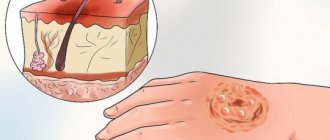
Third degree burns are characterized by severe damage, blistering, and tissue necrosis. Therefore, in the event of such damage, you should immediately consult a doctor and competently provide first aid. Below we will provide a description of this type of injury and tell you how to provide first aid for a 3rd degree burn so as not to worsen the situation.
Symptoms
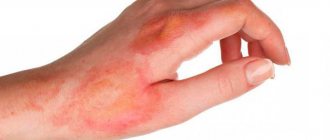
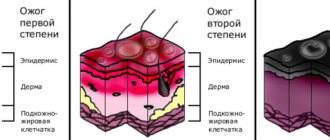
A sign of a 3rd degree burn is necrosis of the skin in the affected area - necrosis, which can be dry or wet. The first occurs when interacting with hot solid objects. The skin at the site of injury becomes brown or black. Wet necrosis occurs when exposed to hot liquids or steam. At the site of injury, the skin takes on a swollen, yellowish appearance and may become blistered.
It is important to distinguish the severity of a 3rd degree burn. It is classified into forms IIIa and IIIb, which differ in the following characteristics:
- in form IIIa, all layers of the skin are damaged, large blisters form, and the wound is covered with a scab;
- form IIIb is more severe, not only the skin is affected, but also the subcutaneous fat. The blisters are filled with bloody contents, the crust looks like a wrinkled scab.
First aid
Providing first aid will help significantly speed up the recovery of the injured person. Necessary measures:
- eliminate the source of damage; if the burn was caused by chemical means, the patient’s clothes should be removed;
- the wound should be immediately washed with cool water for 40 minutes;
- to avoid painful shock, you need to take a painkiller;
- To make the injury go away faster, the injury must be treated with antiseptics and a sterile, dry, non-pressure bandage applied;
- escort the patient to the nearest medical center or call an emergency vehicle.
Treatment methods
There are two approaches to the treatment of 3rd degree burns: conservative, or closed, and surgical.
How to treat a 3rd degree burn is determined by the doctor. The choice of technique depends on the scale of the lesion. Grade IIIA burns require long-term conservative therapy in combination with surgical treatment. Deep burns are treated only with surgical methods in a hospital.
Conservative treatment
First of all, the doctor will assess the severity of the harm and take measures to prevent wound infection. For this purpose, bandages with antiseptic and iodine-containing preparations are used. Daily dressings with drugs that help drain purulent discharge and reject scabs prevent intoxication of the body.
At the regeneration stage, balsamic dressings are used to stimulate the growth of granulation tissue. In the postoperative period, sponge dressings with anti-inflammatory drugs are used.
Surgery
There are several methods, each of which requires a specific sequence of actions:
- surgical removal of necrotic tissue from the wound;
- necrotomy - dissection of the scab to viable tissue to improve blood supply;
- necrectomy - excision of necrotic tissue in order to create conditions for epithelization or in preparation for skin transplantation;
- amputation of a limb or part thereof on an arm or leg;
- excision of granulations;
- skin plastic surgery in areas of high functionality and aesthetically important areas.
Physiotherapy
At the initial stage of treatment, physical therapy is used to relieve pain and prevent infection. At the granulation stage - to accelerate the rejection of necrotic tissue and stimulate epithelization. In the postoperative period - in order to accelerate the survival of implants and prevent the formation of scars and contractures.
As the burn site heals, the following methods are used: ultraviolet irradiation, ultrasound, laser irradiation, phototherapy, cryotherapy, ozone therapy, magnetic therapy in accordance with the algorithm prescribed by the doctor.
Thermal burn - symptoms and treatment
Medical care for burn injuries is currently subject to the order of the Ministry of Health of 1991 No. 54 “On measures for the further development and improvement of medical care for burn victims.”
First aid for thermal burns
For patients with burns, first aid should be provided immediately at the scene of the accident.
- First you need to stop the action of the thermal agent:
- extinguish the flame on clothing;
- remove the victim from the high temperature area;
- remove smoldering clothing or clothing soaked in hot liquid if it is not soldered to the wound surface. If the tissue is stuck, you need to carefully trim it around the wound.
- In the first 10-15 minutes from the moment of injury, you need to cool the burned surface: for 1st and 2nd degree burns - with cold running water for 10-15 minutes; for a 3rd degree burn, apply a cold, damp, sterile bandage or clean cloth. This will significantly reduce the effect of the thermal agent and stop it from spreading deeper into the tissue. This procedure also reduces swelling and pain. All these points have a beneficial effect on further wound healing.
- Before emergency medical services arrive or before you consult a doctor yourself, it is recommended to perform a dressing using sterile gauze pads or clean sheets.
What not to do for burns
In case of burns, you should not:
- Carry out any manipulations on the wounds.
- Prick or try to remove blisters.
- Use ice to cool the burn area, as it can lead to additional injury - frostbite.
- Separate stuck objects.
- Tearing off the stuck tissue will further injure the victim and cause additional pain.
, it is not recommended to use various powders, ointments and sprays as first aid for burns They can make it much more difficult to determine the depth of the lesion and clean the wound.
Treatment of burns with folk remedies
It is not recommended to use traditional medicine methods such as toothpaste, sunflower oil, diluted boric acid, urine, etc.
It is important to remember that only specialist doctors (surgeons, combustiologists, traumatologists) can provide qualified medical care. Self-diagnosis and self-medication can be dangerous to health [5][9].
When to call an ambulance for a burn
An ambulance should be called in the following cases:
- with deep burns or if their size is larger than the victim’s palm;
- the skin in the burn area is charred or whitened;
- blisters appeared;
- there are other injuries;
- the patient is in a state of shock - trembling, sweating profusely, his skin becomes sticky, breathing quickens, weakness or dizziness appears;
- the victim is pregnant;
- patient under 5 or over 60 years of age;
- the person is known to have heart disease, lung disease, liver disease or diabetes, or has a weakened immune system, for example due to HIV, AIDS or chemotherapy for cancer;
- the victim inhaled smoke, which causes a cough, sore throat, difficulty breathing, and noticeable burns on the face [19].
Outpatient burn treatment
The frequency of visiting the doctor depends on the severity of the burn. In mild cases, the first visit is scheduled a day after the injury, then you need to visit the doctor about once a week. At the appointment, the doctor treats the wound, assesses the depth of the burn and the need for skin grafting.
If an infection is associated with the burn, then you need to visit a doctor as soon as possible. When a wound becomes infected, adjacent areas of the skin turn red, pus is released intensely, and black or red spots appear in the burn area.
During outpatient treatment, it is important to keep the burn surface clean. The doctor may prescribe ointments that are applied to the wound and then covered with a dry gauze bandage. The dressing should be changed daily. Biosynthetic dressings do not need to be changed if there is no suppuration [20].
Treatment of burns in hospital
Treatment for burn injuries is consistently one of the most expensive. Treatment methods for patients with thermal injuries are now fundamentally different from those generally accepted 10-15 years ago. Modern algorithms for the treatment of burn wounds have been developed largely due to advances in the study of burn disease. The results of treatment of patients with burns have improved significantly due to the development and implementation of active surgical tactics in clinical practice. The basis is early necrectomy followed by skin grafting in order to quickly restore the integrity of the entire skin.
The essence of necrectomy is the excision of non-viable tissue using a scalpel and/or special equipment (hydrosurgical scalpel, dermatome). This is necessary to prepare the wound for closing the defect. If the wound area is small, it is possible to perform autodermoplasty (skin grafting) with local tissue. If the affected area is large, autodermoplasty is performed with a free skin flap, i.e. using one’s own areas of unaffected skin. The skin graft is harvested under general anesthesia using a special instrument - a dermatome. The thickness of the flap is usually 0.3-0.4 mm. Then it is placed on the wound surface, fixing the edges with sutures or metal staples [5].
Innovative methods for diagnosing and treating children with burn injuries include determining the depth of the burn, active debridement (surgical treatment of wounds), and treatment of wounds with negative pressure. The modern approach to the treatment of burn wounds is carried out through the earliest possible preparation for autodermotransplantation [16].
The most effective from a modern point of view is cleansing the wound surface from necrotic masses using hydrosurgical systems . Their main principle is the ability to carry out operations without tools, using a special solution that moves at great speed. The jet in pulsation mode provides cleaning and treatment of wounds, and also makes it possible to excise tissue. The system removes tissue fragments formed during wound cleaning [11]. The hydrosurgical system allows surgeons to set the desired mode and treat even complex wounds as efficiently as possible, with the formation of the desired edge configurations.
Currently, the use of a negative pressure apparatus . The essence of this method is to create a controlled local subatmospheric pressure, i.e., a vacuum, directly in the wound. A constant or variable level of negative pressure is created using a special dressing that isolates the wound surface from the external environment [4]. Vacuum therapy has already received comprehensive scientific substantiation and recognition among specialists in the field of treatment of wounds of various etiologies.
When treating children with burn injury, it is important to pay attention not only to the wound surface itself, but also to the psychological state of the child himself and the relatives caring for him (most often the mother). The mother’s task at the stages of treatment and rehabilitation is to help minimize physical and psychological disorders in the child.
Treatment of deep and/or extensive burns requires long-term hospitalization (about 2-3 months or more). Then comes the rehabilitation period, which can last for years. Typically, recovery, like treatment, includes financial costs [1][6][7]. All this negatively affects the psychological state of the mother.
The longer the victim’s mother experiences physical and mental exhaustion, the worse the prognosis for the child’s long-term adaptation [3][10]. In order to reduce chronic stress and develop adaptive abilities in mothers, individual or group psychotherapy is recommended [8]. Family therapy should be included in the rehabilitation treatment of burned children [2][10].
Prevention of burns
Third-degree burns are especially dangerous for children and the elderly, so it is important to take preventive measures. What does it mean:
- Always check the water temperature before bathing your child;
- use only working electrical appliances;
- do not place pots and kettles with boiling water on the edge of the table;
- Do not keep matches and lighters and other potentially dangerous objects in a visible place.
Consequences of burns in children
Treatment of burns in children does not end with discharge from the hospital. It is important that the child can return to his normal lifestyle as soon as possible. If his limbs are damaged, he needs to be taught to walk, run, and jump again. If a person has been injured as a result of a burn, the main thing is to overcome the psychological complexes associated with changing the child’s appearance in order to reduce the ridicule of peers to zero and fully socialize. This is a long, painstaking process in which both relatives and doctors must participate together with the patient. A child cannot be left alone with his problem: he must know that life does not end with this injury, no matter how severe it is!
Complications and consequences
The victim often experiences neuropsychiatric disorders, disturbances in the functioning of the kidneys and liver, the formation of scars and contractures, loss of limbs or parts thereof.
The prognosis of how long it takes for a burn site to heal depends on the area and depth of the lesion, as well as the age of the patient. High mortality rates are observed among older people over 60 years of age and children.
Life-threatening burns represent 10% of the surface of the face or perineum and 15% of the surface of other parts of the body.
How to understand that a person has suffered from an electric shock?
Symptoms of an electrical burn include:
- Shallow breathing
- Cardiopalmus
- Loss of consciousness
- Convulsions
The victim may complain of weakness, dizziness, and nausea. Be sure to examine him for the presence of electrical marks (if a person has been under voltage for some time, then there may be many of them - multiple electrical burns).
Deep damage is indicated by the appearance of swelling at the site of contact with the current source, tension in the mouse and a complete lack of sensitivity.
Operating principle of fractional CO2 laser
This is a latest generation device that acts on the skin with micropulses - the laser evaporates scars not as a continuous sheet, but pointwise, leaving microscopic untreated areas. As a result of this gentle action, the skin recovers faster, and accordingly, the rehabilitation period is reduced to a minimum.
Also to combat post-burn scars in our clinic we use: ClearSkin 1540Nm and ClearSkin 1540Nm in-motion (Fractional non-ablative erbium laser Er:Glass 1540nm)
The effect of the procedure is achieved due to the possibility of creating scar tissue at a depth of up to 2 mm. many microthermal treatment zones. The depth of impact affects the entire thickness of the scar without damaging its surface layer.
Therefore, rehabilitation is very short and comfortable!
When the laser beam impacts the deep layers of scar tissue, old collagen and excess pigment are destroyed. After the procedure, intensive cell regeneration processes are launched. The advantage over other lasers is that the skin does not need to spend time on long-term healing of the top layer; the activation of the natural internal resources of the skin begins immediately, which allows you to get excellent results in several sessions.
ClearLift 4D (fractional non-ablative Q-Switched laser with a wavelength of 1064 nm)
Upon reaching the dermal layer, the Q-Switched 1064 nm laser creates a photoacoustic effect similar to a microexplosion; at the site of this effect, a rarefaction area is formed, breaking up the structure of scar tissue, and then filling with new full-fledged molecules. In one flash, 25 point areas are formed, between which remains untouched dermal tissue, which is the source of remodeling of scar structures.
Moreover, this entire process is absolutely painless; moreover, the light, barely noticeable warmth has a relaxing effect. The Q-Switched 1064 nm laser penetrates the skin to a depth of 3 to 5 mm, making the procedure safe for use even on areas with thin skin. Since the top layer of skin - the epidermis - remains intact, the skin looks presentable immediately after the procedure and in the following days, the effect increases over 1.5 months, this is the period necessary for the production of new collagen.
Classification of scars after burns
Doctors distinguish 4 types of post-burn scars:
- Normotrophic - Almost does not stand out on the surface of the skin. Over time, it may become completely invisible.
- Atrophic – Thinner than normal skin, over time becomes flabby and unsightly.
- Hypertrophic - The scar protrudes above the surface of the skin and has a dense consistency.
- Keloid - Refers to a severe form of scarring that protrudes from the skin, is itchy, and is bright red in color.
The Aloderm expert clinic has powerful potential for the treatment of post-burn scars of any location!
Due to the specific features of the effect of each laser on scars, and the characteristics of the scars themselves, our clinic specialists select the most optimal laser therapy option in each specific case, taking into account the location of the problem, age and other characteristics.