What diseases can provoke pathology?
Pathological inflammatory enlargement of the lymph nodes in the groin - regional or inguinal lymphadenitis - indicates a progressive disease of the organs from which lymph collects in the nodes, causing their enlargement.
- The lower lymph nodes collect material from the lower extremities.
- The upper lymph nodes in the groin are responsible for “cleanliness” in the area of the side of the torso, lower abdomen, and buttocks.
- The middle lymph nodes collect lymph from the duodenum and anus.
An increase in the “bag” in the groin indicates either an inflammatory process in the organs being served, or an infection in adjacent areas.
In most cases, the cause of enlarged inguinal lymph nodes is:
- bacterial / viral infection of the reproductive organs (syphilis, infectious granuloma, chancroid, gonorrhea, herpes in the groin, toxoplasmosis, tuberculosis, furunculosis);
- physical overload, swelling of the legs;
- in 92% of cases, enlargement of the groin lymph nodes accompanies injury to the genitals and perineum;
- neoplasms (including malignant ones - lymphosarcoma or lymphoma) also lead to inflammation of the lymph nodes in the groin area.
In the practice of diagnosing lymphadenitis, approximately a third of cases occur due to drug withdrawal reactions. Enlarged lymph nodes can be caused by the introduction/withdrawal of steroids and the end of the chemotherapy program.
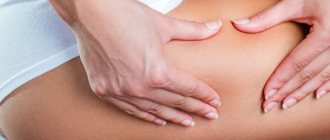
Lymphadenitis - a lump in the groin area
11.11.2021
There are many unusual inflammatory tumors, malignant and benign neoplasms on the human body. Neutralizing each of them requires its own special approach. A lump in the groin area can be represented by either a small swelling or a massive formation.
In any case, such an anomaly should be shown to an experienced doctor . During the examination, the latter will probably prescribe a number of medical procedures. Well, then everything will depend on the type of growth that appears. Most likely, the formation will disappear on its own after a few days, but there are situations when surgical removal is clearly unavoidable.
Lump in the groin in men - causes and treatment
A lump in the groin in men is the very first symptom of inflammatory processes in the lymph nodes. And in this case, it clearly smells like hernia Diagnosis of such a disease is carried out through self-examination or medical examination. This will only give a superficial idea of the severity of the disease. Next you need to undergo a more serious examination.
This type of formation appears in men in the upper part of the inguinal fold. The size of their healthy lymph nodes can be compared to a bean, but when it becomes inflamed, the size increases, literally, to a walnut. When a lump appears in the groin, males feel a sharp or dull pain in this area. In addition to the above symptoms of the inflammatory process, there is also a significant increase in body temperature.
Lymphadenitis in the groin area can occur due to infection with a variety of genital infections. Among the latter, viruses are often observed. In this case, treatment will be more predictable than in the presence of malignant or benign tumors. Lymph nodes can become inflamed during prostatitis . And during the course of various types testicular A male lump in the groin is more rarely observed as a consequence of swelling of the scrotum. But for children (boys), this disease is explained by the fact that the testicle does not descend from the abdominal cavity.
Lymphadenitis (inflammation of the male inguinal lymph nodes), which appears between the groin and also the leg, can be removed by modern doctors not only through surgery. There are many medications on sale, the use of which promotes complete resorption of inflammatory formations.
A lump on the pubis in representatives of the stronger sex may also appear after a sudden weakening of the muscles that are located in the wall of the abdominal cavity. Moreover, such a nuisance can provoke not only enormous physical exertion, but even a severe cough. Because of all this, intestinal loops often protrude directly under the skin. Thus, a hernial sac is literally instantly formed and unprecedented pain appears in the groin, which is unbearable. When a hernia is subjected to excessive stress under the influence of physical stress, the skin that is located above it swells very quickly, acquiring a red tint. If a hernia is strangulated, you obviously cannot avoid surgical medical intervention.
Lump in the groin in women - causes and treatment
A lump in the groin in women can also occur due to a variety of factors. There are a lot of variations in the process of treating a lump near the groin. Most often, representatives of the fairer sex discover such formations on their own. Well, then, it’s up to the doctors . Most likely, they will diagnose you with harmful enlarged lymph nodes. In this case, it is necessary to identify the causes of damage to these natural protective barriers of the body. Viral infections are considered the most common of them.
In case of inflammatory processes in the organs of the female reproductive system, a lump under the skin in the groin can be treated faster and more productively than in the case of cancer. The most trouble awaits you when malignant processes appear in the body. Even the use of high-precision instrumental examination, including computed tomography or biopsy, does not always help to identify all the nuances regarding tumors.
And finally, remember that it is better to show the above abnormal formations that appear on the body to a doctor , since only medical professionals can promptly save you from the serious consequences of illnesses. And it doesn’t matter whether the lump is in the groin on the right, left or in the center - the main thing is that such an anomaly needs to be eliminated.
Published in Lymphology Premium Clinic
Therapy for regional lymphadenitis
The danger of regional enlargement of nodes is in the absence of obvious pain in the groin. In 80% of cases, there is an enlargement of the lymph nodes without pain. This complicates diagnosis and leads to unintentional delayed treatment. While early detection of diseases that provoke lymphadenitis in the groin significantly increases the chances of treatment without complications.
Enlarged lymph nodes in the groin are treated only comprehensively. Initially, it is necessary to determine the source of the problem - the area of localization of inflammation. Without this (getting rid of the primary disease), treatment of the lymph nodes in the groin will be accompanied by relapses.
Much depends on the degree of increase and form of infection. For non-purulent forms of diseases in the groin, pharmacological therapy (antibiotic ointments/gels or oral administration) in combination with restriction of mobility may be sufficient. If suppuration begins against the background of enlarged lymph nodes, a surgical procedure may be required - opening and cleaning the lesions in the groin.
In some cases, medication and physical therapy for enlarged inguinal lymph nodes may be accompanied by the use of herbal-based drugs (dandelion, peppermint, herbs) in order to enhance the sedative effect in the inguinal lymph nodes.
Pelvic tumor in women
Pelvic tumor in women: treatment, risks Tumors
can occur in the pelvic organs, such as the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. The causes of these neoplasias are completely different.
To monitor the formation and development of these tumors, you need to visit your gynecologist frequently. If the neoplasm is benign, it may not require surgical intervention and will go away after some treatment. If the neoplasia turns out to be malignant, then you need to contact an oncologist.
Symptoms will often depend on the nature of the tumor. Common clinical manifestations will be:
- Diarrhea or constipation;
- Pain in the lower abdomen, unilateral pain;
- Pain during menstruation;
- Vaginal discharge;
- Uterine bleeding not during women's days;
- Pain during sexual intercourse;
- Bloating in the intestines;
- Urinary incontinence;
- Temperature;
- Frequent urination;
- Vomiting and nausea;
- Weight loss;
- Deterioration of general condition, weakness.
We list the main types of pelvic tumors:
- Implantation of a fertilized cell outside the uterus during an ectopic pregnancy;
- An abscess in the ovary or fallopian tube, resulting from inflammatory and infectious diseases in the pelvic organs;
- Benign ovarian cysts (endometriomas);
- Benign tumors of the gynecological type (fibroids);
- Torsion is a violation of the blood supply to the ovary;
- Cancer.
First, the doctor must study the medical history, listen to the patient’s complaints and analyze them, examine the patient, take general and advanced blood and urine tests, conduct a transvaginal ultrasound, CT and MRI, and perform a cytological examination based on a biopsy.
It must be remembered that not all neoplasias are dangerous, but many require conservative treatment. There are signs of acute pathologies that require urgent help. These are ectopic pregnancy and egg torsion.
An ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed by a positive pregnancy test, pain in the pelvic organs, bleeding, and ultrasound results.
Testicular torsion is accompanied by severe pain in the side where it occurred, vomiting, nausea, and is diagnosed during examination in a chair and according to ultrasound results.
If the patient has an ectopic pregnancy, it must be terminated promptly. To do this, either laparoscopy or salpingostomy (salpingectomy) is done, and metrotrexate can also be administered intramuscularly.
If a woman has inflammatory diseases of the organs of the body, then antibiotics and antibacterial therapy are prescribed; today, even with abscesses, surgical intervention is not required. It is done only when the abscess capsule ruptures.
Endometrioma is treated in different ways. Here they resort to conservative medicine, remove cysts, use wait-and-see tactics, and use reproductive technologies.
Benign fibroids are treated by taking hormones and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as surgical treatment, ultrasound albation.
In case of egg torsion, surgery is performed immediately to prevent necrosis and damage to the ovary.
Cancer of the breast organs in women is treated surgically, with chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and radiation therapy.
Treatment is chosen depending on factors such as:
- Type of cancer according to histology;
- Localization;
- Organ;
- Stage of cancer;
- The presence of swelling in the abdominal cavity;
- Genetic diseases;
- State of the body;
- Age factor;
- Nature of the tumor (recurrent or primary).
Tumor under the ear
The risk of torsion is high if women have large ovaries.
The risk of fibroids increases in older women, in women with early onset of menstruation, and in women with greater weight.
The risk of malignant tumors increases if there is a genetic predisposition, endometriosis, excess weight, age over fifty, a woman gaining a lot of weight, or using hormonal drugs after menopause.
The Onco.Rehab clinic offers high-quality diagnostics and effective treatment methods for the problem that has arisen. Be healthy!
Features of treatment
By the way, do not confuse hidradenitis in the groin
with ordinary boils.
Unlike them, the structure of the formations turns out to be simpler, since there is no rod, but the disease itself, of course, is more severe and takes longer to treat. In the case of an acute form of the described disease, calling a surgeon at home
will help you significantly alleviate the situation.
If you start a treatment course in a timely manner, you can do without surgical intervention. In this case, it will be necessary to take special antibiotics, carry out dry heating, and undergo ultrasound and ultraviolet examination.
Injections of a drug such as novocaine should also come to the rescue. When a relapse of the disease occurs, the therapeutic course should be aimed at destroying staphylococcus. Be that as it may, it is highly not recommended to start the disease and medical assistance is necessary after the initial symptoms have arisen.
You should also not forget to maintain personal hygiene. This is one of the main factors influencing the reduction of risks associated with the formation of hidradenitis. In cold temperatures, do your best to keep your body temperature at an optimal temperature. People who have a certain predisposition to the disease described should occasionally treat with alcohol those areas of the body that may be potentially dangerous.
Useful information on the topic:
- Calling a surgeon to your home
- Callus
- Abscess on finger
- Ingrown nail
- Felon
- Wart removal
- Removal of condylomas
- Abdominal ultrasound
- Removal of papillomas
- Treatment of bedsores
- X-ray
- Removing stitches
- Gastroscopy
- Colonoscopy
How is the operation performed?
Inguinal lymphadenectomy may be performed during surgical removal of the primary tumor. Most often, the lymph nodes in this case are removed en bloc along with the malignant neoplasm. Another option is delayed intervention. In this case, removal of lymph nodes is carried out in the second stage, either after additional diagnostic methods (morphological examination of the cutting edges, sentinel lymph node biopsy), or in the long-term period, when the pathology is already progressing.
The procedure itself for removing inguinal lymph nodes can be performed by two methods - open, or traditional, and closed - endoscopic. In an open operation, an extensive tissue incision is made, leaving long scars. During endoscopic intervention, all manipulations are performed through small punctures. This method causes less tissue damage, does not leave large scars, and is also less likely to cause complications such as lymphedema, skin flap necrosis, scrotal or vulvar swelling, and wound infection.
This operation itself is technically very complex and, as a rule, takes longer than removal of the primary lesion. Of course, it requires a highly qualified surgeon.
During the healing stage after removal of the inguinal lymph nodes, constant monitoring of the condition of the wound is necessary. Bandages should be changed according to the doctor's recommendations. At first, it may be necessary to puncture the surgical area to evacuate the accumulated fluid. Gradually, the need for the procedure will disappear.
It is also necessary to ensure that the wound does not become infected. If redness, swelling, swelling, increased pain, unpleasant odor or purulent discharge appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
After surgery, local numbness of the skin is possible. It develops due to the fact that nerve endings are crossed during the intervention. In some patients, sensitivity is restored over time.