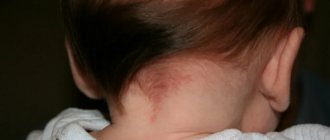
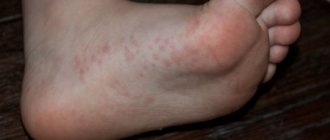
A rash on the labia is a symptom that signals diseases of a different nature. To eliminate the problem, it is first necessary to determine the cause of the unpleasant manifestation.
To do this, you need to contact our multidisciplinary medical center, which employs qualified specialists and has all the conditions for conducting high-precision instrumental and laboratory diagnostics.
Make an appointment with a dermatologist by phone or by filling out the online form
| Select a clinic | Demodicosis | Rash on shoulders | Calling a dermatologist to your home |
Causes of rash on the labia
The main factors contributing to the appearance of a rash on a woman’s labia include:
- allergic reactions to various irritants;
- wearing tight and synthetic underwear;
- failure to comply with basic rules of personal hygiene;
- postpartum syndrome;
- excessive use of cosmetics for intimate hygiene;
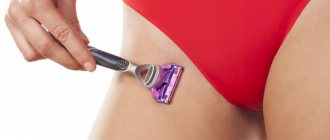
- violation of technology during hair removal;
- dermatic, gynecological, venereal diseases;
- hypothermia, overheating;
- oncological processes;
- hormonal imbalances;
- stress and nervous tension.
To determine the cause, it is recommended that when a symptom appears, you consult a doctor and undergo prescribed diagnostic tests, because pathology may indicate very serious illnesses that require urgent treatment.
Changes in the color of the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs
Such color changes can be a consequence of various factors, among which the most common are the following:
- allergic reactions;
- venereal diseases;
- infectious diseases (fungal, bacterial);
- inflammatory pathologies;
- violations of hygiene rules;
- mechanical damage.
Thus, itching, rash, discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs can be a consequence of numerous factors affecting a person, both individually and in various combinations. Naturally, only a urologist can identify them and determine an effective treatment method, and you should contact them immediately if such problems are detected.
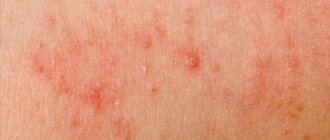
Types of rashes on the labia
There are several types of rashes:
- White pimples. They often appear on the labia majora after hair removal, during a cold and go away after certain hygiene procedures. If the rash occurs on the labia minora, it is better to consult a doctor, as this may indicate the development of serious pathologies.
- Subcutaneous. These are small lumps under the skin that form tubercles - lipomas, wen. If there is no infection, this problem goes away on its own and does not require special treatment.
- Small red ones. Such formations are most often a sign of allergies or premenstrual syndrome and should not cause much concern. But if the rashes have increased in size and begin to cause severe discomfort and pain, then you urgently need to make an appointment with a doctor.
- Watery. Small blisters with liquid inside are one of the signs of genital herpes. In this case, there are symptoms such as itching, burning, and pronounced hyperemia of the skin surrounding the formation. It is important to undergo diagnostics and treatment with immunostimulating drugs selected by a doctor.
- Dark red seals. Rashes that appear on the labia closer to the anus, with peeling skin and absence of pain, may indicate that the woman is infected with syphilis. This cannot be done without a serious examination and qualified therapy.
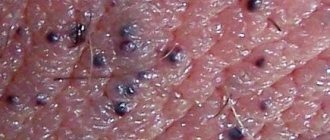
- Warts. Formations that look like small warts with an uneven contour are papilloma, which disappears on its own with a well-functioning immune system, otherwise immunostimulating treatment is prescribed.
- Rash with a cheesy coating. These two symptoms, appearing in combination with itching, unpleasant odor and pain when urinating, indicate the development of candidiasis (thrush). Pathology often occurs against the background of long-term use of antibiotics and weakening of the body’s protective functions.
Despite the fact that sometimes rashes on the labia are completely safe and can go away without any consequences on their own, for the purpose of prevention, if uncharacteristic formations appear, it is worth consulting a doctor.
Common symptoms and manipulations in dermatology:
- Skin rashes
- Calling a dermatologist to your home
- Itching in the urethra
- Itchy skin
- Skin rash
- Prevention of casual sex
- Skin neoplasms
- Pyoderma
- Pityriasis rosea
- Streptoderma
- Scabies
- Peeling skin
- Fungal infections
- Skin infection
- Pus on the skin
- Blisters on the skin
- Papillomas on the foreskin
- Sexually transmitted diseases
- Skin structure
Purulent rashes
If the white color of the rash is due to pus accumulated inside, then this indicates infection. There may be several reasons for this.
Suppuration of the follicle when infection penetrates into it is caused by injury to the skin during shaving, as well as by the ingrowth of hairs in the bikini area.
Constantly wearing synthetic underwear creates a greenhouse effect on the skin, in which pathogenic microbes multiply well.
Sexually transmitted diseases also appear as purulent pimples: chlamydia, gonorrhea, ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis. They are often accompanied by fever, itching, burning, pain when walking, or sexual intercourse. In these cases, doctors diagnose vulvitis - inflammation of the external genitalia or vulvovaginitis - if the inflammatory process also affects the vagina.
Another sexually transmitted infection that manifests itself as blisters with pus is genital herpes. These watery pimples are itchy and cause severe discomfort.
What tests should be taken for a rash on the labia?
To diagnose the cause of a rash on the labia, a number of laboratory and instrumental examinations are prescribed:
- a general analysis of urine and blood shows the general condition of the patient, identifies inflammatory processes;
- polymerase chain reaction (PCR), is prescribed to determine the DNA of the pathogen, the most informative method that can detect diseases at very early stages;
- immunofluorescence reaction (RIF) detects antigens through the use of a special substance;
- cultural method, an effective procedure that allows you to determine the presence and type of pathogen by placing the biomaterial in an environment favorable to the virus;
- vulvocolpocervicoscopy, examination on a gynecological chair using a microscope to study the nature of the rash.
The doctor may also recommend undergoing an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), a serological method, or an immunogram. An ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs, tests for hormones, tumor markers and other diagnostic measures that can find the main cause of the unpleasant symptom are often prescribed.
Rash on the labia of a child
Genital rashes can appear not only in adults, but also in children. At the same time, the reasons for the development of pathology differ significantly.
A rash on the labia of a child appears for the following reasons:
- diathesis;
- psoriasis;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- fungal, herpetic, infectious lesions of the genital organs;
- prickly heat;
- scarlet fever, rubella, measles;
- failure to comply with basic hygiene rules.
Rashes appear if a girl’s diaper and underwear are not changed in a timely manner, hypothermia, overheating occurs, and an allergic reaction to various allergens develops: food, creams, powders, detergents, diapers, synthetic panties, etc.
Initially, parents should contact a pediatrician, who, based on the results of the examination, will refer them to a specialist appropriate to the problem.
Sometimes, to eliminate the pathology, it is enough to simply change the diet, brand of diaper, baby care products, or stop taking medications. But in some cases, you need to undergo serious qualified treatment, selected by a competent physician.
When the first symptoms appear, you should not delay visiting a doctor, as a simple rash can signal serious health problems. The sooner parents contact a specialist, the fewer complications and other negative consequences there will be.
Itching of the genitals
Itching in the genital area may have the following localization:
- on the skin of the genital organ (both in individual places and over all surfaces);
- inside the genital organ (usually accompanied by a burning sensation and other pain, as well as various kinds of pathological discharge);
- on the head of the penis (may also be accompanied by burning and pain).
The causes of itching can be divided into 3 groups:
- External influence (violation of hygiene standards, poor quality of underwear, allergic reactions, stressful situations, mechanical damage, etc.).
- Sexually transmitted diseases (male thrush (candidiasis), balanitis (balanoposthitis), trichomoniasis, genital herpes, gonorrhea, ureaplasmosis, etc.).
- Diseases of the genitourinary system (urethritis, cystitis, etc.).
What diseases cause a rash on the labia?
Rashes on the labia often become a symptom of diseases such as:
- Allergy.
Allergic reactions can be caused by intimate cosmetics, lubricants, underwear made from non-natural materials, condoms, pads, hair removal and taking certain medications. The pathology is also characterized by swelling, itching and burning in the genital area. - Scabies.
The disease appears due to infection with scabies mites. Characteristic manifestations: a large number of small follicular rashes. Pimples can turn into bloody crusts that cause severe itching. - The body's response to the partner's ejaculate. This pathology, called burning sperm syndrome, occurs in 30% of women who are sexually active.
- Vulvovaginitis.
This is a fungal disease that occurs due to the proliferation of a fungus such as Candida. Additional symptoms are cheesy discharge, burning, itching. - Syphilis
. A sexually transmitted disease that can lead to a large number of dangerous consequences. In this case, one of the signs of the development of an STI is a small pink rash. - Genital herpes
. This is a pathology of viral origin, manifested by a scattering of bubbles filled with liquid, which, after opening, turn into ulcers that cause pain. In addition to the rash, body aches, itching, and fever often appear in parallel. - Molluscum contagiosum
. One of the main signs of dermatitis is small, dome-shaped, compacted nodules. - Inguinal athlete's foot
. Localized in the genital area and adjacent areas. It is characterized as a fungal infection.
Also, a rash in the labia area may indicate the development of the human papillomavirus, thrush, oncology, bartholinitis, Fordyce granules.
Why do the labia become inflamed?
1. Sexual infections, STDs, dysbacteriosis.
2. Cyst of the vulva, vagina and/or labia.
3. Ingrown hairs as a result of shaving or depilation.
4. Yeast infection. Typical symptoms of thrush include vaginal discharge, irritation, inflammation, redness and tenderness. You will also experience severe itching at the entrance and inside the vagina, pain during sexual intercourse, and burning when urinating.
5. Genital warts. Pimples on the labia, like “bumps” on the vagina, can be condylomas. Formed as a result of infection caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). It is the most common sexually transmitted disease (STD); They may also appear on the cervix, clitoris, urethra, or inside or outside the anus. Genital warts look like growths or tubercles, are usually painless, and flesh-colored. They may be accompanied by itching, discharge, and burning.
Condylomas are removed by surgical procedures, including and combining options:
- Removal by radio wave method,
- Electrocoagulation or “burning”
- Cryodestruction or “freezing”,
- Laser therapy,
- Cutting off warts
- Interferon injections.
Untreated condylomas can lead to serious complications. The HPV that causes them is the leading cause of cervical cancer and can also cause vulvar cancer.
6. Genital herpes (HSV type 2). The labia become itchy and swollen due to a herpetic infection. It can be transmitted sexually. Painful red bumps or blisters appear, which can be localized on the genitals and nearby areas. In women, herpes rashes appear near the vagina, on the vulva, hymen, and the mucous membrane of the labia minora and labia majora.
7. Lichen sclerosus of the vulva. This is a rare skin condition that mainly affects women after menopause. It often appears on the vulva and around the anus as bumps or blisters. Having this condition poses a slightly higher risk of developing vulvar cancer. Common symptoms of lichen sclerosus include:
- Blisters that may be filled with blood
- White spots that look like wrinkled patches of skin
- Fragile, thin, shiny skin,
- Bruising and bleeding
- Pain during sexual intercourse or during urination.
8. The tumor process may begin with swelling and inflammation of the genital organs and the formation of small “warts” on the labia minora. The tumor can be in the form of a dense formation of small size. In the future, painful ulcers with rounded edges, filled with purulent or bloody contents, may appear on the labia. The lip may become large and have an unpleasant odor. In this situation, it is necessary to urgently contact a gynecologist for advice and to conduct a series of diagnostic tests. Inflammation of the labia in women and cancer of the external genitalia are very similar in their clinical picture. And it is sometimes possible to keep the fine line between these diseases only after the results of a biopsy. However, cancer of the external genitalia is rare and usually occurs in older patients.
9. Uncomfortable underwear. Due to the synthetic material of the panties, the skin in the intimate area does not breathe and begins to sweat, as a result the skin becomes dry, which subsequently leads to itching of the labia, they swell and begin to itch.
10. Long-term wearing of pads. If you wear pads for a long time and forget to change them, this causes irritation of the labia minora and itching and internal burning appear in the vagina and clitoris area.
11. Vulvitis. If the labia are swollen, but in addition there is painful urination and unpleasant, foul-smelling greenish-yellow discharge, and the skin itches, this may indicate inflammation of the external genitalia.
Vulvovaginitis can also develop as a result of active, rough, skin-damaging masturbation. This mainly occurs in teenagers, as well as girls who practice some forms of extreme sex, for example, BDSM. Wearing dirty panties and failure to follow basic rules of intimate hygiene also contribute to infection.
SWELLING LABIA IS NORMAL, NO TREATMENT IS NEEDED!
IMPORTANT NUANCE: Nature initially dictates that women’s labia minora swell during sexual fantasies, direct mechanical stimulation of a woman’s reproductive external genitalia, or in the case of direct sexual contact - and this is absolutely normal. After the end of sexual intercourse or the cessation of sexual stimulation, arousal gradually subsides and the genitals return to their original size. This natural physiological process usually takes an hour or two after peak arousal, sometimes such regression drags on for four to twelve hours. Moreover, it has been noted that if after sex the labia are swollen and the woman does not have an orgasm, the outflow of blood is much slower, which can ultimately contribute to the development of a number of gynecological problems.
Also, the blood supply to the reproductive organs changes cyclically, depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle.
ANALYSIS AND DIAGNOSTICS
Inflammation in the intimate area in women, especially in the presence of purulent or other unpleasant vaginal discharge, requires an immediate visit to a gynecologist for a comprehensive diagnosis. First of all, you need to take tests to find out the reasons why the labia are itching, skin folds are swollen, and discomfort has appeared in this delicate area. The necessary examination in this case will be the following.
Minimum: Gynecological examination, smear for flora, PCR analysis for “hidden” infections, tank culture for flora, general urine test.
According to indications: Colposcopy, oncocytology of the cervix, blood tests (hormones, allergens, biochemical, general analysis), ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
Inflammation of the gland on the labia
Painful inflammation in the labia (on one or both sides) can cause bartholinitis, inflammation of the large gland of the vestibule of the vagina. It is a paired organ and is located deep in the subcutaneous tissue at the base of the labia majora. Its main function is to produce a viscous mucous secretion and moisturize the intimate area during sexual intercourse. The inflammatory process in the gland of the labia is most often caused by gonococci, staphylococci, less often by streptococci, E. coli, Trichomonas and other microorganisms that penetrate the excretory duct of the gland from the vagina or urethra. Risk factors also lie in non-compliance with the rules of intimate hygiene, weakening of the body, impaired microflora and weakened immunity.
Which doctor should I contact for a rash on the labia?
If a rash appears in the labia area, it is initially recommended to consult a therapist who will differentiate and make a primary diagnosis. Based on these results, the specialist will select a specialist doctor.
The list of such doctors includes:
- gynecologist;
- dermatologist;
- venereologist;
- endocrinologist;
- allergist.
Each of these specialists will be able to make a final diagnosis, prescribe a series of examinations and select effective, safe treatment. If the cause is external irritants, incorrect attitude to hygiene, incorrectly chosen cosmetics or pads, then the appointment ends with a therapist, who recommends eliminating all negative factors.
Treatment
Conservative therapy
The list of general recommendations for most pathologies accompanied by pain in the labia area involves changing hygiene habits, sexual rest, adjusting the diet and nature of the diet, and refusing to use synthetic underwear, highly allergenic or irritating hygiene products. Therapeutic measures for inflammatory and infectious processes include:
- Antibacterial agents.
For bacterial infections, antibiotics are prescribed for systemic and local (creams, suppositories, vaginal tablets) use, selected taking into account antibiotic sensitivity. - Other etiotropic medications.
For polymicrobial vulvitis and vulvovaginitis, combined drugs with antibacterial, antiprotozoal and antimycotic effects are used. Antifungals are effective for candidiasis, and antiviral drugs are effective for HPV and papillomatosis. - Local events.
For vulvitis, vaginal suppositories, douching with antiseptic solutions and herbal decoctions, and sitz baths are recommended. For acute bartholinitis, SMT, UHF and UV irradiation are effective; for chronic bartholinitis, ozokerite, paraffin, infrared laser, and mud applications are effective. - Treatment of background pathologies.
According to indications, insulin therapy or the dose of hypoglycemic agents for diabetes are adjusted, antiallergic drugs are prescribed, deworming is carried out, and infectious foci are sanitized.
Patients with vulvodynia are advised to avoid eating foods high in calcium oxalate (celery, strawberries, chocolate) to reduce the amount of this compound in the urine. For mild pain, exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles are useful. Balneotherapy and physiotherapy are effective. If there are signs of atrophy, suppositories and creams are used to stimulate regeneration. For ovarian hypofunction, hormonal therapy is prescribed.
Antihistamines and sedatives are recommended for patients with vulvar kraurosis. For persistent itching, a pudendal nerve block is performed. Hormonal ointments with estrogens, androgens, corticosteroids and progesterone are used locally. The type of medication is selected taking into account age and endocrine status. Balneotherapy, reflexology, laser therapy, photodynamic therapy, and x-ray therapy are effective. It is necessary to take biostimulants, immunocorrectors and vitamin preparations.
Surgery
In most cases, pain in the labia area is eliminated using conservative methods. Surgeries may be required if the following pathologies are present:
- Bartholinitis:
marsupialization, removal of the cyst, removal of the Bartholin gland, opening of the abscess. - Kraurosis of the vulva:
cryodestruction, laser ablation or denervation of the vulva, if malignant tissue degeneration is suspected - vulvectomy. - Condylomatosis:
radiofrequency ablation, laser vaporization, cryodestruction, electrocoagulation, vulvar resection, vulvectomy.
Where to go with a rash on the labia
At the first signs of rashes, you must make an appointment with specialists at our multidisciplinary medical center, where highly qualified, competent medical staff work. The clinic is famous for its excellent technical base, which consists of instrumental, laboratory diagnostics and a therapeutic building, where you can undergo various types of treatment and the most modern diagnostic measures.
The medical center also offers a service - calling a doctor to your home, which makes it possible to receive medical care, take some tests, and do an ultrasound in the comfort of your home. A specialist’s visit to the patient’s address helps maintain complete confidentiality, alleviate the plight of bedridden, elderly patients and people with disabilities, and save time.
Diagnosis of a rash on the labia
First of all, the doctor conducts a visual examination, determining the nature of the rash. After this, depending on the primary diagnosis, additional tests are prescribed:
- PCR;
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs;
- biopsy;
- vaginal smear examination;
- general blood and urine analysis.
In some cases, samples are taken for different types of allergens.
Answers to frequently asked questions about skin rashes:
- Which doctor should you contact for a skin rash?
- Is the skin rash contagious?
- What diet is necessary for skin rashes?
- What diagnosis is needed for a skin rash?
- Why is a skin rash dangerous?
- Why is it necessary to get tested for a skin rash?
- What diseases does a skin rash indicate?
- What examination is necessary for a skin rash?
- Which skin rash is dangerous?
- How to distinguish an allergic rash from an infectious one
- How to get rid of skin rashes?
- How to get rid of itching skin rash?
- What organs are affected by a skin rash?
- How to prepare for an appointment with a dermatologist?
- How to get checked for skin diseases?
- What diseases does a dermatologist treat?
- What tests should be taken by a dermatologist?
- What diagnostics can a dermatologist perform in the clinic?
- Where to go with a skin disease?
Prevention of rashes on the labia
In order to prevent the appearance of rashes in the intimate area, you must:
- wash your genitals regularly;
- carefully choose intimate hygiene products without dyes or fragrances;
- exclude promiscuous sexual intercourse;
- use condoms during intimacy;
- monitor your hormonal levels;
- visit a gynecologist periodically;
- carefully visit places with large crowds of people: swimming pools, saunas, baths, public showers;
- choose a hair removal specialist with extreme caution;
- do not overcool and do not overheat.
It is also important to choose the right underwear; if you are prone to irritation, it is better to choose natural materials and a classic cut. It is not recommended to purchase low-quality pads with fragrances or abuse douching.
| Appointment with a dermatologist at the clinic. Call a dermatologist at home. | Reception is strictly by appointment, make an appointment by phone: +7 | Prices for services | Reviews about the clinic |
Rash on the labia in pregnant women
Rashes in the genital area in a pregnant woman can appear for the same reason as in non-pregnant women, only in this case the problem can cause great damage not only to the patient, but also to the fetus. The complexity of the situation lies in the fact that when carrying a child, it is quite difficult to choose a safe therapy that would not affect the health of the embryo.
They try to identify any STDs at the pregnancy planning stage and only after treatment, six months later, initiate conception. If the infection was detected during pregnancy, there is a high percentage that the disease will be transmitted to the baby or will negatively affect its development. Therefore, with such diagnoses, a caesarean section is often prescribed.
An infection that causes a rash on the labia can lead to the following consequences:
- pregnancy fading;
- stop in fetal development;
- development of defects and deviations;
- delays in the mental and physical development of the child after birth.
If an STD is detected, the doctor selects special therapy and more carefully monitors the behavior and condition of the fetus. If the rash is caused by external irritants, they must be identified and excluded.
Treatment of rash on the labia
A rash is a symptom, so the main therapy is prescribed taking into account the cause that led to the appearance of a rash in the intimate area. For allergies, antihistamines are prescribed, for fungal infections - antifungal drugs, hormonal disorders are eliminated with hormone therapy, genital herpes is treated with Acyclovir. If a streptococcal infection is detected, streptocide is prescribed; if there is an inflammatory process, the patient is recommended to undergo a course in a hospital.
The therapeutic regimen is selected taking into account test results, the course and complexity of the disease. Additionally, it is advisable to take a vitamin-mineral complex, immunomodulators, and sedatives of plant origin. In some cases, rehabilitation is necessary.
Ointments for rashes on the labia
Topical products help not only fight the problem itself, but also eliminate unpleasant symptoms such as pain, burning, itching, and discomfort. According to experts, this method of treatment is much more effective as it acts at the cellular level and reaches the pathological focus faster.
For genital herpes it is recommended to use:
- Acyclovir;
- Panavir;
- Zovirax.
- For inflammation and syphilis, the following is prescribed:
- Theracycline ointment;
- Erythromycin ointment.
- If affected by a fungus:
- Mycozoral;
- Clotrimazole;
- Nystatin.
You can also use Pimafukort ointment, which helps heal wounds and cracks, Terzhinan, which helps reduce itching and burning. All medications should only be prescribed by a doctor. Before use, it is important to carefully read the instructions and follow all recommendations of a specialist.
Publication date: 2019-12-10
Methods for diagnosing skin diseases:
- Diagnosis of skin diseases
- Diagnosis of skin diseases at home
- Diagnosis of allergic skin diseases
- Diagnosis of bacterial skin diseases
- Diagnosis of viral skin diseases
- Diagnosis of hair diseases
- Diagnosis of nail diseases
- Diagnosis of skin tumors
- Skin scraping
- Blisters on the skin
- Dermatoscopy
- Demodex tests
- Diagnosis of sexually transmitted infections
- Mushroom tests
- Skin scraping
Red dots on the head of the penis - what could it be?
Rashes on the head of the penis, as well as on the foreskin, are not the norm. Typically, they are caused by inflammation (balanitis), which is caused by bacteria, fungi or viruses. Here are the most common reasons for the appearance of red dots on the head of the penis:
- Thrush or candidal balanoposthitis This is a fungal infection of the head and inner layer of the foreskin. Small red dots on the head of the penis are only the earliest manifestation, at which stage it is advisable to immediately consult a doctor. Without treatment, weeping erosions with a white coating will form at the site of the spots, the head will swell, itching and burning will appear, and it will become difficult to urinate. If bacteria get into the erosion, the fungal process will be complicated by a purulent one: a yellow-green discharge, pain will appear, and the inguinal lymph nodes will increase. In the future, the purulent process will lead to narrowing of the foreskin and surgical treatment. Timely prescribed antifungal drugs will solve the problem of red spots in the first three days.
- Red dots on the head of the penis, combined with itching and burning, may be the first sign of genital herpes. In their place, within 24 hours, bubbles with transparent contents may appear, which will cause pain and begin to open, become wet and heal without scars. When microbes enter wounds, the process can become purulent and require not only antiviral drugs, but also antibiotics. The lymph nodes in the groin also become swollen and painful. The temperature may rise. Herpetic rashes can spread to the foreskin, skin of the penis, and perianal area. Adequate antiviral and immunostimulating treatment will correct the situation and prevent relapse.
- Damage to the head in gonorrhea can also be represented by red dots. In this case, as a rule, the appearance of dots is accompanied by mucopurulent or purulent discharge from the urethra, which makes urination sharply painful or difficult. The disease can be diagnosed by simple cultures or by the express method, PCR.
- Trichomonas, mycoplasma balanitis This disease can be represented by red dots in combination with spots, edema of the head, swelling of the external opening of the urethra, from which yellowish or gray mucous discharge is observed. Since the symptoms of such balanitis are nonspecific, its nature can be clarified by taking a PCR test for hidden infections.
If the head of your penis is covered with red dots, do not resort to folk methods and self-medication, remember that this is not only about your health, but also the health of your other half and future offspring. Approach the issue responsibly and contact a specialist.