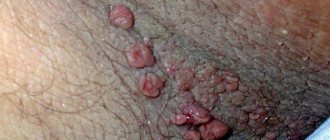
New growths on the skin do not always cause physical discomfort, but they negatively affect the psychological state. Such a disease is warts, a pathology caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). Mostly children and young people suffer from warts. Warts are expressed by the proliferation of virus-infected skin cells. They are not dangerous, but can be injured by mechanical action, bleed, and open access to secondary infection.
Rice. 1. A wart is caused by a virus.
Composition and release form
The drug is available in several dosage forms:
- Pills. Prescribed for the treatment of papillomas in different parts of the body. They are used orally, so they allow you to fight the main problem from the inside. After completing the course of therapy, the level of pathogenic pathogens in the body is noticeably reduced.
- Ointment. Applied topically, it is effective against the most common human papillomavirus infection, which is localized on the surface of the body. The antiviral agent is applied directly on top of the warts, so there is a pronounced therapeutic effect at the local level. When the ointment is distributed on the skin, the main substance penetrates the bloodstream, preventing viral pathologies in the future.
- Solution. Mainly used for chronic forms of the disease. The concentration of the drug is selected by the doctor taking into account the clinical picture and the results of an analysis for the content of viral agents in the blood. In this case, it is highly recommended not to self-medicate, so as not to provoke a worsening of the condition.
The main component is acyclovir, its content differs depending on the dosage form.
pharmachologic effect
Acyclovir has a pronounced antiviral property. It is used to treat papillomas, warts and other infectious conditions that arise as a result of the penetration of dangerous pathogens into the body.
But it is worth understanding that the drug exhibits pharmacological activity only in close contact with viral cells. The medicine affects the hereditary apparatus, preventing the further development of the disease. The resulting products are excreted along with urine.
The active substance Acyclovir is characterized by low bioavailability. Therefore, it easily penetrates into all tissues and cellular structures, including blood. But due to this property, the antiviral drug is not used in the treatment of women during pregnancy and breastfeeding, since the main component passes into breast milk.
Treatment of warts with Acyclovir
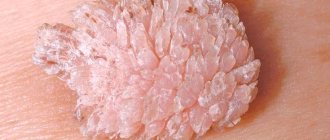
You can come across the claim that Acyclovir removes warts, although this is ambiguous. Acyclovir is an antiviral agent and is suitable for getting rid of viral diseases of various natures. For example, Acyclovir copes well with herpes, but with HPV its use is not always effective. The drug can help only at the early stage of the disease, when warts just appear. Acyclovir is available in the form of cream, ointment and tablets. When applied externally, the components are absorbed into the epidermis and prevent the spread of HPV from diseased cells to healthy ones. Over time, the warts dry out and fall off. Acyclovir cream simultaneously moisturizes the skin, so scars do not form at the site of eliminated warts. In case of serious damage to the body by warts and a weakened immune system, Acyclovir tablets are prescribed.
Rice. 3. Acyclovir cream is applied to the warts.
Indications
The drug is prescribed for the treatment of the following conditions:
- Infectious lesions of the skin and mucous surfaces due to herpes viruses.
- Chicken pox.
- Shingles.
- Herpes localized in the genital area.
- Primary and secondary herpes diseases in persons with immunodeficiency.
- Viral pathologies among people with a normal level of immune status.
Modern methods of treating genital warts
Genital warts (synonyms: condylomata acuminate, viral condylomas, genital warts, genital warts) are diseases caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). Diseases caused by HPV are among the most common contagious viral infections in humans. HPV is a small, round, double-stranded DNA virus with a diameter of 50 to 55 nm. To date, more than 80 types of HPV have been described (Table 1). Infections caused by HPV are highly specific to the epidermis, since HPV has a tropism for epithelial cells of the skin and mucous membranes.
Genital warts are highly contagious. Infection occurs through contact, most often sexually. The virus can survive for a long time on infected objects. Small abrasions, cracks or abrasions serve as entry points for the virus. The virus can also spread by autoinoculation. Lack of personal hygiene, wearing tight underwear, maceration of folds in obese people, as well as immunodeficiency conditions contribute to the development of lesions over a large area of the skin.
Over the past 20 years, there has been an increase in the incidence of genital warts. In the United States, genital warts (or genital warts) are one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases. The incidence of genital warts exceeds 106.5 cases per 100 thousand US population, which is about 0.1% of the entire population [1]. Close attention to this disease is explained by the fact that some of the types of HPV that cause genital warts can lead to malignancy of the process. The most potentially dangerous are types 16 and 18. It is no coincidence that it is important to promptly diagnose and treat genital warts. Recurrence of genital warts is not always associated with re-infection, but can be caused by reactivation of the virus.
Clinical picture. The incubation period lasts from 3 weeks to 6 months and averages about 2.8 months. Men and women are equally susceptible to this disease. The average age of patients ranges from 22 to 25 years.
Typically, genital warts are localized on the genitals and in the perianal area. In HIV-infected patients, genital warts may appear in unusual places, such as the face, eyelids, and ears. In men, the most common locations are the penis, urethra, scrotum, perianal, anal and rectal areas [2]. The elements of the rash are flesh-colored, can be represented by smooth papules the size of a pinhead, and in the initial stages of development are not always noticeable on the penis. To identify them, a test is carried out with 5% acetic acid. After treatment of the skin, the color of the papules becomes whitish. Subsequently, the papules grow and take on a warty or thread-like shape, resembling cauliflower or cockscomb. As a rule, genital warts are multiple and located in groups.
In women, the clinical picture of genital warts can be varied. Classic exophytic lesions on the external genitalia are common and easily detected during examination, but they can also be accidental findings during colposcopy or sigmoidoscopy. On the labia minora and on the vestibule of the vagina, condylomas are moist, velvety or multiple finger-like growths and occupy a significant area. Condylomas in the cervical canal are found in 20% of women infected with HPV and with genital warts localized on the external genitalia. Localization of genital warts on the cervix or in the cervical canal is considered an unfavorable factor, as it can contribute to the development of cervical cancer [3].
Even with timely and rational treatment, genital warts often recur. This is due to the fact that the virus can remain in an inactivated state for a long time in apparently healthy areas of the skin and mucous membranes.
Differential diagnosis of genital warts is carried out with secondary syphilis (condylomas lata), molluscum contagiosum, bowenoid papulosis, lichen planus, lichen planus, angiokeratomas, angiofibromas on the coronal sulcus of the glans penis, folliculitis, soft fibroma, pilar cyst (Table 2).
Diagnosis of genital warts is usually not clinically difficult. Additionally, in some cases, a test is carried out with 5% acetic acid. To do this, a medical napkin moistened with a solution is placed in the area of the expected localization of genital warts for 5–10 minutes, after which the rash acquires a whitish tint [4].
When diagnosing genital warts, it is necessary to conduct testing for syphilis and HIV infection.
A biopsy is indicated for those patients who suspect precancerous lesions or squamous cell carcinoma. Removing genital warts does not reduce the risk of developing cervical cancer. Therefore, all women who have a history of genital warts should undergo an annual cytological examination of cervical smears in order to timely detect the oncological process.
Treatment and prevention
Using condoms reduces the risk of infecting sexual partners. It is impossible to completely remove HPV; you can only remove genital warts, easing the patient’s condition and reducing the risk of infecting a sexual partner. There are several treatment methods for genital warts. They all have certain disadvantages.
Cryodestruction is one of the most commonly used treatment methods. The affected surface is treated with liquid nitrogen using a cotton swab or spray. The treatment is repeated every 1–2 weeks until all condylomas are completely removed. The method rarely leads to scarring and is low cost. Cryodestruction can cause severe pain. It is not always possible to treat the entire affected surface at once. In some cases, hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation may develop after cryodestruction.
Diathermocoagulation is a painful method of treatment and leaves behind permanent scars, therefore it is used only for the removal of single condylomas.
Laser removal is carried out using carbon dioxide and neodymium YAG lasers (yttrium aluminum garnet lasers). Scars may remain after removal.
Drug treatment methods. Condilin (podophyllotoxin) - 0.5% solution in 3.5 ml bottles with an applicator. The component of Condilin, podophyllotoxin, is the most active in the composition of the plant extract of podophyllin; when applied topically, it leads to necrosis and destruction of genital warts. The advantage of this treatment method is that the patient can independently treat the affected areas of the skin in accessible areas. Using a plastic applicator, the drug is applied to the condyloma; All condylomas are gradually wetted, but no more than 50 pieces at a time (in area no more than 10 cm2). The drug should be applied with caution, avoiding healthy areas of the skin. The first time the treatment is carried out by a doctor or nurse, teaching the patient how to apply the drug correctly. After treatment, the preparation must dry to avoid irritation of the surrounding skin or ulceration. Condilin is applied 2 times a day for 3 days, and then take a 4-day break. The duration of treatment should not exceed 5 weeks. Contraindications for the use of the drug are pregnancy, lactation, childhood, and the use of other drugs containing podophyllin.
Solcoderm is a mixture of acids: 65% nitric, 98% acetic, as well as lactic and oxalic acid and copper nitrate; Available in the form of a solution (ampoules of 0.2 ml). After it is applied to the surface of the skin, it turns yellow, after which mummification of the treated tissue occurs. Treatment must be carried out by medical personnel. The drug is applied to the surface using a glass capillary or applicator, after which the drug must dry. It is allowed to treat an area of no more than 4–5 cm2 at a time. If necessary, treatment can be repeated after 4 weeks. Application of the drug may be accompanied by severe burning and pain, in some cases hyperpigmentation and scarring may occur.
Interferon preparations are injected directly into genital warts. The procedure is painful and requires repeated treatment.
Trichloroacetic acid in a concentration of 80–90% is applied directly to the condylomas. Its remains are removed with talc or sodium bicarbonate. If necessary, treatment is repeated at intervals of 1 week. If after 6-fold treatment genital warts remain, then it is necessary to change the treatment method.
Literature
- KR Beutner, TM Becker, KM Stone. Epidemiology of HPV infections // J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1988; 18: 169–172.
- S. M. Syrjanen et al. Anal condylomas in men // Genitour. Med. 65: 1989; 216–224.
- MJ Campion. Clinical manifestations and natural history of genital human papillomavirus infection // Obstet. Gynecol. Clin. North. Am. 1987; 14: 363–388.
- D. E. Fitzpatrick, D. L. Eling. Secrets of dermatology // M.: ZAO Publishing House BINOM, 1999. 511 p.
L. P. Kotrekhova, Candidate of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor K. I. Raznatovsky, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor of St. Petersburg Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education, Moscow
Contraindications
Obvious contraindications for Acyclovir are:
- Serious heart pathologies.
- Kidney diseases, especially chronic forms, acute failure.
- Nervous diseases.
- Increased hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
- Time of bearing a child and breastfeeding.
- Children under 3 years old.
The antiviral drug is used with extreme caution in the treatment of elderly people and the presence of dehydration.
Side effects
Taking Acyclovir in any dosage form can provoke the development of the following side effects:
- Headache, even migraine.
- Dizziness.
- Intense aching pain in the kidney area.
- Dyspeptic disorders - vomiting, feeling of nausea, stool disturbances, abdominal discomfort.
- Shortness of breath.
- Signs of an allergic reaction - skin rashes, itching. Rarely, anaphylactic shock and urticaria.
- Systemic manifestations include fatigue, malaise, fever, tissue swelling and visual disturbances.
- Increased sleepiness.
- High excitability.
As a rule, the drug is quite well tolerated by patients. Side effects are observed in rare cases; patients with acute renal failure and other severe concomitant pathologies are most susceptible to them.
Instructions for use
The medicine must be used strictly according to the instructions and after consultation with the attending physician. Self-medication is highly discouraged. Taking an antiviral drug directly depends on the form of release:
- Pills. Intended for oral administration. Take during or after meals according to the following scheme: 5 times a day, 1 piece, with a sufficient volume of water. Depending on the indications and the patient’s well-being, the therapeutic dose can be increased to 8 tablets. The highest daily dose of Acyclovir should not exceed 10 tablets.
- Ointment. Used locally, the product is applied directly to the affected area of the skin in a small amount. Frequency of administration: every hour until the wart completely disappears. The course of therapy is no more than 10 days.
- Powder for preparing a solution. Used internally. It is first recommended to undergo laboratory tests to determine the level of viral cells in the body. This form should only be taken as directed by a specialist. The duration of the treatment course is no more than a week.
If long-term therapy is required, in this case a minimum break of 10 days is taken. After which the doctor can extend the treatment course if necessary.
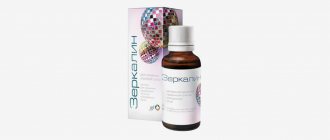
Method of using Acyclovir for warts and side effects
If you have warts, apply Acyclovir ointment or cream every 4 hours. When Acyclovir is prescribed orally, the dosage is 4 tablets of 200 mg per day. A package of 20 pieces is enough for 5 days. This is exactly what the course of treatment consists of. In case of a complex course of the disease, taking Acyclovir can be extended to 10 days. You cannot take the pills for longer, even if during this time recovery and getting rid of warts have not occurred. Along with Acyclovir for warts, you need to take immunomodulatory drugs and vitamins: Supradin, Immunal, Neurovitan, Anaferon, Lykopid, folic and ascorbic acid. External use of Acyclovir for warts causes virtually no side effects.
Rice. 4. Acyclovir tablets are taken orally for multiple warts.