Dermatovenerologist
Khasanova
Alina Rashidovna
9 years experience
Make an appointment
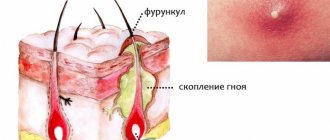
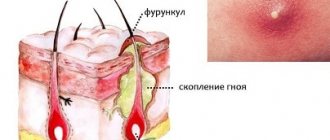
If staphylococcal bacteria enter the hair follicle of the skin, it can cause serious inflammation. An accumulation of pus with tissue necrosis that has captured the affected area along with the sebaceous glands and tissue is called a boil, and the disease itself is called furunculosis. Its appearance is quite painful, and its development is relatively fleeting. To avoid infection of the skin and the spread of the inflammatory process to healthy tissues, at the first signs of pathology you should seek medical help.
Symptoms of the disease
The formation of a boil manifests itself as follows:
- a small raised cone-shaped nodule above the skin;
- change in skin tone over the tubercle to red-violet;
- increased pain in the inflamed area;
- swelling of surrounding tissues;
- the formation of a white dot in the center of the painful area;
- opening of an abscess;
- discharge of necrotic hair follicle and purulent masses.
To establish a diagnosis and treatment, you should contact a surgeon.
Treatment of pustules on the face
There are systemic and topical medications designed to combat ulcers on the face; treatment should be selected by a dermatologist. When making a diagnosis and prescribing therapy, the doctor relies on the clinical picture. As a rule, when pustules appear, combination treatment including systemic antibacterial drugs is required.
For mild to moderate acne, a dermatologist may prescribe medications with azelaic acid, for example, Azelik®5,9 gel. It normalizes keratinization processes, reduces the level of free fatty acids, and exhibits antimicrobial activity against Propionibacterium acnes and Staphylococcus epidermidis5. Azelik® gel reduces the metabolism of neutrophils and their synthesis of free radical forms of oxygen5.
*acne
Complications of a boil
The disease may seem quite safe, but this is not so - a boil can cause complications that pose a serious threat to human health:
- furunculosis;
- phlegmon;
- erysipelas;
- carbuncle;
- lymphadenitis;
- inflammation of the veins;
- cutaneous lymphatic nocardiosis;
- inflammation of the vagina and uterus - formed in women from boils on the genitals;
- meningitis;
- accumulation of pus in the brain matter;
- abscesses in various tissues and internal organs;
- sepsis.
Prevention methods
You can reduce the risk of infection with staphylococcal bacteria and the development of furunculosis if:
- keep your body clean, take a shower regularly;
- carefully treat injuries and cuts;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- exercise regularly;
- diversify your diet, focusing on foods high in vitamins.
In addition, it is important to promptly treat emerging diseases of internal organs, as well as dress according to the season, avoiding overheating or hypothermia of the body.
General characteristics of the disease
Furuncle is a common disease - about 17% of dermatological patients are observed with it. Currently, an intensive increase in patients with the presence of boils in the nose and nasal cavity has been recorded. This significantly increases the likelihood of developing a chronic pathology – idiopathic non-allergic rhinitis.
The disease is common among adults, but boils can also appear in children. Men are susceptible to this disease more often than women. An increase in the incidence of furunculosis is observed during periods of vitamin deficiency - in autumn and spring.
The causative agent of the boil
The formation of a boil is mainly due to the penetration of Staphylococcus aureus into the hair follicle. These bacteria can normally be found on the skin and are not dangerous. However, when introduced into the hair follicle, an inflammatory process begins.
The disease begins to develop with reduced immune activity. When the immune system is unable to fully prevent the spread and growth of pathogenic microorganisms, they begin to rapidly multiply and penetrate the pores. This leads to deterioration of the skin microflora and the formation of abscesses.
Kinds
Depending on the location and development characteristics, general and local furunculosis are distinguished.
- The local type of disease occurs in a limited area of skin. Its cause is the incorrect treatment of one rash or violation of sanitary requirements in matters of skin care.
- General furunculosis covers a significant area of skin and is characterized by numerous rashes. More often it occurs against a background of weakening of the body, disturbances in the functioning of the immune system, long-term chronic diseases or during a period of remission, with anemia or disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system.
The course of furunculosis can be acute or chronic. In the first case, inflammation occurs simultaneously or with a short time interval, and the disease makes itself felt by increased body temperature, headache and a feeling of weakness. The chronic form of furunculosis develops with prolonged physical fatigue, with overheating or hypothermia of the body, as well as against a background of weakened immunity. Regardless of the type of disease, if symptoms of furunculosis appear, you should contact a dermatologist as soon as possible to clarify the causes of the boil and develop effective treatment tactics.
Prerequisites for development
It has been found that in the presence of certain skin characteristics or in the absence of proper care for it, the risk of the formation of boils increases significantly. People with these characteristics should monitor their health more closely and improve their immunity. The main factors that contribute to the formation of boils include the following:
- Increased sweating. Sweat contains aggressive salts that negatively affect microflora. The protective qualities of the skin are reduced, thereby creating an optimal environment for the causative agent of the disease.
- Presence of skin diseases or damage to the skin. Various cracks and rashes are excellent starting points for infection, thanks to which the pathogen is able to bypass several levels of defense in the body.
- Irritated skin due to regular discharge from the ears or nose due to chronic illnesses. The constant presence of pathogens on the skin leads to a decrease in its protective properties.
- Constant scratches, cuts and abrasions. Bacteria from the genus Staphylococcus can easily penetrate the hair follicles through various damage to the skin, which leads to the development of the disease.
- Use of low quality skin cosmetics.
- Lack of personal hygiene. On uncleaned skin, frequent friction causes irritation, which is an excellent conductor for the causative agent of the boil.
- Disruption of the natural microflora of the skin due to regular exposure to irritants due to certain activities. Dust and lubricants are particularly hazardous.
If these features are present, it is necessary to carefully monitor the condition of the skin. It is very important to properly care for the skin, and in case of damage, immediately treat it with antiseptic agents and protect it with a bandage or plaster. If a boil has formed, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
Treatment of furunculosis at JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg)
Qualified therapists and dermatologists of JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg) in the Central Administrative District of Moscow are ready to receive and examine patients with suspected furunculosis. To confirm the diagnosis, it is recommended to undergo a comprehensive examination in your own laboratory center. Treatment is prescribed on an individual basis, and its progress and results are strictly monitored by specialists. Each client is guaranteed tactful and attentive treatment, confidentiality of personal information, as well as comfort and safety during diagnostic and treatment procedures.
How to open a boil yourself?
Dermatologists categorically do not recommend trying to cope with inflammation on your own, wanting to squeeze out the purulent contents and the core of the boil at home. This is dangerous due to secondary infection, the spread of the inflammatory process to healthy tissue, the formation of new areas of inflammation and blood poisoning. The decision to open a boil is made only by a surgeon at a specialized medical institution, and only he has the right to carry out such manipulations.
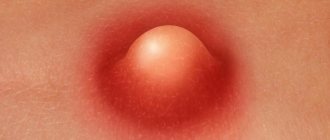
What does a boil look like?
A boil is a visible lump or red bump with a purulent head on the surface of the skin. When you touch its surface, you feel relatively severe pain, the skin around it is noticeably inflamed, and its temperature is increased. The most common places of development are the back of the head, the back of the hands, the lower back, and the face. The rash can be single or massive; its symptoms do not depend on the number of points of inflammation.
Why do boils appear?
This question can be answered accurately only after a thorough diagnosis of the boil. Among the most likely causes are infection of the hair follicle of the skin with staphylococcus bacteria against the background of vitamin deficiency, violation of personal hygiene rules, wearing too tight clothes, poor-quality antiseptic treatment of abrasions and skin injuries. The disease can also be caused by intense work of the sebaceous and sweat glands, the secretion of which is a favorable environment for bacteria.
Reasons for the formation of boils
The main reasons for the formation of boils include decreased immunity or hormonal imbalance in the body. In accordance with the specific cause, a treatment plan is prescribed - with or without hormonal agents.
In a healthy body, the immune system serves as an insurmountable obstacle to the causative agent of abscesses and is able to resist dangerous bacteria, preventing them from entering the tissues and hair follicles from the surface of the skin. After a decrease in the body’s protective functions, the immune system ceases to intensively fight pathogens, and often completely stops perceiving them as a threat and makes no attempt to destroy Staphylococcus aureus. This behavior of the body is observed after a recent viral infection, which seriously affected the immune system. Long-term use of psychotropic drugs, local hypothermia or hypothermia also cause a decrease in immunity.
If the appearance of a boil is associated with hormones, then it is often related to complications of diabetes. When blood circulation is impaired, tissues do not receive sufficient nutrition, which leads to a decrease in the protective activity of the skin. As a result, the causative agent of the disease can easily enter the hair follicle and start the inflammatory process.
Under the professional supervision of a doctor, a boil can be completely cured.
Stages of boil development
This disease has three stages of development. Please note: you should consult a doctor at the initial stage of boil formation.
- Infiltration stage, i.e. accumulation of fluid in tissues. At this stage, the abscess is just beginning to form. The infiltrate is concentrated near the hair follicle, where the staphylococcus has entered. Swelling and hardening of tissues occurs. The size of the reddened area of inflammation is 1-3 cm in diameter. Often the patient complains of a tingling sensation at the site of inflammation, which becomes stronger when touched. At first the pain is not strong, but gradually becomes more pronounced.
- Stage of purulent-necrotic process. It begins on the third or fourth day from the moment of inflammation. In the middle of the boil, a core is formed, consisting of dead cells and thick purulent masses. From above, the rod appears above the skin and looks like a white abscess. When the tension of the skin over the rod becomes too intense, it diverges and purulent accumulations come out, then the furuncle cavity is completely cleared.
- Healing stage. After the wound heals, there will be no scar left from a small boil. After a large boil, there is a slight even scar, which should disappear over time.
Complications of the disease often develop at the second stage, when problems arise with the release of purulent-necrotic fluid. An attempt to remove a boil by squeezing can also have serious consequences.
Methods for treating boils
There are two treatment methods: drug therapy and surgery. Specific tactics depend on the stage and severity of the disease.
Drug therapy
Treatment with various medications is suitable if you seek help in a timely manner. Local therapy is generally required; broad-spectrum antibiotics are used in rare cases.
At the first stage of the disease, the inflamed area is cauterized with a pharmaceutical solution of iodine several times a day and dry heat is applied to it. The use of compresses is strictly prohibited, as this can lead to a severe deterioration in the patient's condition.
When the formation of the boil core begins, to speed up the process, bandages with ichthyol ointment should be applied to the abscess. This medicine helps to draw out purulent masses and reduce the duration of tissue restoration in the future. It is necessary to treat a boil with medication after mandatory consultation with a doctor.
During the healing stage, bandages with ointments containing an antibiotic are applied to the inflamed area, as well as drugs that significantly accelerate the tissue healing process. In case of severe suppuration of the boil, immediately after the rod comes out, a special drainage can be placed and the recesses can be washed with antiseptic agents.
It is impossible to cure the disease entirely and for a long period with the help of folk remedies.
Surgery
Removal of a boil by surgical intervention is permissible only in advanced cases: when there is already an abscess or there is a high probability of developing complications of the disease. The method helps to immediately improve the patient's condition. In such a situation, it is important to remove the purulent-necrotic core of the boil as soon as possible and carry out antiseptic treatment of the tissue. All actions are carried out under local anesthesia, often on an outpatient basis. Hospitalization is only necessary for a large abscess or serious subcutaneous abscess that requires regular medical monitoring.