Inflammation of the facial nerve is an unpleasant ailment that does not go away painlessly. The main complaints of patients are sharp attacks of pain in the face, in the upper and lower jaws.
This inflammation is considered one of the most common among facial pains. Most often, the disease proceeds without a trace, but if treatment is neglected, paralysis may occur.
The disease most often occurs in women over 50 years of age; men are treated with this disease much less frequently. People with a genetic predisposition, such as a narrow bone canal, are also at risk. Due to this anatomical feature, there is an increased risk of pinching due to impaired blood supply and various inflammations.
What is the facial nerve?
The trigeminal nerve, also known as the facial nerve, is the largest of the twelve cranial nerves. It originates in the ear, after which it branches, the first path reaches the frontal part, the second is located at the jaw. The nerve goes around almost the entire surface of the human face; it literally controls it.
Every person has two facial nerves - one on each side of the head. It is in contact with other cranial nerves and has supersensitive fibers.
Doctors divide the disease into two types - primary and secondary. The primary one manifests itself as a complication from a cold, in this case the normal nutrition of the nerve is disrupted. Secondary occurs with severe intoxication against the background of inflammatory or infectious diseases, as well as tumor processes.
Why does swelling of the eyelid occur?
The skin's ability to stretch, loose structure and a large number of blood vessels lead to fluid quickly accumulating in the eye area.
There are various reasons for the appearance of swelling of the eyelids, but from the symptoms you can understand what triggered fluid retention in the body.
If the swelling of the eyelid is bilateral, combined with other edema of the body, and the skin on the eyelids is pale and cold to the touch, this indicates renal or heart failure, as well as severe anemia.
Swelling of the eyelid also occurs with head injuries and angioedema.
Many inflammatory eye diseases, such as the following, are also accompanied by swelling of the eyelids:
- stye, abscess, blepharitis, contact dermatitis and other inflammations of the eyelids;
- diseases of the paranasal sinuses;
- acute purulent, pseudo- and membranous conjunctivitis;
- phlegmon, acute dacryocystitis and other diseases of the lacrimal sac;
- ednophthalmitis, iridocyclitis and other pathologies of the eyeball.
Swelling of the eyelids (most often unilateral) is characterized by redness of the skin, pain on palpation and a local increase in temperature.
Causes of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve on the face
Usually the disease is caused by infection or bacteria. List of reasons why inflammation of the facial nerve may occur:
- Temporomandibular joint injuries
- Tumors (benign and malignant) of the brain and facial area
- Anomalies of skull development
- Skull injuries - birth, fracture, base, damage to the face or jaw
- Polio
- Pulmonary tuberculosis
- Otitis
- Sinusitis
- Chronic caries
- Inflammation after tooth extraction or treatment
- Hypertension
- HIV and AIDS
- Poisoning
- Inflammation of the middle ear
- Severe hypothermia of the head
- Changes in hormonal levels in women
- Gum inflammation
- Ramsay Hunt syndrome
- Stroke
- Bell's palsy
Causes range from minor to life-threatening illnesses. Each of the reasons determines the further treatment of the patient. In some cases, special tests are performed for diagnosis - auditory, lacrimal, infectious, salivary or gustatory. In this way, the functioning of the receptors and sensory organs is checked.
Symptoms of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
Experts include short-term, but acute and intense pain in different parts of the head as the main symptoms of facial neuralgia. Shooting attacks spread over the entire surface of the face - lips, eyes, nose, upper and lower jaw, gums and tongue.
Patients also report the following symptoms:
- Metallic taste in the mouth
- Muscle weakness
- 2-3 days before facial expressions are affected, pain occurs behind the outer ear, spreading to the face, back of the head and eyes
- Facial asymmetry
- Inability to close the eye on the affected side
- Drooping corner of the mouth
- Dry mouth
- Slurred speech
- Cross-eyed strabismus
- Uncontrollable tearing
- Disorders of taste buds
- Increased drooling
- Facial muscle spasms
- Increased or decreased facial sensitivity
- Temperature increase
Due to discomfort and pain, the patient begins to develop a phobia and increased anxiety. He tries to avoid poses and movements that provoke discomfort.
Types of skin diseases around the eyes and eyelids
Among the huge number of diseases caused by inflammation of the eyelids, several of the most common groups can be distinguished:
- bacterial lesions of the skin of the eyelids (abscess of the eyelid, phlegmon);
- inflammatory diseases of the glands and edges of the eyelids (blepharitis, barley, chalazion, meibomitis, demodicosis);
- violations of the shape and position of the eyelids (entropion, eversion, ptosis, lagophthalmos);
- allergic diseases (eczema, dermatitis, angioedema);
- developmental abnormalities of the eyelids and tumors (coloboma, papilloma, lipoma, nevus).
Bacterial lesions of the skin of the eyelids
Abscess of the century
An abscess is inflammation and redness of the eyelid with the formation of a cavity filled with pus. Often an abscess appears after an infected eyelid wound.
Causes of eyelid abscess:
- ulcerative blepharitis;
- boils;
- barley;
- purulent processes in the paranasal sinuses and orbit of the eye.
Sometimes the abscess opens on its own, and the inflammation subsides. But in most cases, a non-healing fistula appears at the site of inflammation.
Treatment of an abscess is sanitation of the eyelids and opening of a purulent formation on the eyelids with the mandatory use of antibiotics and sulfonamides.
Phlegmon
Cellulitis is an extensive inflammation of the tissues of the eyelid that occurs against the background of untreated stye. It is characterized by fever, headache, severe swelling of the eyelid and redness of the skin.
Treated with antibacterial agents, antihistamines.
Inflammatory diseases of the glands and edges of the eyelids
Blepharitis
Blepharitis is an inflammation of the eyelids, which causes redness, burning, itching and pain on the skin.
The following types of blepharitis are distinguished: allergic, meibomian, demodectic, infectious, scaly. Read more about blepharitis here.
Barley
Barley is an acute, infectious inflammation of the eyelids, resulting from pathogens entering the eyelash hair follicle or the sebaceous gland of the eyelid. Visually, stye looks like a small nodule on the eyelid.
You can read about how to properly treat stye on this page.
Meibomyitis and chalazion
Meibomyitis and chalazion are diseases associated with the appearance of a pathological process in the meibomian glands.
Meibomia appears when the duct of the sebaceous gland of the eyelid is clogged. Characterized by an acute course of the disease.
Chalazion is a chronic form of meibomitis. If a chalazion is left untreated for a long time, it turns into an eyelid cyst. Sometimes, for diagnostic purposes, it is necessary to puncture the eyelid cyst to identify the nature of the neoplasm.
Treatment and removal of a cyst on the eyelid occurs using classical techniques or laser treatment.
For more information about the symptoms and treatment of this pathology, see here.
Demodicosis
A disease of the eyelids caused by the Demodex mite. It is characterized by the appearance of yellow mucus in the eyes, gluing and breaking of eyelashes, itching and burning of the eyes.
To cleanse the eye from foci of infection, cleaning (sanitation) and rinsing of the lacrimal ducts are used. Read about the treatment of demodicosis on this page.
1 Diseases of the skin around the eyes and eyelids. Diagnosis and treatment
2 Diseases of the skin around the eyes and eyelids. Diagnosis and treatment
3 Diseases of the skin around the eyes and eyelids. Diagnosis and treatment
Violations of the shape and position of the eyelids
Turn of the century
When the eyelid is inverted, its main edge is turned onto the eyeball. Because of this, the eyelashes touch the surface of the cornea and conjunctiva, the eyes become red, irritated, and tears constantly flow from them.
Causes of pathology:
- convulsive or spastic contractions of some parts of the orbicularis oculi muscle;
- cicatricial contractions of the conjunctiva and cartilage of the eyelid that occur in certain chronic eye diseases (for example, trachoma).
The most effective method of treatment is surgery. Plastic surgery for entropion of the eyelid is also possible.
Eversion of the century
Ectropion is an inversion of the edge of the eyelid. With this inflammation of the eyelid, the conjunctiva turns out in a certain area or throughout the entire eyelid, which leads to its drying out.
The fact that the eye is constantly open, even at night, contributes to clouding of the cornea, the appearance of keratitis and other diseases.
Causes of eversion of the eyelid:
- age-related changes in the eye with sagging of the lower eyelid;
- paralysis of the orbicularis oculi muscle;
- tightening of the skin of the eyelids due to injuries, burns (cicatricial eversion), systemic diseases of the body.
First, it is necessary to eliminate the main causes that caused this disease. Surgical procedures can then be used.
Ptosis
Ptosis is an abnormally low position of the upper eyelids in relation to the eyeballs. This leads to vision defects and rapid eye fatigue. Ptosis can be congenital or acquired.
Causes of ptosis:
- damage to the oculomotor nerve;
- damage to the muscle that elevates the upper eyelid;
- strokes, encephalitis and other neurological diseases.
Treatment of the disease is mainly surgical.
Lagophthalmos
Lagophthalmos is incomplete closure of the palpebral fissure, which leads to damage and drying of the cornea and conjunctiva.
Causes of the disease:
- eyelid injuries,
- jades,
- short eyelids from birth.
In addition to treating the underlying disease, artificial tears and disinfectant drops are prescribed. In severe forms of the disease, surgical intervention with partial suturing of the palpebral fissure is used.
Allergic inflammation of the eyelids
Allergic diseases of the eyelids are accompanied by severe itching, swelling and inflammation of the eyelids.
In eczema , the skin of the eyelids is covered with papules, vesicles and pustules. Characteristic rashes appear not only on the skin of the eyelids, but also on the body. The pathology develops after suffering eyelid dermatitis or contact with allergens. At the end of the disease, crusts and serous exudate appear on the skin of the eyelids.
Characteristic signs of urticaria are swelling of the eyelids, itching and burning of the skin of the eyelids. Subsequently, blisters appear on it.
With contact dermatitis , 6 hours after contact with the allergen, swelling and inflammation of the eyelids develop with itchy papules and vesicles. Usually both eyes are affected at once.
Treatment of allergic inflammation of the eyelids is medicinal.
1 Diseases of the skin around the eyes and eyelids. Diagnosis and treatment
2 Diseases of the skin around the eyes and eyelids. Diagnosis and treatment
3 Diseases of the skin around the eyes and eyelids. Diagnosis and treatment
Anomalies of eyelid development and tumors
Coloboma
Coloboma of the eye is one of the most unpleasant diseases, which is expressed in the absence of some eye membranes. Coloboma of the eyelid is the most common. The pathology appears on the upper eyelids, but sometimes affects the lower eyelids too.
Coloboma is usually triangular in shape, where the base of the triangle is the ciliary edge of the eyelids. Since the defect affects all layers of the organ of vision, there are no eyelashes and glands in the area of coloboma.
In most cases, it is congenital, but can also occur as a result of injury and other illnesses. Another type of congenital coloboma, iris coloboma, is one of the main causes of vision loss in childhood.
Coloboma is a serious danger to the eye, as it leads to degeneration of the cornea, keratitis and other secondary diseases of the organs of vision, as well as blindness!
The most effective treatment for coloboma is surgery. Surgery for coloboma involves excision of damaged tissue and movement of a musculocutaneous flap to the site of the defect. With the help of plastic surgery, the correct edge of the eyelids is formed, which prevents the appearance of ptosis, entropion, and other complications.
Benign formations of the century
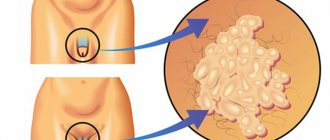
Papilloma of the eyelids
Papilloma appears on the lower eyelid usually in people over 60 years of age.
It grows slowly, looks like gray-yellow papillae, and has a spherical or cylindrical shape. In 1 case out of 100, papilloma can turn into cancer. Treatment of eyelid papilloma is surgical.
Senile wart
A senile wart is a flat and even formation of brown, yellow or gray color. It grows in older people along the lower ciliary edge of the eyelids. Treatment: cryodestruction or laser removal.
Cutaneous horn
The cutaneous horn is a dirty gray formation protruding above the eyelid. Electro- and laser excision are used for treatment.
Nevi
Nevus (or mole ) is a benign formation on the skin, from light brown to black. Nevi on the eyelid can be inherited, appear due to long exposure to the sun, disruptions in the hormonal system, or after taking certain medications. Hanging moles can appear in old age. If the formation does not bother you, there is no need to treat it.
If unpleasant symptoms appear: itching, pain, growth, blurred vision, you must consult an ophthalmologist to investigate the nature of the mole and receive the necessary treatment.
Atheroma
Eyelid atheroma ( epidermal cyst ) is a painless, dense formation that appears on the eyelid due to blockage of the sebaceous gland ducts.
Over time, the atheroma begins to increase in size and can impair vision. In this case, surgical procedures are performed. After removal of atheroma of the eyelid, there are usually no complications.
Diagnosis of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
Depending on the affected area and the set of symptoms, the strategy for diagnosing the disease is determined. To determine the location of nerve damage, the severity and dynamics of recovery, doctors prescribe a hardware diagnostic method, for example, electromyography. MRI and CT scans are used to determine the presence of tumors in the brain.
The patient may also be referred for a general or biochemical blood test, x-ray of the lungs, ultrasound of soft tissues or ophthalmoscopy.
You can be confident in the quality of the procedures performed in the clinic and the high accuracy of the results of MRI, CT and other methods of diagnosing various diseases. Medunion performs magnetic resonance imaging of all types: head, spine, abdominal cavity and joints using modern equipment.
Treatment for inflammation of the facial nerve
Drug treatment
Treatment of trigeminal neuritis is complex. The disease is first treated with medication - the patient is prescribed drugs that will alleviate the situation. These include painkillers, decongestants, vasodilators and B vitamins. Most often, the recommended medications are tablets, but you can speed up the recovery process by using ointments and gels. Sometimes doctors prescribe intramuscular injections.
In special cases, the recovery process of the facial nerve may be slowed down. Then the patient is prescribed glucocorticosteroids, which improve the metabolic processes of nervous tissue. Various biostimulants and hyaluronidases also contribute to a speedy recovery.
You cannot prescribe medications for yourself. Be sure to see a neurologist or neuropathologist at the first symptoms to determine the diagnosis and treatment strategy. Recovery medications are recommended to patients on a case-by-case basis, paying attention to the presence of chronic diseases, symptoms, and so on.
Surgery
Another way to treat the facial nerve is surgery. However, doctors turn to this option quite rarely - only when the trigeminal nerve is ruptured. Surgery is also required if there is no effect from the conservative method after six months or a year. Surgical intervention is only relevant during the first year of the presence of the disease; later, the muscles on the face irreversibly atrophy.
The surgical process involves suturing the damaged area of the facial nerve to restore its motor function.
Massage
The next treatment method is massage for the treatment of the facial nerve. The purpose of this method is to remove swelling, improve blood circulation, restore sensitivity and conduction of nerve impulses. Massage is contraindicated for tuberculosis, oncology, atherosclerosis and elevated temperature.
Initially, the massage therapist works only with the healthy side of the face, collar area, neck and area above the shoulders. Basically, the master uses rubbing, stroking, kneading and vibration.
For noticeable desired changes, it is necessary to conduct ten to twenty massage sessions from five to fifteen minutes. The duration is determined based on the degree of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, the goals of therapy and the dynamics of recovery.
Physiotherapy
The next treatment method is physical therapy. It alleviates the severity of symptoms, helps to activate metabolic processes in tissues and restore the functions of the facial nerve.
Doctors prescribe this course of treatment from the first days of the onset of neuritis. The list of physical procedures includes:
- Ultrasound
- Laser irradiation of blood
- Electrophoresis of drugs
- Microwave therapy
- Exposure to ultra-high frequency electricity
- Ozocerite treatment
- Myoelectrostimulation
- Darsonvalization
This complex is indicated for the first week of treatment. Doctors prescribe it together with medication. This tandem helps speed up the process of restoration of the facial nerve. And its most important advantages are the absence of side effects and painlessness.
Alternative Methods
There are also alternative treatment methods. These are procedures aimed at restoring facial muscles and eliminating the symptoms of facial neuritis. Such procedures include:
- Clay or paraffin masks
- Acupuncture
- Reflexology
- Injections to eliminate muscle disorders
- Therapeutic baths
- Taping – stretching the face using adhesive plasters
- Immunosorption – purification of blood from antigens and antibodies
- Biofeedback – facial muscle training
Gymnastics for the face
Also, in conjunction with complex treatment, you can do facial exercises. Before this, you need to consult with a specialist; the doctor will draw up an individual list of exercises based on the severity of the process, location of the lesion and symptoms. Typically, such gymnastics takes about ten minutes a day.
A standard set of exercises includes relaxing and tensing individual facial muscles. For example, to restore articulation, it is recommended to pronounce the sounds “u”, “o”, “and”. Afterwards, you need to bring your lower lip under your upper teeth and reproduce the sounds “v” and “a”.
Gymnastics for inflammation of the trigeminal nerve:
- Close eyes
- Raise your eyebrows
- Frown
- Squint
- Smile with your mouth closed
- Smile with your mouth open
- Puff up your cheeks
- Pull them back
- Whistle
- Widen your nostrils
- Curl your lips
- Raise your upper lip and return to the starting position
- Lower your lower lip and return to the starting position
- Take water into your mouth
- Rinse your mouth
- Close your mouth
- Run the tip of your tongue along your gums
- Move your tongue right and left
Homemade beauty recipes
Honey is famous for its healing and antiseptic properties. It perfectly tones the skin, makes it soft, velvety, and perfectly tightens pores. Honey can be used in its pure form, diluted with water and used as a tonic, or used to create cleansing and nourishing masks. After using the honey product, wash your skin and apply a nourishing cream.
Wipe oily skin and directly affected areas daily with a cotton pad soaked in lemon juice or strongly brewed green tea.
Walnut (its leaves) also helps reduce inflammation on the skin and thereby prevent further spread of comedones. To prepare the decoction, pour 2 tablespoons of walnut leaves (dry) into a glass of boiling water and boil for 5 minutes. Then cover the broth with a lid and leave to brew for another 25-30 minutes. After this, strain the broth and use it, rubbing it on problem skin several times a day.
Traditional medicine also helps in the treatment of marks and scars left after large acne. Melissa essential oil and blue volcanic clay cope well with this problem. Mix a few drops of oil with clay and dilute with water to form thick sour cream. Apply the paste on your face for half an hour, then rinse with warm water. The therapeutic effect of this mask is achieved due to the ability of lemon balm to relax the skin, heal wounds and tighten scars. Repeat the mask 1-2 times a week.
If your pores are large, a mixture of chamomile flowers and sage leaves will help tighten them. Take 1 teaspoon each of chamomile and sage, pour boiling water over them and let it brew for 20-30 minutes. Apply lotions to problem areas with this infusion.
Disease prevention
Doctors recommend eliminating effects on the body that cause inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. Here are some recommendations to help avoid illness:
- Avoid drafts and hypothermia
- Keep your head warm during the cold season
- Monitor your blood pressure
- Timely treatment of infectious and bacterial diseases
- Have a routine check-up with an oncologist
- Avoid skull and head injuries
You can sign up for an individual consultation, take tests or undergo treatment at the Medunion private clinic. You can easily make an appointment with us by calling 202-95-54 or online, directly on the website, by clicking on the “Online booking” button.
We have been working in Krasnoyarsk since 2006 and provide high-quality medical services to the population. The staff consists of highly qualified doctors of broad and narrow specialization.
Simple Tips to Calm Skin Inflammation
Understanding the root cause of skin inflammation is the first step to eliminating it. Once you have identified the problem, you can adjust your skin care or lifestyle as needed.
Here are some simple tips to calm skin inflammation:
- Avoid direct sunlight. Sun damage is one of the leading causes of skin inflammation, so be sure to wear a broad-spectrum sunscreen of at least SPF 30.
- Manage your stress levels. Chronic stress can cause or worsen skin inflammation, so take time to rest during the day and engage in relaxing activities to reduce stress levels.
- Eat a balanced diet. A balanced diet low in carbohydrates and sugars is good for your skin. Try a diet rich in fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains and healthy fats (including fish) with limited amounts of red meat.
- Avoid extreme temperatures. Exposure of the skin to extreme temperature changes, such as cold weather followed by hot showers, can increase inflammation.
- Be careful with exfoliation. When your skin is inflamed, the last thing you can do is accentuate the inflammation with exfoliation. Avoid harsh scrubs and consider taking a break from exfoliation to focus on gentle cleansing and moisturizing.
- Take a break from your daily skin care routine. Skin inflammation can make your skin especially sensitive even to ingredients you use regularly, so consider taking a break from your skin care routine and avoid having to hide your inflammation with heavy makeup.
The tips mentioned above can help with mild and occasional skin breakouts, but if it becomes a chronic problem you need to seek help. A dermatologist or other skin care specialist can help you get to the bottom of your skin inflammation and give you advice on how to deal with it.