Original title of the article: “The effectiveness of using the Stop Demodex series of drugs in the complex treatment of patients with demodicosis”
Pritulo O.A., Ngema M.V., Prokhorov D.V., Smolienko V.N., Vintserskaya G.A., Ravlyuk D.A. State Institution “Crimean State Medical University named after.
S.I. Georgievsky" Demodicosis is a chronic parasitic disease of the skin of humans and animals, widespread in all climatic zones of the globe. Its causative agents are demodicid mites, representatives of the group of Arachnids, the family Demodecidae, most adapted to the parasitic lifestyle [3,6,8,11,13,15].
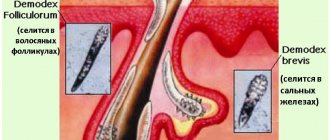
It has now been proven that the causative agents of human demodicosis are mites Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis, belonging to the phylum Arthropoda, the class Arachnida, and the genus Acarina. They are representatives of an independent family Demodecidae from the order Trombicliformes [1,2].
Pets also suffer from demodicosis. Infection of cats and dogs by Demodex cati (a parasite of cats) and Demodex canis (a parasite of dogs) mites causes a disease known as glandular red mites, which can be accompanied by severe inflammation of the hair follicles and sebaceous glands, hair loss, peeling, thickening of the skin, the formation of pustules, sometimes boils, generalization of the pathological process and even end in death.
According to the concept of the life pattern of species, mites Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis belong to permanent monoxenic skin parasites; in addition, mites are community-hospital, that is, they parasitize together on the same host [5]. In accordance with the high level of topical and trophic specificity, the causative agents of demodicosis predominantly affect the skin in the area of nasolabial folds, chin and eyelids [7,9,14].
Demodex folliculorum is most often found in the area of the nose and outer ear in 38% of cases, in the forehead in 30%, and in the perioral area in 29% [10]. As for Demodex brevis, its primary localization is the skin of the upper half of the chest and neck.
Depending on the predominance of certain symptoms, several clinical forms of demodicosis . Some researchers distinguish erythematous-squamous (or seborrheic), papular, papulovesicular, pustular, rosacea-like, combined and asymptomatic forms.
Others note low-symptomatic, erythematous-squamous, acneiform, rosaceomorphic, sycosiform, small-nodular forms, while others note erythematous, pustular, papular, and combined forms. Depending on the prevalence of the A.A. process. Antonev et al [1]. The following forms of demodicosis are distinguished: limited (with localization of rashes mainly in the folds and near the corners of the eyes), diffuse, in which the entire skin of the face is affected; common when the inflammatory process extends beyond the face.
According to the course of the disease, acute, subacute and chronic recurrent demodicosis are distinguished. According to the clinical picture, the following forms of skin demodicosis have been identified: low-symptomatic erythematous-squamous, papular, pustular, combined and cystic [4].
In addition, there are several types of arrangement of efflorescences during demodicosis :
- central type , in which the rashes are localized mainly in the T-zone (the central part of the forehead, the glabella, the back and wings of the nose, the nasolabial zone, the central part of the chin) - the zone of greatest density of the sebaceous glands;
- medial type - the rashes are located mainly in the area of the frontal tubercles, the central part of the cheeks and the area of the chin protuberance;
- asymmetrical type - rashes are found only on one side of the face; lateral type - rashes are located on the sides of the face;
- total type - rashes are distributed evenly over the entire surface of the face.
The clinical picture of human demodicosis may resemble the clinical picture of rosacea, acne vulgaris, photodermatosis, and seboroid. Often, on a congestive-hyperemic, slightly swollen, flaky background with symptoms of oily seborrhea, follicular rashes of the small-papular and small-pustular type are located. Also, some researchers note that the clinical picture of demodicosis resembles rosacea, identifying demodicosis with rosacea.
1.What is demodicosis and the factors that provoke it?
Demodicosis (demodex, skin mite)
microscopic mite Demodex folliculorum, which inhabits the sebaceous glands of the skin and hair follicles of the eyelids.
This parasite most often causes problematic facial skin and acne on the body (back, chest, shoulders). There is an opinion that inflammation and ulcers on the skin are associated with adolescence and do not require treatment.
However, the disease often remains with a person throughout his life. This indicates that adolescence is only a background for the onset of skin parasite activity. Hormonal changes and immune instability during growing up only create favorable conditions for the activity of skin mites, with which the body is already infected for some reason. The mite lives everywhere, and sooner or later it gets on the skin of any person. However, it colonizes and begins to actively reproduce only under certain conditions:
- increased skin oiliness;
- weakened immune system;
- metabolic disorders;
- violations of lifestyle, hygiene;
- chronic diseases that reduce the protective properties of the skin;
- constant stress factors.
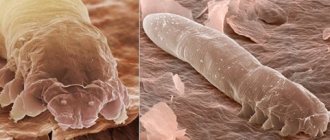
Demodex folliculorum parasite
It has an oblong shape, it is almost transparent, the size of an adult is 0.1 - 0.4 mm.
It is impossible to distinguish it without special equipment. The mite feeds on skin cells and sebum. The parasite lives only a few days. The individual is designed in such a way that it does not have excretory organs. During its life, the tick only feeds and produces offspring. Then he dies. The development of the larva from the egg also takes 2-3 days. Thus, it can be assumed that intensive treatment destroys all adult parasites and the larvae they lay within a week. However, in practice everything is not so simple. The chronic course of demodicosis is caused by constant reinfection of a person
from his own household objects. There are especially many skin mite larvae on towels, pillowcases, combs and massage hair brushes, and cosmetics.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Clinical variants of demodicosis
Demodicosis in humans can develop as a primary independent disease, or it develops against the background of existing skin diseases (perioral dermatitis, rosacea, acne, seborrheic dermatitis, etc.), aggravating their course.
Primary demodicosis
In primary demodicosis, inflammatory skin elements resolve after antiparasitic therapy. About 40% of cases of primary demodicosis develop in patients suffering from rosacea.
Primary demodicosis is characterized by:
- the onset of the disease over the age of 40 years;
- The areas most often affected are around the mouth, eyes and outer ear;
- inflammatory elements are located asymmetrically and are accompanied by itching;
- acne and rosacea are absent;
- high content of mites on the skin;
- positive effect of the antiparasitic treatment.
Secondary demodicosis
Secondary demodicosis develops against the background of diseases accompanied by a sharp suppression of the immune system (HIV infection, leukemia, etc.), long-term use of corticosteroids and cytotoxic therapy, or develops against the background of acne and rosacea, complicating their course. This form of the disease is registered in 33% of patients with acne.
Secondary demodicosis is characterized by:
- the disease appears at any age;
- lesions are widespread;
- presence of anamnesis and clinical picture of relevant diseases.
Papulopustular rashes on the skin of the face are a reason for diagnosing demodicosis.
Rice. 8. Demodectic mange on a woman’s face.
2. Symptoms of the disease
In low concentrations, the demodex mite does not manifest itself in any way. The skin's own immunity does not allow the parasite to have a negative impact on it. But under certain unfavorable conditions, the protection weakens, and the tick begins to actively feed and reproduce. Sebum contributes to this. Signs appear on the skin, collectively called “problem skin”: acne and pimples, enlarged pores, inflammation of the sebaceous glands. Most often, the parasite is localized on the chin, nose, cheeks, and forehead. The skin becomes unhealthy, oily shine appears, firmness and elasticity are lost. Mite damage to the eyelids also leads to inflammation, sometimes even leading to eyelash loss. The skin becomes lumpy, painful, itching and a tickling sensation on the skin often occur - these are parasites moving along the surface. Demodex is especially active in the evenings and at night.
Visit our Dermatology page
Forms of demodicosis in humans
Depending on the nature of the manifestations on the skin, several forms of demodicosis are distinguished, the symptoms of which are characteristic of the corresponding diseases. Not to be confused with these diseases!
Acneform form
The acneiform type of demodicosis is characterized by the appearance of papules and pustules on the facial skin, which are similar to acne.
Rice. 16. Demodectic mange of the face in women. Acneform form of the disease: papular (photo on the left) and papulopustular (photo on the right).
Rosacea-like form
The rosacea-like type of demodicosis is characterized by the appearance of papules against a background of diffuse erythema. Demodex brevis (short mite) causes the appearance of inflammatory infiltrates and granulomas in the deep layers of the dermis, which are similar to the granulomatous form of rosacea.
Rice. 17. Rosacea-like form of demodicosis: in the form of diffuse erythema (photo on the left), granulomatous form (photo on the right).
Seborrheic (erythemo-squamous) form
The seborrheic form of demodicosis is characterized by the appearance of redness and rash on the facial skin, accompanied by lamellar peeling.
Ophthalmic form
The ophthalmic form of demodicosis occurs with damage to the eyeballs and eyelids. Redness, dryness, irritation, sensation of a foreign body in the eye, fatigue are the main symptoms of eye demodicosis. Itching of the eyelids, redness and swelling of their edges, the appearance of scales or crusts on the eyelids are the main symptoms of demodicosis of the eyelids.
Read in detail in the article “Demodicosis of the eyelids and eyes”
Rice. 18. Demodectic mange of the eyelids. Lamellar peeling is clearly visible (photo on the left). On the ciliated edge of the eyelid, scales form a “collar” around the eyes (photo on the right).
The role of demodex mites in the formation of androgenetic alopecia
There is an assumption that the presence of mites in the hair follicles aggravates the development of androgenetic alopecia. During inflammation, T-lymphocytes are activated, which induce collagen synthesis, resulting in fibrous degeneration of hair follicles.
Rice. 19. Demodicosis of the scalp.
3.Diagnosis of the disease
After a visual examination and conversation with the patient, the dermatologist prescribes a microscopic examination
.
Material for analysis is taken by scraping the epidermis from the affected areas of the skin. It is also recommended to analyze eyelashes
taken from different parts of the eyes. Express analysis makes it possible to get instant results. During the study, adult ticks, their eggs and shed chitinous shells are discovered. In order for the dermatologist to see a complete picture of the density of mite colonization of the skin, it is recommended not to wash your face for 24 hours before the examination. What is important for making a diagnosis in this case is not the fact of detecting a tick in itself, but the number and activity of the parasite, as evidenced by the number of larvae and eggs.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
About the brand Demodex Complex
For more than 30 years, Demodex Complex has been a leader in the field of skin care for demodicosis. We are recognized and trusted by dermatologists as one of the leading and most recommended brands.
Our products are designed to kill demodex mites, restore and improve skin health, and protect against recurrent demodex mites. We give you and your family the feeling of confidence that comes from glowing, healthy skin.
4. Treatment of demodicosis
Treatment and prognosis for patients with demodicosis is always a very individual issue. Efforts should be aimed not only at cleansing the skin of mites, but also at eliminating the factors that cause the weakening of skin protection. In parallel with medical procedures, it is also worth taking seriously sanitization, and even better, replacing some household items potentially contaminated with demodicosis larvae.
Thus, treatment includes three components:
- 1. Removing the tick from the surface of the skin and creating unacceptable conditions for the life and reproduction of skin parasites.
- 2. The maximum possible elimination of the causes that served as a favorable background for the onset of the disease.
- 3. Treatment of living space and objects in contact with the skin to reduce the risk of re-infection.
Methods and means of influencing ticks have been developed quite well. As a rule, the most effective treatment is associated with the use of sulfur-containing drugs
(ointments, lotions, masks).
Demodex tolerates this substance very poorly. The parasite is quite well protected by several layers of shells from the action of other unfavorable factors, but stops feeding and laying eggs in an environment saturated with sulfur. In some cases, treatment with metronidazole
. As a result of treatment, the chain of continuous reproduction of the tick is interrupted. An important component of treatment for skin mites is the removal of excess oil from the surface of the skin, since skin secretions are the basis of the parasite’s diet.
To implement the second component of treatment, consultation and examinations with doctors of different specialties
: endocrinologist, neurologist, gastroenterologist, gynecologist. Eliminating chronic infections, metabolic disorders and hormonal imbalances eases the burden on the immune system. The body's own defenses are restored.
Despite the fact that the life cycle of the skin mite is quite short, long-term treatment (1-3 months) is most effective. Constant contact with an infected environment forces the demodex larvae that come into contact with the skin to be destroyed again and again. to minimize the likelihood of re-infection with ticks as much as possible
To do this, the dermatologist prescribes
a number of rules for the patient, which must be followed strictly
so that the living space is completely sanitized and the effect of treatment is long-lasting:
- daily change of towels;
- daily replacement of pillowcases;
- washing bed linen at 90 degrees;
- using disposable towels and cotton pads to wipe the skin;
- replacing all cosmetics with new ones, which are now used only after treating the skin surface with antiseptic preparations;
- avoiding scratching and contact of fingers with the skin of sick and then healthy areas;
- renewal or thorough sanitation of hats, scarves, handkerchiefs, glasses, razors - anything that came into contact with contaminated skin.
Demodectic mange against the background of rosacea
Demodicosis complicates the course of rosacea in 88.7%. The disease is more common in women over 30 years of age. The phymatous form of the disease is more common in men. The pathological process is characterized by redness of the skin of the face, associated with the expansion of small superficial vessels, the appearance of papules and pustules. Papules increase in size over time and merge, forming dense infiltrates. The sebaceous glands become hyperplastic. Fibrosis develops. Persistent redness and fibrous lumps on the nose are called rhinophyma.
There are many reasons for the development of diseases. Factors contributing to the development of the disease can be divided into endogenous and exogenous.
Rice. 20. Erythematotelangiectatic form of rosacea. Multiple telangiectasias (dilated subcutaneous arterioles) are visible on the skin.
Rice. 21. The photo shows the papulopustular form of rosacea. Against the background of erythema (redness), multiple rashes are visible, which are papules with thin scales on the surface. The affected areas are infiltrated and swollen.
Rice. 22. Demodex brevis (short mite) causes the appearance of inflammatory infiltrates and granulomas in the deep layers of the dermis, which are similar to the granulomatous (phymatous) form of rosacea. The photo shows the phymatous (papular-nodular) form of rosacea.
Rice. 23. Severe form of rosacea.
Rice. 24. The ocular form of rosacea is registered in 50% of patients. Inflammation of the eyelids, redness of the conjunctiva, iritis and keratitis are the main manifestations of the disease.
results
Results of a study of the acaricidal effect of the drug D-18, its base and a reference drug (ivermectin 1%) on mites of the genus Demodex
are presented in the table.
Average time of death of Demodex mites in the experiment, hour Note.
* - p≤0.05 - significance of the difference in the studied trait in comparison with intact ticks and ticks surrounded by the base of the drug. An acaricidal effect of the drug D-18 was noted, comparable in time of death of ticks with the results obtained for the comparison drug (ivermectin 1%); no statistically significant differences were found between these experimental groups.
The absence of differences between the studied characteristics of D-18 ointment and the reference drug (ivermectin 1%) indicates an equally pronounced acaricidal effect when using the drugs.
Important information
Compound
The powder is created on the basis of natural ingredients. It includes:
Dimethicone – promotes moisture retention.
Silica gel – provides increased water resistance.
Hydrogenated lecithin - restores skin elasticity and helps eliminate flaking.
Titanium dioxide is an effective UV filter that protects the skin from solar radiation and preserves its youth.
There are no parabens and other harmful components, as well as oils in the powder. The packaging is a stylish mirror case, which has a separate section for a sponge.
How to prepare for analysis
To obtain reliable information about the presence of a parasitic mite on the eyelashes or facial skin, the following rules must be followed before taking the test:
- Do not wash your face with products containing a high alkaline content for 24 hours before the test;
- stop using decorative and medicinal cosmetics, ointments and creams two days before visiting a doctor;
- Avoid contact with eyelashes with shampoo two days before the test;
- You cannot use eye drops the day before the procedure, with the exception of drops that are prescribed for serious eye diseases.
The parasitic mite is most active in the evening hours, as it does not tolerate ultraviolet light. Therefore, the most favorable time to submit a scraping for demodex is the evening hours. But in medical laboratories, material is collected for demodex in the morning, which can make it difficult to identify the causative agent of the disease, provoke its active reproduction and aggravate the patient’s condition.
References
- Fromstein, S., Harthan, J., Patel, J. et al. Demodex blepharitis: clinical perspectives. Clin Optom (Auckl), 2022. - Vol. 10. - P. 57-63.
- Jacob, S., VanDaele, M., Brown, J. Treatment of Demodex-associated inflammatory skin conditions: A systematic review. Dermatol Ther., 2022. - Vol. 32(6).
- Bitton, E., Aumond, S. Demodex and eye disease: a review. Clin Exp Optom., 2022.
- Elistratova, L.L., Potaturkina-Nesterova, N.I., Nesterov, A.S. Current state of the problem of demodicosis. Fundamental Research, 2011. - No. 9-1. — P. 67-69.
How to test for demodex
The method of collecting material for scraping for demodex depends on the location of the mite and is carried out strictly in laboratory conditions.
Facial skin scraping involves examining particles of the epidermis that are taken from the affected areas. The doctor, using a scalpel or eye spoon, scrapes off the diseased particles of the epidermis or takes the contents of the pimple for examination. Testing for Demodex from eyelashes involves examining several of the patient's eyelashes. For analysis, the doctor takes four eyelashes from the lower and upper eyelids. Taking material for demodex testing is a painless procedure that can cause only slight discomfort to the patient.
The material taken for analysis is placed in a special solution (glycerin or alkaline) on a glass slide and examined under a microscope. The study consists of counting subcutaneous mite individuals.
Also, to determine the general condition of the patient and identify concomitant diseases (anemia, allergic reactions, inflammatory processes or bacterial infections), a general blood test is prescribed, which is recommended for all patients without exception.