Bacterial skin diseases are dermatological diseases caused by bacteria. These include pyoderma caused by streptococci, staphylococci or other gram-negative bacteria and other bacterial skin diseases - erysipelas, erythrasma, actinomycosis or Lyme disease.
Also included in this group of diseases are skin tuberculosis, syphilis and gonorrhea (they are described in separate chapters).
Causes of bacterial skin diseases
The content of the article
Human skin is the largest organ in the human body. Its surface is not sterile and is populated by numerous microorganisms, which under normal conditions do not cause infection.
The growth of pathogenic bacteria responsible for infections is prevented by tightly packed epithelial skin cells, an acidic pH (5.4-5.9), a relatively dry environment, and natural antibacterial substances in the skin. Therefore, bacterial skin diseases are relatively rare.
However, certain conditions associated with injury to the epidermis, disruption of its protective function (skin inflammation) or a general decrease in immunity (tumors, diabetes, AIDS) contribute to the involvement of the skin in the inflammatory process.
A different situation arises in the case of Lyme disease, since in this case the pathogen enters the human body through a tick bite.
Folliculitis and fever
As the name suggests, it is an inflammation of the hair follicle. This condition manifests itself in the appearance of a single vesicle or numerous vesicles filled with purulent contents, sometimes riddled with hair in the center. Changes may appear on the face, trunk or limbs. Sometimes they are associated with depilatory procedures or shaving.
Folliculitis
The chronic form of folliculitis occurs more often in men on the face, especially on the chin, and less often on the scalp. This form is characterized by a duration of several months and the appearance of inflammatory tumors in the skin.
Treatment of acute inflammation of hair follicles with low intensity consists of skin disinfection and the use of topical medications containing an antibiotic. However, treatment for folliculitis is often difficult and lengthy.
Diagnosis and treatment of pustular skin diseases
The manifestations of pyodermatitis are varied and depend on the bacteria affecting the skin, as well as on the body’s protective abilities. But most often, when infected with staphylococcus, the hair follicle is affected with the formation of an inflamed purulent nodule. Streptococcal pyoderma appears in the form of blisters on the skin of the face, in the nose, and in the corners of the lips.
Diagnosis of bacterial diseases is made on the basis of the clinical picture and anamnesis; in some cases, additional laboratory tests are performed to clarify the diagnosis.
The main goals when drawing up a treatment program are as follows:
- Identifying and eliminating the cause of the disease
- Prescribing a special diet to improve the general condition of the body
- Strengthening the immune system
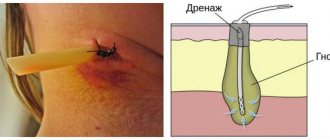
- Elimination of external signs of the disease: external treatment with ointments and antiseptic dressings. In case of severe stage of the disease, surgical treatment is possible
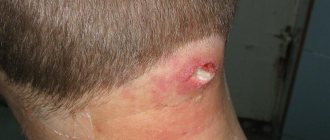
Among bacterial skin diseases, the most common are furunculosis, folliculitis, and hidradenitis.
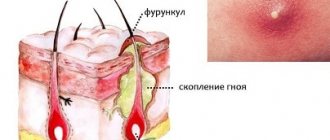
Furuncle
It is also an inflammation of the hair follicle and surrounding tissues. The difference with follicular inflammation is that during the formation of a boil, death and destruction of the tissue around the follicle occurs. A tumor is formed containing dead tissue, which either spontaneously or as a result of intervention is separated, leaving a skin defect.
Furuncle
The damage takes several days to form and is often painful. The skin is initially bright red and swollen, and after a few days a pimple forms on its surface. After healing, a scar may remain.
Folliculitis
Folliculitis is an acute inflammation of the hair follicle, characterized by the formation of bright red purulent nodules that are painful to the touch.
The duration of the disease is from 3 to 7 days.
Kinds:
- ostiofolliculitis is a superficial folliculitis, in which the formation of purulent nodules ranging in size from 2 to 5 mm is noted. They are spherical in shape with a hair in the center. After a few days, the purulent nodule dries out and forms a yellowish-brown crust, after which no skin scars remain after rejection.
- deep folliculitis is an acute purulent lesion of the hair follicle, in which inflammation spreads deep into the follicle. After the crust forms and falls off, the purulent nodule gradually resolves, leaving slight peeling and pigmentation on the skin. In a more severe form of deep folliculitis, an ulcer forms on the skin with further transition into a pinpoint scar.
Folliculitis can be single (occurring in a limited area of the skin) or multiple (scattered over the skin).
Folliculitis can develop on any area of the skin where there is hair, most often on the face, scalp, and extensor surface of the extremities. The disease is promoted by mechanical irritation of the skin (friction, scratching, shaving), contamination of the skin with chemicals, and excessive sweating.
Furunculosis
Most often, the development of one boil occurs quickly, and healing occurs within a few days. However, it should be remembered that in the case of boils in the facial area, especially around the orbit, nose, upper lip and auricles, due to the specific vascularization of these areas and the close proximity of important structures of the central nervous system within the skull, serious complications can occur.
Furunculosis is a condition in which many boils occur. Numerous changes tend to coalesce and form larger tumors. These symptoms often occur in malnourished people with underlying medical conditions such as cancer or diabetes.
Treatment of boils should be carried out by a dermatologist. For a single boil, topical antiseptics and astringents are usually sufficient. Multiple boils or clustered boils should be treated with systemic antibiotics. Fusion of purulent tumors requires surgical intervention.
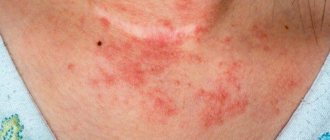
Rosacea
This is an acute inflammation of the skin and deeper tissues.
The disease can occur at any age. Skin lesions are most often localized on the face and lower extremities. The inflammatory focus of the skin is bright red, swollen, clearly demarcated from the environment, the skin is smooth and shiny. The disease is characterized by a sudden onset. Skin changes are accompanied by fever, chills and cold-like symptoms.
Rosacea
This disease can cause serious systemic disorders and should always be treated by a doctor. Without treatment, rosacea can lead to the spread of purulent infection into surrounding tissues, introducing bacteria into the bloodstream and thus causing sepsis.
The main therapeutic method for rosacea is the use of antibiotics in general. Compresses with astringents can be used locally.
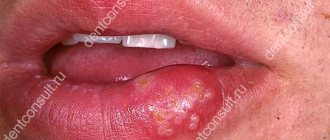
Infectious impetigo and hepatitis
This is an acute bacterial skin disease that often affects children. As a result of the growth of bacteria, blisters filled with serous or purulent contents form on the skin. After a few days, the blisters burst, forming crusts with a characteristic honey-yellow color.
Infectious impetigo
The changes usually occur around the mouth and nose, but can occur anywhere. If the infection covers the deeper layers of the skin, small ulcers occur. Skin changes are not accompanied by general symptoms. Impetigo is highly contagious, so the epidemic can affect kindergartens and boarding schools.
The disease always requires medical consultation. Treatment with topical disinfectants and antibiotics is most often effective and sufficient.
Skin infections
Skin infections are divided into bacterial, viral, fungal and parasitic. These include diseases such as scabies, warts, herpes, fungal diseases, lichen, etc. For the development of the disease, the infectious agent alone is not enough. For its active activity and reproduction, certain conditions are necessary, for example, a weakened immune system. If a person has a strong immune system, the disease may not occur.
Causes
Infection is one of the leading causes of skin diseases. The infection multiplies, causing an inflammatory response. In addition, any infection releases toxins into the body, which disrupt the functioning of the filter organs. Toxins released by infections are primary and aggressive allergens. The presence of infections in the body significantly increases the allergic component. The organs responsible for detoxification (liver, kidneys, lymphatic system) with a huge amount of toxins will no longer cope with their work and fully perform their functions. Essentially, skin diseases are a pathological way of percutaneous removal of toxins from the body.
Types of skin infections and their symptoms
Scabies - a characteristic symptom is itching at night, which prevents you from sleeping and is very annoying. Scabies can also be recognized by small itchy pimples and a gray line extending from them - this is the course of the mite. Warts. In fact, they are a benign tumor caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). There are several types of warts: common, genital warts, plantar warts, flat warts and senile warts. This disease is very common. They are skin tumors, often small. Although sometimes they can merge and grow to impressive sizes. Herpes. In this case we are talking about herpes type 1. There are also other types of herpes viruses, but they are no longer related to skin diseases, but rather affect internal organs. So, herpes virus type 1 (or herpes simplex virus) is an infection that lives in almost all of us. According to statistics, 9 out of 10 people on earth are infected with herpes. The first symptoms: small sores can be seen on the lips or near the nose. In the first hours, the skin begins to swell and hurt a little, causing discomfort. Symptoms of an aggravated herpes virus, in addition to skin manifestations, may resemble a common cold - weakness, fever, etc. Fungal diseases. There are a huge number of fungi that, when they get on human skin, hair and nails, cause them to change. You can become infected with a fungal infection, like other skin diseases, through contact with a carrier (including animals), when using common hygiene items, shoes, as well as in bathhouses and swimming pools, that is, where it is warm and damp, especially if there are mechanical damage to the skin. Symptoms of fungal diseases can include: itching, burning, redness, peeling, weeping, cracks, peeling of scales, the formation of round plaques with a flaky raised rim, changes in the color and texture of the nail, the appearance of clearly defined lesions on the scalp of the skin in which the hair becomes dull, brittle and eventually fall out, the appearance of black spots, severe seborrhea or dandruff. Ringworm. These are diseases that can also be caused by viral microorganisms and fungi. Infectious varieties include ringworm, pink, multicolored (or pityriasis). A common symptom of these diseases is a rash in the form of scaly plaques of discolored and completely different sizes, causing itching. Exudative erythema multiforme. An infectious disease with an acute course. The seasonal form develops more often in spring or autumn. Caused by infection against the background of cold factors. The toxicoallergic form occurs due to intoxication of the body with medications or after vaccination (more often in children). Both forms are characterized by skin rashes in the form of pinkish spots or slightly raised papules. Bubbles filled with serous and sometimes bloody contents may appear in their middle. The disease is also accompanied by general malaise and fever. Pain in the throat and joints is often felt. Ostiofolliculitis or staphylococcal impetigo. The causative agent is often Staphylococcus aureus. The main cause of the disease is poor hygiene and excessive sweating. It is characterized by the appearance on the skin of small semicircular rashes filled with purulent contents. Their size is approximately the size of a pinhead. There is a hair in the center of the abscess. Accompanied by painful sensations in the area where the rash is located. In the absence of adequate treatment, the infection can spread deep into the epidermis, provoking the development of folliculitis and the appearance of boils. Pyoderma. A wide group of pustular diseases caused by bacteria: streptococci, staphylococci and pathogenic fungi. The main symptom is follicles that appear mainly on the skin of the face, back, chest, armpits and scalp. If you do not seek help from a doctor in a timely manner, there is a high risk of developing sepsis, a life-threatening condition. Actinomycosis. Bacterial skin disease with a chronic course. The main symptom is the appearance under the skin of a dense, lumpy neoplasm (infiltrate), which consists of several nodules fused together. The skin in this area takes on a bluish-reddish tint. As the disease progresses, the infiltrate breaks through, forming fistulas from which purulent contents are released. Thrush or yeast stomatitis is often diagnosed in newborns or weakened children. It is characterized by the appearance of a white film (plaque) on the oral mucosa.
Diagnostics
In diagnosing skin diseases, it is especially important to detect hidden infections that deprive the immune system of the ability to function normally. The condition of internal organs, the disruption of which can cause skin diseases, is also assessed. Therefore, an examination for skin diseases consists of a carefully verified list of tests and examination by doctors of a different specialization (for example, a cosmetologist-dermatologist), who are designed not only to detect skin diseases (often this can be done with the naked eye), but to identify the true causes of all existing in the body disorders. With this systematic approach, the treatment provided is often enough to save the patient from skin disease for a long time, and often for life.
Treatment
Treatment of infectious diseases is carried out comprehensively. Conventionally, all treatment is divided into several stages, which depend on the established diagnosis and the individual characteristics of each patient’s body. Various treatment methods are used: medications, including antibiotics of different groups. Homeopathic remedies, phytotherapy and physiotherapy methods are also used. In certain cases, cryotherapy procedures are effective. Depending on the disease, ultraviolet irradiation of the blood may be necessary. In addition, medications are prescribed that improve the functioning of internal organs and strengthen the immune system. For external use, certain ointments, gels, mash and creams are used. Effective folk remedies are used as additional treatment. Treatment is usually carried out on an outpatient basis, although in particularly severe cases the patient is advised to be referred to a hospital.
Erysipelas
Erysipelas is caused by capillary hair bacterium. This is a pathogen found in animals, most often in cattle, less often in birds and fish. Infection occurs through direct contact with raw meat, poultry or fish, so skin lesions are most often localized on the hands and fingers.
Erysipelas
The disease is not transmitted from person to person. Initially, swelling and erythema appear at the entry site. The lesion then spreads peripherally with a tendency to heal centrally. The changes are not accompanied by general symptoms.
Diagnosis of the disease requires consultation with a dermatologist. The choice of treatment is general antibiotic therapy under medical supervision.
Contagious skin diseases
What time of year do you like best? Winter? Spring? Summer? Autumn? For me personally, summer is hot, reckless, a time of vacation and summer vacation. Summer ends, and everyone returns to the city from their vacation spots, students move into dormitories. It was then that there was an increase in the detection of contagious skin diseases: scabies and microsporia.
Scabies
Scabies is one of the most common contagious parasitic skin diseases caused by the microscopic scabies mite Sarcoptes scabiei. The only host of Sarcoptes scabiei is humans. It should be noted that scabies mites of animals (cats, dogs, pigs, horses, etc.) do not take root in human skin and cannot cause the development of true scabies in humans (damages to the skin of animals by mites are called sarcoptic mange). After stopping contact with a sick animal, a person begins to self-heal.
Scabies became known more than 4000 years ago in ancient Babylon, China, Assyria, and Egypt. In ancient Rome, scabies was called "scabies", in ancient Greece - "psora". In his writings, Aristotle described the discovery of scabies mites as “the presence of the smallest animals in vesicles with transparent contents.” And only after the creation of an optical microscope was the role of scabies mites in the development of the disease proven.
The causative agent of scabies is small in size (female 0.25-0.4 mm, male 0.15-0.2 mm), practically invisible to the naked eye, adapted to life in the thickness of the skin and feeds on the stratum corneum of the epidermis. The male lives no more than 1-3 days; after fertilization of the females, he dies. The reproductive period of the female lasts about one month. She lays 1-2 eggs per day, and about 50 eggs throughout her life.
Infection usually occurs through close bodily contact, usually when sharing a bed with a sick person at night. During the day, ticks are dormant, and in the evening and at night they become active (the female gnaws passages and lays eggs, young adult ticks come to the surface of the skin, where they mate, and the larvae come out and scatter over its surface, so that they can then penetrate inside again) .
Scabies can also be contracted through underwear, bedding, and clothing. Scabies becomes most widespread when people are overcrowded, social and personal hygiene standards are violated (infrequent changes of linen, irregular washing, use of one towel, washcloth, etc.).
The duration of the incubation period (the period from infection to the appearance of the first signs of the disease) averages up to 2 weeks.
The main symptom of the disease is:
- skin itching, worse at night;
- the appearance of scabies on the hands, wrists, elbows, feet, mammary glands of women, genitals of men;
- the appearance of nodular and vesicular rashes, scratching, bloody crusts on the torso (abdomen, buttocks, chest), anterior - lateral surface of the thighs.
A characteristic feature of the disease in adults is the absence of manifestations of the disease on the skin of the face, neck, soles, interscapular area and axillary fossae; in children, scabies can be located everywhere.
If you or your family members experience the above symptoms, you should definitely consult a dermatologist. There is no need to self-medicate, as this will blur the clinical picture of the disease and make it difficult to make a correct diagnosis. Moreover, improper treatment leads to a protracted course of the disease, disrupts the general health of the patient, and most importantly, to infection of loved ones. Timely qualified treatment and compliance with doctor’s recommendations leads to complete recovery. If there is a person with scabies in the family, then during treatment he should be to some extent protected from the rest of the family members. A person with scabies must have his own towel, bed linen, and, of course, he must sleep at night separately from other family members to avoid infecting them with scabies mites. All personal belongings of the patient must be properly disinfected. It is recommended to boil bed linen, underwear, and towels in a 1-2% soda solution or with any washing powder for 10 minutes from the moment of boiling (when boiling, mites die almost instantly). The patient's outer clothing (dresses, suits, etc.) that he wore must be ironed on both sides (preferably with steaming). Fur coats, leather and suede products are hung in the open air for at least 5 days in the warm season or for one day in the cold (ticks outside the “host’s” body die during this time; the cause of tick death, as experiments have shown, is not starvation, but moisture deficiency). In the room where a person with scabies is located, it is necessary to carry out wet cleaning daily using disinfectants or a 1-2% soap-soda solution. When cleaning, special attention should be paid to objects that the patient’s hands often come into contact with, for example, door handles or armrests of chairs.
To prevent re-infection with scabies, it is very important that the treatment the patient receives is adequate and complete. When trying to self-treat scabies, it often happens that the external signs of the disease are eliminated, but the mites remain in the patient’s skin and continue to multiply and infect other people. Therefore, seeking professional medical help is necessary not only to get rid of the unpleasant disease yourself, but also to protect your family and friends from scabies.
Compliance with the rules of personal hygiene is of great importance for the prevention of scabies: timely washing, neatness and other cleanliness skills.
Everyone, both adults and children, love animals. Love for animals , especially in children, is natural. It develops in them kindness, cordiality, tenderness, and patronage of the weak. The closest animals to humans are cats and dogs. Many of them are kept in apartments. There are also many homeless people running from yard to yard. And how can you calmly pass by them if they are still small? Often children, and even adults, take stray animals home or simply play with them. It is everyone’s sacred duty to cultivate in children a love for nature, for all living things, however, when purchasing an animal for a child or for yourself, you need to remember that together with a friend, the possibility of infection with microsporia can enter the apartment.
Microsporia
Microsporia is the most common infectious skin disease of humans and animals. It gets its name from the small size of the spores that form its pathogens.
The causative agents of microsporia are fungi - dermatophytes (literally - growing on the skin) of the genus Microsporum, which nest in the surface layers of the skin and hair. In their microscopic structure, they are similar to ordinary forest mushrooms, since they have mycelium and have adapted to parasitize the skin of humans and animals, causing fungal diseases in them. Microsporia pathogens can remain viable for up to 10 years in the external environment. They are very tenacious, tolerate heat and frost well, but die under the influence of disinfectants and when boiled in soap solutions
Fungi that cause microsporia are common among stray animals: cats, less often dogs; domestic cats, dogs and animals such as hamsters, guinea pigs, etc. are also affected. But most often the main source of infection is stray cats. They, running through the streets, from one yard to another, become infected from each other.
Infection occurs:
- in contact with a sick animal in rare cases with a sick person,
- through household items infected with them: personal belongings, bedding, bath accessories, carpets, upholstered furniture, bedding for animals, baby strollers left on the staircase where cats and other objects can sleep,
- objects of the external environment: dust on staircases, basements of residential buildings and garbage disposals, sand on playgrounds, etc.,
- hairdressing equipment: combs, hair clippers, negligees, shaving brushes.
The incubation period is from 5-7 days to 5-6 weeks.
In sick animals , areas of hair loss (bald patches) are noticeable in the form of round or oval spots, most often in the head area (on the muzzle, the inner surface of the ear), neck, and limbs. These areas are areas of baldness with sparse broken hairs covered with scales and crusts. By merging, they can cover a large surface of the animal’s body, losing their original shapes. Sometimes an animal may look healthy, but be a carrier of microsporia.
People in children under 14 years of age. When smooth skin is affected, round or oval lesions of a pinkish-red color appear. Their surface is covered with scales, bubbles and thin crusts along the periphery. Their sizes usually do not exceed 1 – 2 cm in diameter. Their number varies from one to many. Sometimes the lesions merge. Single lesions of round or oval shape usually develop on the scalp. The affected hair breaks off and protrudes 4–8 mm above the skin level, and is covered with whitish scales at the base.
In case of fungal diseases, timely consultation with a dermatologist is very important. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate; you risk not only blurring the picture of the disease, but also prolonging the treatment time.
To prevent infection with microsporia, you must strictly follow the rules:
- do not allow children to play with stray animals, pick them up and carry them into the house;
- do not allow animals into playgrounds;
- when walking pets, do not allow them to come into contact with stray animals;
- keep pets in specially designated areas, do not take them to bed, regularly check animals with a veterinarian;
- do not throw sick animals into the street, take them to a veterinary hospital;
- When purchasing animals, be sure to check them with a veterinarian;
- observe personal hygiene rules - wash your hands thoroughly with soap after contact with animals,
- do not use other people’s hats, clothes, combs, or towels.
Remember that the most important thing in the prevention of all diseases is to observe the rules of personal hygiene!
Actinomycosis
The disease is caused by the bacterium Actinomyces israeli. This microorganism can live in the human mouth without causing disease. As a result of injury to the mucous membrane, the pathogen can penetrate deeper, causing actinomycosis. The development of the disease is predisposed by inflammation of the oral cavity accompanied by tooth decay, periapical infections of the teeth, and inflammation of the gum pockets. Skin changes occur on the face and neck.
Initially, they take the form of inflammatory tumors, which then disintegrate, forming fistulas, that is, channels that emerge from the surface of the skin. In purulent discharge from fistulas, characteristic yellowish grains are found. Skin changes may be accompanied by general symptoms such as fever and flu-like symptoms. Actinomycosis can also affect the internal organs of the chest and abdominal cavity.
Diagnosis and treatment of the disease requires the mandatory participation of a dermatologist, and sometimes a surgeon. For treatment, general antibiotic therapy is prescribed. Surgical treatment is used to empty pus reservoirs and remove fistulas.
Is it possible to completely cure bacterial dermatological diseases?
In most cases of bacterial skin diseases, treatment with antibiotics is effective and leads to complete recovery. However, in patients with compromised immune systems, such as those with diabetes, cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, or HIV infection, bacterial skin infections can be chronic or recurrent and pose a serious health problem, causing serious complications.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
Unfortunately, contagious skin diseases are always present in human society and can affect people living even in favorable conditions. These diseases are completely curable; it is only necessary to promptly consult a dermatologist when the first signs of the disease appear.
The most common contagious skin diseases are lice, scabies and mycoses (fungal skin infections).
Pediculosis
- a common parasitic disease of humans, the causative agent of which is blood-sucking insects - lice.
There are 3 types: head lice, body lice and pubic lice.
Infection occurs through close household and sexual contact, or through the use of the patient’s belongings.
The first sign of this disease is itching, which is the result of an allergic reaction to the saliva of lice introduced into the skin during blood sucking. With head lice, itching is most often in the back of the head, temples, and behind the ears. Body lice is accompanied by almost unbearable itching all over the body, worsening at night. Moderate itching and burning with pediculosis pubis occurs in the anus and genital area, less often in the eyelid area.
Skin manifestations: Traces of scratching, hemorrhagic crusts, redness (with lice pubis, bluish tint) and papules in places where lice suck blood. Complications are possible in the form of a secondary infection (pyoderma), dermatitis and eczematization of the skin.
Recommendations for the prevention of head lice:
- Regular and careful personal hygiene;
- It is important to use only your personal items and hats;
- Perform a weekly change of bed linen and a daily change of underwear;
- To reduce contact with objects and other people, avoid having your hair down;
- Use a rubber cap in the pool;
- In case of lice infestation, you must immediately seek medical help to prescribe adequate treatment.
- Do not allow children to play with stray animals, pick them up and carry them into the house;
- Do not allow animals into playgrounds;
- When walking your pets, do not allow them to come into contact with stray animals;
- Keep pets in specially designated areas, do not take them to bed, have animals checked regularly by a veterinarian;
- Do not throw sick animals outside, take them to a veterinary hospital;
- After handling animals, wash your hands thoroughly with soap;
- After getting a haircut at the hairdresser, immediately wash your hair with warm water and soap;
- Do not use other people's hats, clothes, combs, or towels.
Microsporia, trichophytosis
– common fungal diseases caused by fungi of the genus Microsporum and Trichophyton.
Infection occurs through contact with a sick animal (cats, dogs, hamsters), in rare cases with a sick person, through infected household items, environmental objects: for example, dust on staircases, hairdressing equipment: combs, hair clippers, brushes for shaving, etc.
Signs of the disease:
In sick animals, areas of hair loss (bald patches) are noticeable in the form of round or oval spots, most often in the head area (on the muzzle, the inner surface of the ear), neck, and limbs. Sometimes an animal may look healthy, but be a carrier of microsporia.
A person's smooth skin and scalp may be affected, and rarely, nails. When smooth skin is affected, round or oval lesions of pinkish-red color appear, their surface is covered with scales, blisters and thin crusts along the periphery. Single lesions of round or oval shape usually develop on the scalp. The affected hair breaks off and protrudes 4-8 mm above the skin level, and is covered with whitish scales at the base.
If the scalp is affected, treatment is carried out in a skin clinic, since long-term systemic antifungal therapy requires regular monitoring, and daily hair removal and treatment of hair in the area is also necessary.
In case of fungal diseases, timely consultation with a dermatologist is very important. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate; you risk not only blurring the picture of the disease, but also prolonging the treatment time.
Recommendations for the prevention of fungal infections:
Scabies
– a contagious parasitic skin disease caused by the scabies mite. Scabies can be contracted through underwear, bedding, and clothing. During the day, ticks are dormant, and in the evening and at night they become active. Scabies becomes most widespread when people are overcrowded and standards of public and personal hygiene are violated.
Main symptoms of the disease:
- skin itching, worse at night;
- the appearance of scabies on the hands, wrists, elbows, feet, mammary glands of women, genitals of men;
- the appearance of nodular and vesicular rashes, scratching, bloody crusts on the body (abdomen, buttocks, chest), thighs.
By following simple rules of personal hygiene, you will protect yourself from scabies infection:
- Regular hand washing;
- Take a shared shower daily;
- Do not forget about frequent changes of linen and regular sanitization of outerwear;
- New clothes must be washed before wearing;
- Treat outer clothing purchased at markets with steam or put it in a plastic bag and tie it tightly (if left without air, ticks will die in a few days).
- All personal hygiene items must be strictly individual.
If you or your family members experience any of the above symptoms, you should definitely consult a dermatologist. There is no need to self-medicate, as this will blur the clinical picture of the disease and make it difficult to make a correct diagnosis. Moreover, improper treatment leads to a protracted course of the disease, disrupts the general health of the patient, and most importantly, to infection of loved ones. Timely qualified treatment and compliance with doctor’s recommendations leads to complete recovery. Therefore, seeking professional medical help is necessary not only to get rid of an unpleasant disease yourself, but also to protect your family and friends from contagious skin diseases.
And most importantly, treatment for each specific patient MUST be carried out simultaneously with anti-epidemic measures (disinsection of hats, clothing, bedding and premises, etc.) in order to avoid re-infection.