Causes of mycosis of nails
Mycosis of the nails and feet develops as an inflammatory process caused by various fungi pathogenic to humans. According to laboratory tests, the most common causative agents of mycoses of the nails and feet in adults are considered to be fungi of the genus Trichophyton; slightly less frequently, mycoses of the nails on the toes and hands are caused by fungi of the genus Epidermophyton and Candida.
Scraping for nail mycosis is not carried out at the MedArt medical center.
Penetration of a pathogenic pathogen into the body and infection of a healthy person is possible both through direct contact with a patient with a fungal disease, and through the use of personal items (shoes, clothing, manicure instruments, bathroom rugs, etc.). Another common way to acquire mycosis of the nails and feet is by visiting swimming pools, bath complexes or gyms.
There are factors that contribute to the development of mycosis of the nails and skin of the feet. These include violation of the integrity and barrier role of the skin in the form of cracks and abrasions of the epidermis. The appearance of skin cracking is caused by constant trauma to this area of the body, increased sweating and subsequent maceration of the skin, excessive dehydration and dryness of the skin. Among the general conditions of the body, greater susceptibility to the disease of mycosis of the nails and feet can be influenced by the presence of flat feet or impaired blood flow in the vascular bed of the lower extremities
It has been noted that in patients with diabetes mellitus, autoimmune diseases, and some blood diseases, nail mycoses, which begin locally, become aggravated over time and become generalized. The use of certain medications, for example, glucocorticosteroids, antibiotics or immunosuppressants for concomitant diseases, also leads to the spread of mycosis of the nails and feet to other tissues.
Sampling for Fungal Nail Infection: 5 Things You Need to Know
“How should I take samples for nail fungus? What to consider and what to pay attention to?” - masters often ask. Specially for ProPodo - an expert column. Elena Ovchinnikova, a bacteriologist of the highest category, head of the microbiological department of the IMD laboratory, answers a common question.
One of the most important stages in the diagnosis of onychomycosis is cultural examination. It is this that allows you to determine whether nail damage is caused by fungal flora, find out what type of fungus caused the disease and what drugs it is sensitive to.
Accurate laboratory diagnosis of onychomycosis depends on how the biomaterial was selected, its storage, transportation and interpretation of the analysis results [2]. Podiatrists often face difficulties in obtaining adequate, good quality samples and interpreting culture results.
To increase the information content of microbiological diagnostics and reduce the risk of a false negative result, if you are taking a fungal test for the first time, you need to clearly know 5 things.
Patient history
Before testing for onychomycosis, it is important to collect a detailed medical history. How long ago did the nail lesions develop, was the patient treated, what antifungal drugs were used (after all, very often people self-medicate fungus). It is also important to clarify whether the nail damage is caused by other diseases, whether a problem with the nail plate has arisen as a result of taking any medications, after a manicure, or exposure to, for example, detergents. In any case, an analysis for onychomycosis will be mandatory, however, a detailed history taking will allow one to suspect nail damage of another etiology.
Preparation rules
To obtain a correct test result for nail fungus, it is important that the patient stop taking antifungal drugs, both systemic and local, two weeks before sampling [1].
Before collecting material, it is recommended to trim the nail, wipe the finger and nail with damp gauze moistened with saline or distilled water to remove dirt and dust. Then it is necessary to treat the nail plate and nail folds with 70% alcohol to eliminate foreign flora and cream residues, if any [2].
Material
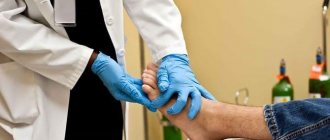
For cultural research, material from the nail bed and from under the nail plate is best suited; sampling is optimally carried out with a large cutter at low speeds.
A sufficient volume of selected samples increases the chances of obtaining positive results, since a small amount of material may contain few elements of the fungus, and a small amount of biomaterial will not be enough for a full microscopy and cultural study.
Collection point
In case of superficial form of onychomycosis, a cutter is used to take a sample from the surface of the nail plate.
In the most common distal-lateral subungual form of onychomycosis, material selection should be carried out with a large cutter at small speeds. Important: be sure to turn off the device’s vacuum cleaner, if equipped. In addition, the boundaries of the area of the undamaged nail should be captured, since the most active elements of the fungus are located at the border between them and the affected areas of the nail [1].
For paronychia, scrapings are made from the proximal ridge and from under it [3]. Specimens suspected of candidal onychomycosis should be taken from the affected nail bed closest to the proximal and lateral margins [1].
Interpretation of results
The results of cultivation may be as follows:
- positive result;
- growth of fungi in association;
- lack of fungal growth, i.e. negative result.
A positive result indicates infection of the nails by one type of fungus, for example, dermatophytic fungi such as Epidermophyton floccosum or Trichophyton spp., non-dermatophytes of the genus Aspergillus, Fusarium or other types of molds, yeast or yeast-like fungi of the genera Candida or Trichosporon.
The growth of fungi in association can be detected both in the actual presence of several pathogens, and in the event of an incorrect technique for selecting material for analysis, as well as improper preparation of the patient. The IMD laboratory's analysis technique reduces the risk of obtaining unreliable results if there is a sufficient amount of materials. This is achieved through a combination of an advanced microscopy method using a fluorescent microscope using the calcofluor white dye and the method of sowing three points on two media in parallel, after which the fungus is identified to the species with an accuracy of 99.9%.
Lack of fungal growth may indicate either a true absence of pathogens or a false negative result. About 30-50% of samples may be false negative due to incorrect sampling or collection of non-viable fungal elements in the distal part of the nail, as well as improper patient preparation. [1]. In order to avoid such situations, it is necessary to follow the rules for the preparation and selection of material, which can be obtained by contacting the IMD team.
If you are interested in additional information on mushrooms, the IMD laboratory team is ready to provide it. Contact: Ivan, product manager of the mycology department. +380678092182
Literature:
1. Leelavathi M. and Tzar M.N. Brief Report: Nail Sampling Technique and its Interpretation. Malays Fam Physician. 2011; 6(2-3): 58–59.
2. Tosti A. Onychomycosis Workup. Medscape.Oct 05, 2022.
3. Rastamovna A.A. Evaluation of laser therapy for onychomycosis using Q-Switched. Monograph.
Symptoms of mycosis of nails
The main signs of mycosis of the nails and feet include:
- local itching of the skin, burning, redness (hyperemia) of the skin;
- increased peeling, detachment of the epidermis in the form of layers;
- thickening and excessive keratinization of the skin;
- the appearance of superficial or deep cracks on the foot, in the spaces between the toes;
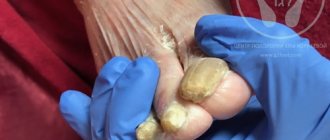
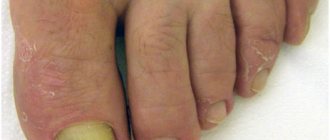
- a noticeable change in the color, shape or structure of the nail plate of one or more fingers;
- redness, swelling and maceration of the skin between the fingers, the formation of blisters.
There are several clinical forms of mycoses of the nails and feet, depending on the type of pathogenic pathogen. Some diseases occur with predominantly cracking of the epidermis and peeling, others with severe weeping and the appearance of diaper rash.
Research methods
The fungus is detected using microscopy.
Research methods include:
- scraping for demodex;
- analysis for fungus detection.
In order to identify the pathogen, it is necessary to find out which of the four groups of pathogenic fungal infections it belongs to:
- Keratomycosis. Caused by pathogenic microorganisms that affect the upper layers of skin and hair, while the surrounding tissues are not involved in the inflammatory process.
- Epidermomycosis. It manifests itself as inflammation of the skin with deeper tissue damage.
- Trichomycosis. With insufficient attention to one's health and untimely treatment, the disease progresses and turns into purulent inflammation with the development of local changes.
- Dermatomycosis. It is observed in patients with a weakened immune system and metabolic disorders. Fungal microflora penetrates into the deep layers of the dermis, the disease most often affects children and elderly people with chronic pathologies.
Medical offers to sign up for diagnostics and tests. In our laboratory it is possible to take all types of tests in Tula. Tel. for recording.
The doctor visually assesses the patient’s condition in order to then prescribe the necessary diagnostic tests:
- General analysis of urine and blood.
- Scrapings from affected areas to determine mycotic infection.
- Collection and inoculation of biomaterial samples.
The collection of biomaterial is carried out by a laboratory assistant by grinding the nails in order to subsequently conduct a study to detect dermatophyte spores or pseudohyphae of mycelium. The basis of the study is microbiological analysis. Before treatment and during antifungal therapy, a dermatologist may prescribe a biochemical blood test to determine the development of a fungal infection.
For a comprehensive diagnosis of nail mycoses and making the correct diagnosis, a number of tests are carried out to determine:
- stage of the disease;
- how far the fungus has spread in the patient’s body;
- patient's sensitivity to drugs;
- degree of risks and complications.
Why do you scrape nail fungus?
It is quite difficult for an ordinary person to diagnose mycosis by appearance. However, experienced dermatologists usually recognize the presence of fungus visually. To confirm the suspected diagnosis, you need to take an analysis of nail scrapings.
In addition, there are many diseases whose symptoms resemble fungal infections. Therefore, the most objective result can be obtained only by conducting a laboratory study.
In addition to scraping, the doctor may prescribe a hemotest to identify nail plate fungus. This test is a blood test to determine whether there are various types of infections in the body.
This test is prescribed before the start of treatment, during therapy and at its end. The analysis makes it possible to determine not only the type of infectious agent, but also to understand whether the body has affected internal organs.
Prevention of nail fungus
It is more rational to adhere to simple rules of prevention now than to treat nail fungus in the future.
- Regularly check and inspect your nails, feet, and skin between your toes for spots, peeling, and cracks.
- Be responsible when purchasing shoes - they should be moderately loose, made from natural materials that allow air circulation.
- Use replaceable shoes in public places, such as: bathhouse, sauna, swimming pool, beach.
- Don't use someone else's shoes.
- For nail care services, choose trusted nail salons that sanitize tools after each client.
- To avoid acquiring toenail fungus, you should wash and dry the areas of your lower extremities between your toes every day.
- Socks, knee socks, and tights should be made from natural materials and changed regularly.
- To avoid re-infection, you should disinfect everything that the infected person has interacted with: clothing, bedding, shoes, floors, bathtub, shower, etc.
Dermatomycoses include:
- microsporia (causative agent - Microsporum genus); trichophytosis (fungi of the genus Trichophyton);
- epidermophyton (Epidermophyton floccosum);
- rubromycosis (Trichophyton rubrum);
- epidermomycosis (athlete's foot) of the feet (Trichophyton mentagrophytes).
What is being investigated:
When conducting an analysis for fungi, blood, sputum, scrapings from the skin and mucous membranes, hair or nails are examined. The analysis can be carried out by microbiological methods (microscopy, culture), PCR and ELISA methods.
The material for analyzing nail fungus is scraping with a sterile scalpel from different parts of the nail plate. If the skin is affected, a scraping is made from the border of the lesion - this is where the highest concentration of the pathogen is. If the scalp is affected, then in addition to the skin flakes, hair is also taken for examination. They are carefully removed using tweezers.
Profile “Beauty of hair, nails, skin”
Hair
- Do not use medicated hair products 2 weeks before the test. Dyed, bleached, permed hair is not suitable for research.
- Hair should be clean and dry. Using scissors, cut one tuft of hair (the thickness of a match) from the occipital, temporal, parietal and frontal parts of the head.
- After this, place all the bundles in one envelope and seal it. Write your full name on the envelope. and research code.
Types of nail fungus
There are three clinical types of nail fungus:
- normotrophic - the color of the nail plate changes, yellowish and white areas appear. The nail does not lose its shine and thickness within normal limits;
- hypertrophic - the nail plate acquires a yellowish tint, thickens, deforms and splits in the future. The shine of the nail is lost, crumbling on the sides is possible;
- onycholytic, or atrophic - the nail becomes thinner, and the damaged area peels off from the nail bed.
Depending on the location of the infection, the following forms are divided:
- distal (at the tip of the nail);
- lateral (on the sides of the nail);
- proximal (at the posterior skin fold);
- total (over the entire surface of the nail).
Heavy metals in hair (complex)
Attention: Hair must be clean and dry: without hairspray, gel, styling fluid or other cosmetics. Dyed hair is collected for analysis no earlier than 2 months after dyeing. 2 weeks before collecting hair for analysis, do not use medicated shampoos, gels, lotions, balms, or anti-dandruff products. Do not use anti-gray medications (anti-gray hair, etc.) for 3 months. Tools for cutting hair (scissors or razor) must be clean.
Collection rules
- Wash your hands thoroughly.
- Use scissors to cut off some hair, as close to the roots as possible, from different parts of the head. For analysis, 50 mg of hair is needed, which is approximately a bundle the thickness of two matches.
- After this, place the hair in one envelope and seal it. Write your full name on the envelope. and research code.
Types of tests for fungus
The following types of biomaterial are used to diagnose fungal diseases:
- Discharge of the genitourinary organs (analysis of semen and prostate secretions, smears from the urethra, uterine walls and cervical canal);
- Nail plate;
- Hair;
- Skin;
- Blood;
- Urine;
- Feces;
- Upper respiratory tract discharge (nasal and throat swab);
- Lower respiratory tract discharge (sputum);
- Discharge from wounds, ears and eyes;
- Bile;
- Puncture fluids (cerebrospinal fluid, articular fluid, pleural and abdominal effusion, etc.).
When should you get your nail scrapings tested?
Nail fungus is a disease that has symptoms similar to other pathologies. Therefore, dermatologists refer patients for nail scrapings in the following cases:
- when the color of the nail plate changes. If the nail is no longer transparent, turns grey, yellowed or brown, this indicates an existing problem. If the lesion has affected the entire surface, then the inflammatory process has been continuing for a long period.
- when the mobility and density of nails changes. If there are pathologies, a piece of the nail may move away from the finger. Over time, the plate begins to peel off, becomes thick and hardens.
- when the shape of the nails changes. Sometimes, with a fungal infection, the plate becomes convex. With pathological processes in the legs, people begin to complain of discomfort when walking, running and other active activities.
The procedure for scraping nails for fungus is quick and does not cause discomfort, so it can be easily performed even on pediatric patients.
A dermatologist uses a sterile disposable scalpel, special scissors or a dissecting needle to take nail scrapings for fungus. These instruments make it possible to remove affected tissue elements from the nail plates without coming into contact with healthy skin. The resulting biological material is placed on glass, placed in a sterile tube and delivered to the laboratory. There, a specialist conducts a microscopic examination of the nail scrapings.
Symptoms and when you can’t pass a medical examination
Answering the key question of the article, “will you be able to pass a medical examination to work with fungus,” we can say that everything depends on the stage, the degree of manifestation. And the symptoms here develop as follows:
Sign up
- The fungus begins with itching of the feet (on the sides, between the toes, the pads of the nails);
- then whitish peeling occurs;
- then the nail (as a rule, the process begins with the thumbnail) changes its structure and shape: it becomes thinner, cracks, breaks off;
- its color begins to change (dirty yellow, dark brown spots appear), the nail is gradually destroyed, and a new one grows in the form of a thickened, loose growth, an unpleasant, fetid odor appears from the affected area;
- it is possible that a secondary infection may occur and a purulent process may develop.
Starting from the third point, during a medical examination it will be difficult to hide the active form of nail fungus. Those. in case of obvious symptoms, a medical examination, in most cases, will require a course of treatment. Because nail fungus is extremely contagious. And the survival rate of fungal spores is simply phenomenal. For example, in shoes, in a dry and dark room, spores retain their virulence not even for years, but for decades.
Preparation for analysis
For an accurate diagnosis, you need to properly prepare:
- Avoid water procedures using disinfectants for several days.
- Do not use perfumes and cosmetics in places from which you will need to scrape.
- Do not do manicures, pedicures, and especially do not cover your nails with varnish (any kind).
- Before going to the laboratory, do not cut your nails for 7 days.
- Do not use medications that may affect the test result.
A scraping cannot always show the presence and nature of a fungal infection, so you should undergo additional research - a PCR test and bacterial culture to determine the pathogen and select an effective drug.