A boil is a purulent inflammation of the hair follicle and surrounding layers of skin. Boils on the chest can form in both men and women. In the stronger sex, the hairline is pronounced; in girls, the hairs are almost invisible, but they are definitely present. Therefore, anyone can detect a boil in the bust area. This localization does not contribute to rapid healing, since the skin on the chest often sweats, the regeneration process is delayed, and patients experience pain and discomfort. Boils become especially dangerous during breastfeeding.
What it looks like and why it appears
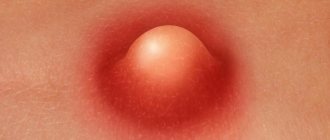
A boil on the chest looks like a red bump. The main reasons for its appearance are the penetration of pathogenic microbes through the skin into the hair follicle. Most often the causative agents are saprophytic or pathogenic staphylococci, less often streptococci. The hair follicle has suitable conditions for the rapid proliferation of microbes. An increase in bacterial masses provokes the body's defense reactions. The layers of skin around the infected bulb become inflamed and thickened, so a hyperemic infiltrate is visible.
Symptoms of a boil on the mammary gland:
- the appearance of a local compaction on the skin, a tubercle;
- redness of the skin area around the infiltrate;
- discomfort or pain in the area of the seal;
- After a few days, white contents are visible under the skin.
The main reasons for infection lie in impaired elasticity and integrity of the skin barrier. Any abrasions, scratching, insect bites, diaper rash on the chest lead to microcracks and small wounds. Through them, streptococci and other pathogenic bacteria enter the deep layers of the dermis and cause chiria on the chest.
Symptoms
Since in the initial stages of development the boil looks like an ordinary pimple, a woman does not always pay attention to it. And this is in vain, since the infection continues to develop and can lead to undesirable consequences.
A few hours after detection, a reddened pimple can greatly increase in size due to a productive inflammatory process. The structure of the boil thickens, and after a few days pus begins to appear.
After the boil has fully matured, its walls rupture and pus comes out, which indicates that the infection has stopped developing. With purulent furunculosis the following is also observed:
- pain at the site of pimple formation;
- increased temperature ;
- pain during feeding if there is a boil on the nipple;
- general weakness and deterioration of health.
Stages of furunculosis
It takes several days for a breast abscess to form. From the introduction of infection to tissue healing in an uncomplicated process on the mammary gland, on average, 5-10 days pass. Lack of proper care for the pathological area and the skin around it, and incorrectly selected treatment tactics can lead to complications that delay recovery.
A boil on a woman’s breast, like in men, develops in several stages:
- The first is the infection of the hair follicle.
- The second stage is the appearance of inflammation in tissues that are close to the infected hair follicle. Gradually, the skin thickens and turns red, an infiltrate appears in the upper layers of the skin, and pain occurs. The development of furunculosis in several places on the chest can lead to an increase in body temperature.
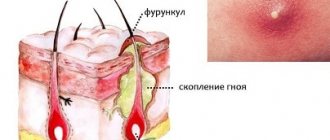
- The third stage is the formation of purulent contents in the center of the boil. During this period, white or yellow exudate is visible under the skin. The hairy root dies and turns into a necrotic rod; it is located in the center of the chirium.
- The next stage is the opening of the pustule and the outflow of purulent contents to the outside. After opening the abscess, tissue inflammation and pain should decrease.
- The final stage of the disease is the regeneration of damaged tissues. If the lesion was deep, a scar may form on the chest after the boil.
Abscesses and boils on the mammary gland can become complicated if there is insufficient treatment or if purulent contents are squeezed out. In this case, the infection will spread to neighboring areas and deeper, which will lead to the appearance of extensive abscesses and pronounced necrotic processes.
What is a boil?
Furunculosis is a disease in which purulent-infectious sacs form under the skin. Boils can be either single or multiple. On average, one abscess heals in 10-12 days of proper treatment. The main causative agent of this infectious disease is Staphylococcus aureus or white Staphylococcus.
The process of formation of an abscess occurs in several stages:
- red pimple appears on the skin
- the formation thickens , purulent fluid accumulates inside;
- symptoms appear (weakness, elevated body temperature, etc.);
- In the future, the skin may rupture and pus comes out.
The boil itself is a pimple that contains particles of dead tissue, which form a purulent core. After it comes out, a scar remains at the site of the boil; over time, it becomes almost invisible.
Are breastfeeding and pustular lesions compatible?
Whether you can breastfeed or not depends on what kind of boils have formed on the breast, that is, whether the lesion is deep, whether necrosis is pronounced, and the location of the abscesses in relation to the nipples. It is important to understand that the cause of furunculosis on the body is most often staphylococci. This pathogenic microorganism can be transmitted to the baby during feeding.
It is very dangerous for newborn babies to receive a portion of milk containing Staphylococcus aureus. The microbe easily takes root on the intestinal villi and provokes dysbiosis with subsequent symptoms of acute enterocolitis.
If there is one small abscess on the mammary gland, and it is distant from the nipple, then you can not interrupt breastfeeding. It is important to wash your hands thoroughly, not touch the surface of the boil, and treat the nipple before feeding so as not to provoke the transmission of infection to the child.
If there are several boils, it is recommended to conduct a microbiological examination of the milk, that is, check for the presence of bacteria in it. The study will help determine further feeding tactics. The result of the analysis will have to wait about 7 days.
Where is it localized?
Common localizations of the process of suppuration on the chest are the area around the nipple, the folds under the mammary glands. Boils most often occur on the sternum in women.
The reasons lie in an uncomfortable bra that rubs the skin. “Bones” in underwear can lead to wounds on the sternum, and when they become infected, an abscess appears.
In a man, a boil on the chest can be located in any location. Furunculosis most often affects those places where active sweating occurs during physical activity. Therefore, the most favorable conditions for the development of chiries are the central part of the chest, in the area of the xiphoid process.
On the skin glands
A boil on a woman’s chest is located mainly where the skin is easily injured or rubbed. For example, at the place of the bra border. Low-quality synthetic underwear can cause irritation on the skin, so you need to choose a bra based on the composition of the fabric. Synthetics do not absorb sweat, which is constantly produced by the sebaceous and sweat glands. The ducts of the sebaceous glands on the skin of the chest will become clogged and inflamed, leading to furunculosis.
Under the breast
If a woman has large breasts, then she needs to be especially careful about hygiene procedures in the folds under the mammary glands. A boil under the breast forms because this area is subject to increased sweating. Various microorganisms are always present on the surface of the skin, and poor hygiene supports their growth and reproduction. There are often scratches, abrasions and other damage under the breasts. They cause infection to penetrate into the skin and develop a boil.
It is difficult to treat a boil under the mammary gland due to the constant friction of these places. This localization requires that the affected area be wiped with a drying antiseptic. It is not recommended to use talc on the wound surface. You can use the powder for prevention on healthy skin.
On the nipples
A boil on the nipple cannot appear because the red area on the chest is devoid of hair follicles. Abscesses sometimes appear at the border of the areola.
Especially often, boils in the chest area at the border of the halos area form in the first weeks of breastfeeding. Delicate skin, not accustomed to the feeding process, quickly dries out, microcracks appear, which are easily infected. If chiria is not treated correctly, pus can enter the mammary glands and cause complications.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of developing boils, a woman needs to:
- when breastfeeding, try to avoid microcracks in the nipples, and if they appear, be sure to treat this area with antiseptic agents;
- adhere to the rules of personal hygiene;
- owners of large busts are advised to carefully treat the area under the breasts in case of heavy sweating;
- eat more vitamins and nutrients;
- avoid cuts and microtraumas in the chest area;
- a patient with diabetes needs high-quality treatment;
- Avoid hypothermia or overheating of the body.
Furunculosis is a dangerous disease. If treated incorrectly and untimely, the infection can spread to other parts of the body.
This can lead to an abscess for a woman or much worse consequences. Taking medications should only be started after consultation with a surgeon.
To prevent infection from entering the body, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle , follow all the rules of hygiene, eat right and boost your immune system. This disease in nursing young mothers can harm the baby, so it is necessary to start treatment on time, and if there are boils on the nipples, temporarily stop breastfeeding.
What is the danger
Breast boils are dangerous due to complications in which the infection spreads from the chest area to other organs and systems.
Possible complications of a boil on the chest:
- If the infection spreads through the glandular ducts from the layers of the skin deeper into the mammary gland, mastitis develops. Purulent inflammation of the mammary gland is often treated surgically, leaving a scar on the woman’s chest.
- The entry of a large number of microbes from the source of the boil into the blood can lead to sepsis. Blood poisoning is very dangerous, as it leads to necrosis of internal organs and multiple inflammatory processes throughout the body.
- In the absence of therapy or incorrect treatment tactics for a large boil, the infection can enter the brain through the blood and lymph, leading to encephalitis and meningitis.
Pregnant women are susceptible to the occurrence of a purulent process on the chest. During pregnancy, the mother's immune system weakens, which leads to boils and other skin pathologies.
If you have furunculosis, it is important to seek help from a doctor to prevent intrauterine infection of the fetus.
In the early stages of pregnancy, the introduction of staphylococcus or other bacteria into the amniotic fluid and embryonic tissue often leads to the death of the fetus.
How to treat a boil on the chest
Features of the treatment of a boil in the chest area depend on the stage of the process and the degree of tissue damage. If the necrotic core of the boil is located deep and has a large area of damage, then surgical treatment will be required. A small abscess that matures quickly can be cured at home. It is necessary to urgently consult a medical specialist in case of such complications:
- increased body temperature;
- strong pain;
- increase in redness up to several centimeters in diameter.
Pregnancy or breastfeeding require careful treatment tactics. Women from these categories are treated only under the supervision of a doctor, so as not to harm the child.
Medications
There are local medications - antiseptic solutions, antibactericidal agents, anti-inflammatory ointments. They are applied directly to the inflamed area of the chest.
Doctors often recommend treating boils with Ichthyol ointment or Vishnevsky's liniment. These drugs have powerful antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effects. Levomekol, Akriderm and others are prescribed for ointments that contain antibiotics.
Surgical methods
If extensive furunculosis has developed on the chest, the help of a surgeon will be required. The specialist will make small incisions, slightly shifted from the center of the abscess, to ensure the release of purulent-necrotic exudate. Then the wound is treated with an antiseptic solution, for example, furatsilin.
To cure a deep boil on the mammary gland, the doctor leaves drainage after opening. Antibacterial ointments are applied to the wound every day, and bandages are changed so as not to provoke re-infection of neighboring tissues.
How to treat at home
Folk remedies for the treatment of chiria on the mammary gland can be used only when there is one boil with a diameter of up to 1 cm. In other cases, the help of doctors is necessary.
At home, you can cure a boil on the chest using honey. A napkin with honey should be applied every day. In 3-4 days, the boil should open on its own, and the inflammation should decrease.
The juice of natural antiseptics - onions and garlic - is widely used in folk medicine. These products must be used several times a day. Positive dynamics should appear already on days 2-3 of treatment.
Treatment
If the patient goes to a medical facility in the first stages of the development of a boil, then, as a rule, local treatment is prescribed. It includes:
Self-medication is dangerous with complications!
Attention
Despite the fact that our articles are based on trusted sources and have been tested by practicing doctors, the same symptoms can be signs of different diseases, and the disease may not proceed according to the textbook.
Pros of seeing a doctor:
- Only a specialist will prescribe suitable medications.
- Recovery will be easier and faster.
- The doctor will monitor the course of the disease and help avoid complications.
find a doctor
Do not try to treat yourself - consult a specialist.
- prescribing a course of antibiotics (used for both single and multiple boils);
- applying ointments ;
- procedures of ultraviolet irradiation, UHF, infrared radiation.
If a woman comes to the doctor at the stage of opening the boil, he will determine whether the purulent core has completely come out and remove its remains. In case of large boils, surgical intervention is performed.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
It is performed under local anesthesia; the doctor completely removes the pus through a small incision and carefully sutures the wound. A few hours after the operation, the patient is allowed to go home.
When self-treating this problem, it is recommended to treat the wound with antiseptic agents several times a day.
In no case is it recommended to squeeze out the boil yourself; this can lead to an increased inflammatory process, as a result of which the person gets an abscess.
How to treat a boil
A dermatologist treats boils.
While the wound is healing, it must be covered with sterile gauze bandages or adhesive tape. To prevent the infection from spreading to other parts of the body, it is not recommended to wet the wound until complete healing.
For boils it is prohibited:
- Squeeze out yourself or open them with sharp objects (you can not squeeze out the rod completely, this will lead to even greater inflammation).
- surgical is required .
- Do not take antibiotics yourself; only a specialist can prescribe the correct treatment.
- If a woman works in the service sector (educator, teacher, health worker), then during the treatment of this disease she must be removed from her duties.
- You should not delay
contacting the clinic and wait for the boil to open on your own, this can lead to a severe abscess.
An internal boil on a woman’s chest is very dangerous, since many nerve fibers and blood vessels pass around the mammary glands. The infection can spread throughout the body.
Young mothers need to be very careful during lactation, as milk can transmit the infection to your child. Therefore, with boils on the nipples, doctors recommend stopping breastfeeding until the patient has completely recovered.
You should not resort to treatment with folk remedies, as this can only aggravate the problem and cause the infection to spread to other parts of the body.
With improper care after cleansing the purulent core, a relapse is possible at the site of boil formation. During pregnancy and lactation, special medications are selected for a woman that do not harm either her or the child.
Prohibitions: what you absolutely cannot do
Incorrect treatment tactics and independent manipulation can lead to serious complications.
What not to do with boils on the chest:
- Squeeze out the abscesses, otherwise the infection will spread to adjacent healthy tissues.
- Use compresses, create conditions for the surface of the skin to become wet. If the boil does not dry out, the pus will accumulate inside and will not be able to break out.
- Engage in self-treatment when new boils or other signs of complications appear.
- Use medications for a long time that do not lead to positive dynamics on days 3-5. The infection can be mixed, and the remedy does not act on all possible pathogens of the purulent process. Then there will be no effect from the treatment.
Preventive measures
The body's immune system prevents the appearance of boils on the skin. To minimize skin lesions from boils and carbuncles, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system.
To maintain the body’s built-in strength, it is recommended:
- hardening;
- nutritious nutrition with sufficient amounts of vitamins and minerals;
- avoiding drafts and sudden changes in temperature;
- timely treatment of acute respiratory diseases;
- in the presence of chronic diseases, one should try to establish stable remission.
Compliance with preventive measures will help activate the body's own defenses. Strong immunity fights infections at the stage of their introduction, which is why inflammatory skin diseases, such as boils, do not develop.