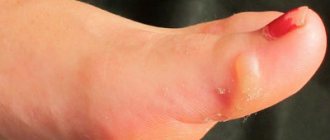
Root or core callus is the most difficult type of callus to treat. A callus has a core (root) that is located deep in the skin and can even penetrate into soft tissue. This is a late stage of dry callus development.
Externally, such a callus looks like an area of keratinized skin, and inside it a funnel is visible. The formation is quite dense and causes pain when walking. In some cases, it is completely impossible to walk with such a callus - when the rod is already located deep enough and has penetrated into the soft tissue, squeezing the nerve endings.
Most often, calluses appear on the toes, under and between them, and on the heels. Interdigital calluses are the most painful.
Causes of such calluses
Root calluses are formed under the influence of internal and external factors. External - long-term and intense friction that occurs due to wearing too tight or uncomfortable shoes, as well as high-heeled shoes. Such a callus can also form as a result of a foreign body (for example, a splinter) getting into an untreated wound in a timely manner.
Callus can also appear due to internal reasons:
- the patient has dermatological diseases;
- increased sweating;
- lack of vitamins and microelements in the body;
- diabetes mellitus
Types of calluses and treatment methods
Gvozdevaya
A rare type of callus.
Does not have a hole or black spot in the middle.
Outwardly it resembles a nail, the head of which is on top.
It has a small round shape.
Rod
A distinctive feature of this callus is its structure.
The surface of the skin acquires a slight compaction, and under it there is a base.
The main inconvenience is severe pain due to the root located in the tissues.
Such a deep callus can be removed by contacting a medical center for hardware or surgical intervention.
There are several ways to get rid of a callus, for example drilling.
Cryotherapy, as a result of which the callus is frozen, and it dies off on its own.
Laser action that evaporates the liquid contained in the callus, which leads to drying of the rod and the formation itself.
Water
A similar callus can be observed when wearing uncomfortable shoes.
A blister appears that is filled with blood or lymph fluid. The outer skin is thin and easily torn from external influences.
A watery callus should not be pierced or picked off on its own. The treatment procedure is aimed at eliminating mechanical effects at the site of injury.
As a result, the neoplasm will heal on its own, and the contained lymphatic fluid will dissolve and help restore the skin.
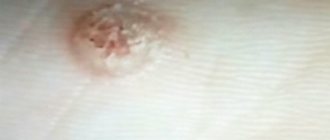
Dry
Occurs in various parts of the body. It is a small keratinized part of the skin. It feels hard and unpleasant to the touch.
Treatment should be carried out even in the absence of painful symptoms.
To do this, steam your feet in warm water with various additives such as soda, soap, potassium permanganate or tea tree oil.
Corns
This callus is similar to the one described above.
However, it only appears on the soles of the feet.
It has no definite boundary and varies in size.
The cause of the appearance is general dry skin, frequent walking and wearing hard shoes.
Cone
It appears as thickenings on the big toes. Sometimes it causes discomfort when walking.
The cause may be heredity.
Development occurs for no apparent reason.
Bumps also occur when wearing uncomfortable shoes for a long time.
If the callus is exposed to regular mechanical stress, it can turn into a bunion. This type of callus occurs on the big toes near the joints and contains fluid inside.
The result is severe pain when walking.
Treatment for a bump or bunion should begin by changing your shoes to more comfortable ones. If the callus does not cause pain and does not grow, then there is no reason to worry. But when it becomes a hindrance, you should visit a surgeon.
Outdated
Without timely action, the rubbed parts of the skin turn from new calluses into old ones, the skin on which is keratinized. Such formations are most uncomfortable on the toes. The treatment is long and difficult. Modern pharmacology provides many means to get rid of rough skin. Their action is based on softening and then removing the growth.
The most well-known method for removing calluses on the feet is cutting. To do this, you need the following: a bath with hot water, soap and soda.
- Keep your feet in it for 15 minutes.
- As a result, the old skin will become softer and the top layer can be removed.
- Then apply a patch or lubricate the area with salicylic acid.
The procedure is carried out carefully. The drug should be kept away from healthy skin to avoid damage.
Diagnosis of calluses
For an experienced podologist, a visual examination of the patient is sufficient to identify the core callus. Correct diagnosis is essential to creating an effective treatment plan. That is why it is important to consult a specialist in a timely manner - a callus can easily be confused with a plantar wart, which forms on the same areas of the foot, but requires different therapy.
As additional studies, the patient may be prescribed blood tests for:
- sugar level;
- glycated hemoglobin;
- human papillomavirus (HPV);
- human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
Calluses (core calluses, corns)
Calluses and calluses are limited areas of hyperkeratosis at the site of periodic pressure and friction. Corns are more superficial, cover a larger area of skin, and are usually not accompanied by symptoms. The core callus lies deeper, in a limited area of the skin and is often accompanied by pain. The diagnosis is made by appearance. Treatment is carried out by manual abrasion with or without the use of keratolytics. Preventative measures include biomechanical corrections, such as changing shoes. Surgery is rarely required.
The development of corns and calluses is caused by periodic pressure, usually found in the area of bony prominences (eg, heel bones, metatarsal heads).
A callus consists of a well-demarcated hyperkeratotic plug, about the size of a pea or slightly larger, that is embedded in most of the underlying dermis. Bursitis of the underlying adventitia may develop. The cutaneous horn develops in the area of protruding bones, especially on the toes and plantar surface.
A water callus can form in the area of the interdigital folds. In most cases, cutaneous horns occur as a result of wearing tight shoes, but small cutaneous horns on areas of the skin of the palms and soles that are not exposed to increased mechanical stress may be a manifestation of congenital punctate keratosis.
Calluses do not have an accumulation of horny masses in the center and their surface is smoother. They usually occur on the hands or feet, but can appear on any part of the skin, especially in people whose work involves repeated mechanical impact on certain areas (for example, the area of the lower jaw and collarbone in violinists).
Clinical manifestations
Calluses are usually asymptomatic, but if the friction is very strong, thickening and irritation of the skin may occur, accompanied by a moderate, unpleasant burning sensation. Sometimes the unpleasant sensations from calluses on the toes can mimic manifestations of interdigital neuralgia.
The callus may be painful or tender when pressed, and sometimes a bursa or pocket filled with fluid will form.
Diagnostics
A callus can be differentiated from a plantar wart or callus by cutting and removing the thickened skin. After removal of the horny masses, with callus, smooth, transparent skin is exposed, while with a wart, a clearly demarcated formation appears, sometimes represented by soft macerated tissue or centrally located black dots (pinpoint bleeding), which are thrombosed capillaries. When the horny masses are removed from the skin horn, a clearly demarcated yellowish-brown transparent core is revealed, disrupting the normal structure of the papillary dermis.
Treatment
Manual removal (pumice, laser destruction, cryodestruction)
Keratolytics (eg, 17% salicylic acid collodion, 40% salicylic acid patch, 40% urea), taking precautions to avoid contact with healthy skin. Healthy skin can be protected by pre-applying Vaseline before applying the keratolytic.
Foot Care Specialist (Patients who are prone to developing persistent, painful corns and calluses may require regular care from a podiatrist. Patients who have impaired peripheral microcirculation, especially if they also have diabetes, require regular intensive foot care.)
- Using orthopedic insoles
- Changes in foot biomechanics
- Shock absorption and foot biomechanics
Using orthotic pads and changing the biomechanics of the foot can help prevent callus formation and make existing callus easier to treat. Although pressure on the affected area is difficult to eliminate, it should be reduced and redistributed. If hyperkeratotic formations occur on the foot, it is important to use soft, comfortable shoes; it should have enough free space for the first finger so that it can move freely there. Fashionable shoes often limit the freedom of movement of your toes. You should avoid shoes, the wearing of which causes discomfort in the affected area. Pressure can be redistributed using pads or rings of suitable shape and size, protective bandages made of thick cotton fabric with a satin or twill weave or sponge rubber, arched inserts (orthopedic inserts) or metatarsal plates or grids. For calluses and calluses in the ball of the foot area, an orthotic insert should not be used the entire length of the foot, it should only reach the ball of the foot or the part of the shoe just behind the callus or callus. Surgical offloading or removal of the offending bone is rarely necessary.
Doctor Atayan E.A.
Treatment of root callus
The treatment regimen is selected depending on the cause of callus formation and always involves the removal of the stratum corneum and the core of the formation. It is important to completely remove the root of the callus, otherwise the problem will recur again and again.
The easiest way to remove dead skin is with a hardware pedicure. The specialist selects the diameter of the machine's cutters, which are used to cut the skin, depending on the size of the callus and the depth of its core.
After removing the rod, its bed is treated with an antiseptic. Then an antibacterial ointment is placed in it.
Medicines and drug therapy
A callus on the toe or sole can be treated with pharmaceutical preparations based on salicylic acid. The preparations are applied only to the affected area; it is prohibited to apply the preparations to healthy skin. The following medicinal formulations are best suited:
- Super Anticallos is a drug for removing growths, containing the active ingredients urea and lactic acid.
- Balm Karavaeva (Vitaon) with herbal extracts. The product is very effective and can be used to treat deep root germinations.
- Nemozol is a cream containing concentrated salicylic acid and has already proven effectiveness.
- Sto-corn is a liquid substance packaged in a bottle with a dispenser. Ease of use is a big plus, but the therapy will be long, but regular use provides very good results.
Advice! If the dermatologist determines the presence of a fungus or viral infection, antifungal drugs such as Acyclovir, Penciclovir, Lamisil will be prescribed.
The Salipod plaster is a good way to combat calluses. An effective remedy rarely fails to treat growths caused by a fungal or viral infection. Application of the patch is incredibly simple:
- Apply a patch to a dry and clean lesion;
- Secure Salipod with a regular plaster;
- Do not remove the bandage for 3-4 days, then remove the bandage;
- Steam the foot and remove the rod.
If the rod part has gone deep enough, you should repeat the procedure again with wearing a bandage for 3 days. After removing the rod, a deep wound remains, which must be lubricated with an antiseptic and protected from dirt. In addition to this type of patch, pharmacies offer quite a few other identical products and their use is the only cases when piercing the growth is allowed, and then only after preliminary steaming in hot water.
Advice! Orthotics should be worn during medication treatment to relieve pressure on the foot or heel.
Medicines are not the only option; in some cases, doctors prescribe more modern methods for removing ingrown calluses:
Surgitron device: principle of operation and areas of application of the radioknife
- Laser removal is effective in very advanced cases. The laser beam burns the core base and removes all pathogenic bacteria, minimizing the risk of inflammation after the procedure.
- Hardware drilling (removal) is the process of removing a deeply embedded rod. After the procedure with a special device, the doctor puts an antibacterial agent into the wound to prevent relapses and infection of the affected area.
- Cryodestruction with liquid nitrogen is a proven method of burning out a seal with a central rod. The efficiency and painlessness of the operation, as well as the absence of the risk of secondary germination, are the advantages of the procedure.
- The radio wave ablation method is a painless operation in which radio waves evaporate water from abnormal cells, destroying the formation. Pros: no impact on adjacent healthy tissue.
- Electrocoagulation – removal of growths by exposure to alternating current. A protective crust remains at the site of burning, which acts as a biological bandage. After 10-12 days, the crust disappears on its own, leaving clean skin.
All treatment methods are prescribed only after examination by a dermatologist. It is strictly forbidden to use medications for self-medication due to the possibility of developing a fungal infection in the callus. Even a safe patch can lead to the proliferation of bacteria and the rapid development of the disease. In this case, the lesion will increase in area and depth, but it will be much more difficult to cure it.
Possible complications of core calluses
Lack of timely treatment of callus can lead to complications. The root of the callus is able to penetrate deep enough into the skin, squeezing the nerve endings. The patient's gait may change, even to the point of lameness, which even leads to disability - the pain caused by the callus can be so intense.
Calluses on the heels can bleed and fester. In this case, you need to contact a specialist immediately - such symptoms indicate the presence of an inflammatory process in the callus.
How is dry callus diagnosed?
If you suspect the presence of a dry callus, you must make an appointment with a podiatrist. An experienced specialist will be able to make a correct diagnosis during a visual examination, on which the effectiveness of treatment will depend.
The following symptoms are typical for callus:
- Sensation of a dense knot extending into the deep layers of the dermis
- Yellowing of the callus
- The appearance of acute pain upon contact with a callus
- Small hole in the center of the formation
Podologist's advice
- Treat wet calluses in a timely manner, which over time can transform into dry calluses and then into core calluses.
- Wear shoes that fit comfortably. Avoid shoes with too thin soles. Don't wear stilettos all the time.
- Socks should be made from natural fabrics.
- Use antiperspirant for your feet if you suffer from excessive sweating.
- Maintain personal hygiene and do not wear other people's shoes.
- Watch your weight and use orthopedic insoles if necessary. It is not recommended to select them yourself; to do this, contact a specialist.