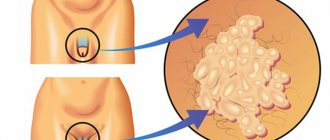
Molluscum contagiosum is a dermatological pathology, which is characterized by the appearance of specific benign formations on the skin (less often on mucous membranes). Pink, dome-shaped nodules with a smooth surface and a depressed core can reach 2-5 mm (rarely 1.5 cm) in diameter. The rashes are concentrated in groups, affecting large areas. Locations - any areas of the skin (arms, face, head, chest, abdomen and groin area), except for the feet and palms.
Subjective symptoms are absent or mildly manifested - papules can cause minor itching. Treatment is aimed at removing a pronounced cosmetic defect and preventing the spread of pathology to neighboring areas.
Interesting: Waxy papules resemble pearls, and upon close examination, they resemble a mollusk shell, which was the name for the disease. The disease does not pose a direct threat to human health. However, if damaged, there is a high risk of secondary infection, which can cause suppuration. The pathology is also highly contagious. It needs to be treated to protect others from the risk of infection.
Molluscum contagiosum: causes of appearance
Almost anyone can get molluscum contagiosum, as this disease is viral in nature. But most often the pathology is diagnosed in children and adolescents, which is explained by several factors:
- The body's defense system is not fully formed.
- Insufficient personal hygiene skills and habits.
- Frequent tactile contacts in a peer group.
The immune system of animals is resistant to this disease, so they do not get sick. People become infected through direct contact with a carrier of the virus or through shared hygiene and household items. But cases have also been diagnosed when patients became infected through the water of a public swimming pool, through dust in the premises - the virus is able to live for some time outside a living organism.
Molluscum contagiosum: routes of transmission
Among the main causes of infection are the following:
- Direct physical contact in a group of people - molluscum contagiosum is often diagnosed in a child who attends a child care facility. Pathology is found in entire groups of schoolchildren and preschool children.
- Infection in the family, infection through sexual contact. In large families, the spread of infection occurs very quickly. And people who are sexually active with different partners get sick much more often than those who are committed to monogamy.
- People visiting swimming pools, gyms, beaches. The virus is transmitted through the use of shared showers, sports equipment, and benches.
Important: If a person has other skin diseases that are accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the epidermis, the molluscum contagiosum virus penetrates the body and spreads faster.
Molluscum contagiosum: symptoms
After infection, it may take 6-9 months for the virus to make itself felt. Under unfavorable factors - a cold, hypothermia - the virus can activate faster. Groups of small rashes appear on the skin in the form of nodules filled with fluid. More often than others, the skin of the face, chest, abdomen, and limbs is affected. Molluscum contagiosum in adult patients who became infected through unprotected sexual contact is characterized by the localization of “pearls” in the genital area and pubis.
Since the rash does not itch or hurt, the patient may not recognize the pathology for a long time. But if the papules are damaged mechanically (by clothing) or with concomitant skin pathology (dermatitis, urticaria), the lesions can become inflamed. Local nonspecific therapy with anti-inflammatory drugs helps to attenuate acute symptoms, but the virus cannot be cured in this way; relapses are possible.
There are known cases of self-healing, when the papules of molluscum contagiosum disappear within several years, and the disease no longer appears. This happens when stable immunity is formed.
Symptoms
Each disease has its own symptoms, but there are a number of common signs that unite viral skin infections:
- increased body temperature, malaise, fever;
- the appearance of rashes, papules with serous or purulent contents on the skin;
- the appearance of redness, hyperemia around the rash;
- The rashes often itch, and if you scratch them, a scar or “hole” may remain in their place;
- when the contents of the papules are squeezed out, the rash spreads over the skin;
- Often the patient has indigestion, diarrhea, diarrhea or vomiting.
Molluscum contagiosum: diagnosis
Visually, molluscum contagiosum is quite specific, so diagnosing the disease in most cases is not difficult. However, only for a qualified specialist. Without the necessary knowledge, it is easy to confuse the pathology with other skin diseases.
In specialized clinics, a method for examining skin formations is used, such as dermatoscopy. Using a digital dermatoscope (a device that magnifies the image of the skin sixteen times), the doctor can accurately determine the nature and nature of the tumor.
In some cases, a puncture of the capsule is performed to obtain fluid and its subsequent laboratory analysis - under a microscope, intracytoplasmic bodies can be seen.
How does genital molluscum contagiosum manifest?
If infection with the virus occurred through sexual contact, molluscum contagiosum can be found on the genitals. These are the same groups of pink nodules with a diameter of up to 5 mm, which are located on the head of the penis, on the labia, on the pubis, on the inner surface of the thighs and look like cones with a sunken core. Giant mollusks reaching 1.5 cm in size are rarely found. It is large papules that are often injured by underwear and become inflamed. This is why the disease is dangerous. Inflammation in the genital area can lead to serious health problems - an abscess.
Removal methods
If conservative treatment does not lead to positive results, then the following may be prescribed:
- mini-operations to remove the mollusk with tweezers by plucking out the nodules with further disinfection of the affected area;
- cryodestruction by freezing papules with liquid nitrogen;
- electrocoagulation by applying a high-frequency current to the body of mollusks, followed by treatment with brilliant green or potassium permanganate;
- laser therapy.
If the body is strong, then the virus can be defeated in 2-3 months. But the mollusk is fraught with relapses and after some time it can appear on the body again when the body’s defenses decrease. When infected with this virus, patients are advised to get tested for HIV, since it can cause the disease.
Molluscum can be treated well with folk remedies by lubricating the affected areas:
- celandine juice, garlic;
- decoction of string;
- juice of bird cherry leaves;
- celandine juice up to 5-6 times;
- ointment or alcohol tincture of calendula by applying 3-4 times a day.
You can prepare this recipe:
- grind the garlic and squeeze out the juice;
- add butter, stir;
- apply the paste to the nodules 3 times a day.
Or prepare an infusion from the series (2 tablespoons per 1 glass of boiling water), bring to a boil, leave for 1 hour, strain and wipe the affected areas.
How to treat molluscum contagiosum?
You should not try to remove molluscum contagiosum with folk remedies at home. Squeezing the rash is not allowed. After all, mechanical damage to the capsule can lead to the spread of pathogenic fluid. In this case, the virus can spread to neighboring areas of the skin. And in the presence of microcracks, the localization of the disease increases.
It is strongly recommended to treat molluscum contagiosum in an outpatient setting at a specialized medical center. You need to make an appointment with a dermatologist.
Modern dermatology offers several effective methods for treating the disease. All of them are aimed at removing pathological formations from the surface of the skin:
- removal with surgical tweezers;
- laser treatment;
- cauterization with liquid nitrogen;
- radio wave knife.
Important: Laser removal of molluscum contagiosum is the method of choice when the final aesthetic result is important (for example, when removing capsules on the eyelids, around the eyes and lips, on the neck) and painlessness (for example, when treating a disease on the genitals).
For isolated manifestations of small diameter, the doctor may prescribe conservative treatment with antiviral pharmaceuticals - ointments, gels, tablets.
Laser treatment of molluscum contagiosum
- Treating molluscum contagiosum with a laser means avoiding scars at the site of exposure. This cannot be achieved by cauterization with nitrogen or mechanical removal of formations with surgical instruments. The laser beam is targeted, healthy tissue is not damaged, and therefore the recovery period is minimal.
- The wounds do not become infected or bleed. Under the influence of the laser, the infectious virus dies.
- Short laser pulses are not recognized by pain receptors, so the procedure is performed without anesthesia or under local anesthesia. This is especially important when removal is carried out on sensitive skin and genital mucosa in men and women, or on any areas of children's delicate skin.
- After the procedure there is a minimal recovery period. Wound healing medications and a sterile dressing may be recommended. After 3-4 days, the skin is completely restored, no marks remain on the skin.
- High treatment speed is another advantage of laser treatment. In one session, a dermatologist can remove 15-20 papules. The absence of serious contraindications allows this technique to be used by children and older people.
If you are interested in laser treatment for molluscum contagiosum, we recommend contacting the Lasersvit clinic. They will help you get rid of the defect with high efficiency and in a short time.
Treatment
Modern medicine has not invented antibiotics that would completely kill the unpleasant virus. Treatment of the disease is based on suppressing viral activity, removing nodes and strengthening general health. Is it worth removing contagious nodes? Undoubtedly. They contain an infection that can spread quickly when in close contact with other people. Typically, special ointments are used to suppress the activity of pathogenic microflora:
- Acyclovir (costs around 100 rubles);
- Viferon (not only fights the virus, but also strengthens the immune system, cost about 150 rubles);
- Cycloferon (most effective in the initial stages of the disease, cost around 200 rubles).
Along with the use of the ointment, it is recommended to take immunomodulators and vitamin complexes.
Now let's get back to deleting. You can’t do this on your own; you could end up with complications. The most commonly used clinical techniques are:
- A surgical intervention during which the node is removed using special tweezers.
- Cryodestruction, which involves destruction of the node at super-low temperatures (liquid nitrogen is used).
- Laser removal (the tumor is burned out with a laser beam along with microbes).
- Electrocoagulation based on the influence of electric current.
All these methods are available even for pregnant women, regardless of the stage of pregnancy.
Molluscum contagiosum: prevention
Prevention of a contagious disease consists of following the rules of hygiene. Children should be taught from childhood to take care of the cleanliness of their bodies, especially their hands. If we are talking about sexual intimacy with a new partner, it is very important to use contraception. This will protect not only from molluscum contagiosum, but also from more dangerous sexually transmitted diseases.
When visiting a swimming pool or gym, using a personal washcloth and towel will help you avoid infection. Avoid using common hygiene items completely.
Carry out thorough cleaning of the room and workplace using disinfectants. This will help kill the virus that is present in the dust. It is recommended to iron underwear that is dried outdoors. The temperature will kill any pathogenic flora that may have settled on the fabric.
If one family member is diagnosed with this disease, it is important to ensure that the virus is not transmitted to other relatives. In addition to increased disinfection of common areas, surfaces in common rooms, and in hygienic rooms, try to avoid tactile contact until the patient has undergone treatment. If a pathology is detected in a child, children should be abandoned.
Water supports the life of the virus well. The patient should refrain from visiting public swimming pools and baths during treatment.
Grimpoteuthis / Grimpoteuthis
Because of its unusual appearance, this inhabitant of ocean waters is called the eared octopus. There are two fins on the head that resemble large ears.
They like to hide at depths of up to 7,000 m, but usually live and feed in the range of 500 to 100 m. It was first discovered and scientifically described in 1932.
Small octopuses grow no more than 20 cm, but the largest specimen in history weighed 6 kg, and its body length was 1 m 80 cm.
9