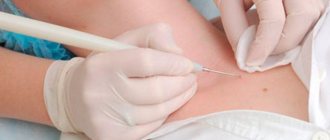
Today, very often doctors are asked for help in removing warts of various locations. Electrocoagulation is considered the most effective technique. One of the main advantages of this procedure is the removal of warts even in hard-to-reach places. The only exception is warts that are localized on the sole. They have a rough and dense structure. Warts are removed with a special device – an electrocoagulator.
What are the methods for removing warts?
When a patient goes to a medical institution with similar problems, he is offered removal in different ways. As a rule, these are laser coagulation, liquid nitrogen or cryodestruction (removal occurs by freezing), electrocoagulation (new growths are burned out with electric current), radio wave technique (removal with high-frequency radio waves) and surgery (warts are cut out with a scalpel).
Naturally, before making a choice in favor of any technique, it is necessary to fully study its principle and consult with your doctor. Perhaps in your case the chosen method of getting rid of warts is not suitable for you.
We care about your health
If you want to remove a mole quickly and without pain, contact the Medkvadrat clinic. The procedures are performed by qualified surgeons and dermatologists. In their work, specialists use effective methods: laser and radio wave surgery, electrocoagulation. Modern equipment allows treatment of adults and small children.
Moles are benign skin growths that occur in people of any age with different skin types. They form on all parts of the body: on the face, neck, arms and legs. They can be convex and flat, vascular and pigmented.
The most common types of moles are:
- Pigmented nevi are clusters of melanocyte cells that form the pigment “melanin”. They have the form of a spot, nodule or plaque. Their size and number largely depend on heredity.
- Papillomas are thread-like or cone-shaped warts on a thin stalk. Their appearance is associated with carriage of the HPV virus, which is most often transmitted by contact. The virus lies dormant in the body and manifests itself when immunity decreases.
- Warts – usually look like flat, “flattened” flesh-colored plaques. May be single or multiple. The cause of warts is the HPV virus.
- A keratoma is a flat, brown plaque with a rough surface that can crumble and crack.
- Atheroma or wen is a flesh-colored formation that protrudes above the surface of the skin in the form of a hemisphere. Formed when the excretory duct of the sebaceous gland is blocked.
- Vascular moles (hemangiomas) are red spots or nodules of varying intensity. The cause of its appearance is vascular pathology.
If the formations on the skin are single, small in size and do not bother you, there is no need to touch them. However, there are cases when surgical treatment cannot be avoided.
When is mole removal performed: papillomas, nevi, warts?
It is necessary to get rid of formations if:
- The bulging formation is bothering you. You constantly injure him with accessories, clothes or a razor. In this case, a mini-operation is required, since against the background of damage, the nevus cells degenerate and become malignant.
- A mole spoils the appearance. Modern hardware surgery allows you to completely get rid of growths of any location: face, neck, eyelid skin. You will not feel pain, and not even a pigment spot will remain at the site of formation.
What methods are used to remove moles and papillomas?
The most popular methods:
- cryodestruction (cauterization with liquid nitrogen);
- mechanical removal with a scalpel or tweezers;
- electrocoagulation (exposure to electric current);
- laser treatment;
- radio wave surgery (radio knife).
The most progressive and gentle methods are laser and radioknife treatment. The procedures are well tolerated, so in 1 session you can get rid of several formations at once.
At the Medkvadrat clinic, doctors use both methods. Each of them has its own characteristics and advantages.
Laser mole removal
The doctor acts on the formation with a powerful laser pulse for several seconds. The thermal energy that is generated in the skin leads to the gradual destruction of pigment or vascular formation. The doctor acts on the mole locally: damage to neighboring areas of the skin does not occur.
Advantages:
- Safety. The laser “seals” small vessels, so no blood is released during the procedure and there is no risk of infection.
- Minimal pain. The area of influence of the laser beam is so small, and the effect occurs so quickly that the person does not experience significant pain.
- Good cosmetic effect. Laser treatment is performed on the face, neck and other open areas of the body. Since no open wound is created, the skin heals very quickly and without scarring.
Radio wave surgery.
The radio wave method involves local exposure of living tissue to high frequency electric current (100-300 Hz). Under the influence of radio waves, cells literally evaporate from the surface of the skin.
The device that uses the radio wave treatment method is called “Surgitron”.
During the procedure, the doctor cuts off the mole with a non-contact scalpel. As with laser exposure, the mini-operation is bloodless, since the radioknife “solders” the walls of the capillaries.
Advantages:
- Relative painlessness.
- Minimum exposure time.
- Fast healing.
- There is no risk of complications (if performed correctly).
- It is possible to conduct a histological examination to confirm the benignity of the formation.
Removal of moles and papillomas in “Medkvadrat”: in questions and answers.
Which doctors perform this procedure?
Only qualified specialists, surgeons, dermatologists and cosmetologists treat benign skin tumors in our center.
At the clinic on Kashirskoye Highway, appointments are provided by:
Sheptiy O.V. – surgeon, dermatologist, candidate of medical sciences. Specializes in the treatment of adults and children with vascular pathology: port-wine stains, hemangiomas. Work experience – 28 years.
Epikhin N.V. – dermatologist, laser surgeon. Specializes in laser treatment of vascular disorders: telangiectasia, hemangiomas, port-wine stains. Medical experience – 18 years.
Tamazova L. A. – dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, candidate of medical sciences. Performs tumor removal using laser, surgitron, and liquid nitrogen. Medical experience – 15 years.
Melnikova Yu. G. – dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, candidate of medical sciences. Diagnosis of skin tumors using a dermatoscope. Removal of moles (nevi, papillomas, warts, keratomas) using cryodestruction methods, electrocoagulation, and radioknife.
At medical centers in Kurkino, receptions are provided by:
Russkov S. Yu. – dermatologist, doctor of the highest category. Diagnosis and laser surgical treatment of warts, papillomas, keratomas, basal cell carcinomas, kandilomas, keratomas, hemangiomas, nevi. Medical experience – 29 years.
Markova E. A. – dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, candidate of medical sciences. Removes warts, papillomas and other benign skin formations. Total experience – 17 years.
Can the patient choose his own treatment method?
The method of exposure - laser, radio knife, mechanical removal - is determined by the doctor. The method of treatment depends on the type of formation. Thus, laser treatment is used for flat pigmented moles and vascular spots. Convex nevi and flesh-colored papillomas can be easily removed using the radio wave method.
If a surgeon or cosmetologist has doubts about the benign quality of the formation, before the intervention, the specialist refers the patient to a consultation with an oncologist or performs a dermatoscopy.
What device is used in the clinic for laser treatment?
Doctors at our clinic work with a modern VbeamPlatinum laser device. It is intended for the correction of vascular changes and pigmented formations of the skin, warts, post-acne spots, scars and scars.
VbeamPlatinum differs from similar devices in the increased length of the laser pulse. For this reason, treatment is faster, and the doctor has the opportunity to influence formations located deep in the skin.
The device is equipped with a built-in dynamic cooling system, so you feel virtually no pain during mole removal .
Does the center perform histological examination?
Yes, histological examination is carried out. The biomaterial is sent to the laboratory immediately after treatment. There is no need to return for the results: when the analysis is ready, the conclusion will be sent to you by email.
Does the doctor provide pain relief?
Laser and radio wave treatments are usually well tolerated without pain relief. If the patient has a low sensitivity threshold, the doctor uses an anesthetic: gives an injection, applies a cream or spray.
Our specialists perform removal of large formations and formations of a large area under general anesthesia. The clinic has comfortable rooms where the patient can recover after the procedure.
Young children undergo mild sedation (short anesthesia).
What benign skin lesions are removed at the center?
Our doctors treat any benign skin tumors: warts, nevi, keratomas, atheromas, hemangiomas, papillomas, etc.
Make an appointment with a specialist right now! Contact phone number.
Pros and cons of electrocoagulation
Content:
- What are the methods for removing warts?
- Pros and cons of electrocoagulation
- In what cases is electrocoagulation contraindicated?
- How is electrocoagulation performed?
- Rehabilitation after electrocoagulation
Each technique has its advantages, but electrocoagulation has the most positive aspects. Firstly, the procedure is quite quick compared to others, and at the same time it is absolutely painless. During the removal of skin formations, there is completely no risk of bleeding, and this, in turn, prevents infection of wounds and the onset of the inflammatory process.
Electrocoagulation is considered one of the safest removal methods, since only warts are burned off by electric current, and the skin around them is not affected. After such procedures, the patient recovers quickly, and the rehabilitation period passes faster. In isolated cases, a relapse may occur. Also, an equally significant advantage is the price of the procedure, because compared to others, it costs several times less.
As medical practice shows, some time after removing a wart using electrocoagulation, as a rule, there are no repeated growths in this place.
If we consider the negative aspects of this technique, we can highlight only one disadvantage. Sometimes patients experience itching and burning at the site of the burn. As experts explain, this is the result of individual intolerance to local anesthetics.
Preparing to remove moles with an electric knife
Proper preparation is the key to the successful completion of every medical procedure. Cauterizing a nevus with an electric knife is no exception, but in most cases does not require special preparation. We prescribe tests before the procedure for removing a nevus using electrocoagulation if you have a history of heavy bleeding or there are doubts about the benignity of the mole. In the above situations you will need:
- Clinical blood test.
- Coagulogram (determination of blood clotting indicators).
- Blood test for tumor markers.
Since removal of moles with an electrocoagulator does not require general anesthesia, there is no need for a “fasting” regime on the eve of surgery.
In what cases is electrocoagulation contraindicated?
Unfortunately, not all patients are allowed to undergo this technique for removing warts. Typically, doctors prescribe other procedures for patients with:
- individual intolerance to procedures associated with exposure to electric current;
- impaired blood clotting process;
- oncological processes;
- chronic diseases during exacerbation;
- acute infectious diseases.
Electrocoagulation is easily tolerated and still remains in demand, despite the emergence of new and more modern techniques for removing tumors on the skin.
Contraindications to electrocoagulation
Excision of warts with electric current is not performed in the following situations:
- Active herpetic infection;
- Tendency to form keloid scars;
- Malignant neoplasm;
- The location of the wart in the area of large vessels (this can lead to bleeding);
- The presence of inflammatory, infectious or purulent processes in the area of the procedure;
- Allergic reaction to drugs for local anesthesia;
- Exacerbations of diseases.
Before excision of warts, the patient is seen and examined by a specialist. Based on the results of the examination, the doctor prescribes a number of laboratory and general clinical examinations. A comprehensive examination allows not only to identify the presence of possible contraindications to surgery, but also to detect the nature of the wart, as well as assess its size and depth of location.
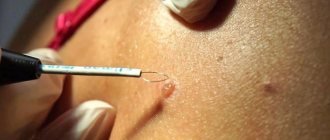
How is electrocoagulation performed?
Compared to other procedures, electrocoagulation is simple to perform. According to statistics, just one procedure is enough for complete removal. You can also remove several large warts at the same time. It is the size of the wart that determines the speed of the procedure. This may take a minute or even a few seconds.
Before removing a wart, the patient is given local anesthesia, and the skin is pre-treated with antiseptics.
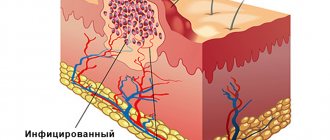
Direct removal is carried out using a loop located on the device. It is applied to the wart and a certain electric current is applied. Thus, the wart tissue is thermally damaged and dies. If the wart dies, why doesn't it start bleeding? The high temperature of the loop also cauterizes the blood vessels that fed the wart. Therefore, bleeding does not start, and this avoids infection.
The site of the wart is covered with a dense crust (scab). After several days, the process of complete tissue healing proceeds smoothly. Once they heal, the crust will fall off on its own.
Before the procedure itself, all jewelry made of metal is removed from the patient. Otherwise, heating may cause burns.
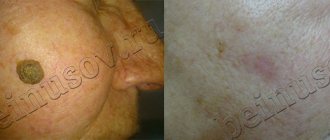
Many patients, especially women, are interested in the question of scars. The wound itself heals in an average of ten days after the wart is removed. After the crust falls off, a pink spot remains on the skin (as doctors say, this is young skin). If doctors removed a small formation with a shallow core, then over time it will blend in with the color of the skin.
If during the development of a wart a deep layer of skin was affected, then a light spot remains in place, but don’t worry, it will go away over time.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Refusal to cauterize a mole
Refusal to remove the tumor in some cases leads to undesirable consequences. This is especially true for protruding birthmarks located in those parts of the body that can be easily injured. This, in turn, leads to heavy bleeding or degeneration of the nevus into a cancerous tumor. If the mole is located on an open area of the body, constant exposure to ultraviolet rays may also contribute to this. These complications pose a serious threat to human health. Therefore, it is better to seek medical help from a specialist in time and undergo, if not removal, then at least a visual examination and obtain a conclusion that the mole is not a malignant formation. But remember that you can 100% declare this only after histological analysis.
Interesting fact! There is a belief that a birthmark is located above a diseased organ and warns a person about a possible disease. Official medicine does not find confirmation of this. Most likely, this belief came to us from Eastern practices.