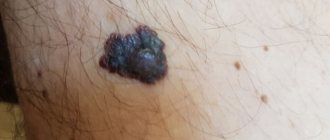
Red moles (angiomas) are vascular neoplasms, the diameter of which ranges from several millimeters to several centimeters. Most often, angiomas appear during fetal development (congenital angiomas), but they can also occur after birth.
Small red moles can be localized on the stomach, arms, legs, back, chest, face, neck, and also on internal organs. Depending on the shape, there are three types of red moles: dotted, cavernous and stellate.
Why do red moles appear on the body?
Red moles are formed by a large number of microscopic blood vessels (hemangiomas) and lymphatic vessels (lymphangiomas). The main reason for the appearance of red moles is dysfunction of the circulatory and lymphatic systems. Angiomas are divided according to type:
| Types of angiomas | |
| Types of angiomas depending on the morphological structure | hemangiomas that develop from blood vessels |
| lymphangiomas, which form from lymphatic vessels | |
| Types of angiomas depending on the cellular structure | monomorphic, consisting of the same type of cells |
| polymorphic, which combine several cell types | |
| Types of angiomas depending on type | simple (capillary) angioma - occurs due to the proliferation of capillaries |
| branched angioma - a branched network of dilated capillaries | |
| cavernous angioma - wide spongy cavities filled with blood | |
| combined angioma, combining cavernous and simple types | |
| Types of angiomas depending on location | spine - predominant location in the thoracic and cervical regions, affecting one or more vertebrae |
| skin - red moles on the body | |
| brain - vascular angiomas in the brain substance | |
| liver - single or multiple vascular neoplasms located in different parts of the organ | |
| kidneys - angiomas are formed from the veins and arteries that supply the organ | |
The most common causes of angiomas on the body are:
- hormonal changes in women (during pregnancy, taking oral contraceptives);
- skin injuries;
- genetic characteristics of the organism;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver and pancreas;
- long exposure to sunlight and frequent visits to the solarium.
Why can a mole get bigger?
As I have written many times, a mole consists of nevus cells. They are a bit like melanocytes, which are what cause our skin to turn brown after tanning. They, like melanocytes, produce pigment and therefore most moles are brown. Pigment cells divide very rarely, if not almost never divide. However, this can occur under the influence of certain factors. The most studied of these causes are sunlight and pregnancy.
Intense sunlight
is a damaging factor for our skin.
The pigment melanin, which was mentioned above, protects our skin from its negative effects. Sometimes the intensity of production of this substance is not enough for protection and the body gives a signal to divide nevus cells and melanocytes. As a result of this, we may see an increase in our moles and the appearance of new ones.
Read more about sun protection in this article.
Pregnancy.
I will assume that many of the women reading this article have noted the growth of existing moles and the appearance of new ones in this difficult period of life.
The fact is that during pregnancy you can grow a whole new person in 9 months. For tissue growth, hormones are needed, which are secreted by the body in considerable quantities. The child grows, and along with him, the nevus cells of moles also come under the influence of the mother’s hormones. As a result, just like when exposed to sunlight, we can notice the growth of moles and the appearance of new ones
.
In addition to these two factors, there are probably others, however, they are still waiting for their researchers.
What does the appearance of red moles on the body mean?
If red moles appear on the body, this may be a simple cosmetic defect, or it may indicate pathological processes occurring in the body. In some cases, the occurrence of angiomas indicates poor nutrition, prolonged exposure to the sun, and a sludge buildup in the body.
Red dots like moles may indicate increased estrogen levels in the body, liver dysfunction and increased insulin in the blood. In addition, in some cases, angiomas appear as a response of the body to a lack of iodine, magnesium, chromium, vitamins C and K.
PRECAUTIONARY MEASURES
People with red moles should not have special restrictions. These formations do not require special care or specific treatment.
But some recommendations from experts should still be followed. As mentioned above, the only thing that can be dangerous is mechanical impact, hence the possibility of damage.
Specialists at LIC clinics recommend removing angiomas in places where there is a risk of injury. Also, avoid excessive sunbathing near water, as water increases exposure to ultraviolet rays. But if it so happens that you cannot avoid them at all, then you should use protective creams with a filter of at least SPF 30.
What to do if red moles appear on the body?
If red moles appear on the body in large numbers, single angiomas increase in size, or trauma to the red mole occurs, you should consult a dermatologist. Diagnosis of angiomas that are located on the surface of the skin is usually done by visual examination and palpation.
If there is a suspicion of the presence of red moles in the internal organs, additional research will be required to detect them. Skeletal angiomas are determined using x-rays of the spine, ribs, pelvis, bones and skull. Angiography (contrast X-ray examination of blood vessels) allows identifying red moles in the lungs, kidneys, brain and other internal organs. The structure of the angioma and the features of its location are determined by ultrasound examination.
After the diagnosis, the dermatologist will determine whether it is necessary to treat the red mole. So, the absolute indication for removing red moles is their rapid growth.
In addition, indications for treatment of angiomas are:
- localization in the neck and head;
- disruption of the functioning of the internal organ in which the angioma is located;
- extensive tissue damage around the red mole.
Treatment of red moles involves their removal, which can be done in various ways. Treatment methods for angiomas include:
- laser therapy;
- radio wave method;
- cryotherapy (removal of angiomas using liquid nitrogen);
- diathermoelectrocoagulation (cauterization with electric current);
- hormone therapy;
- ligation of the arteries that feed the angioma;
- surgery.
Effective therapy for red moles can only be prescribed by a dermatologist. Treatment of angioma with folk remedies is not recommended.
WAYS TO REMOVAL RED MOLES IN THE FACE CLINIC
At the FACE clinic, red moles are removed in several ways.
The surgical method involves removing small red moles on an outpatient basis. But this procedure is not suitable for excision of angiomas on the face.
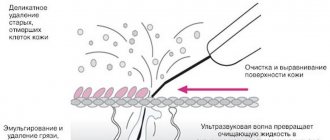
The laser removal method is the most popular because it is applicable even for deep-lying angiomas.
Initially, the surface of the angiomas is treated with a special anesthetic gel, or an anesthetic drug is injected with a syringe, after which the mole is exposed to laser radiation. After 24 hours, a crust appears at the site of laser exposure, which disappears after 1-3 weeks without additional intervention.
Also, in clinics of PERSONS they practice cauterization of moles using coagulation or carbon dioxide and nitrogen, which does not pose a danger to human health and does not leave scars on the skin. Local anesthesia is first administered, so the patient feels pain during the procedure.
Are red moles dangerous?
Unlike melanoma (a malignant tumor), angioma is a benign formation. Single red moles on the body that do not increase in size and do not cause discomfort do not require treatment and are not dangerous.
But in some cases, red moles can lead to complications. Internal angiomas, depending on their location, can cause shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, epilepsy, impaired vision and hearing. In addition, angiomas can lead to complications if:
- red mole growing;
- there is a possibility of injury;
- many red moles appeared on the body;
- there is a risk of the mole transforming into a malignant formation.
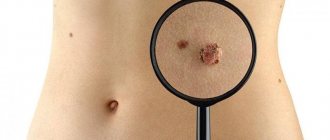
How to distinguish a large mole from melanoma?
Here it is important not to “rely on” only one sign. In the ABCD rule, which, of course, is very important in diagnosing melanoma, there are at least 3 other signs - A
(asymmetry) -
asymmetry
,
B
- (border) -
edge, border
and
C
- (color) -
color
.
All three of these characteristics are assessed only together, and not separately. This means that even if a mole is slightly asymmetrical, but has a smooth edge, is evenly colored and its size does not exceed 5 mm, most likely everything is fine with it. Moreover, there is such a type of moles - dysplastic nevi
, which most often have 2 signs at once - an uneven edge and an asymmetrical shape. However, in the vast majority of cases they are benign.
Preventing the appearance of red moles
It is impossible to prevent the occurrence of congenital angiomas. A congenital red mole in a child is most often a short-term formation and disappears by the age of 5-7 years. Therefore, if the child does not complain of pain or itching in the area of the angioma, there is no need to worry.
In order to avoid the occurrence of angiomas after birth, it is necessary to follow these recommendations:
- avoid prolonged exposure to direct sunlight and frequent visits to the solarium;
- follow a sleep and nutrition schedule;
- lead a healthy lifestyle.
If you have a red mole, it is important to monitor its development and contact a dermatologist at the first signs of injury or change in size. With timely consultation with a doctor, it is possible to prevent complications of angiomas and, if necessary, begin therapy on time.
6
2
8
Article rating:
4.12 out of 5 based on 42 ratings
Author: Christopher Vasily Alekseevich
Dermatologist, pediatric dermatologist. Highest category. Work experience 24 years.
Congenital nevi
Separately, it is worth dwelling on congenital large moles (nevi). Moles that appear during the first year of life are also called congenital. Studies have shown that the risk of developing into melanoma in such nevi is higher than in those that appeared during life. This is especially true for congenital moles whose size exceeds 20 cm. For them, the risk ranges, according to various sources, from 6 to 30%. Many dermato-oncologists recommend removing such nevi immediately
when the child reaches 10-12 years of age, when the risk of anesthesia is less than at an earlier age.
Diagnosis and treatment
Although the etiology of most birthmarks is still unknown, some have a family connection. Diagnosis is based on history and appearance.
Diagnosis of birthmarks
Most birthmarks are only cosmetic, but some types of nevi are associated with an increased risk of skin cancer. Therefore, for any nevus (pigmented birthmark) that changes color or size, itches or becomes inflamed, careful observation is required. A biopsy may be necessary to rule out malignant changes.
Treatment for birthmarks depends on their type, as well as the presence of other troubling conditions. This usually involves surgical or laser treatment.
Vascular birthmarks are also treated with laser photocoagulation, which targets the affected blood vessels with a laser.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can make an appointment by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
Types of moles
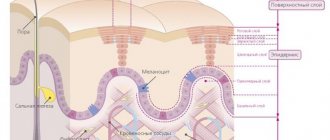
First of all, all moles are divided into epidermal and dermal.
Let us first consider the epidermal varieties of nevi. Such moles on the surface layer of the epidermis are, in turn, divided into specific and nonspecific.
Nonspecific moles are divided into:
- A borderline nevus is a mole with which a person can be born, or such a spot can appear at any age. Most often, such moles occur on the arms (palms), legs (feet) and even on the genitals. Visually they look like a spot or papule. The color of such a spot is uniform: it can vary from different shades of brown to black. The size of such spots usually does not exceed 1-2 cm.
- Intradermal nevus is the most common type of mole. Visually, they resemble a hemisphere, which seems to rise slightly above the surface of the skin. Such moles can be located on any part of the skin; the diameter usually does not exceed 1 cm. The color of such a nevus is also always uniform, either different shades of brown or black. Such moles bleed at the slightest attempt to injure them and may decrease in size.
- Complex nevus is a transitional form of congenital nevus, which visually looks like a papule, or a group of papules. Complex moles do not have a specific location.
Specific nevi are:
- Epithelioid nevus is a benign formation, most often they are single, but multiple formations of this type are not less common. Most often they appear on the legs and face. These moles reach 1-2 cm in size, are easily injured, and can disappear spontaneously.
- A mole of balloon-forming cells. This is the rarest type of nevus. Visually presented in the form of a spot, or papule. The main characteristic feature of such moles is their color. This is a brown mole with a yellow rim around the edges.
- Setton's mole is a nevus surrounded by discolored skin. It can be either single or multiple. Most often, such moles appear in people with vitiligo or other autoimmune pathologies in the body. They may disappear spontaneously on their own.
Dermal varieties of moles are:
- The Mongolian spot is a mole of quite impressive size (6-10 cm) in newborns. Localization is in the area of the sacrum, or buttocks, or thighs.
- Nevus of Ota is a type of skin defect, single or multiple, dark blue in color. They are located mainly on the face, in the area of the eyes, nose, and cheeks. They also occur on the mucous membranes of the nose, mouth and even eyes.
- Ito’s nevus is visually the same as the previous type, only the location of such moles is the neck, shoulder blades, and supraclavicular region.
- A blue nevus is a dense and smooth nodule that lacks hair growth. The sizes vary from 1 to 3 cm. The color can be gray or black.
In addition to dermal and epidermal moles, there are mixed types of moles. They, in turn, are divided into combined (which combine the characteristics of several nevi) and congenital. Congenital nevi can be either clear or blurred. They are similar to acquired ones and their main feature is their rather large size: they can be 1 cm, or they can occupy the entire surface of a limb, neck, or torso. A distinctive feature of congenital moles is their inability to disappear spontaneously.
The most dangerous are nevi of melanocytic origin. These are moles that most often transform into a malignant tumor.
Such moles are called dysplastic (atypical) nevi. This kind of moles are not congenital and are exclusively acquired. This is a single or multiple spot, which can be either round or oval of irregular shape. A distinctive feature of such a mole is its uneven edges with an accent in the center in the form of a papule.
The color of such a nevus is also heterogeneous: it can be a variety of brown, red, pink and even red colors. The size of such a nevus is also quite impressive. Such formation is rarely less than 6 mm. Such moles can be located on any skin surface of the body, less often they appear in the face area.
Removal of moles on the face in Moscow
To remove a mole in Moscow, we recommend contacting the Veronika Herba City Health and Beauty Center. Our clinic has a number of advantages:
- Modern equipment.
To carry out measures to remove moles, we use the method of radio wave destruction using the SURGITRON generator, which allows us to reduce the operation time to 20-30 minutes. The procedure takes place in a modernly equipped operating room that meets approved standards.
- Qualified specialists.
Due to the fact that our center has existed for 18 years, our experienced dermatologists have performed more than 1000 successful operations and gained enormous experience in removing skin tumors.
- Removing moles without pain
, since local anesthesia is selected individually for each of our clients.
- Before performing the operation, we We carry out a full examination
, the purpose of which is to make sure that the mole is not a malignant neoplasm.
- Transparency of work
. Your doctor will tell you about all the stages of the operation to remove a mole and post-operative prevention, as well as what parameters determine the price.
- Saving time .
We have an individual approach to each client, so the time of the procedure will be agreed upon taking into account your wishes and plans.
You don't have to spend a lot of time performing complex and unpleasant procedures at home. It is much easier to seek help from real professionals - the Veronika Herba beauty and health center, equipped with effective and modern equipment. There are two such centers in Moscow – near Timiryazevskaya metro station and Otradnoye metro station.
Why clients choose Veronika Herba Beauty and Health Center:
- This is a beauty center where you can take care of yourself at a reasonable cost, while your face and/or body will be treated not by an ordinary cosmetologist, but by one of the best dermatologists in Moscow. This is a completely different, higher level of service!
- You can receive qualified help at any time convenient for you. The beauty center is open from 9:00 to 21:00, seven days a week. The main thing is to agree with your doctor in advance on the date and time of your appointment.
Sign up for a consultation with a specialist by phone +7 (495) 085-15-13
, and you will see for yourself!
Indications for removal of moles (nevi):
1. Cosmetic.
2. The presence of constant irritation of a mole (location on the neck, chest, waist area, scalp, perineum). Removal of moles on the palms, soles, and genitals is mandatory. Undesirable effects on moles are also tanning, solarium, trauma during massage, washing, or haircut. It is unacceptable to pull hair out of a mole - if you are not tired of the sight of a “hairy” mole, it should be removed.
3. Atypical appearance of the mole (intense and/or uneven pigmentation, irregular and poorly defined borders, large sizes (more than 10 mm), asymmetrical shape, as well as similar changes and rapid growth of the mole, the appearance of a pigment corolla around, inflammation and itching, erosion and bleeding).
4. Congenital nevi.
The above points are the reason for a mandatory examination and diagnosis of the mole by a dermato-oncologist, who will determine further tactics.
Removing moles on the back immediately after surgery:
Doctor: Grishko R.V.
I would also like to refute the common myth about the inviolability of moles, because... Only removal of the formation followed by histological examination is a guarantee of your health.
FAQ
Today, the “gold standard” is the removal of moles using an ablative laser.
The CO2 laser used in the clinic has the following advantages:
- Thanks to the small thickness of the beam (200 µm), it is possible to precisely influence the tissue;
- The procedure for removing a mole is radical and one-time;
- Lack of direct contact of the device with the wound, asepsis, hemostasis (the wound does not bleed);
- Favorable effect on regeneration, rapid wound healing, virtually no scar.
Pigmented birthmarks
A pigmented birthmark gets its color from the presence of an abnormal group of pigment cells in the skin. The colors of pigmented birthmarks can vary from black to brown.
Pigmented birthmarks
Although most moles are small and round, there are large specimens that have different colors. Moles can be either smooth, so they are flush with the skin, or raised above the surface of the skin.
Birthmarks can have a smooth or rough texture. Some commonly encountered moles in everyday life are called by special names that characterize their color. For example, there are "cafe au lait" moles, which take their name from their typical light brown color. Some people develop dark brown "coffee" moles.
Mongolian spots are another common type of nevi that are bluish-gray in color and are most often found in dark-skinned children. They are usually present at birth and visible over the back and buttock area.