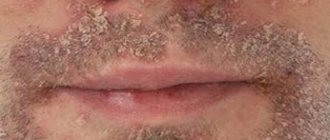
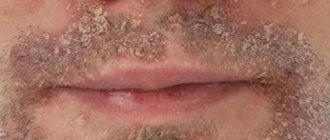
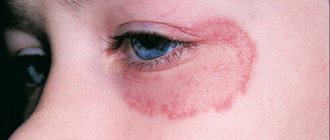
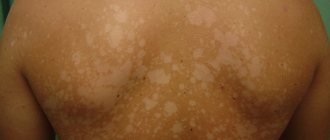
Feline lichen in humans requires immediate treatment, which in turn proceeds with maximum complexity.
Ringworm is a contagious disease that is transmitted from an infected organism to a healthy one. Pathology manifests itself in the form of small red spots with pronounced boundaries. Most often, stray dogs or cats become carriers. People who pet a sick animal have a very high risk of infection.
Ringworm can be transmitted from cat to person. When the infection came from an animal, it is microsporia; if from an unhealthy person, it is trichophytosis.
What is feline ringworm
Feline ringworm is a highly contagious (highly contagious) infection. The natural reservoir for microorganisms is often cats, although the infection can be transmitted from dogs and rodents.
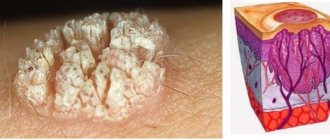
Once the fungal spore gets on the skin, it germinates like a seed. Thanks to special substances on the surface of this reproductive structure, it attaches to the body. 4–6 hours after this, germ tubes form and penetrate into the surface layers of the skin.
The thread-like formations (hyphae) of the fungus grow in depth and breadth. They receive the nutrients they need for growth from the surrounding tissues. Hyphae damage the outer layer of skin, hair, and hair follicles. After about 7 days, they also begin to reproduce.