Today, treatment of burns is a pressing problem. According to state statistics for 2022, at least 30,000 people suffered thermal or chemical injuries. This is one of the most common household injuries. However, you can often get a burn at work, where safety conditions are not met.
If burns occur, you must be able to provide proper first aid in a timely manner. How quickly you help yourself or the injured person will determine his further condition and the speed of treatment.
The human body is able to regenerate itself and remove minor burns without serious consequences for health. More serious burns require immediate medical attention to prevent complications. Such wounds need to be monitored to prevent infection and regularly treated with anti-inflammatory medications or anti-burn wipes.
If you find yourself close to a burnt person, you really need to know how to treat a burn, otherwise you will do more harm than good with your actions.
Causes of burns
A burn can occur due to exposure to:
- fire;
- hot liquid or steam;
- hot metal, glass or other objects;
- electric current;
- radiation (x-rays or radiation therapy);
- ultraviolet radiation (sun or solarium);
- active chemicals.
It is worth noting that the causes of burns may be different, but all types of such injuries are classified depending on the degree of damage caused and symptoms:
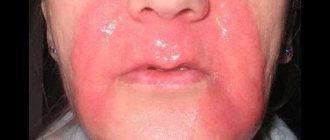
- First degree. This burn affects only the outer layer of the skin. The injury is characterized by redness, swelling and pain. The victim is given first aid and a short course of treatment is prescribed.
- Second degree. This burn leads to damage not only to the epidermis, but also to the underlying layer - the dermis. The lesion is characterized by redness, whitening or mottled skin, pain and swelling. It is possible to develop blisters from burns and severe pain.
- Third degree. With this type of damage, the fat layer under the skin is affected. Burnt areas of the body become charred, blackened or white. Third degree burns often disrupt the functioning of the nervous and respiratory systems.
First steps to neutralize thermal burns
- remove the victim as far as possible from the heat source;
- If clothing or equipment is smoldering, you should get rid of it immediately. If clothing is stuck to the skin, you must carefully cut it off or remove it;
- apply dry ice or use cold water to the damaged area;
- treat damaged areas of the body with burn ointment;
- In case of serious injuries, call an ambulance.
Neutralization of chemical burns
- Rinse the affected area with a strong stream of water. Under no circumstances should you treat a wound with oil.
- If a burn is caused by quicklime or sulfuric acid, it should be
- treat with a dry cloth, the use of water is unacceptable;
- apply a sterile antiseptic bandage.
There are situations when people get severe burns. Treating them outside the hospital requires special knowledge and skills. If a person does not have them, it is better to immediately consult a doctor.
First aid for burns
Under no circumstances should you remove dead skin or open blisters yourself, apply ice, butter, various ointments and medications to the burned area, or cover the burn with cotton bandages or adhesive tape. If you are burned by chemicals, you must remove part of the clothing on which the substance has come into contact and pour plenty of cool water over the affected area. For extensive burns, it is recommended to take a 10-minute shower or lie in a cool bath. After water procedures, it is important to pat your skin very carefully, put on loose clothing and see a doctor.
For a limited burn, it is necessary to place the burned area of skin under cold water for 10-15 minutes or apply a sterile ice pack; apply a sterile bandage; Give the patient a painkiller and if your health worsens, consult a doctor. For extensive burns, apply a loose sterile bandage; give an anesthetic and drink an alkaline-salt mixture (1 teaspoon of table salt and ½ teaspoon of baking soda, dissolved in 2 glasses of water), after providing first aid, take the victim to the hospital. In case of burns, a large amount of sodium ions leaves the vascular bed along with the plasma (0.5–0.6 mEq/% burn/kg of patient body weight). Therefore, fluid therapy, first of all, aims to fill the vascular bed and restore its sodium content.
Chemicals, with the exception of powdered ones, are washed off with water; Powdery substances must be brushed off after moistening them with water. Burns caused by acids, alkalis or organic substances (for example, phenols, cresols, petrochemical products) should be washed with copious amounts of water, and the burn area should be washed for at least 20 minutes.
Degree of burns
There are three main degrees of burns: first, second and third. The rating of each grade is based on the severity of the skin damage, with grade one being the most minor and grade three being the most severe.
Signs of damage look like this:
- first degree burns: the epidermal layer is damaged, the skin is red, slightly swollen;
- Second degree burns: blisters appear and skin peels off;
- third degree burns: tissue necrosis is observed, the skin becomes white, a crust forms;
There are also fourth degree burns. This degree includes all the symptoms of a third degree burn. The damage penetrates beyond the skin and spreads to the tendons and bones. It is in this case that scars remain after a burn.
Chemical and electrical burns require immediate medical attention because they can affect internal organs, even if external damage is barely visible.
The type of burn does not depend on the cause of its occurrence. A scald, for example, can cause all three types of burns—thermal, chemical, and physical—depending on how hot the liquid is and how long it remains in contact with the skin.
Degrees and treatment of burns
Features of treatment and further regeneration of the skin will depend on the degree of the burn, its depth and size.
There are four degrees of burn:
- 1st degree burn. The outer layer of skin is damaged. As a result, there is slight redness of the epidermis and swelling, which may be accompanied by pain. Typically, burn marks disappear after 2-3 days;
- 2nd degree burn. The upper, stratum corneum layer of the skin is affected, and sometimes the next layer is damaged. Blistering, redness and pain are quite common. If you choose the right treatment method and use appropriate therapy, after 10-12 days there will be no trace of the burn;
- 3rd degree burn. It is one of the most serious skin injuries. It spreads to the deep layers of the skin, affecting the upper subcutaneous tissue. Blisters and scabs appear. The wound takes a long time to heal;
- 4th degree burn. The skin becomes charred and the subcutaneous bones are damaged. All skin layers and tissues located underneath die. In this case, immediate hospitalization will be required.
In order to properly provide the necessary assistance and not harm the victim, it is worth understanding the cause of the injury. This will not cause any difficulties if you have an idea of the types of burns:
- thermal burns can be obtained when the skin interacts with boiling water, fire, or a hot object;
- a chemical burn is caused by a chemical or alkaline agent;
- radiation burn occurs as a result of ultraviolet radiation;
- A radiation or electrical burn occurs when in contact with an electric current or a voltaic arc.
For quick healing when receiving a first-degree burn, it is important to provide first aid in a timely manner. To do this, it is necessary to urgently eliminate the cause of the burn. Cool the affected skin area with ice or cold water.
It is not recommended to immediately apply anti-burn cream or ointment to the wound. Initially, you need to clean the intact skin located in close proximity to the burn with ether, then wipe with alcohol. Sodium chloride can be used to remove dead tissue from a wound.
A victim with a severe burn, before the ambulance arrives, should be given an anesthetic, analgin, ketanal or pentalgin, and an antihistamine in the form of claritin, tavegil or suprastin. Dexpanthenol is effective for burns.
If there is no vomiting, you can drink mineral water or liquid with dissolved salt and soda with a dosage of 0.5 tsp. per liter of water.
If you receive severe burns, you should not self-medicate; you should immediately seek medical help.
Treatment after burns
If you receive minor injuries, you can try to neutralize them on your own. If you have knowledge of how to treat superficial wounds, you can handle this yourself.
Ointment or gel for burns from boiling water helps well with kitchen problems. If second or third degree burns have been sustained, hospital treatment is required. It should be done in a clinic under the supervision of doctors. The therapist will recommend how to treat the burn or how to treat a burn with blisters.
Classification of burns
The difference between oil burns and an open flame or boiling water is the greater damage to health when comparing the same scale of disaster. The oil has good adhesion (tenacity) to any materials, including leather. Also, its temperature is several times higher than that of water and steam. Consequently, the consequences for the victims are more painful. Skin lesions are classified into 4 groups:
- 1st degree burn.
Characterized by redness and slight swelling. Such damage does not cause harm to the body as a whole, and the “marks” can disappear within a few hours or within a day. The pain is significant, but passes quickly. A similar injury can occur from a squealing frying pan on the stove or in production during work involving hardening of parts. - 2nd degree burn.
Accompanied by prolonged pain. It is dangerous because the affected area often reaches 30% of the body. Requires immediate treatment. - Third degree.
The skin darkens and takes on a scabby structure. The lesion is dangerous due to infection, therefore, qualified assistance is required immediately. - Fourth degree.
It is possible to save a person only if there is a nearby emergency room. Incidents of misfortune are rare, but they do happen. The damage is catastrophic - tissues, even bones, become charred. Today, timely assistance can save life, and plastic surgery will correct the situation as much as possible.
Compliance with safety regulations
- the only way to avoid burns from boiling oil. At home they use an apron, at work they use special clothing and personal protective equipment.
Skin restoration after a burn
What helps with burns is careful hygiene and regular wound care.
After injury, a blister immediately forms on the skin, filled with clear plasma, which can seep through the burned tissue. With proper treatment, inflammation and suppuration can be avoided, and regeneration will occur faster.
Within a few days, the blisters from the burns will begin to subside and peel off, and new skin will begin to form under the blister. At this time, the wounds may itch, but you should not touch the affected area - by the end of the first week the itching will go away on its own.
If the wound is neglected, a process of suppuration may develop. It may be accompanied by fever, sudden weakness and chills. With such a history, regeneration of the skin may take weeks. In this case, compacted growths and ridges are likely to appear.
LEATHER. SKIN STRUCTURE. SKIN FUNCTION
SKIN is one of the most complex organs of our body, subject to the strongest physical and physiological stress. Skin is the largest organ of our body. The complex structure of the skin with its numerous vessels, nerves, sebaceous and sweat glands is necessary to perform certain functions.
Skin is: -Preventing fluid loss by the body; -Protection of internal organs from the negative influence of external influences; -Ability to evaluate pressure, touch and vibration. Nerve endings and receptors inform the body about temperature and pain effects; -Barrier functions. This is protection against bacteria and microorganisms; -Protection from ultraviolet radiation; -Maintaining optimal body temperature.
The skin consists of two layers: EPIDERMIS and DERMI
. Under these layers is subcutaneous fatty tissue.
EPIDERMIS
- avascular upper thin layer of skin (does not have its own blood supply). The epidermis receives nutrition from the capillary bed of the dermis due to the diffusion of nutrients. The epidermis consists of numerous layers of living cells, on top of which are dead cells.
The layers of the Epidermis can be represented as follows:
- Basal (germ layer).
The lower layer of the Epidermis. Consists of cells capable of regeneration (cell division) - cylindrical keratinocytes. The basal layer ensures constant regeneration of the Epidermis, however, cell division is regulated by certain factors: hormones, vitamins, kelons. Keylons are simple substances that suppress growth and regulate the functioning of the basal layer. Thanks to keylons, basal cells have limited growth (proliferation). Beneath the stratum basale is the basement membrane, which separates the stratum basale from the dermis. - Spiny.
Contains up to 6 layers of irregularly shaped cells. They have little activity for cell division (limited mitotic activity). - Grainy.
The death of Epidermal cells begins in this layer. Contains up to 3 layers of cells. - Brilliant.
The stratum pellucida consists of anucleated cells in which intense enzymatic activity is observed. Eleidine is formed in the stratum lucidum. Eleidin is a substance rich in fats and proteins with a high refractive index of light, looks like a homogeneous dense shiny layer, which gives its name to this layer of cells. The shiny layer protects the body from the effects of various aqueous solutions. - Horny.
The stratum corneum consists of anucleated keratinized cells (keratin is a protein that has high mechanical strength and performs protective functions), which are called corneocytes. The cells of the stratum corneum lie with some overlap, like brickwork, and are firmly connected to each other by the finest fibers (tonofibrils). The stratum corneum has 15 to 20 layers of cells, with the outer layer continually being shed as detached flakes of skin.
So, in general, the Epidermis works like this: in the lower, basal layer, cells are constantly dividing. After division, one of the newly formed cells passes into the next layers of the Epidermis. From layer to layer, cells lose contact with nutrients coming from the Dermis and lose the ability to divide. The closer a cell approaches the surface of the skin, the more strongly external environmental factors begin to act on it, keratinization of the cell occurs, the cell loses its nucleus and turns into a scale of the stratum corneum.
The stratum corneum, the upper layer of the epidermis, easily allows low-molecular substances such as oxygen from the environment to pass through. Bacteria, which are significantly larger in size, are not able to overcome the upper layer of the Epidermis, therefore the Epidermis is the skin protection that is optimal for the body. In the Epidermis, the processes of cell division of the lower Basal layer, regulated by keylons, the gradual transition of cells to the upper layers, transformation into keratin scales and, finally, exfoliation of the outer scales in the stratum corneum occur in a balanced manner. Complete renewal of the Epidermis lasts from 10 to 30 days.
The high strength of the Epidermis serves as a good barrier to various substances and does not allow them to penetrate the body. This also applies to most cosmetics.
DERMIS
- the frame, the skin itself, which provides its mechanical properties: elasticity, strength and extensibility. These properties are provided by connective tissue that has elastic fibers, Elastin, which allows the Dermis to stretch, and collagen fibers, which strengthen the Dermis.
The following structures are located in the Dermis: blood vessels, sweat glands, nerve endings, hair roots with sebaceous glands. Deeper is the subcutaneous fatty tissue - the hypodermis. It absorbs the effect of mechanical factors on the skin and participates in the thermoregulation of the skin. In this part of the skin there are clusters of fat cells separated by bundles of collagen fibers.
Treatment of scars after burns
If you are interested in how to get rid of the external consequences of a burn, you need to know that in case of serious damage to the skin, the scar will remain in any case. Here you will need the help of a cosmetologist who will help restore the normal appearance of the skin.
Typically, for such an operation, a scar excision technique is used, after which several cosmetic sutures are applied to the tissue. When the sutures are removed, the damaged area is treated with ointments that prevent the formation of new scars on the skin.
For particularly difficult cases, for example, burns from boiling water, the laser resurfacing technique is used. Modern equipment allows you to completely remove scars and achieve perfect skin. If the severity of the burn is insignificant, chemical peeling with fruit acids is recommended.
Remedies for burns
How to treat a burn, and what kind of surgical assistance can be provided independently in the field or at home?
The use of creams such as Levomikol or Rescuer is guaranteed to help with minor injuries, such as briefly touching a hot pan. Dexpanthenol works very well for first degree burns. If the degree of damage is more serious, creams can only be used as a preventive measure and there is no point in relying on them.
Anti-burn products such as sprays or gels - for example, Burnshield Anti-burn Hydrogel - are more effective because they are dispersed and are better absorbed by the skin. These drugs combine two functions - anti-inflammatory and analgesic.
Buy
Buy
Buy
There is another type of treatment - special anti-burn dressings. They are recommended when the patient needs to be outdoors. Such dressings prevent dirt and dust from entering the wound.
Modern anti-burn drugs: a review of effective agents
There are a variety of anti-burn products on the market: sprays, gels, ointments and creams that have an anti-inflammatory, disinfecting, healing and soothing effect that promotes healing of the affected area. Some drugs are effective in themselves, while others need to be used as adjuncts.
Panthenol
Panthenol is an anti-burn drug, used to treat burns of varying severity, available in the form of a spray, gel, ointment, cream and aerosol.
The main active ingredient is dexpanthenol, which accelerates the regeneration of skin cells. Panthenol spray is used immediately after a sun or thermal burn - it has an anti-inflammatory effect. At the treatment stage, it is better to give preference to Panthenol ointment, gel or cream.
Olazol
Olazol is a remedy that is effective for thermal burns. Available in aerosol form. Due to the components included in the drug (chloramphenicol, anesthesin, sea buckthorn oil, anhydrous lanolin, etc.), Olazol has an analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effect.
A very effective remedy for thermal damage of 1st and 2nd degree.
Furaplast
A drug for external use, which is intended for the treatment of burn wounds. Due to furatsilin, which is part of the drug, Furaplast has an antiseptic effect. The drug is applied to the burn site in an even thin layer to form a special protective film. The film lasts for several days; if it is damaged, Furaplast must be reapplied.
Important: Furaplast will not be able to help if inflammatory processes or suppuration have begun in the damaged area of the skin.
Another active ingredient, furatsilin, has an antiseptic effect.
Please note: it is not recommended to use Furaplast if inflammation and suppuration have begun at the burn site - the film will not allow the skin to breathe.
Solcoseryl
Solcoseryl ointment and gel is an effective remedy for burns of 1st, 2nd and even minor injuries of 3rd degree. The main active ingredient is cattle blood extract, while the drug is purified from protein. This composition helps to increase metabolism in skin cells, resulting in rapid healing.
The gel and ointment are applied directly to the surface after preliminary cleansing of the skin using a disinfectant solution.
Bepanten
Bepanten has an analgesic effect. Due to dexpanthenol, which is included in its composition, Bepanten is able to accelerate the healing process of wounds after burns. Bepanten can also be used as a first aid remedy for burns. The drug is commercially available in the form of ointment and cream. In addition, Bepanten is suitable as first aid for 1st and 2nd degree burns: the ointment has an analgesic effect.
La Cree
La-Cri cream for sensitive skin was created specifically to relieve skin irritations. Including those occurring after minor burns.
This remedy includes extracts of licorice, violet, string and bisabolol, which reduce inflammation. Walnut extract has an antimicrobial effect, while panthenol and avocado oil soften the skin and stimulate its regeneration.
Due to the absence of dyes and fragrances, La-Cri ointment can be used even by newborns. It will become a reliable assistant after burns in children and adults - see for yourself!
To reduce the risk of general burns
At home, you can quite simply reduce the risk of burns; you just need to follow a few recommendations:
- Do not leave cooking or already cooked food on the stove unattended;
- frying pans are placed on the stove with handles towards its back;
- any hot liquid must be placed out of the reach of children and animals - boiling water is a common cause of thermal burns;
- Do not store electrical appliances near water;
- Do not cook in flammable clothing;
- You should block your child’s access to electrical and gas appliances;
- Protective caps must be put on sockets that are not in use;
- you should not smoke at home;
- smoke detectors require regular maintenance and battery replacement;
- the house or apartment must be equipped with a fire extinguisher;
- Chemical burns are caused by chemicals - they must be stored in a place inaccessible to children and animals.