Burns from boiling water, hot oil or any other hot liquids require an adequate and timely response, and if this happens, first aid should be provided immediately. Both the depth of tissue damage and the area of damage, as well as the healing period, will depend on this.
If this is a minor injury, you can provide first aid for a hand burn with boiling water yourself, but for serious injuries (3rd-4th degree burns), you should trust the doctors. Under no circumstances should the resulting blisters be opened, as this can lead to tissue infection. It is forbidden to sprinkle starch on burns, treat the wound with vegetable oil, iodine and other alcohol-containing liquids. All this can only increase pain and slow down healing. In case of particularly deep burns, when dirt and fragments of clothing have entered the wound, you should not try to clean the wound yourself, but rather wait for the doctors to arrive.
Stages of first aid for burns with boiling water
First aid for a burn with boiling water should be provided in stages, following the following sequence of actions:
- Remove clothing that has been doused with boiling water to eliminate the risk of it sticking to the wound.
- Place the wounded area in a container of cold water or under running water to relieve pain and stop tissue damage.
- If you have an anti-burn agent in your home medicine cabinet, such as Branolind, apply a bandage to the wound.
- Secure the bandage with a bandage or plaster.
- If the burns are large and deep, taking painkillers is acceptable.
When you need medical help for a burn with boiling water. The faster first aid is provided for a burn with boiling water, the more favorable the prognosis.
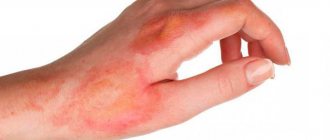
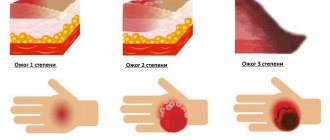
It is important to first assess the extent of skin damage. Doctors distinguish 4 degrees of burns, each of which has its own characteristic signs. By knowing them, you can determine the severity of the problem and act accordingly.
- Burn degrees:
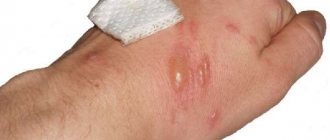
Slight redness and swelling, rarely small blisters.
- Redness and swelling, which are accompanied by blisters and a thin scab.
- Deep tissue damage, right down to the muscles. There is always a scab and blisters burst.
- The lesion reaches the bone, and areas of the skin die. Possible blackening and charring of tissues.
First aid at home for burns with boiling water can be provided for grades 1 and 2, when up to 1% of the body area is damaged. This is an area no larger than the palm of your hand. The exception is burns of the face, feet and genitals. Even with mild damage, scars can form here.
If the burn at first glance can be attributed to 3-4 degrees, you need to immediately call an ambulance.
Treatment after burns
If you receive minor injuries, you can try to neutralize them on your own. If you have knowledge of how to treat superficial wounds, you can handle this yourself.
Ointment or gel for burns from boiling water helps well with kitchen problems. If second or third degree burns have been sustained, hospital treatment is required. It should be done in a clinic under the supervision of doctors. The therapist will recommend how to treat the burn or how to treat a burn with blisters.
What can you do at home?
Considering that not everyone has the opportunity to purchase expensive pharmaceutical drugs, you can use home remedies to help with a burn from boiling water. However, such products, even if they are used to treat 1st degree burns, do not act as effectively and quickly as ointments and sprays intended for this purpose, and treatment of more serious lesions should be carried out exclusively with specialized products under the supervision of a physician.
One of these products used to provide first aid for a household burn on a small area of the body is household burn plasters from HARTMANN.
Skin restoration after a burn
What helps with burns is careful hygiene and regular wound care.
After injury, a blister immediately forms on the skin, filled with clear plasma, which can seep through the burned tissue. With proper treatment, inflammation and suppuration can be avoided, and regeneration will occur faster.
Within a few days, the blisters from the burns will begin to subside and peel off, and new skin will begin to form under the blister. At this time, the wounds may itch, but you should not touch the affected area - by the end of the first week the itching will go away on its own.
If the wound is neglected, a process of suppuration may develop. It may be accompanied by fever, sudden weakness and chills. With such a history, regeneration of the skin may take weeks. In this case, compacted growths and ridges are likely to appear.
LEATHER. SKIN STRUCTURE. SKIN FUNCTION
SKIN is one of the most complex organs of our body, subject to the strongest physical and physiological stress. Skin is the largest organ of our body. The complex structure of the skin with its numerous vessels, nerves, sebaceous and sweat glands is necessary to perform certain functions.
Skin is: -Preventing fluid loss by the body; -Protection of internal organs from the negative influence of external influences; -Ability to evaluate pressure, touch and vibration. Nerve endings and receptors inform the body about temperature and pain effects; -Barrier functions. This is protection against bacteria and microorganisms; -Protection from ultraviolet radiation; -Maintaining optimal body temperature.
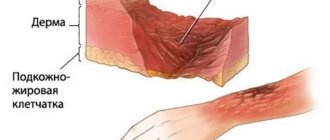
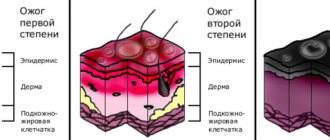
The skin consists of two layers: EPIDERMIS and DERMI
. Under these layers is subcutaneous fatty tissue.
EPIDERMIS
- avascular upper thin layer of skin (does not have its own blood supply). The epidermis receives nutrition from the capillary bed of the dermis due to the diffusion of nutrients. The epidermis consists of numerous layers of living cells, on top of which are dead cells.
The layers of the Epidermis can be represented as follows:
- Basal (germ layer).
The lower layer of the Epidermis. Consists of cells capable of regeneration (cell division) - cylindrical keratinocytes. The basal layer ensures constant regeneration of the Epidermis, however, cell division is regulated by certain factors: hormones, vitamins, kelons. Keylons are simple substances that suppress growth and regulate the functioning of the basal layer. Thanks to keylons, basal cells have limited growth (proliferation). Beneath the stratum basale is the basement membrane, which separates the stratum basale from the dermis. - Spiny.
Contains up to 6 layers of irregularly shaped cells. They have little activity for cell division (limited mitotic activity). - Grainy.
The death of Epidermal cells begins in this layer. Contains up to 3 layers of cells. - Brilliant.
The stratum pellucida consists of anucleated cells in which intense enzymatic activity is observed. Eleidine is formed in the stratum lucidum. Eleidin is a substance rich in fats and proteins with a high refractive index of light, looks like a homogeneous dense shiny layer, which gives its name to this layer of cells. The shiny layer protects the body from the effects of various aqueous solutions. - Horny.
The stratum corneum consists of anucleated keratinized cells (keratin is a protein that has high mechanical strength and performs protective functions), which are called corneocytes. The cells of the stratum corneum lie with some overlap, like brickwork, and are firmly connected to each other by the finest fibers (tonofibrils). The stratum corneum has 15 to 20 layers of cells, with the outer layer continually being shed as detached flakes of skin.
So, in general, the Epidermis works like this: in the lower, basal layer, cells are constantly dividing. After division, one of the newly formed cells passes into the next layers of the Epidermis. From layer to layer, cells lose contact with nutrients coming from the Dermis and lose the ability to divide. The closer a cell approaches the surface of the skin, the more strongly external environmental factors begin to act on it, keratinization of the cell occurs, the cell loses its nucleus and turns into a scale of the stratum corneum.
The stratum corneum, the upper layer of the epidermis, easily allows low-molecular substances such as oxygen from the environment to pass through. Bacteria, which are significantly larger in size, are not able to overcome the upper layer of the Epidermis, therefore the Epidermis is the skin protection that is optimal for the body. In the Epidermis, the processes of cell division of the lower Basal layer, regulated by keylons, the gradual transition of cells to the upper layers, transformation into keratin scales and, finally, exfoliation of the outer scales in the stratum corneum occur in a balanced manner. Complete renewal of the Epidermis lasts from 10 to 30 days.
The high strength of the Epidermis serves as a good barrier to various substances and does not allow them to penetrate the body. This also applies to most cosmetics.
DERMIS
- the frame, the skin itself, which provides its mechanical properties: elasticity, strength and extensibility. These properties are provided by connective tissue that has elastic fibers, Elastin, which allows the Dermis to stretch, and collagen fibers, which strengthen the Dermis.
The following structures are located in the Dermis: blood vessels, sweat glands, nerve endings, hair roots with sebaceous glands. Deeper is the subcutaneous fatty tissue - the hypodermis. It absorbs the effect of mechanical factors on the skin and participates in the thermoregulation of the skin. In this part of the skin there are clusters of fat cells separated by bundles of collagen fibers.
Is it possible to lubricate burns with brilliant green and iodine?
Zelenka and iodine are the first things that come to mind when it comes to what to apply to burns. However, this should not be done; in rare cases, you can carefully apply a small amount only around the wound itself. Consequences of using iodine and brilliant green:
- chemical burn;
- pain;
- burning;
- blisters.
The action of iodine and brilliant green solutions only aggravates the resulting damage from boiling water. They also slow down the regeneration process in case of burns. These products should not be used by people with allergies.
When to see a doctor
Self-treatment of a burn with boiling water is only possible for minor injuries. You will need specialist help if:
- the area of the body affected is more than 5-10%;
- burns of the second degree and higher;
- severe swelling appeared on the second day after the injury along with high fever;
- the patient complains of chills and severe pain;
- inflammation or suppuration;
- presence of blisters.
Drug therapy is primarily aimed at relieving pain, eliminating possible infectious infection and regenerating damaged tissue.
KEYLONS. A LITTLE ABOUT THE MECHANISM OF CELL CYCLE REGULATION
Research in the field of skin regeneration and the general mechanisms of the cell cycle has been conducted since the middle of the last century. R. Weiss and J. Kavanau, W. S. Bullough and T. Rytomaa, V. I. Prilutsky and Yu. A. Romanov are the founders of the theory of cell division. P. Nurse, Leland H. Harwell and R. Timothy Hunt are modern researchers of the principles of regulation of the work of individual cells and the body as a whole.
Disruption of the process of cell division (impairment of cell mitosis) is a source of not only cancer. Limited regeneration leads to aging of cells and aging of the body as a whole. In case of injuries and pathologies, low tissue regeneration significantly prolongs the healing process.
Outstanding examples of self-repair are known to everyone: severed tails, damaged hearts, and spinal cords in amphibians are restored (repaired) in a very short time. What signals does the body give to tissues so that they begin to grow, what is the growth factor? But first, about the life path of cells. A cell is the elementary unit of all living organisms. All living things are made up of cells. Regeneration, cell reproduction by mitosis occurs as follows: genetic material is reproduced inside the cell (this ensures the genetic identity of the daughter cells), after which the cell divides.
The process of cell division from the start of the mechanism to the actual division is called proliferation. Proliferation is regulated both by the cell itself and its environment. The main signal for triggering the cell division mechanism is provided by the plasma membrane of the cell. The membrane has special receptors on its surface that evaluate the “environment” around the cell and trigger the process of proliferation. These signals can come from neighboring cells, as well as from the interaction of cells with various compounds that stimulate entry into the cell cycle. These compounds are called growth factors.
But in tissues there are also substances that limit cell division. These are the Kaylons.
Keylons
- substances contained in tissue (simple proteins or glycoproteins) that specifically suppress cell division and DNA synthesis in this tissue. Keylons do not have species specificity. The action of kelons is to suppress or slow down the rate of cell division in the tissues that produce them. For example, keylons of the Basal Layer of the Epidermis act only on the Epidermis.
Cell regeneration is described by a growth regulation model. This model explains how body tissues carry out self-regulation. Any tissue capable of regeneration consists of two types of cells: cells capable of dividing and cells that cannot divide: proliferating and differentiated cells. The behavior of proliferating cells is controlled by differentiated cells: Kaylons are produced in differentiated cells and act on cells capable of dividing - proliferating cells. If for some reason the number of differentiated functioning cells decreases (for example, after injury), the inhibitory effect of the keylons weakens and the population size is restored. This ensures a balance between tissue growth and loss and explains the regeneration process.
BURN DISEASE. CLINICAL SYNDROMES
In burn disease, four clinical syndromes can be distinguished: Burn shock, Intoxication, Infection, Convalescence. There are no sharp boundaries between these syndromes.
BURN SHOCK. It occurs as a result of a neuro-reflex and neuro-endocrine reaction of the body. As a result of a strong inflammatory process in a burn victim, the central and peripheral blood supply is disrupted, the permeability of vascular and cellular membranes increases, the volume of circulating blood decreases with a violation of the ratio of its formed elements and plasma (hypovolemia), plasma escapes from the vascular bed and plasma loss through burn wounds. Plasma loss during burn shock depends on the depth and area of the burn.
Thus, with superficial burns, predominantly external loss of plasma is observed, and with deep burns, plasma enters the surrounding tissues and swelling occurs.
During a burn, the evaporation of fluid through damaged skin increases significantly, leading to a large loss of fluid from the victim’s body. Loss of fluid reduces the mass of circulating blood, resulting in a sharp deterioration in glomerular filtration of urine. Burn shock usually occurs within 2-3 days. Signs of burn shock include: an excited or inhibited state, in severe cases, consciousness is confused or absent; decreased pulse blood pressure, decreased amount of urine excreted by the kidneys (oliguria), vomiting, thirst, chills, muscle tremors.
INTOXICATION. As a result of the appearance in the victim’s body of toxic products, under-oxidized compounds, and bacterial tissue, a period of acute burn toxemia begins. Body temperature rises, loss of appetite occurs with the development of signs of toxic damage to internal organs (toxic myocarditis, hepatitis). During this period, it is necessary to carry out active detoxification measures (forced diuresis, plasmaphoresis, hemosorption).
INFECTION. At the third stage of burn disease, infection begins to progress. Metabolic disorders and weakened immunity give rise to infection of the body. Infection significantly complicates the course of the wound process - it maintains intoxication, suppresses restoration processes in tissues, and can affect various organs.
RECONVALESCENCE (recovery). It occurs from the moment of complete closure of granulating wounds. An important factor in recovery is prompt closure of burn wounds.
To reduce the risk of general burns
At home, you can quite simply reduce the risk of burns; you just need to follow a few recommendations:
- Do not leave cooking or already cooked food on the stove unattended;
- frying pans are placed on the stove with handles towards its back;
- any hot liquid must be placed out of the reach of children and animals - boiling water is a common cause of thermal burns;
- Do not store electrical appliances near water;
- Do not cook in flammable clothing;
- You should block your child’s access to electrical and gas appliances;
- Protective caps must be put on sockets that are not in use;
- you should not smoke at home;
- smoke detectors require regular maintenance and battery replacement;
- the house or apartment must be equipped with a fire extinguisher;
- Chemical burns are caused by chemicals - they must be stored in a place inaccessible to children and animals.