A mole is a benign tumor resulting from a defect in the development of nevus cells.
It is characterized by the formation of pigmented neoplasms or spots on the conjunctiva, skin, mucous membranes.
They consist of melanocytes - cells that produce melanin.
A benign mole can be congenital or acquired.
It can be flat or raised above the skin, hard or soft, uniform in consistency or interspersed.
It can have different colors - from black to red.
Types of benign moles:
- Borderline nevus. Benign flat moles that look like brown spots with a diameter of up to 1 centimeter. Localized on the surfaces of the hands, feet, labia, penis, nipple. Over time, they may disappear spontaneously;
- Epidermal. A congenital pathological formation of brown color, covered with hair, oval or round in shape. There are epidermal benign moles with uneven edges, clear boundaries, a bumpy and folded surface, and hanging moles. In 5% of cases, large benign moles (giant) are diagnosed, occupying the entire anatomical segment or most of it, located on the head, torso, upper/lower extremities;
- Dysplastic (atypical). An acquired tumor that develops due to uncontrolled division of melanocytes. Localized on the limbs/torso, it looks like an uneven asymmetrical bumpy spot with torn edges. It is located in an intermediate place between superficially migrating melanoma and acquired nevus;
- Nevus Spitz. It is characterized by diffuse pigmentation, a tendency to grow rapidly, and is located on the cheek, neck, nose;
- Vascular (nevus of Unna). A red mole on the lip, bridge of the nose, and the back of the head, which is characterized by slow regression and lack of growth.
Which moles are benign and which are not can only be diagnosed by a doctor after a thorough examination and dermatoscopy.
If cancer is suspected, a targeted biopsy and histology of the altered area of skin must be performed.
Causes of brown spots
The color of human skin is determined by the amount of melanin pigment produced by the main layer of epithelium, which protects against the dangerous effects of ultraviolet radiation. A mole with a brown halo appears when the production of melanocyte cells fails, due to the following reasons:
- weakened immunity, often after exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- suffered stress, nervous breakdowns;
- an aging body causing hyperpigmentation throughout the body;
- pregnancy, postpartum period;
- hormonal imbalances during puberty in adolescents, menopause in women;
- taking hormonal medications;
- abuse of sunlight, solarium;
- the possibility of injury to the formation;
Congenital
The causes of congenital birthmarks are considered to be the process of migration of melanoblasts during intrauterine development. They are benign and do not pose a danger to the child. All information about moles and spots is embedded in DNA and is inherited from parents to children.
Acquired
The reasons for the appearance of acquired spots are the development and maturation of the body, the influence of internal and external factors.
The first acquired spots may appear at the age of one year.
They are not dangerous if the shape is not asymmetrical, the color is uniform and the size is no larger than the tip of a finger. Freckles are considered a common type of acquired element.
What types of “moles” are there?
When pronouncing the word “mole,” the patient means a permanent spot or nodule on the skin. In fact, there are hundreds of types of benign skin formations that can be called this. Here are the most common ones.
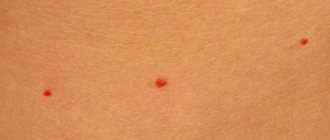
Hemangioma or “red mole”
This is a benign formation consisting of vascular tissue cells. At least one hemangioma can be found in every adult. They look like red/cherry dots or appear as spider veins (spider hemangioma). They can appear spontaneously throughout life, sometimes at the site of injury or inflammation (for example, at the site of a pimple). This is an absolutely benign formation, it does not turn into cancer. To be removed for cosmetic purposes only.
Keratoma
A benign skin formation consisting of epidermal cells. In the old books they were called “senile”, but this definition is not used now, since they can also occur in young people. A keratoma looks like a gray or brown spot protruding above the skin with a rough surface. Their typical location is in areas exposed to solar radiation (face, chest, upper limbs) or places of constant trauma (under laundry straps and elastic bands). Keratomas almost never become malignant, but they can actively grow, itch and bleed. Therefore, dynamic monitoring of these formations is necessary. Can be removed for cosmetic purposes.
Acrochordon (fibroepithelial polyp or “papilloma”)
A benign skin formation, representing a soft polyp on a flesh-colored stalk. Usually occurs in places of mechanical friction and in skin folds, the elements can be located in groups. Doctors often associate these tumors with the papilloma virus. Acrochordons are recommended to be removed as they tend to grow and spread and can become a serious cosmetic problem. They do not pose a danger to life or health.
Melanocytic nevus (mole, birthmark)
A benign congenital or acquired skin formation consisting of melanocytes (pigment cells of the skin). This is a flat spot or plaque raised above the skin, most often brown in color. More than 10 types of nevi have been described. On average, an adult has 20-30 such moles on his body. They appear and grow under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. Requires dynamic monitoring, the risk of degeneration into melanoma is 1:200,000. They can be removed by a dermatologist, dermato-oncologist or cosmetologist with subsequent referral for histological examination.
Is a brown halo around a mole dangerous?
Nevi spread throughout the body, occupying varying depths of the skin. Depending on the location, the risk of the tumor degenerating into melanoma is determined. Some doctors believe that moles and spots appear in places close to diseased organs.
Areas of possible injury (head, face, neck, arms, legs) are considered dangerous.
It is necessary to control large vascular elements located on the forehead, hands, feet, neck and back.
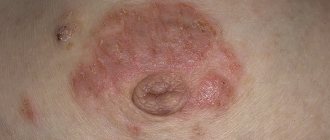
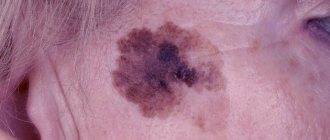
A benign mole is usually surrounded by healthy skin color. Framing a nevus with red, brown, blue, dark or light color is an alarming signal that requires immediate help from a dermatologist or oncologist. A change in the color of the halo signals the beginning of degeneration into cancer. Dangerous signs of different types of color:
White spot
The appearance of a white rim occurs due to the death of the skin pigment melanin. It can be a sign of both benign and malignant nevus. The white edging initially appears along with the mole; this pathology is a consequence of the genetic disease vitiligo.
Red
A hyperemic halo (red) means the beginning of the process of degeneration of the formation into melanoma or an inflammatory process. This case requires prompt treatment and surgical intervention. An exception is a stripped nevus, where the redness is the result of injury.
Blue
Blue discoloration of the halo is a sign of possible transformation. A transitional condition that requires the attention of an oncologist. After examination, dermatoscopy is prescribed, and possible excision of the disturbing formation.
Brown
A frame of light brown or dark brown color is considered an unfavorable sign, indicating the spread of a pigment spot. Associated with the degeneration of melanocytes containing brown pigment, spreading around the circumference.
Black spot
A sign of increased accumulation of melanin in the epidermis. The color change affects not only the area around the site, but also the nevus itself. The beginning of the transformation of the formation into a malignant tumor.
These changes in color are a sign of malignancy of the nevus. Changes occur due to the activation of metabolic processes, leading to the restructuring of mole cells at the biochemical level. Timely response to various types of moles and their color framing will help to avoid serious consequences.
How to distinguish a malignant mole from a benign one
The presence of a nevus carries a potential threat of developing melanoma.
That is, an aggressive malignant tumor characterized by early lymphogenous and hematogenous metastasis.
In 50% of clinical cases, melanoma is formed from congenital and dysplastic nevi.
The size of the tumor-like neoplasm is also of great importance.
Malignancy of moles with a diameter of more than 2 centimeters is observed in 5-20% of cases.
The malignancy of the nevus is caused by constant trauma to it with shoes/clothing, bruises, cuts, and abrasions.
In people with many moles (20 or more), the risk of developing melanoma increases 3 times.
Melanoma symptoms:
- rapid increase in pigment tumor in height and area
- loss of pronounced contour, change in shape
- change in shade: weakening/increasing intensity of color, the mole shines, gradually becomes lighter or darker
- the appearance of ulcers, nodules, crusts, bleeding
- a benign mole grows, hurts, itches, falls off
- itching, inflammation, accompanying tumors appeared
Nevi are especially dangerous when they are localized in areas of constant injury - under the collar, bra, belt.
It is recommended to remove them by surgical excision.
Should the stain be removed or lightened?
If the stain does not pose a danger, is a benign formation that does not cause discomfort, you do not need to remove it, but carefully monitor it using photography techniques.
If the slightest changes appear, you should visit a doctor.
At the doctor's appointment, the area causing concern will be examined and after dermatoscopy a final diagnosis will be made. A mole with a rim of brown or other color is dangerous and requires surgical or laser removal. The procedure involves complete excision of the malignant tumor, with minor damage to healthy skin. Helps prevent further spread of melanoma cells. Removal must take place in a clinic using a special device. You should not go to beauty salons to solve this problem. Improper excision will lead to serious complications, possibly fatal.
The procedure for lightening moles is harmful; a highly qualified specialist will not resort to it; there is a risk of transformation of the nevus.
Symptoms of nevus malignancy
Dangerous symptoms occurring with the formation are considered:
- a sharp change in the color of the halo around the mole to black, red, blue, brown or white. A distinctive feature of a white rim with a benign formation is the gradual appearance of color, and a malignant one - a sudden appearance;
- change in the shape of the nevus, the edges blur, acquiring an uneven contour;
- the appearance of spots of various colors on the tumor: black, burgundy or purple;
- the mole begins to grow and becomes asymmetrical;
- itching appears, the tumor begins to itch;
- nevus peeling;
- the appearance of an inflammatory frame;
- papillomas and warts with elements of necrosis may appear near the mole;
- burning and tingling nevus;
- cracks appear that can bleed and hurt;
- a change in the color of the nevus, possibly complete blackening or the appearance of a black dot on the surface.
If you detect at least one sign, visit a doctor. Do not postpone your visit for a long time. By identifying melanoma in time, complications can be avoided.
When should you be wary and consult a doctor to rule out malignancy of the nevus?
- changing the shape of a mole from round to asymmetrical
- rapid growth of moles, sizes more than 6 mm.
- the contours of the mole have become uneven, the edges are “ragged”
- change in color of the mole, it becomes uneven or blue-black
- the surface of the mole has become glossy and shiny
- an ulcer spontaneously appeared on the mole
- loss of hair that previously grew from a mole
- the mole has become dense to the touch
- the appearance of “child” elements around the mole
- feeling of itching in the mole area
- enlargement of nearby lymph nodes
If you consider yourself at risk, have discovered one of the above signs, or are simply worried about this, make an appointment with a dermato-oncologist. And please never forget to use sunscreen.
Possible complications and precautions
Knowing the causes and signs of the degeneration of benign formations into a cancerous tumor, you can avoid dangerous complications. Melanoma is a serious consequence. Treatment in the early stages will give positive results. If you delay visiting the hospital, the consequences will be serious and will require a lot of effort and money. If the tumor is not removed in time, it will metastasize, affecting the lymphatic system and distant organs. Removing them will not be easy. Treatment will not bring positive results, and death is possible.
You can protect yourself by following simple preventive measures:
- do not sunbathe in the sun during dangerous hours (between 11 o'clock in the afternoon and 5 o'clock in the evening);
- use sunscreen;
- visiting a solarium is not recommended;
- timely treatment of damaged nevi;
- Regular examination of all moles and spots.
If suspicious signs appear, see a doctor immediately. Vigilance is never superfluous; timely and high-quality treatment will help avoid complications.