LEATHER. SKIN STRUCTURE. SKIN FUNCTION
SKIN is one of the most complex organs of our body, subject to the strongest physical and physiological stress. Skin is the largest organ of our body. The complex structure of the skin with its numerous vessels, nerves, sebaceous and sweat glands is necessary to perform certain functions.
Skin is: -Preventing fluid loss by the body; -Protection of internal organs from the negative influence of external influences; -Ability to evaluate pressure, touch and vibration. Nerve endings and receptors inform the body about temperature and pain effects; -Barrier functions. This is protection against bacteria and microorganisms; -Protection from ultraviolet radiation; -Maintaining optimal body temperature.
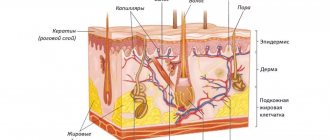
The skin consists of two layers: EPIDERMIS and DERMI
. Under these layers is subcutaneous fatty tissue.
EPIDERMIS
- avascular upper thin layer of skin (does not have its own blood supply). The epidermis receives nutrition from the capillary bed of the dermis due to the diffusion of nutrients. The epidermis consists of numerous layers of living cells, on top of which are dead cells.
The layers of the Epidermis can be represented as follows:
- Basal (germ layer).
The lower layer of the Epidermis. Consists of cells capable of regeneration (cell division) - cylindrical keratinocytes. The basal layer ensures constant regeneration of the Epidermis, however, cell division is regulated by certain factors: hormones, vitamins, kelons. Keylons are simple substances that suppress growth and regulate the functioning of the basal layer. Thanks to keylons, basal cells have limited growth (proliferation). Beneath the stratum basale is the basement membrane, which separates the stratum basale from the dermis. - Spiny.
Contains up to 6 layers of irregularly shaped cells. They have little activity for cell division (limited mitotic activity). - Grainy.
The death of Epidermal cells begins in this layer. Contains up to 3 layers of cells. - Brilliant.
The stratum pellucida consists of anucleated cells in which intense enzymatic activity is observed. Eleidine is formed in the stratum lucidum. Eleidin is a substance rich in fats and proteins with a high refractive index of light, looks like a homogeneous dense shiny layer, which gives its name to this layer of cells. The shiny layer protects the body from the effects of various aqueous solutions. - Horny.
The stratum corneum consists of anucleated keratinized cells (keratin is a protein that has high mechanical strength and performs protective functions), which are called corneocytes. The cells of the stratum corneum lie with some overlap, like brickwork, and are firmly connected to each other by the finest fibers (tonofibrils). The stratum corneum has 15 to 20 layers of cells, with the outer layer continually being shed as detached flakes of skin.
So, in general, the Epidermis works like this: in the lower, basal layer, cells are constantly dividing. After division, one of the newly formed cells passes into the next layers of the Epidermis. From layer to layer, cells lose contact with nutrients coming from the Dermis and lose the ability to divide. The closer a cell approaches the surface of the skin, the more strongly external environmental factors begin to act on it, keratinization of the cell occurs, the cell loses its nucleus and turns into a scale of the stratum corneum.
The stratum corneum, the upper layer of the epidermis, easily allows low-molecular substances such as oxygen from the environment to pass through. Bacteria, which are significantly larger in size, are not able to overcome the upper layer of the Epidermis, therefore the Epidermis is the skin protection that is optimal for the body. In the Epidermis, the processes of cell division of the lower Basal layer, regulated by keylons, the gradual transition of cells to the upper layers, transformation into keratin scales and, finally, exfoliation of the outer scales in the stratum corneum occur in a balanced manner. Complete renewal of the Epidermis lasts from 10 to 30 days.
The high strength of the Epidermis serves as a good barrier to various substances and does not allow them to penetrate the body. This also applies to most cosmetics.
DERMIS
- the frame, the skin itself, which provides its mechanical properties: elasticity, strength and extensibility. These properties are provided by connective tissue that has elastic fibers, Elastin, which allows the Dermis to stretch, and collagen fibers, which strengthen the Dermis.
The following structures are located in the Dermis: blood vessels, sweat glands, nerve endings, hair roots with sebaceous glands. Deeper is the subcutaneous fatty tissue - the hypodermis. It absorbs the effect of mechanical factors on the skin and participates in the thermoregulation of the skin. In this part of the skin there are clusters of fat cells separated by bundles of collagen fibers.
KEYLONS. A LITTLE ABOUT THE MECHANISM OF CELL CYCLE REGULATION
Research in the field of skin regeneration and the general mechanisms of the cell cycle has been conducted since the middle of the last century. R. Weiss and J. Kavanau, W. S. Bullough and T. Rytomaa, V. I. Prilutsky and Yu. A. Romanov are the founders of the theory of cell division. P. Nurse, Leland H. Harwell and R. Timothy Hunt are modern researchers of the principles of regulation of the work of individual cells and the body as a whole.
Disruption of the process of cell division (impairment of cell mitosis) is a source of not only cancer. Limited regeneration leads to aging of cells and aging of the body as a whole. In case of injuries and pathologies, low tissue regeneration significantly prolongs the healing process.
Outstanding examples of self-repair are known to everyone: severed tails, damaged hearts, and spinal cords in amphibians are restored (repaired) in a very short time. What signals does the body give to tissues so that they begin to grow, what is the growth factor? But first, about the life path of cells. A cell is the elementary unit of all living organisms. All living things are made up of cells. Regeneration, cell reproduction by mitosis occurs as follows: genetic material is reproduced inside the cell (this ensures the genetic identity of the daughter cells), after which the cell divides.
The process of cell division from the start of the mechanism to the actual division is called proliferation. Proliferation is regulated both by the cell itself and its environment. The main signal for triggering the cell division mechanism is provided by the plasma membrane of the cell. The membrane has special receptors on its surface that evaluate the “environment” around the cell and trigger the process of proliferation. These signals can come from neighboring cells, as well as from the interaction of cells with various compounds that stimulate entry into the cell cycle. These compounds are called growth factors.
But in tissues there are also substances that limit cell division. These are the Kaylons.
Keylons
- substances contained in tissue (simple proteins or glycoproteins) that specifically suppress cell division and DNA synthesis in this tissue. Keylons do not have species specificity. The action of kelons is to suppress or slow down the rate of cell division in the tissues that produce them. For example, keylons of the Basal Layer of the Epidermis act only on the Epidermis.
Cell regeneration is described by a growth regulation model. This model explains how body tissues carry out self-regulation. Any tissue capable of regeneration consists of two types of cells: cells capable of dividing and cells that cannot divide: proliferating and differentiated cells. The behavior of proliferating cells is controlled by differentiated cells: Kaylons are produced in differentiated cells and act on cells capable of dividing - proliferating cells. If for some reason the number of differentiated functioning cells decreases (for example, after injury), the inhibitory effect of the keylons weakens and the population size is restored. This ensures a balance between tissue growth and loss and explains the regeneration process.
WOUNDS. BURNS (BURN WOUNDS). TYPES OF BURNS
A wound is any open injury associated with a violation of the integrity of the skin or mucous membranes, with possible destruction of underlying tissues.
Wound healing is the wound process of restoring damaged tissue: restoring its integrity and strength.
Depending on the nature of the damaging factor, wounds can be divided into the following types: Mechanical, Burn, Chronic (trophic skin ulcers). In the presence of several types of damaging factors, the wound is usually called combined.
Wounds are dangerous
primarily bleeding, and, as a result, the development of anemia. As a result of the shock received from injury, dysfunction of vital organs can occur. Depending on the cause of the injury (the etiology of the wound) and the size of the wound, the body may become infected.
The problem of intoxication of the body is especially acute with large areas of burn wounds.
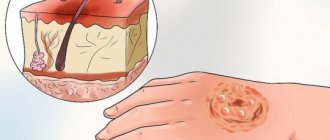
BURN - damage to tissue (skin or mucous membranes) under the influence of various factors: high temperature (thermal burns), chemicals (chemical burns), ultraviolet or ionizing radiation (radiation burn), electric current (electrical burn).
BURN. GRADES OF BURN WOUNDS
The severity of injury in a thermal burn is determined primarily by the depth and area of the thermal injury:
First degree burn (epidermal burn): redness (hyperemia) and slight swelling. Only the Epidermis is affected. Treatment under bandages or open method. Hospitalization is indicated for burns of more than 15% of the body surface.
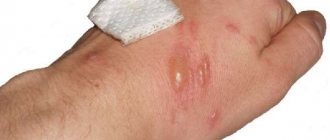
Second degree burn (superficial dermal burn): the appearance of “bubbles” filled with serous contents. Peeling of the epidermis. The epidermis and upper layer of the dermis are affected. Outpatient treatment is allowed if the burn area is less than 10% and anatomically significant areas (face, neck, perineum) are not affected. But hospitalization is possible depending on the area of the burn, its location, and the age of the patient.
IIIA degree burn: Skin after a burn is diagnosed by a thin mobile scab and large blisters filled with serous contents with an intense yellow coloring. The Epidermis and Dermis up to the reticular layer are affected. But the follicles, sweat glands, and omental bursae remain undamaged by the burn, which will initiate epithelization of the wound. IIIA degree burns are called borderline, because... the lesion is not uniform over the entire surface. The burn can go deeper into the underlying tissues, including due to infection. Victims diagnosed with a IIIA degree burn can be treated on an outpatient basis if the burn surface does not exceed 5% of the body area and no significant anatomical areas are affected.
IIIB degree burn: The entire thickness of the skin is affected: up to the subcutaneous fat. A brown scab forms on the surface. Requires surgical treatment.
IV degree burn: The skin is affected to its full depth and the underlying tissue is destroyed. Subcutaneous fat, muscles and bones are charred. Diagnosed by a dense dark brown or black scab, fused to the underlying tissues. Requires surgical treatment.
Stages of a burn
This injury has four stages of development:
How to treat a burn with hot water?
I. Burn shock. It can last three days. In this case, the acid-base and water-electrolyte balance of the body is disrupted, and kidney function is disrupted.
II. Acute burn toxemia. Lasts about two weeks. During this time, blood circulation and kidney function are normalized, due to which the absorption of toxins from the affected area begins. If kidney function does not recover (in extremely severe burns), renal failure develops.
III. Septicotoxemia. This stage occurs only with severe burns and accompanies the beginning of wound cleansing. As a result of blockage of blood vessels during circulatory dysfunction, damage to various organs (gastrointestinal tract, lungs, etc.) occurs.
IV. Convalescence. The final stage, which continues until complete recovery.
BURN DISEASE. CLINICAL SYNDROMES
In burn disease, four clinical syndromes can be distinguished: Burn shock, Intoxication, Infection, Convalescence. There are no sharp boundaries between these syndromes.
BURN SHOCK. It occurs as a result of a neuro-reflex and neuro-endocrine reaction of the body. As a result of a strong inflammatory process in a burn victim, the central and peripheral blood supply is disrupted, the permeability of vascular and cellular membranes increases, the volume of circulating blood decreases with a violation of the ratio of its formed elements and plasma (hypovolemia), plasma escapes from the vascular bed and plasma loss through burn wounds. Plasma loss during burn shock depends on the depth and area of the burn.
Thus, with superficial burns, predominantly external loss of plasma is observed, and with deep burns, plasma enters the surrounding tissues and swelling occurs.
During a burn, the evaporation of fluid through damaged skin increases significantly, leading to a large loss of fluid from the victim’s body. Loss of fluid reduces the mass of circulating blood, resulting in a sharp deterioration in glomerular filtration of urine. Burn shock usually occurs within 2-3 days. Signs of burn shock include: an excited or inhibited state, in severe cases, consciousness is confused or absent; decreased pulse blood pressure, decreased amount of urine excreted by the kidneys (oliguria), vomiting, thirst, chills, muscle tremors.
INTOXICATION. As a result of the appearance in the victim’s body of toxic products, under-oxidized compounds, and bacterial tissue, a period of acute burn toxemia begins. Body temperature rises, loss of appetite occurs with the development of signs of toxic damage to internal organs (toxic myocarditis, hepatitis). During this period, it is necessary to carry out active detoxification measures (forced diuresis, plasmaphoresis, hemosorption).
INFECTION. At the third stage of burn disease, infection begins to progress. Metabolic disorders and weakened immunity give rise to infection of the body. Infection significantly complicates the course of the wound process - it maintains intoxication, suppresses restoration processes in tissues, and can affect various organs.
RECONVALESCENCE (recovery). It occurs from the moment of complete closure of granulating wounds. An important factor in recovery is prompt closure of burn wounds.
Hot water burn: treatment
Patients with third or fourth degree burns are referred for inpatient treatment. In addition, in some cases (for example, a thermal internal burn of the foot with hot water), doctors resort to surgery, covering the burned area with skin and skin grafting.
Doctors have several priority tasks:
- promoting the rapid rejection of dead skin layers;
- formation of dry scab;
- prevention of purulent-inflammatory process;
- removal of toxic substances from the victim’s body.
In addition, hot water burns can cause burn disease in the patient. This complication occurs when a person is exposed to boiling water for a long time.
OBJECTIVES OF TREATMENT OF BURNS
FIRST AID FOR BURNS
The goal of treating burns is to preserve the life of the victim and restore the skin. In this regard, it becomes important to provide first aid:
- Stop the victim's contact with the damaging factor.
- Prevent microbial contamination.
ACTIVE TREATMENT OF A BURN
During further treatment, the doctor prescribes the following measures:
- Restoration of microcirculation to preserve the paranecrotic zone.
- Protection against infection and suppression of bacterial growth in the affected area.
- Excision of necrotic tissue.
- Stimulation of regeneration processes (granulation and epitilization).
- For dermal burns - surgical restoration of the skin.
Experts' opinion
The conducted clinical study proves the high efficiency, safety and tolerability of products for daily care of children's skin. As a result of therapy, a decrease in the activity of the inflammatory process, a decrease in dryness, itching and flaking was noted. The products will also be effective in the treatment of minor burns.
Sources:
- Schneiderman Paul, Grossman Mark, Differential diagnosis in dermatology. Atlas, Publishing house: Binom, 2017
- Reken Martin, Schaller Martin, Sattler Elke, Burgdorf Walter, Atlas of Dermatology, MEDpress-inform publishing house, 2018
- Yagodka Valentina Stepanovna, Medicinal plants in dermatology and cosmetology, Naukova Dumka publishing house, 1991
EPLAN: PROTECTION, FIRST AID, TREATMENT OF BURNS
EPLAN - SKIN PROTECTOR
Eplan is able to penetrate the upper layers of the Epidermis, completely fill the free intercellular space of the Epidermis and create an additional barrier layer, which provides skin protection for a long time. Skin protection after treatment with Eplan lasts up to 8 hours.
EPLAN does not disrupt the intercellular connections of the stratum corneum of the skin, so the skin does not lose its strength and natural protective functions.
When EPLAN is applied to intact skin: EPLAN does not penetrate into the deep layers of the epidermis (Basal layer) and does not affect the natural proliferation of Epidermal cells, does not change the water-lipid balance of the skin.
EPLAN IS EFFECTIVE AT ALL STAGES OF BURN DISEASE.
EPLAN reduces pain in the burn site by blocking irritation of damaged nerve endings in the affected area, protects the skin after a burn from environmental influences and infection, and does not allow the body to lose fluid through the burn wound.
EPLAN reduces the flow of decay products of dead tissue into the victim’s blood and prevents intoxication. When treating large areas of burns, such as the treatment of burns with boiling water, steam, sunburn, the use of the drug does not lead to toxic damage due to the formulation itself - EPLAN is not toxic and does not contain hormonal components.
When treating burnt skin, EPLAN acts as an antiseptic, preventing infection of the burn wound (both for first aid for a burn and for protection against secondary infection), and eliminates skin itching.
FIRST AID AND TREATMENT OF BURN WOUNDS: EPLAN TASKS TO PREVENT INFECTION
EPLAN has high antimicrobial activity. The reason for this is the lanthanides that make up Eplan.
Phagocytosis is a process in which special blood cells and body tissues (phagocytes) capture and digest pathogens of infectious diseases and dead cells.
The phagocytic activity of blood leukocytes leads to rapid cleansing of the wound from pathogenic microorganisms: leukocytes begin to more actively destroy bacteria, and EPLAN does not interfere with the access of oxygen to the wound area. Thus, the use of EPLAN in the treatment of burn wounds can be considered as a drug for local enhancement of the patient’s immune status.
EPLAN is non-toxic, made without the use of antibiotics or hormonals. The use of the drug EPLAN becomes especially important in first aid for burns with boiling water and treatment of infected wounds with a large affected area. EPLAN is effective in treating the following injuries: treatment of burns with boiling water, steam, treatment of sunburn, thermal burn.
EPLAN IS A CATALYST FOR SKIN REGENERATION.
The effect of EPLAN as a drug for skin regeneration, skin restoration, rapid healing of wounds and burns is due to the presence of lanthanides in its composition. Lanthanides influence the process of cell proliferation. Application of EPLAN to damaged skin, a burn or a wound, triggers the process of lanthanide exposure to the membranes of proliferating skin cells, which leads to stimulation of their cell division. EPLAN cannot be considered as an inhibitor of kylon tissue activity, therefore its effect is local and has no aftereffect after use.
EPLAN WITH BANDAGE
Eplan-cream and Eplan-solution for the treatment of wounds and burns EPLAN WITH BANDAGE: maintains a moist environment and temperature of the wound, prevents the formation of a scab, provides access of oxygen to the wound, does not create obstacles to the removal of exudate from the wound into a dressing, prevents infection of the wound. EPLAN does not contain toxic components, antibiotics, hormonal or analgesic agents, and wound dressings with EPLAN allow the bandage to easily come off the wound without damaging injured healing tissue.
First aid for a thermal wound
First of all, when you receive a wound, you should not panic. If you are at home, to alleviate the condition, it is enough to immerse the affected areas in cold water until the pain stops . In case of a burn, your first aid kit should have the following items:
- Panthenol 5% in the form of cream or aerosol. Among the agents that can improve microcirculatory disorders and wound cooling, 5% water-soluble anilocaine ointment “Anikol” is also used. The use of antioxidants, for example Soderm ointment, vitamin E promotes faster recovery of the affected skin area.
- Sterile bandage to cover the wound.
- Hydrogen peroxide 3% or another antiseptic if the burn also causes contamination of the wound. Important! If the wound comes into contact with the ground, vaccination against tetanus is necessary.
BEST WOUND-HEALING OINTMENT FOR BURNS EPLAN CREAM: TREATMENT METHOD
When the skin is locally exposed to temperatures above 55-60 degrees Celsius, aggressive chemicals, electric current or ionizing radiation, a BURN occurs. In assessing the severity of a burn, the area of the body surface affected by the burn is of great importance; there are 4 degrees of burns.
Degree I is characterized by damage to the most superficial layer of the skin (epidermis), consisting of epithelial cells. In this case, redness of the skin appears, a slight swelling accompanied by pain. After two to three days, these phenomena disappear on their own, and no traces remain after the burn, except for minor itching and flaking of the skin.
Stage II is characterized by the formation of blisters with a yellowish liquid against the background of redness of the skin. Blisters can form immediately after a burn or after some time. If the blisters burst, bright red erosion is revealed. Healing at this stage usually occurs by 10-12 days without scarring.
III degree burns are characterized by greater depth of damage with tissue necrosis (necrosis) and the formation of a burn scab. The scab is a dry, light brown to almost black crust; When scalded, the scab is soft, moist, and whitish-gray in color. There is a IIIA degree, in which the epithelial elements of the skin are preserved, which are the starting material for independent wound healing, and a IIIB degree, in which all layers of the skin completely die and the resulting burn wound heals through scarring.
IV degree burns are accompanied by charring of the skin and damage to deeper tissues - subcutaneous fat, muscles and bones.
Burns of I-IIIA degrees are considered superficial, and burns of IIIB-IV degrees are considered deep. It is possible to accurately determine the degree of burn (especially to distinguish IIIA from IIIB degrees) only in a medical institution using special diagnostic tests. In domestic conditions, thermal burns most often include: burns with boiling water, steam, iron, sunburn, etc. Burns and scalding with boiling water account for almost 40% of all deaths of children under 15 years of age. In a milder form, this is the most common type of injury for people of all ages.
How to treat burns with a burn remedy - EPLAN?
For first and second degree burns, we suggest using the drug EPLAN in ointment and liquid form. The affected area is lubricated with Eplan and, as it absorbs and dries, the treatment is periodically repeated until complete healing. If burn blisters occur, the exfoliated skin should be removed, but you do not need to open the blisters yourself before going to a medical facility, because this can lead to wound infection. Treat the edges of the wound with an antiseptic (hydrogen peroxide, miramistin, chlorhexidine), apply sterile wipes soaked in the drug and secure with a gauze bandage. Change dressings every other day. Epithalization begins on days 7-9, from the moment granulations appear. The treatment process under bandages is continued with EPLAN liquid (12-14 days). At the healing stage, the edges of the wound are treated with dry sterile wipes (without antiseptics).
If EPLAN is immediately applied to damaged areas, redness and inflammation disappear, and blisters with serous fibrous contents do not appear.
What to do in case of a burn?
Table of contents:
- Classification of burns
- Severity
- First aid for burns
- What is not recommended to do if you have a burn?
- Which doctor should I contact?
- Treatment of burns
- "EversLife-SP" and "EversLife - Gel" for healing burns
Everyone has received a burn at least once in their life: handling a hot frying pan, burning on the beach, touching a dangerous plant or jellyfish, etc. As a rule, such household injuries are the result of carelessness, ignorance or inattention. You can deal with minor injuries on your own, but in some cases you cannot do without the help of a doctor. In this article we will talk about what kind of burns there are, how to understand whether you need to urgently consult a doctor or just use a reliable remedy from your home medicine cabinet, as well as about proper treatment and skin care after a burn.
Classification of burns
A burn is damage to the skin that occurs due to contact with hot objects and liquids, hot steam, chemicals, electricity, and other reasons. Depending on whether the burn is superficial or deep, and what caused the injury, the scheme of competent first aid and subsequent treatment depends.
Therefore, you need to have an understanding of the types of burns.
Taking into account the causes of occurrence, the following types of burns are distinguished:
- Thermal - a person receives them due to high temperature. Such situations often occur in domestic conditions - for example, as a result of contact with fire, hot liquid, a hot object or steam. The damage they cause can be either mild and superficial or very severe, threatening health and life.
- Chemical - they appear due to various substances. At home, burns of this type are usually caused by compounds containing acid or alkali. This could be “chemicals” for cleaning or maintenance.
- car, laundry detergent, or acetic acid used in cooking.
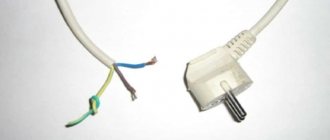
- Electrical - occurs when current is applied to the skin, soft tissues and organs due to improper handling of household appliances or if the equipment is short-circuited, when touching wires or exposed contacts. A mild burn of this type is accompanied by minor damage to the surface layer of the skin. But more serious cases can result in widespread and deep injuries that affect internal organs and impair their function.
- Radiation - most often occur due to prolonged and intense exposure to ultraviolet rays. For example, working in the countryside under the scorching sun or relaxing on a sun lounger at times when the UV index is high can cause sunburn. However, such burns are usually superficial and relatively easy to treat. Another, much more dangerous source of radiation burns is radiation injuries from ionizing radiation.
- Combined - formed under the influence of several damaging factors.
Burns also differ in the location of the damage:
- on the skin;
- on the mucous membrane;
- in the respiratory tract;
- on internal organs.
Severity
The severity of the burn is directly related to the depth of the lesions. There are 4 degrees, and each of them is characterized by certain symptoms.
Grade I
The burn affects the superficial layers of the skin. The damage is accompanied by redness, slight swelling, severe or moderate pain, and a local increase in temperature. There may also be discomfort when moving. For example, if your hand or fingers are injured, the pain intensifies when you try to move them or when you touch the burned area. With simple treatment, first-degree burns disappear without traces within 2–3 days in adults and 3–5 days in children.
Grade II
The deeper layers of the skin are affected and blisters filled with fluid form. Inflammation occurs around them, and when the bubble is removed, weeping wounds of varying sizes may appear in its place. Grade II injuries are accompanied by swelling and redness. With such a burn, a person experiences burning pain, which for some time can interfere with sleep and leading a normal lifestyle. As the blister heals, it falls off and a crust forms at the site of the wound.
To provide first medical and sanitary aid for thermal and sunburns of 1st and 2nd degree, “EversLife - SP” should be used.
Grade III A
The skin is damaged very deeply; a so-called scab forms at the burn site - a dense gray-brown crust. The painful sensation before its formation is acute, since the damage affects the layers of skin with nerve endings. Sensitivity is reduced, regeneration is very slow, and skin grafting is often required. The risk of developing burn disease increases.
Grade III B
Irreversible damage affects not only the skin, but also the subcutaneous tissue.
For local treatment of 2nd and 3a degree burns and temporary closure after surgical treatment of 3b degree burn wounds, use the EverLife-Gel hydrogel dressing.
Grade IV
An extremely severe burn with charring of the skin and underlying tissues, muscles and bones are damaged.
The degree of burn cannot be the only guideline when providing first aid and planning further actions. For example, with grade I injuries that seem mild at first glance, but with a large area of damage, a burn disease may develop, which cannot be treated independently. This condition is characterized by disruption of the activity of internal organs and all body systems. For severe and extensive burns, treatment and care should be carried out only under medical supervision.
First aid for burns
Let's look at the rules of first aid for minor household burns.
First degree thermal burn of a small area - burn of a finger, hand, etc.
- Immediately stop exposure to high temperature;
- If you are burned by boiling water, steam or a hot object, wash the affected area of the skin with cool boiled water to reduce the pain;
- We apply the combined hydrogel product “EversLife-SP” (disinfectant and wound healing).
Thermal burn II degree
- Stop exposure to high temperatures;
- We apply the combined hydrogel product “EversLife-SP” (disinfectant and wound healing);
- Apply a sterile bandage. It should be changed daily to prevent infection.
Skin burn with vinegar essence
- We wash the wound with clean running water;
- To neutralize the effect of vinegar essence, apply a solution of soda, soap or ash. They are all alkalis, an antidote to acid;
- We use a product with a healing and analgesic effect “EversLife-Gel” openly or under a sterile bandage.
If the vinegar burn affects the eyes, call an ambulance; In this case, you cannot use “neutralizers” yourself.
Iodine burn
- We wash the area of skin that received iodine with running cool water;
- We use toothpaste, crushed chalk, tooth powder, sugar or soap solution as a “neutralizer”;
- If necessary, apply a healing hydrogel agent.
Treatment of burns with iodine can be carried out at home, since the damage is most often first degree. But if signs of allergy appear or the damage has spread over a large area, you need to consult a doctor.
Minor electric burn (1st degree)
- Stopping exposure to electricity. The person providing assistance to the victim must be safe.
- We treat the skin with an antiseptic;
- We apply the anti-burn hydrogel agent “EversLIFE-SP”.
- Even if the burn caused a small mark on the skin, you should definitely see a doctor. If the injury occurred due to high voltage current, and the resulting damage is extensive and deep, it is necessary to call emergency medical assistance.
Hogweed burn 5
- We blot the area where the plant juice has come into contact with a cloth, without smearing the juice on the skin;
- We protect the affected area from the sun and, if possible, go indoors;
- Wash with a solution of soap and soda;
- Treat with an antiseptic;
- We apply the anti-burn wound-healing hydrogel agent “EversLife-SP”.
In the future, a hogweed burn may require treatment with special means and observation by an allergist.
Jellyfish Burn 6
- We immediately leave the sea water;
- If the jellyfish or its fragments remain on the body, remove them from the skin, protecting your hands with gloves or at least a towel;
- We wash the burn site with an antiseptic; You can use alcohol-containing solutions or Evers Life alcohol wipes;
- If possible, make a lotion with a cotton swab dipped in soda solution;
- If blisters appear, apply a clean, damp bandage and go to a medical facility.
Ointment for jellyfish burns should only be prescribed by a doctor. Even if the injury is mild, special treatment for a jellyfish sting may be needed to avoid complications.
If a burn of any kind affects a large area of skin, mucous membranes, eyes and respiratory tract, as well as if the injury is severe or a child is injured, urgent medical attention is needed.
What is not recommended to do in case of a burn?
- When treating a burn with a blister, for example on a finger or hand, it is not advisable to open the blister at home - it is better to see a doctor to make a puncture and remove the membrane. A weeping wound may open under it, into which pathogenic bacteria can easily enter, causing inflammation and other complications.
- Do not touch damaged skin with dirty hands, even if the burn is first degree. Before applying a wound healing agent or when changing a bandage, your hands should be washed and treated with an antiseptic.
- Do not apply ice, cold metal or use ice water to the injury site, so as not to cause additional frostbite to the affected area. Such actions may provide temporary and short-term relief, but then the pain will only intensify. To relieve discomfort, you can wash the burned skin with clean, cool, but not too cold water.
- You cannot provide first aid without taking care of your own safety. This rule is especially important if a person needs help with an electrical or chemical burn.
- Contrary to the widespread “folk” tradition, you should not lubricate the damaged area with oil or fat-containing preparations - they can increase the severity of the damage due to the fact that they create a “film” on the damaged area.
- It is not recommended to use substances containing alcohol for antiseptic treatment - they can cause additional burns, increase pain, dry out already damaged skin, impairing regeneration.
Which doctor should I contact if I get a burn?
If you have a mild first-degree skin burn, you can contact a physician at the clinic. If the injuries are grade II, help can be provided by a surgeon or emergency room doctor.
Doctors who treat third- and fourth-degree burns are combustiologists. “Severe” victims, patients with burn disease and other complications are referred to them. It is extremely difficult to find a combustiologist in a district clinic; as a rule, doctors of this profile work in large or specialized medical institutions.
Treatment of burns
General treatment of household burns is aimed at:
- Protection against infection;
- Maintaining normal regeneration;
- Eliminate discomfort.
Local treatment of minor burns (1st degree) can be carried out at home using good over-the-counter preparations for external use, including EversLife-Gel and EversLife-SP
When treating second degree thermal burns when blisters appear, the following methods are used:
- Open With the open method, thanks to the constant flow of fresh air, the burned skin dries naturally and heals easily. The disadvantage of this method is a higher risk of infection. Additionally, touching, rubbing, or any other mechanical force on the damaged area can slow down recovery and cause discomfort. Therefore, in case of a burn, it is worth using EversLife-SP, which will prevent infections and help
- Closed With the closed method, moisture-absorbing sterile dressings with a healing agent or EversLife-SP are applied to the burn site, for example, when treating blisters. They absorb fluid discharged from wounds and protect against secondary injury and infections. The bandage must be changed regularly. The closed method of treating burns is often used when the skin on a moving part of the body or in contact with clothing is damaged. The disadvantages of the closed method are possible painful dressings and relatively high consumption of materials7.
- Mixed Open and closed methods can be used simultaneously, alternating throughout the entire treatment period. The open method is chosen when the victim can be at rest and the burn wound will not be subject to mechanical stress (touching, friction of clothing, stretching). Applying the EverLife-SP bandage will protect the wound from infection and unnecessary irritation, for example, if a person needs to move actively.
To treat inflammation during a burn, which can occur as a complication, antibacterial drugs and additional treatment of the burned area of skin are sometimes prescribed. At the healing stage, you need to reduce the mechanical impact on the affected area - this way recovery will take less time, and the wound will heal without leaving any traces. During this period, it is advisable to use special products that support regeneration and have an antiseptic effect, for example, EversLife-Gel gel or EversLife-SP bandage.
"EversLife-SP" and "EversLife-Gel" for healing skin burns
Domestic burns can be treated at home using anti-burn products. These include anti-burn hydrogel products “EversLife-SP” and “EversLife-Gel”, intended for minor skin damage8. The anti-burn wound healing effect of the product is based on the synergistic effect of stimulating skin regeneration processes with composite mixtures of chitosan-gelatin polyelectrolyte complex and dexpanthenol.
In addition, an important feature of EversLife-SP and EversLife-Gel is its analgesic and antimicrobial effect, due to which the pain subsides and the person feels better. Thanks to this, “EversLife-SP” and “EversLife-Gel” will become indispensable assistants for the mother of a baby or teenager.
The gel in the EversLife-SP and EversLife-Gel dressings with a light texture is easily absorbed and does not stain hands and clothes. This product is indispensable for a home, travel or children's first aid kit. Also, for skin restoration, protection and a speedy recovery from a mild household burn, “EversLife-SP” and “EversLife-Gel” can be used by both adults and children.
Conclusion
It is important to remember that most often in our lives we encounter minor burns, the main cause of which is carelessness and failure to follow safety rules when cooking, cleaning using cleaning products and operating household appliances. That is why the best way to prevent such injuries is caution and attentiveness.
Maybe you'll like it
Hemostatic agent "EversLife-Hemo"
Anti-burn agent "EversLife-SP"
Wound healing agent "EversLife-Gel"
Wound dressing Vilovond POVI Pad
SUNBURN. PREVENTION AND TREATMENT
TIPS FOR TREATING SUNBURN
When going on a trip, do not forget that the skin is defenseless against active sunlight, and the desire to quickly get a brown tan is understandable, but not entirely correct. The result of prolonged and uncontrolled exposure to the sun is a sunburn. This is characterized by poor appetite, sometimes vomiting, insomnia, fever, and tachycardia. Against this background, drowsiness may occur. Children suffer especially hard from sunburn.
What should you do to protect yourself and your family from sunburn?
Firstly, you need to actively moisturize your skin and drink as much water as possible, because the very first negative effect that solar ultraviolet radiation has is dehydration. Secondly, in the first hours after getting a sunburn, you can take antihistamines (suprastin, tavegil, etc.) - this will reduce skin inflammation and simple painkillers (ibuprofen, paracetamol) - this will reduce pain. Thirdly, use EPLAN burn ointment (or solution) to treat the affected area. Repeat the procedure 3-4 times a day. We recommend that you first lubricate the affected area with the solution in order to instantly relieve redness and swelling. EPLAN solution also has a cooling and analgesic effect. To consolidate the effect and soften the skin, we recommend continuing treatment of sunburn in the evening, using EPLAN cream. Fourth, to protect the skin from sunburn, we recommend applying Eplan solution to the skin 10-15 minutes before going out into the sun. Eplan forms a protective film on the skin, which will protect the skin from burns in the future.
Must remember! Changes in the structure of the skin are irreversible after any burn (including sunburn and boiling water burns); in the future, the skin may constantly react in a more severe form to new portions of sunbathing.
Detailed information on the use of EPLAN for the treatment of burns, wounds and skin lesions in the EPLAN section: AREAS OF APPLICATION
FIRST AID FOR BURNS WITH BOILING WATER AND STEAM
A burn is an open injury or destruction of the skin and mucous membranes. For burns, not only the type of damage factor matters, but also the duration (exposure) of its action.
The skin is the outer covering that protects the body and its connection with the environment, its mass is 4-6%, and together with the subcutaneous layer - 16-17% of the total body weight, its area in average adults is approximately 1.7 m2 . The skin performs a number of important functions: protection from the external environment, thermoregulation, participation in metabolism, water and heat transfer, blood distribution in the body, receptor, secretory, pigment-forming, respiratory, energy-saving (fat depot), immune.
When burned by boiling water or steam, tissue damage occurs quickly; the source of the burn must be removed immediately. Cooling significantly reduces the severity of the burn and relieves severe pain.
Burns from boiling water and steam are a very important problem in adult and child traumatism: burns become especially dangerous for young children and the elderly due to imperfections in the body’s protective functions. Most cases of burn injury occur at home due to negligence.
A superficial burn with boiling water and steam, like a sunburn, should be immediately treated with an anti-burn remedy - EPLAN solution. This will allow injured skin to heal in the shortest possible time. The drug can be used in different age categories. In serious cases, when anatomically significant areas (face, neck, perineum) are affected by the burn, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Detailed information on the use of EPLAN for the treatment of burns, wounds and skin lesions in the EPLAN section: AREAS OF APPLICATION
HOW TO USE BURN OINTMENT IN FIRST AID
There are several stages in providing medical care for burns.
First stage (prehospital)
includes first aid for burns, provided in the form of self- and mutual aid at the scene of the incident. The burn surface for superficial burns is painful, so mechanical cleaning is allowed only in case of severe soil contamination by irrigation with antiseptic solutions. It is necessary to choose the optimal remedy for burns in a particular case. Burn wounds are covered with anti-burn dressings that do not stick to the wounds or sterile dressings with water-soluble ointments (levomekol, levosin, dioxykol, dermazin).
Instead of traditional remedies used in these cases, we recommend the universal, ready-to-use drug EPLAN (ointment and solution). EPLAN has unique properties for providing first aid, especially for sunburn.
EPLAN has the following useful properties: - pronounced absorbent activity (dehydrating activity is 13.5 times higher than that of a hypertonic NaCl solution); -low toxicity; -good permeability in fabric; - no irritating effect; - ease of application on surfaces.
If the ointment (cream) is immediately applied to the damaged areas, redness and inflammation disappear, and blisters with serous fibrous contents do not appear.
For local treatment of burns with EPLAN, two methods can be used: open (without bandages) and closed (with bandages), subsequent dressings are carried out daily or every other day until the wounds are completely healed.
What not to do
Pediatrician at the Fantasy Children's Clinic, Ph.D. Svetlana Mukhortova does not recommend:
- Lubricate the burn with vegetable oil, cream, sour cream and other fermented milk products. A film forms on the skin, air stops flowing to the wound - it overheats, and the depth of the lesion increases. Lactic acids and fermentation products can introduce microbes into the wound
- treat burned skin with brilliant green, iodine, cosmetic lotions - alcohol dries out the skin and causes burning and pain
- apply bandages with urine to the wound. The effectiveness of urine therapy has not been proven
- puncture blisters - microbes with liquid can enter the wound. The blisters will open on their own - as a rule, this happens when the skin has already been renewed and the wound has “healed”
- remove stuck clothing yourself so as not to injure the burn site
- apply snow and ice longer: burned skin does not feel temperature changes - you can get frostbite
- sprinkle the burn with soda, flour, mustard powder, starch or baby powder - the film prevents cooling, and small particles can fester
- apply tight bandages and seal the wound with adhesive tape - air access is reduced
- rinse with running water if bubbles open - this is painful and can lead to germs penetrating deeper.