, as well as its thickness. But, usually, it is very voluminous and affects the lymph nodes. |
Causes
Skin melanoma develops due to a combination of the influence of the underlying cause and environmental conditions, as well as the internal environment of a person. Today, scientists do not have data on the main etiological factor in the development of skin melanomas. There is a theory that melanoma is a polyetiological disease.
Factors influencing the development of this disease are divided into exogenous and endogenous .
The following exogenous factors :
- Place of residence of a person (geographical latitude) and associated solar radiation activity. The influence of the ultraviolet spectrum is one of the most important factors affecting the development of skin melanomas. Its negative impact is also determined by the fact that ozone decreases in the stratosphere, which leads to an increase in the carcinogenicity of solar radiation. There is confirmed evidence that what is more dangerous in this context is not the chronic influence of ultraviolet radiation, but its sudden and very strong influence, sometimes one-time. Sunburns received in childhood and adolescence are important.
- Injuries to pre-existing nevi - bruises, cuts, abrasions, as well as chronic injury from clothing or shoes.
- The influence of chemical carcinogens.
- Fluorescent lighting – a negative effect is observed with intense exposure to fluorescent lighting sources.
- Ionizing radiation.
- Electromagnetic radiation.
- Socio-economic factors also play a role. In particular, it is noted that the incidence is higher among the urban population; that patients tend to have a higher social status. It is also noted that melanomas occur more often in people working in the rubber, electronics, petrochemical, and coal industries; in contact with polyvinyl chloride, plastics, benzene, pesticides, radiation.
- Biological - dietary habits (large amounts of proteins and fats in the diet), bad habits (alcohol abuse), and taking certain medications have a certain influence.
The development of the disease is also influenced by the following endogenous factors :
- Precancerosis – there are a number of conditions against which a tumor can develop. These are xeroderma pigmentosum (hereditary, recessively transmitted photodermatosis), Dubreuil melanosis (lentigo - areas of skin pigmentation).
- Nevus plays a certain role in the etiology of skin melanomas. It should be noted that in addition to pigmented ones, there are non-pigmented nevi. In addition, there are so-called acquired nevi that appear during life, and which a person may not notice until they transform into a malignant formation. Nevi are a morphologically unstable population of cells, since their localization in the layers of the skin changes throughout life. The number of nevi depends on the hormonal background of the body. Nevi should be considered a phenotypically unstable population of cells. The fact that melanomas develop from nevi is generally accepted, but still, research and observation data do not allow us to state that nevi are the cause of absolutely all melanomas.
- Biological - researchers note that the tumor develops more often in people of the white race. A pigmentation disorder in the body, in which the skin reacts inadequately to ultraviolet radiation, also plays a role. Melanoma most often develops in people with weak skin pigmentation and high sensitivity to UV radiation. Those who are prone to sunburn are more likely to get sick. Heredity also plays a certain role. It has been established that melanoma is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. Hormonal fluctuations also influence the development of the disease ( estrogens and androgens ). Certain importance is attached to immune factors - the risk of disease is increased by immunosuppression and immunodeficiency states.
Treatment of melanoma at different stages
The choice of treatment tactics depends on the stage of the disease and the patient’s health status.
It is important to know! Depending on the size of the tumor and clinical signs, the surgeon chooses the optimal treatment tactics. The given example of manipulations can be adjusted based on the individual characteristics of the tumor.
Stage 0 - immunomodulators are prescribed in combination with surgical removal of the tumor.
Stage I - surgery is prescribed in combination with a biopsy of sentinel lymph nodes. Most often, such treatment is supplemented with chemotherapy to consolidate the results.
Stage II - treatment is the same as for the first stage - removal of the tumor and consolidation of the result with chemotherapy and other treatment methods. If metastases are detected in the sentinel lymph nodes, the surgeon excises them.
Stage III - drawing up an individual comprehensive treatment plan, combining surgery, chemotherapy, immunotherapy or targeted therapy.
Stage IV - complex therapy depending on the condition and well-being of the patient, in severe cases - palliative treatment.
After completion of treatment, the patient is recommended to undergo regular examinations to monitor his health and not miss a recurrence of skin cancer.
You can find out the exact cost of melanoma removal and prices for histological examination of the tumor by phone and at the initial appointment at the clinic.
Read more about why laser is unacceptable and the advantages of surgical excision in the article “Scalpel versus laser”
How long will the patient live after diagnosis?
The prognosis for this cancer depends on several factors, one of which is tumor metastasis.
If melanoma has metastasized, the patient’s lifespan depends on the number of affected organs:
- one – seven months;
- two – up to four months;
- more than two organs – less than two months.
One of the factors influencing the patient's life expectancy is the location of the tumor process. The prognosis is more favorable when melanoma is located on the forearm and lower leg, less so on the scalp, hand, foot and mucous membranes.
Melanoma recurs very often. Scientists have found that the malignant process can start again even ten years after complete recovery.
However, when stage I melanoma is detected and this formation is removed in a timely manner, the prognosis is more than favorable (97% of patients survive).
Statistics and forecasts for melanoma
Every year, about 140 thousand new cases of melanoma are diagnosed worldwide. According to statistics, this type of skin cancer affects women more often, and in every tenth patient a genetic predisposition is “to blame.
In recent years, modern medicine has made a big step forward, giving hope to patients diagnosed with melanoma - when diagnosed at the earliest stage of development and prescribed adequate treatment, recovery occurs in more than 90% of cases.
The age of the patient plays an important role in predicting the outcome of the disease. As a rule, the younger the person, the higher the chances of recovery.
Another interesting factor is that people with fair skin are more likely to suffer from skin cancer. But if a dark-skinned person gets sick, it is believed that his disease will be more severe. Predisposing factors for severe melanoma are chronic diseases and health problems.
Benefits of skin cancer treatment at MelanomaUnit
MelanomaUnit is a branch of an Israeli medical center, the basic principles of which are the highest quality of services, experienced specialists and maximum comfort for patients.
We use equipment from the best manufacturers of medical equipment, certified time-tested drugs and innovative technologies aimed at maintaining health.
Our specialists constantly improve their skills by undergoing training in Russia and abroad. MelanomaUnit doctor is to achieve the best result for the patient.
Make an appointment