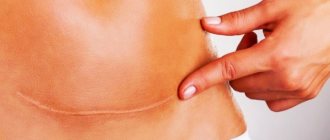
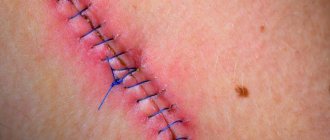
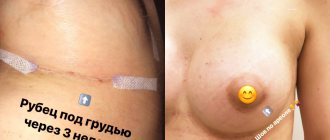
Surgical intervention involving skin incisions does not pass without leaving a trace. Scars remain on the surface of the body. Some of them are small and unnoticeable, while others are large, bright, protruding above the surface of the skin.
It is completely impossible to remove scars after surgery, but it is quite possible to make them miniature and light. Modern cosmetology procedures will help with this.
Types of scars
Postoperative scars are a consequence of intensive growth of connective tissue in the area of skin damage. They can have different shades, sizes and shapes. The following types of scars after surgery are distinguished:
- Normotrophic. Does not protrude above the surface of the epidermis and does not differ from the skin in color.
- Atrophic. It looks like a small depression. Appears when there is insufficient amount of collagen.
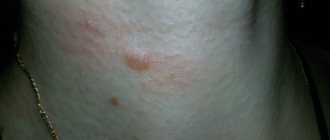
- Hypertrophic. Protrudes above the surface of the skin and has a pink tint.
- Keloid. It has the shape of an elevation and a bluish tint. The skin in the affected area is tight, dry, and may peel. Often the patient is bothered by itching. Over time, keloid scars increase in size.
Scar removal after surgery is an optional procedure. If the scar is small, pale and located on an area of the body that can be easily hidden with clothing, you can refuse the procedure. If the scar causes discomfort and is noticeable to others, it is better not to wait, but to immediately contact a surgeon or cosmetologist.
What and when to eat
During the rehabilitation period, food should be soft, mostly liquid, and have a comfortable temperature. How much you can’t eat after tooth extraction depends on whether there is heavy bleeding or not. If blood clotting is normal, then a protective clot is formed and securely attached within 2 to 3 hours. After this, the restriction is lifted. With complex extraction, the time can increase to 4.6 hours.
It is advisable to exclude spicy, sweet foods, carbonated drinks, alcohol, raw vegetables, fruits with a high acid content. Chewing is carried out on the opposite side of the jaw. It is better not to eat rough, hard food, as you may accidentally touch the wound.
Scars after surgery: what to do at home
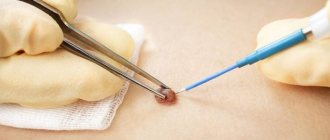
A conservative approach is appropriate for small, fresh scars. In complex cases, treatment of scars after surgery involves the use of cosmetic procedures or surgical excision if other methods have not led to a positive result.
At home, you can use drugs with different pharmacological effects:
- accelerating regeneration;
- improving blood circulation;
- immunomodulatory.
It is possible to use ointments and gels containing enzymes to inhibit the rapid growth of new tissue or stimulate the synthesis of your own collagen. It is important to remember that scar correction after surgery is a long process. The drugs must be used for several months.
Oral hygiene
It is not carried out on the first day to exclude infection and accidental injury. Chlorhexidine can be used almost immediately after tooth extraction, as it does not cause side effects; the main thing is to rinse carefully and according to the instructions. Further hygienic cleaning can be performed once a day with a soft brush, carefully avoiding the surgical area.
Floss is also used to remove food debris from between teeth and a warm saline solution is used to rinse the mouth after each meal. Do not forget about cleansing your tongue, as plaque also accumulates on it, in which bacteria actively multiply.
Removal of sutures after tooth extraction occurs on the 7th - 10th day. By this time, the wounds have already healed and restrictions on hygiene procedures are lifted. Cleaning is carried out twice: in the morning and in the evening.
How to remove scars after surgery: modern cosmetic procedures
If there is a large scar left on the body after surgery, it is better to remove it using cosmetic procedures. Modern methods are safe and effective. There are several options for eliminating scars after surgery:
- Filling with collagen. A method recommended only for atrophic scars. It involves filling the depression with collagen and leveling the surface. The effect lasts for 12 months.
- Cryodestruction. The method involves treating the scar with liquid nitrogen. Damaged tissue is frozen and destroyed, and healthy skin grows in its place. The disadvantage of the method is pain, requiring anesthesia.
- Microwave therapy. The epidermis is exposed to electromagnetic waves, which allows you to achieve lasting results. In some cases, additional cryodestruction is required.
- Microdermabrasion. The surface of the epidermis is polished using chemical compounds - acids, powdered aluminum oxide. The downside is the ability to work only with small superficial scars.
- Dermabrasion. Another grinding option involves the use of special brushes. When carried out correctly, the procedure is safe, but violation of the technique can lead to the formation of new scars.
- Bukki-irradiation. The skin is treated with ultra-soft x-rays, which initiate the reverse development of the scar. The method is used for keloid and hypertrophic scars, but is prohibited in case of circulatory problems.
- Laser irradiation. The most common method recommended by doctors who tell how to get rid of scars after surgery. The method is suitable for different types of skin changes. Laser scar resurfacing is a quick procedure that is performed under local anesthesia.
Surgical intervention
In rare cases, when a scar causes significant discomfort, and a course of laser scar removal after surgery did not help, plastic surgery methods are resorted to. During the manipulation, the doctor excises the damaged tissue and transplants a skin flap of the patient taken from another area. The entire process takes about an hour and is performed under general anesthesia. Next begins the rehabilitation period, which may take several months.
Prolonged wound healing
Diabetes
Atherosclerosis
HIV
64454 03 November
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Prolonged wound healing: causes, diagnosis and treatment methods
Definition
Regeneration (restoration) of skin and tissues is an important and complex physiological process. It depends on the area and depth of damage, concomitant diseases and many other factors.
Long-term non-healing wounds bring significant discomfort to everyday life, as they are accompanied by pain, swelling, discharge of clear fluid, blood or pus from the wound, an unpleasant odor from the wound, and a feeling of fullness in the damaged area.
Types of non-healing wounds
Depending on the cause of occurrence, all long-term non-healing wounds can be divided into traumatic (appearing as a result of mechanical injury, burn, etc.) and trophic (appearing as a result of circulatory disorders in the affected area).
Possible reasons for prolonged wound healing
Prolonged wound healing is a symptom of many pathological conditions characterized by disruption of the normal physiological processes of tissue regeneration.
Factors influencing wound healing:
- Age has a direct impact on the process of tissue repair. Children's wounds heal much faster than those of older people. This is due to a more active metabolism in the child’s body compared to adults.
- Body weight affects metabolic processes in the body. Adipose tissue does not require intensive blood circulation, therefore an increase in its amount several times relative to the norm (obesity) leads to slower tissue regeneration and frequent complications of the wound process. With extremely low body weight, there is a slowdown in metabolism in the body due to a decrease in the amount of energy, therefore, all wounds heal more slowly.
- Adequate blood circulation in the area of damage provides the tissue with sufficient nutrients and oxygen for recovery. Insufficient arterial blood flow and impaired venous blood outflow significantly slow down the course of the wound process and contribute to the development of various complications. Prolonged compression of tissues when in a forced position (for example, in bedridden patients) leads to the development of bedsores, which are also characterized by prolonged healing.
- Wound infection disrupts the regeneration process due to the active proliferation of microorganisms, their impact on tissues and the constant activation of a pronounced inflammatory process. A large amount of purulent exudate is formed, areas of necrosis are formed and general intoxication increases.
- The adequacy of the inflammatory response and the body’s ability to resist the addition of a secondary infection depend on the state of immunity.
- Concomitant diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, severe infections, disorders in the hematopoietic system, cardiac and respiratory failure, slow down regeneration by impairing the formation and delivery of necessary substances to the wound area, as well as the removal of toxic metabolic products from the body.
- The use of certain medications and treatments can have a significant impact on the normal wound healing process. Thus, uncontrolled use of painkillers (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) can lead to a slowdown in regeneration due to the suppression of inflammatory processes that normally occur in any wound. The use of radiation and chemotherapy can also cause delayed wound healing, since not only tumor cells die, but also cells responsible for tissue regeneration. At the same time, the malignant tumor itself takes a large amount of nutrients for its growth, which negatively affects all processes in the body.
Diseases leading to prolonged wound healing:
- Chronic venous insufficiency (also manifested by varicose veins) is one of the most common causes of long-term non-healing leg wounds.
The venous outflow from the lower extremities and the delivery of nutrients to the tissues are disrupted, and hypoxia increases (decreased oxygen flow to the tissues). Subsequently, metabolic disorders occur in the tissues and long-term non-healing trophic ulcers are formed. People suffering from chronic venous insufficiency require constant careful skin care, and in the event of a trophic ulcer, prevention of enlargement of the wound surface and its infection.
- Atherosclerosis of the arteries leads to the closure of the lumen of blood vessels and a decrease in the flow of oxygen to tissues. With atherosclerosis, the metabolic processes of proteins and fats in the body are disrupted, damage to the vascular wall occurs with the accumulation of cells filled with protein-cholesterol complexes in its layers. Subsequently, the damaged vessel grows with connective tissue. The arteries become hard and rigid. Conditions arise for the formation of thrombi (blood clots) in the lumen of blood vessels, which disrupts tissue nutrition and leads to a long wound healing process.
- Diabetes mellitus is an endocrine disease characterized by an imbalance in the delivery of glucose and its use in the body. When blood glucose levels are high, the vascular wall is damaged and many systems malfunction.
With diabetes, any wounds, even the smallest ones, take a long time to heal.The most dangerous wounds are located in the foot area. Such wounds often appear as a result of accidental minor injuries. Chronic or non-healing wounds in diabetes mellitus are characterized by impaired growth of the epithelium (top layer of skin) and prolonged inflammation.
- Chronic heart failure occurs due to various heart diseases and can develop unnoticed over many years. The work of the heart gradually deteriorates, swelling and the need to increase the concentration of oxygen in the blood appear, then shortness of breath and rapid heartbeat.
Blood flow slows down and the flow of oxygen and nutrients to tissues decreases.Edema also slows down the process of tissue regeneration.
- Anemia is a decrease in the number of red blood cells (erythrocytes) and hemoglobin in the blood. The disease is characterized by oxygen “starvation” of tissues.
- Oncological diseases are another reason for prolonged wound healing. The tumor grows and takes over part of the circulating blood with all the nutrients and oxygen. Also, with tumors there is often an intoxication syndrome that affects all processes in the body, including the process of tissue regeneration. Currently, chemotherapy and radiation therapy are widely used in the treatment of cancer. Both methods have long-term non-healing wounds as a side effect.
- Chronic lung diseases are accompanied by impaired gas exchange in them. As a result of this pathological process, oxygen saturation of hemoglobin worsens, oxygen transport to tissues decreases, which slows down wound healing.
- Due to immune problems, wounds in HIV patients heal very poorly.
Which doctors should you contact if wounds are healing for a long time?
Long healing of wounds forces the patient to seek medical help. First of all, a consultation with a surgeon is required. If you have chronic diseases, you may need to consult a hematologist.
Diagnostics and examinations for long-term wound healing
In most cases, the doctor will prescribe the necessary set of laboratory and instrumental research methods.
- Clinical blood test: general analysis with platelet count, leukoformula, ESR (with microscopy of a blood smear in the presence of pathological changes).