Date of publication: 08.28.2020 22:42:00 Date of modification: 04.14.2021 Author: Lada Obereg
Veronika Herba - urban beauty and health center
From this article you will learn:
- Why you may need to remove a keratoma
- What types of keratomas exist?
- Why is keratoma dangerous and why is it necessary to remove it?
- Removal of keratoma: main methods and their features
- Rehabilitation period after keratoma removal
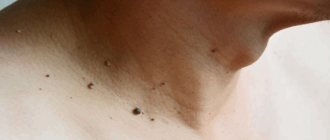
Keratoma removal is a surgical intervention based on the use of one of the possible destructive treatment methods. Thanks to this operation, you can completely get rid of this specific formation on the skin of a dark brown or brown color, similar to a freckle.
When a keratoma first appears, it can be very small, but after a while it grows to 1–2 centimeters. Most often this is a single formation, but sometimes small groups can form. Patients do not feel any pain, but the feeling of discomfort forces people to seek help from a doctor.
What is human papillomavirus?
Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) is a virus that can infect the skin and mucous membranes of the mouth, throat, genitals, and anal area. HPV infection is widespread. Most people with HPV do not develop any symptoms and their immune system clears the virus without any treatment. In some cases, HPV can lead to cancer. We don't know why some people get rid of HPV before it causes cancer and others don't.
to come back to the beginning
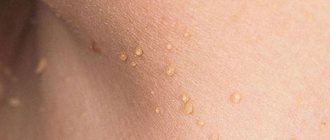
Removal of papillomas on the head in dermatology
Any formations, even large ones, can be removed quickly, painlessly and safely.
Benefits of physical removal:
- instant and guaranteed effect
- formations can be removed in any quantity, of any size
- there is no risk of damage to surrounding tissues if the procedure is carried out correctly
- no pain thanks to anesthesia
- good aesthetic effect
Cryodestruction
Liquid nitrogen is a classic way to remove papillomas.
It has a number of advantages:
- simplicity
- rapidity
- no anesthesia needed
- efficiency
- formations of any localization can be removed
- low price
But there are a number of disadvantages.
After liquid nitrogen, an inflammatory reaction often occurs in the affected area, which is fraught with pain.
Only small formations can be removed.
When trying to remove large papillomas, it is necessary to increase the exposure time to liquid nitrogen, which can result in the appearance of scars.
In addition, there is no material left for histological examination.
Laser
Laser removal of papilloma on the head is becoming increasingly popular.
The method has many advantages:
- no bleeding due to vascular coagulation
- there are no infectious complications, since the laser destroys bacteria
- accelerated tissue healing
But there are also disadvantages.
Only small papillomas can be removed (although larger than when using liquid nitrogen).
They do not separate from the body, but are destroyed.
Laser vaporization involves evaporation of the formation.
They usually do not work in laser cutting mode.
Because after it the tissues do not grow well together (a dense scab forms on the surface).
As with removal with liquid nitrogen, there is no material left that could be sent for histological examination to exclude malignant degeneration.
Electrocoagulation
The method uses electricity to heat tissue.
Electrocoagulation works in both cutting and coagulation (resolution) modes.
Advantages of the method:
- even a large papilloma on the head can be removed
- instant sealing of blood vessels and elimination of bleeding
Flaws:
- Wounds take longer to heal than after laser
- sometimes scars appear
Electrocoagulation is more suitable for removing formations that rise above the skin level.
They can be separated from the body and sent for histological examination.
Radio wave method
The radio wave method is the same as electrocoagulation, only electromagnetic waves have a high frequency.
This is a more advanced removal method.
Papillomas of any size can be eliminated.
Wounds after radio waves are sterile and heal quickly.
If necessary, they can be sutured, as after dissection with a scalpel.
This improves aesthetic results when removing large papillomas.
Are there different types of HPV?
Yes, there are different types of HPV. Some types of this virus cause warts to grow on the skin, mouth, or genitals. Other types can lead to cancer. These are called high-risk types. High-risk HPV can cause a variety of cancers, including cancer of the cervix and vulva in women, the penis in men, and the anus. The most common type is cervical cancer. This is why women have a cervical smear (also called a Pap smear) to check for cervical cancer, which includes testing for HPV.
High-risk HPV can also cause head and neck cancer in men and women.
to come back to the beginning
Ointment for papillomas on the head
There are methods of treating human papillomavirus infection with drugs.
These include removal methods:
- cytotoxic
- chemical
The cytotoxic method involves applying an ointment to the scalp that blocks cell division and causes cell death.
This is a long-term treatment.
The ointment should be applied for several days in a row.
Then a break is taken and the results are assessed.
If the papilloma does not disappear, the course is resumed.
It can be suspended and resumed several times.
Treatment lasts 4-5 weeks.
If there is no result, removal of the papilloma in a more reliable way is indicated.
Another method is chemical.
It involves the simultaneous destruction of papilloma.
The procedure is performed only by a doctor.
Concentrated acid solutions are used.
They simply cause necrosis of the skin in the area where the condyloma is located.
Great care is required when applying such products.
After all, they destroy healthy skin just as easily as skin affected by papillomavirus.
The procedure has both pros and cons compared to the physical removal of condylomas.
Pros:
- low price
- simplicity - no special equipment required
- accessibility - no need to look for a specialized clinic, any dermatologist in a clinic or private office can remove papilloma in this way
Minuses:
- high risk of complications - with a deep chemical burn of the skin, scars may appear on the head
- Sometimes nearby healthy skin gets burned
- the procedure is not always effective
- Suitable only for removing small papillomas
- there is no material left that could be sent for histological examination
There are more disadvantages to using drugs for papillomas on the head than advantages.
Therefore, doctors usually give preference to the physical removal of these formations.
How do people become infected with HPV?
HPV can enter your body when your skin or mucous membranes come into contact with the skin or mucous membranes of an infected person. This usually occurs during vaginal, anal or oral sex with a person who has the virus. Because HPV is so widespread, it is difficult to determine when the infection entered the body and who transmitted it. Moreover, your first symptoms of HPV may appear several years after sex with an infected person. For this reason, it is difficult to find out when you were first infected.
to come back to the beginning
Is it painful to remove papillomas on the head?
Removal without anesthesia would be painful.
However, modern drugs make it possible to completely “turn off” the sensitivity of the skin in the affected area.
Therefore, the patient does not feel anything during the procedure.
There are two types of anesthesia that are used when localizing papilloma on the head:
- appliqué
- infiltration
Application anesthesia involves applying a gel with an anesthetic effect to the skin.
The impact is less profound.
It takes 20 minutes for the effect to develop.
Minor pain may persist during the procedure.
But such anesthesia does not require injections.
Infiltration anesthesia is more effective.
Anesthetics are injected with a thin needle into the skin in the area where the papilloma is located.
The skin here completely loses sensitivity.
The doctor can remove even large formations, and the person does not feel anything.
The drug acts almost instantly.
The injection is usually moderately painful.
A very thin needle is used to inject the anesthetic.
But some anesthetics cause a short-term burning sensation in the skin at the time of injection.
Once the anesthesia wears off, there is usually no pain.
Especially after laser or radio wave removal.
Because with this method, the nerve endings are “sealed”.
After removing the formation, the patient treats the wound with an antiseptic for several days.
No pain medications are required.
Am I contagious?
HPV is not spread by physical contact (such as touching and kissing the cheek or lips), but you can get HPV through vaginal, anal, and oral sex. This means that if you have HPV, your sexual partners may also have the virus. Because most people clear the infection on their own, the chance that your partner will have cancer caused by HPV is very low, even if infected with the high-risk type. If you are diagnosed with cancer caused by HPV, you do not need to change your sexual behavior in any way.
to come back to the beginning
Should my partner get tested for HPV?
- Women should follow routine women's health recommendations, which include regular cervical smears.
- Men do not need to undergo any special examinations or tests as there are no routine or routine HPV tests available for them.
The chance of your partner developing cancer caused by HPV is very low. If your partner has symptoms or concerns, you should discuss this with your doctor.
to come back to the beginning
What can I do to avoid getting HPV and spreading it to someone else?
Condoms and dental dams (a thin, rectangular sheet of latex or silicone that covers the genitals of a woman receiving oral sex) are not as effective against HPV as they are against other sexually transmitted infections (STIs), such as chlamydia and immunodeficiency virus. human (HIV), but their use reduces the likelihood of HPV transmission. Always use condoms or dental dams during vaginal, anal, or oral sex.
You should also get vaccinated against HPV and encourage your partner to do the same.
to come back to the beginning
How can you become infected with HPV?
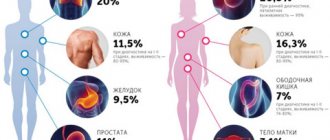
Scalp papilloma is an external manifestation of an internal problem, the HPV virus. According to statistics, its carriers make up 70% of the world's population, regardless of age and gender.
The virus is believed to be most often transmitted through sex. It is also possible to transmit HPV at home, from mother to child during fetal development, birth or breastfeeding.
Once inside the human body, the virus lay dormant for a long time,” i.e. there are no external signs. When the patient’s immunity decreases due to the negative influence of internal or external factors, manifestations of HPV occur - pointed condoms, which are located on the skin and mucous membranes.
In utero
According to statistics, intrauterine infection of a child is rare. This is possible if the structure of the placenta changes, for example, if it is damaged. In a child, alveoli and bronchi do not form in the uterus, so the penetration of HPV into his body leads to the development of respiratory tract papillomatosis. Head papillomas are rare.
The consequences of intrauterine infection are congenital respiratory diseases, the correction of which requires surgical intervention. To avoid adverse consequences, a pregnant woman should be diagnosed with HPV when planning a pregnancy, and if detected, undergo treatment.
At birth
Why do newborns have papillomas on the head, skin, and mucous membranes? The reason for this is vertical infection, i.e. entry of the virus during birth. As a result, sharp condoms appear in the child's mouth and throat. In the future, problems associated with respiratory diseases and low immunity may arise.
If a woman has papillomas on her genitals, doctors recommend not giving birth naturally, i.e. increasing the likelihood of infection, and preferring a caesarean section. Breastfeeding is an additional risk factor.
By everyday means
Scalp papillomas are a consequence of the HPV virus that has entered the body through internal routes, i.e. through microcracks, small wounds, scratches on the skin and mucous membranes. This happens at home like this:
- With towel, bed linen, soap or dishes.
- Wear the same clothes, especially underwear.
- Eating from a plate, cutlery, incomplete washing of ordinary dishes.
- Walk barefoot in public baths, saunas, swimming pools: A moist, warm environment is a good environment for the spread of the virus that causes papilloma on the head.
- Shake hands, kiss, if there are microcracks on your lips, hands.
In addition to the above methods, doctors determine a special mode of transmission - self-infection. When shaving the bikini line, a person damages the papilloma, which contributes to the further spread of the virus.
A similar situation can arise when cleaning the head.
Sexually
Papillomas on the head in the hair are the result of HPV infection, the most common method of penetration is sexual. To transmit a dangerous strain, one intimate contact of any kind is enough, be it vaginal, anal or oral.
The likelihood of infection increases significantly if the partner has microcracks in the genitals. If anal sex is practiced, it is possible that a pointed discharge may form in the anal area.
Among the factors that increase the likelihood of infection:
- early onset of intimate life;
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- partners with papillomas and warts on the head, in other places.
A condom can be used to reduce transmission, but does not guarantee 100% protection. Its effectiveness is especially low if the partner has papillomas in the entire groin area.
Poor health
Once inside the body, the hair papillomavirus can sleep for a long time, i.e. there are no external signs. Its rapid vital activity begins in the presence of a provoking factor—lowered immunity. You can give it triggers:
- colds;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- constant nervous tension, stressful situations;
- advanced age of the patient;
- hormonal disorders;
- uncontrolled oral contraceptives;
- vaginal or intestinal dysbiosis;
- bad habits (smoking, love of alcohol), etc.
When one or more of these factors occur, external manifestations of the virus occur. One of them is papillomas on the head, which become a cosmetic defect and in some cases can degenerate into malignant tumors.
Diagnostics
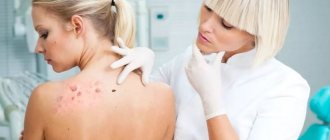
If the patient has papillomas on the head, do not try to remove them yourself using popular methods. To avoid accidental damage to the body, it is necessary to undergo a medical diagnosis. The first and most important step is an external growth examination by a dermatologist and taking a medical history.
If symptoms indicate scalp papilloma, the patient needs additional analysis - a PCR test. It shows whether the HPV virus is present in the body, what type and in what quantity. Depending on the danger of the detected strain and its concentration, the doctor decides what treatment to prescribe.
Video
Removal of papilloma in hair on the scalp
Symptoms of the disease
Hair papilloma on the scalp has two types:
These are elongated branches on a thin stalk, ranging from 1-2 mm to several centimeters in length. These are bristly neoplasias that are slightly yellow in color. They do not hurt, do not itch, and do not develop into malignant tumors. Such papillomas are usually diagnosed in older people.
These are head papillomas with a wide base, slightly convex, up to 4 cm in diameter. They differ in color from the surrounding skin: their color is brownish, darkening over time. Such neoplasms can transform into malignant ones, so they require mandatory medical diagnosis.
Treatment methods
Doctors agree that treatment of scalp papillomas should be comprehensive. It is not enough to eliminate the consequence - a neoplasm that has become a cosmetic defect. It is important to "contain" the virus that caused it in order to boost immunity so that similar things don't happen in the future.
Treatment of the optic disc includes the following methods of action:
- growth removal;
- taking medications;
- vitamin therapy;
- the use of folk remedies in addition to the above activities.
It is strictly forbidden to remove papillomas on the head itself, for example, with sutures or scissors.
Such treatment at home has dire consequences: Inflammation of surrounding tissues, spread of infection, bleeding, birth of a tumor leading to a malignant tumor.
Drug therapy
Drug treatment for scalp papillomas is aimed at “turning off” the virus that has entered the body. The following groups of drugs are used for this:
- Antiviral drugs - used in the form of tablets, injections, vaginal or rectal suppositories. Their goal is to inhibit the activity of HPV. This category of drugs includes isoprinosine (used in courses twice every two weeks with a 10-day break), panavir (used in a course of 5-10 days).
- Immunomodulators - used as tablets or injections. The most well-known agents in this category are polyoxidonium and lycopid.
- Vitamins - used as an adjunct to drug therapy.
- External pharmaceutical products - burning ointments (Verrukacid, Kolomac, etc.), local antiviral drugs (the most famous - epigen intimate spray applied to excrement) are used to combat scalp papillomas.
You may be interested in: Arthrosis of the joints - symptoms, stages, modern diagnostics and methods of effective treatment.
The combination of drugs is selected by the doctor based on the results of the diagnosis. Treatment is not specific to different types of HPV.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies are used as an adjunct to drugs for the treatment of scalp papillomatosis. Many of them are controversial, so their use is possible only after consultation with a dermatologist.
There are the following recipes on how to remove papillomas on the head at home.
The juice is squeezed from the stem of a freshly torn plant and applied to the new growth. The process is repeated until it turns black.
This is a pharmaceutical analogue of freshly squeezed juice of a medicinal plant. The papilloma evaporates, the area around the papilloma is covered with foam, and the product is applied to the site. The number of repetitions of the procedure is until the tumor turns black.
The starting product is grated, mixed with water and forms a thick paste. Then it is applied to the papilloma, covered with a gauze bandage and left overnight.
This product is known for its ability to increase local immunity and stimulate metabolic processes. Thus, the papilloma is smeared daily in the morning and evening until it completely disappears.
Disinfection properties are attributed to this product. A small amount of it is applied to the tumor and not washed off.
After regular treatment, the papilloma should turn black and disappear.
Surgical intervention
To determine how to remove papilloma on the head in the hair, you should seek advice from a specialist. The following methods of their resection are possible:
- use pharmaceutical burners;
- laser removal;
- electrocoagulation;
- cryotherapy;
- classic scalpel resection.
Laser removal is recognized as the most advanced method, as it reduces the healing time of a head wound to 10 days and reduces the likelihood of scars, scratches and relapses to zero. This method is not used for neoplasia, the benign nature of which is doubtful, since the tumor “evaporates”, i.e. no papillomatic tissue remains for histology.
Electrocoagulation is the effect of an electrical impulse. It destroys the neoplasm tissue, and a crust forms in its place, which disappears after a week. The healing time for the operated area is about 14 days. After the operation, the wound must be treated with disinfectants and a plaster or bandage applied for 1-2 days.
Cryotherapy is recognized as a modern and effective method of combating papillomas. Resection with liquid nitrogen is required. Fertilization lightens and then spontaneously disappears. The method is mainly used for small papillomas. Healing time is up to 14 days. The method is contraindicated for people with individual intolerance to cold.
Surgical resection with a scalpel is used for large papillomas on the head and for formations that become malignant. It is performed under local anesthesia and leaves the chance of scarring. If it is necessary to study the removed material, the tissue is sent for histology.
Prevention measures
Papilloma on the scalp is a form of HPV infection. Modern medicine does not offer 100% methods of its prevention, but makes the following recommendations
- Wearing rubber slippers in public baths and saunas;
- infrequent change of sexual partners;
- Condom use;
- Hygiene (washing hands after visiting public places);
- refusal to use personal belongings of a person with papilloma and warts on the skin.
To prevent external signs of the papilloma virus, it is important to maintain a high level of immunity.
This is facilitated by timely treatment of colds, taking vitamins in autumn and spring, ensuring a balanced diet, adequate rest and sleep, and moderate physical activity.
Should I get vaccinated against HPV?
Anyone between the ages of 9 and 26 can get the HPV vaccine to protect against genital warts and the various types of HPV that can cause cancer. It is recommended that children be vaccinated between the ages of 11 and 12 so that they are protected several years before becoming sexually active.
This vaccine is not usually given to people over 26 years of age. However, no matter your age, talk to your doctor to find out if the HPV vaccine may benefit you.
to come back to the beginning
How does HPV cause head and neck cancers?
We don't know for sure how HPV causes head and neck cancers. Most people with high-risk HPV will not get cancer. However, some people cannot get rid of HPV. In this case, the virus can cause damage that will ultimately cause the development of a tumor. It often takes many years for HPV-infected cells to transform into cancer cells. It is impossible to predict who will clear the infection from their body and who will develop cancer. Most head and neck cancers caused by HPV form in the part of the throat where the base of the tongue and tonsils are located.
to come back to the beginning
Why is keratoma dangerous and why is it necessary to remove it?
Keratoma itself does not pose a threat to human life and health. However, due to the fact that over time it is increasingly exposed to negative factors, such as mechanical damage and exposure to ultraviolet radiation, this benign neoplasm can degenerate into a malignant tumor.
Sometimes a keratoma can cause significant discomfort to a person. Itching, burning sensation, inflammation, bleeding, pain - all these are alarming signs. The appearance of these symptoms may indicate that the process of degeneration of the keratoma into a malignant neoplasm has begun.
If you notice new moles, spots on your skin, or strange growths, be sure to visit a dermatologist-oncologist who can conduct research and determine whether the formations on the skin are malignant. Next, it is important to undergo regular medical examinations to prevent the occurrence of cancerous tumors.
Also, in a medical institution, you may be offered to remove keratomas on the face and other parts of the body and get rid of the need to regularly see a doctor.
What about tobacco and alcohol?
People who smoke and drink alcohol are more likely to develop head and neck cancer. However, cancers caused by HPV can develop regardless of whether you drink alcohol or use tobacco products. People with cancer, non-smokers and people who don't drink alcohol have a longer life expectancy and are less likely to develop new types of cancer. For this reason, people with head and neck cancer should stop smoking and limit their alcohol intake. If you need help breaking these habits, MSK can help. Ask your doctor or nurse for more information about our programs, or call the Counseling Center at 646-888-0200.
to come back to the beginning
How long does it take for wounds to heal after mole removal?
It all depends on the area of the base of the removed formation, that is, on the size of the wound itself, as well as on the characteristics of the skin where the mole grew (on the face, neck, and scalp, wounds heal the fastest, and in injured areas or on natural folds of the body - longer) .
On average, the skin after mole removal takes 10-14 days to heal. During this time, the wound should be covered with a dense scab-like crust. It is formed by an oncodermatologist after removal, and then gives the patient detailed instructions for care.
A strict restriction is not to wet the scab during the first 24 hours after mole removal. Then you just need to repeat the treatment after each water procedure.
The wound is considered healed when the crust has fallen off (on its own!) from the surface and the wound site is no longer wet. Healing after mole removal will proceed faster if you follow all the doctor’s care recommendations.
If after removal the mole takes a long time to heal (more than 3 weeks), you must contact the doctor who performed the removal. The sooner a problem is addressed, the less effort it will take to fix it.
Changes at the site of the removed nevus
If, after removing a mole, strange changes occur at the healing site, immediately contact the doctor who removed it.
Reasons for concern may be compaction, vascular growth, itching, burning, pain, or colored areas at the removal site. All these changes do not necessarily indicate recurrence of the nevus. These may be the same keloid changes, rough scarring or scar pigmentation (darkening of the young skin covering the scar - this often happens when the scar is exposed to sunlight immediately after it has healed.)
Resources
There is a lot of information on the Internet about HPV and cancer, but sometimes it is contradictory and unreliable. We recommend contacting the following organizations for further information:
American Cancer Society (ACS) www.cancer.org 800-ACS-2345 (800-227-2345)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention www.cdc.gov/std/hpv/default.htm
Support for People with Oral and Head and Neck Cancer (SPOHNC) www.spohnc.org 800-377-0928
Return to top
Removal of keratoma: main methods and their features
Keratoma removal is a surgical operation, a destructive method of treating skin diseases, which involves excision of excess epithelial formations. Keratoma is a special formation of the epidermis that is dark brown or yellowish in color, resembling a pigment spot. The size of a keratoma can range from small (a few millimeters) to large (several centimeters). Usually this is a single spot, but sometimes they can form small groups. Keratomas are not dangerous to health and usually do not cause significant discomfort to a person. They can go away on their own when the keratinized cells completely exfoliate and fall off.
Doctors say that keratoma is not hereditary, but is the result of the influence of negative environmental factors. The main one is exposure to ultraviolet radiation during uncontrolled exposure to the sun, due to which skin cells die and become keratinized, forming keratomas. Over time, they grow and change color to dark or yellow.
Keratoma is not at all life-threatening and is not a cause for concern. However, it can cause significant physical and aesthetic discomfort to a person. In addition, there is a possibility that when exposed to certain negative factors, it will degenerate into a malignant tumor.
The procedure for removing keratoma has multiple positive reviews. This is the best way to get rid of complexes and prevent the development of serious health problems. It is not recommended to remove keratoma at home. An operation to get rid of a skin tumor must be carried out in a medical clinic only by certified specialists in a way that is most suitable for the patient due to the individual characteristics of his body.