In dentistry, there is a whole group of diseases associated with the appearance of growths in the oral cavity. Among them, epulis stands out - a neoplasm on the gum, which is formed from the alveolar process. Despite its relative benign quality, a person has problems with chewing and swallowing food, and speech becomes less intelligible. A lump in such a place is easily and often injured, bleeds and can cause a serious infection. It is necessary not only to remove the formation, but also to find out why it formed.
Epulis on the gum photo
Signs of epulis on the gums
In everyday use, this disease is more often called supragingival due to its location directly above the mucous membrane between the teeth. According to the general classification, it is a tumor that is formed from epithelial cells of the gums. The neoplasm externally resembles a small bump or papilla; it may have a stalk and is attached to the interdental space. The main growth area is the area of the chewing teeth of the lower jaw; in more rare cases, it appears on the upper half.
There are several types of epulis on the gums and each has its own characteristic features:
- Fibrous: the most common form of the disease. The lump completely matches the color of the mucous membrane itself and does not have a thin base, so it looks like a seal at the neck of the tooth. It develops slowly and does not hurt or bleed when touched. If it reaches a large size, there is a problem with chewing and tightly closing the jaw.
- Angiomatous: this type of tumor has a whole network of tiny capillaries. They give it a red or bluish tint. Externally, such epulis on the gum is covered with tubercles and looks very unesthetic. It is easy to get caught by a toothbrush or denture, so minor bleeding often occurs.
- Giant cell: This form always causes concern among dentists due to its ability to destroy tooth roots and its tendency to become malignant. It has an unpleasant brown blood color and responds with pain to the touch. It is more common in patients over 40 years of age and requires constant monitoring.
Sometimes epulis is detected on the gums, which grows on the basis of bone tissue. This is an acanthomatous form of the disease, more commonly known as ameloblastoma. It occurs in young children and interferes with the exit of a molar tooth. The growth does not cause pain, but it affects the clarity of the baby’s speech.
Prevention
There are no special unique ways to prevent dental disease in children. Ulcers on the gums are the result of untreated caries. Therefore, all preventive measures are aimed at preventing caries:
- oral hygiene (make sure your baby brushes his teeth properly);
- balanced diet;
- rinsing your mouth every meal;
- preventive procedures (remineralization, fluoridation; fissure sealing);
- timely dental treatment;
- preventive examinations at the dentist 2 times a year (some experts recommend once every 3 months if the baby already has treated teeth).
Timely dental treatment for children and proper hygiene will help avoid many dental problems. Teach your child to take care of the health of their teeth and beautiful children's smiles will delight you every day!
Symptoms of epulis in the mouth
Each type of this dental disease is different in appearance. The tumor grows quite slowly, so most patients do not immediately notice a lump near the tooth. It can protrude from only one side or from both. The main symptoms of epulis on the gums:
- A soft bulge of pink or dark cherry color appears on the mucous membrane closer to the neck of the tooth.
- The lump ranges in size from 3 mm to several centimeters and fills the space in the mouth.
- A person feels that the tongue does not have enough free space.
- Sometimes there is external asymmetry of the face and protrusion of the cheeks outward.
- Bleeding occurs after brushing teeth, eating, or biting.
Any epulis, the photo of which resembles a shapeless growth in the oral cavity, looks like deformation of the gums from the inside. If the process is severely advanced, a person may feel loosening of the chewing teeth. With constant injuries from a prosthesis or a brush, bacteria enter the wounds. Therefore, the disease is often complicated by inflammation and the appearance of an abscess, cyst and pulp death.
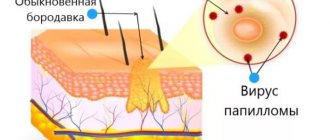
Why are papillomas in the mouth dangerous?
The main danger of papillomas on the mucous membranes is the possibility of their malignant transformation, which is accompanied by an oncological process. It cannot be said that this probability is very high, but most doctors agree that if the epilelium grows excessively, atypical cell growth can become uncontrollable.
In addition, papillomas in the mouth are usually accompanied by constant discomfort, which is associated with the location of a large number of nerve endings and sensitive centers on the oral mucosa. Treatment of papilloma in the throat is necessary due to the likelihood of its growth with subsequent problems with speech activity.
Also, treatment of papillomas in the mouth is justified from the point of view that this particular localization is accompanied by the highest risk of injury to the neoplasm. This can happen while eating, talking, or making facial expressions. In this case, severe bleeding occurs, which is very difficult to stop. In addition, a constant humid environment with an abundance of microorganisms prevents the rapid healing of the wound surface and, on the contrary, contributes to wound infection.
Reasons for the formation of epulis on the gums
In 80% of cases, the neoplasm occurs due to permanent damage to the mucosa. This is a common problem when wearing dentures, metal braces and other aligners. Sometimes the alveolar space is rubbed by the tip of a broken tooth or the edge of an incorrectly installed filling. The epithelium in one area is greatly irritated and cells begin to grow more actively.
In addition to frequent injuries to the oral cavity, the following features and pathologies lead to the appearance of epulis:
- various surges and disruptions in the endocrine system, exacerbation of diabetes mellitus or menopause;
- pregnancy and postpartum period;
- weakened immunity due to chronic diseases of the nasopharynx and endocrine system.
In children, mucosal growth almost always begins during the period of change of baby teeth. At this time, the child’s body is vulnerable to inflammation and complications. The situation is affected by an incorrect bite and the need to wear braces to straighten it.
Gum cancer
This dangerous neoplasm is worth highlighting separately. Mutation cells begin to divide uncontrollably, which is why a red tumor forms on the gum. The disease progresses quickly and over time can develop into jaw cancer.
What are the symptoms?
- General weakness;
- increased body temperature (37 C°);
- loss of appetite;
- constant drowsiness.
The doctor makes an accurate diagnosis after a detailed examination. As a rule, treatment is long and painstaking. With timely medical intervention, the outcome is favorable.
Possible complications
When the soft tissue of the gums begins to actively grow, a person develops a constant feeling of a foreign body behind the cheek or under the tongue. This brings discomfort, creates uncertainty and a reluctance to smile so that others do not notice the defect. The more space the tumor takes up, the more pronounced speech impairments become. This tendency is especially dangerous for children: even an experienced speech therapist will not be able to correctly place the sounds. In addition, patients face the following difficulties:
How to remove epulis from gums
The only option to completely get rid of an unpleasant tumor is to remove it surgically. In mild cases, this is performed by a dentist under local anesthesia. If bone is involved or there is a risk of malignant cells being detected, this major operation should be performed by an oral and maxillofacial surgeon. In the case of the giant cell form, all tissues that came into contact with the neoplasm are additionally removed.
You should not start epulis, the treatment of which at the very initial stage can be carried out quickly and easily for a person. The dentist will gently remove the small bump using a laser or liquid nitrogen. Such interventions are very gentle and practically do not damage the surrounding mucosa. After them, the gums quickly recover and heal. To speed up the process, apply compresses with Solcoseryl or Levomekol ointment to the wound. The latter contains a small amount of antibiotic, so it protects the sutures from infection.
During the entire rehabilitation period, the patient is recommended to treat the operated areas with hydrogen peroxide, and then rinse his mouth with antiseptics such as Chlorhexidine, Miramistin or Chlorophyllipt. In severe situations with suppuration, a course of antibiotics cannot be avoided:
- Biseptol;
- Amoxicillin;
- Azithromycin.
Unfortunately, epulis on the gums may appear again after some time. As a preventive measure, dentists recommend avoiding any injuries and protecting the mucous membrane from hypothermia and burns. It is imperative to visit a specialist every 6-8 months in order to notice the formation of a lump in time and remove it without consequences.
When a lump appears on the gum, most people mistake it for an abscess. However, such formations are not always infectious in nature. One of the types of gum tumors is the so-called epulis, which is usually painless and identical in color to the gum tissue.
Ball in mouth - what is it?
When the inflammation begins to gradually progress, a blister appears on the gum. The main reason for the formation of a lump is poor oral hygiene and prevention. But the ball can also form under the influence of other factors: inflammation occurring in the roots of the teeth, gums, mucous membranes, and periosteum.
The problem is that the disease can be diagnosed in the later stages, with the development of a purulent process. This happens because the patient does not visit the dentist. For patients who experience fear while in a chair, the doctor can give sedative anesthesia, in which the receptors are turned off and the patient falls into a shallow sleep.
Attention! It is better to diagnose the disease early in order to prevent more dangerous consequences, including blood infection and inflammation of the entire jaw.
What is epulis on the gum?
Epulis is a benign tumor-like formation that appears on the gum, usually in the area of the molars. Outwardly, it resembles a mushroom: it has a stem and a cap. The pathology has different sizes and shades, this is largely determined by its shape - from a few millimeters to 2 cm in diameter.
Epulis itself does not pose a threat, but it does cause discomfort to the patient. In addition, the formation is prone to growth, and under unfavorable conditions it can degenerate into a malignant tumor. The disease affects patients of all ages, but most often occurs in people 25-40 years old.
Epulis itself is not dangerous, but under unfavorable conditions it can degenerate into a malignant tumor.
A growth has appeared on the gum: what is the reason?
A lump or growth is a compaction on the gum caused by damage to periodontal tissue, which may appear without any previous signs. Growths appear in people of any age, but mainly in young children, as they unknowingly introduce infection into their mouths. The first thing you need to do when you detect formations in your mouth is to determine the nature of their origin (only a doctor can do this). It comes in two types:
- Infectious. The appearance of cones is caused by the activity of bacteria.
- Non-infectious. Bumps and growths as a result of injury, mechanical or chemical damage.
If a lump has formed in your mouth, you should consult a doctor to rule out possible complications. The doctor will help diagnose the problem and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Reasons for appearance
The causes of a tumor are both external influences and internal processes in the body. The most common:
- injury to the mucous membrane by an overhanging filling or fragments of teeth;
- tartar in advanced form;
- defect of the denture, lack of timely correction;
- soft tissue bruise;
- uncorrected malocclusions;
- chemical, thermal burns.
Even with these factors present, not everyone develops epulis on the gums. Hormonal imbalance is considered a provoking prerequisite for its appearance, so the disease often occurs in adolescence, during pregnancy or menopause.
What to do with it: remove or treat
Epulis on the gums is considered a serious pathology that requires specialist help as early as possible. Delaying a visit to the doctor can cause complications. What treatment will be carried out depends on the type of disease and clinical picture.
Treatment always begins with identifying and eliminating the provoking factor. If the cause lies in internal processes, then therapy is carried out simultaneously with the treatment of epulis. When a tumor is caused by orthopedic or orthodontic structures, tooth damage, poor-quality restoration, etc., the cause is first eliminated. Professional teeth cleaning using a gentle method is mandatory. The dentist may prescribe the use of local antiseptics, hormonal drugs, antibiotics and other types of medications depending on the cause of the pathology.
In most cases, angiomatous and fibromatous epulis of the gums can be cured conservatively. After the causes of the pathology are eliminated, the tumor may begin to decrease in size and even disappear completely. Giant cell epulis is an indication for surgical treatment.
Kinds
Tumors are classified depending on their etiology, size, and structure.
Fibrous epulis
The fibrous formation usually has a hard consistency and is distinguished by the presence of a wide base. The color is most often identical to the gingival tissue; bleeding does not occur spontaneously and can only appear due to mechanical damage (for example, with a hard toothbrush).
The surface has no characteristic features - it can be flat and smooth or bumpy and rough. The most common location is the vestibular surface in the premolar area. There is no pain, the tumor grows in size very slowly.
giant cell
This type most often occurs in elderly patients. Its main manifestations:
- localization – alveolar ridge;
- bleeding on palpation;
- painful sensations;
- color – bluish with a brown tint;
- loosening of adjacent teeth;
- dense, elastic consistency.
This type of tumor is more prone to malignancy than others.
The tumor grows in size very slowly
Angiomatous
Most often develops in children and adolescents. Characteristic features:
- localization – in the area of the tooth neck;
- the tumor is riddled with blood vessels and has a bright red tint;
- the base is wide;
- bleeds when pressed;
- education is soft.
This type is characterized by rapid growth in a short time, and relapses occur frequently. If epulis forms in babies, it can cause delayed teething or the formation of an abnormal bite.
Acanthomatous
Epulis in this form is typical for dogs and cats, but it rarely occurs in people. This is a benign formation that arises from tooth buds, usually on the lower jaw. It looks like small bubbles on the mucous membrane, prone to reappear after removal.
In most cases, formations are benign in nature
Types of growth
New growths on the gums vary in shape, size, and method of formation.
- Angiomatous growth. A soft, bumpy, pink growth that grows very quickly. Often reappears after removal. This growth is diagnosed in children aged 10-12 years; as a rule, it does not occur in adults.
- A fibrous growth is a gum-colored lump. It grows slowly and does not cause pain, so patients are in no hurry to see a doctor.
- Giant cell growth. A rapidly growing neoplasm of red-blue color, from which serous fluid is secreted. The lump is easy to injure.
Treatment
The doctor chooses the optimal treatment method in a particular situation after a thorough diagnosis. It includes visual inspection, palpation, x-ray and microscopic examination.
Medication
It is impossible to completely eliminate the tumor with medication. The main goal of drug treatment is to stop its growth. It is also prescribed after surgical interventions to accelerate tissue regeneration.
The most commonly used antiseptic drugs are:
- Dimexide;
- Polycresulene;
- Chlorhexiine;
- Resorcinol.
All of the listed remedies are external, prescribed in the form of ointments, rinses, irrigations or applications.
It is impossible to completely eliminate a tumor with medications
Are traditional methods effective?
Folk remedies are effective only for preventing the development of infection, as well as for accelerating tissue healing after surgery. Among them, for example:
- Infusion of calendula, sage, chamomile, eucalyptus. 15 grams of the mixture is poured into a glass of boiling water and used for rinsing 4-5 times a day.
- A tablespoon of soda is dissolved in 0.5 liters of warm water. Rinse up to eight times a day.
- A tablespoon of iodized salt is dissolved in 0.5 liters of water until the crystals disappear. Use for rinsing three times a day.
Surgical treatment of epulis
The optimal method of treatment is removal of the tumor, which is performed using a surgical or laser scalpel. The doctor makes an incision and completely removes the tumor, often including the periosteum. The edges of the wound are closed, the area is treated and covered with a sterile napkin.
Sometimes adjacent teeth may also need to be removed. This situation occurs due to their increased mobility. During pregnancy, operations are usually not performed unless there are critical and urgent indications.
The optimal treatment method is removal of the epulis
Using laser
Recently, a laser scalpel is often used for dental operations, including the removal of epulis. This solution can be considered optimal for several reasons:
- the edges of the wound are cauterized directly during surgery;
- disinfection occurs at the same time;
- The time of the operation itself and the rehabilitation period are reduced.
Where to get treatment in Moscow, clinics, prices?
To remove epulis, you must contact dental clinics that have surgeons on staff. Average cost of the procedure (in rubles) in some Moscow clinics:
- Center for Aesthetic Dentistry – 6000.
- Denta-El – 5000.
- Dantistoff – 7500.
- Inpromed – 5500.
- Capital – 7600.
After surgery, it is very important to follow the doctor’s recommendations regarding wound care, treatment and oral hygiene, and diet. This will prevent the development of complications and relapses.
It is also important not to forget that the primary prevention of the appearance of tumors is timely dental examinations, hygiene, removal of tartar, adjustment of dentures, braces and fillings.
Jump to: navigation, search
EPULIS
(
epulis
; Greek epi- on + ulon gum; synonym
epulid
) - tumor-like connective tissue growths on the alveolar processes of the jaws.
In origin
epulis, local damaging factors are of great importance, in particular injury to the mucous membrane from the sharp edges of destroyed teeth, fillings hanging on the gums, incorrectly made crowns or dentures. In women, the development of epulis is often associated with hormonal disorders that occur during pregnancy. Epulis can also form during teething.
There are fibrous (granulomatous), angiomatous and giant cell epulis. A distinctive feature of fibrous and angiomatous epulis is its connection with the teeth. Giant cell epulis can also develop on edentulous jaws.
Epulis occurs in women 3-4 times more often than in men. Fibrous and angiomatous epulis occurs mainly at young and mature ages (from 20 to 50 years), giant cell - at any age.
Fibrous epulis
macroscopically it is a mushroom-shaped formation of small size, round or oval, sometimes irregular in shape, located in the gum area, often on its vestibular surface, on a wide or narrow base (pedicle). Fibrous epulis has a dense, elastic consistency, is painless on palpation, and does not bleed. Its surface is smooth or lumpy, covered with a pale pink mucous membrane, the color of which, as a rule, does not differ from the color of the surrounding mucous membrane. Microscopically, growths of mature fibrous connective tissue are detected, among the bundles of which islands of bone substance, surrounded by osteoblasts, are sometimes detected (tsvetn. fig. 8a, 86). Granulomatous epulis is usually called ulcerated fibrous epulis with abundant proliferation of granulation tissue in the area of ulceration.
Angiomatous epulis
- a formation of round shape, soft-elastic consistency, localized mainly in the area of the alveolar process at the level of premolars and molars. The surface is fine-grained, covered with a mucous membrane of a bright crimson color, often with a cyanotic tint; upon palpation, bleeding easily occurs, which is sometimes pulsating. Angiomatous epulis grows quite rapidly, especially during pregnancy. Microscopically, its tissue is formed by numerous thin-walled blood vessels with lumens of various sizes and shapes, which resembles the picture of an angioma (tsvetn. fig. 9a, 96).
Giant cell epulis
- a formation of round or oval shape, soft or densely elastic consistency, covered with a dark red or brownish-blue mucous membrane. On microscopic examination, in the connective tissue rich in thin-walled vessels, multinucleated giant cells of the osteoclast type (tsvetn. 10a, 106) and mononuclear cells of the osteoblast type are found. Among these cellular elements, accumulations of erythrocytes and hemosiderin deposits lie freely; There are serous and blood cysts, islands of osteoid and bone tissue. According to the WHO classification, giant cell epulis is divided into peripheral giant cell granuloma (originating from the soft tissue of the gums) and central, or reparative, giant cell granuloma (developing in the bone of the alveolar process).
Giant cell epulis grows slowly, but can have progressive growth and reach significant sizes. In such cases, its surface is often injured by antagonist teeth with the formation of erosions and bedsores. With a significant increase in the size of the epulsa, teeth often become loose.
X-ray examination of fibrous and angiomatous epulis does not always reveal bone changes; Often only a shadow of a soft tissue tumor is visible, sometimes with areas of calcification of various sizes. With prolonged growth of fibrous epulis, an x-ray of the jaw may reveal marginal lesions with clear contours at the site of contact of the epulis with the bone. With angiomatous epulis, in some cases a picture of bone hemangioma is observed (see). Giant cell epulis is characterized by vaguely defined bone destruction (central giant cell granuloma).
Treatment
surgical, consists of excision of the epulis within healthy tissues along with the base (pedicle). After excision of fibrous and angiomatous epulis, in case of bone damage, it is necessary to completely remove its softened area - scrape it out with a sharp spoon or using a bur or cutter. The cessation of bleeding from the wound is a sign of complete removal of the epulis. The operation is completed by electrocoagulation of the wound surface and fixation of a tampon soaked in iodoform on it. Teeth in the epulis area are removed if they are mobile or their roots are excessively exposed, as well as if bone destruction is detected by x-ray. Teeth should also be removed if epulis recurs. When excising giant cell epulis, a partial resection of the alveolar process is performed within healthy tissues along with the teeth. The wound is treated with 96% alcohol, and it heals by secondary intention (under a tampon). In some cases, it is possible to close the wound with a mobilized mucoperiosteal flap.
Forecast
With timely and radical treatment, epulis is favorable.
In the prevention of epulis, the main role is played by the prevention and elimination of gum injuries. It is especially important to monitor the condition of gums in pregnant women.
Bibliography:
Abrikosov A.I. On the pathological anatomy of widespread fibrous osteitis, Rus. Klin., vol. 5, no. 23, p. 343, 1926; Vasiliev G. A. Dental surgery with a course of maxillofacial traumatology, p. 296, M., 1973; Evdokimov A.I. and Vasiliev G.A., Surgical dentistry, p. 242, M., 1964,
T. G. Robustova (author of the article and color drawing).
Category: Source: Great Medical Encyclopedia (BME), edited by Petrovsky B.V., 3rd edition
Recommended Articles
- Article reading time:
1 minute
Seals, or bumps on the gums, form in patients of different age categories. They can lead to various dangerous diseases, and therefore require clarification of the root cause of their occurrence and selection of effective treatment.
Benign tumors in the mouth must be removed
Benign tumors of the oral cavity are neoplasms in the oral cavity of a benign nature, which are characterized by limited, slow growth. They can be localized on the mucous membrane of the mouth and lips, as well as in the thickness of the jaws and soft tissues.
The most common tumors are those whose origin is caused by glandular, flat, tooth-forming epithelial tissue, but formations from adipose, muscle tissue, connective tissue structures, blood vessels and nerve trunks are also found.
A person notices changes in the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, inflammation and growths almost immediately. Discomfort intensifies when exposed to hot food or friction with dentures. This could be a papilloma in the mouth - a tumor-like formation on the mucous membrane. It is important to mitigate as much as possible the conditions that predispose to malignant degeneration of the inflamed and overgrown epithelium. By visiting a doctor, you can consult on complex treatment.
The proliferation of epithelial tissue in the oral mucosa is caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). Its particles are present in the bodies of 9 out of 10 adults on the planet. Some people have no idea about this and do not feel any changes at all. Others have to struggle with the unpleasant manifestations of papillomatosis for many years.
What symptoms of papillomatosis in the mouth should you pay attention to?
Regardless of the specific localization of growths on the oral mucosa, several general characteristics of tumors are distinguished. Usually papillomas on the gums and tongue are pink with a whitish tint, their size does not exceed 10 mm. The most characteristic feature is the presence of a narrow or wide base - the so-called “leg”. The upper part is lumpy, with uneven edges.
Feelings of a person who has become the “owner” of a small tumor in the mouth: it interferes with normal chewing of food and talking. Much depends on the specific location of the papilloma. Typically, the localization of formations is associated with the tongue, gums, lips, and lateral surfaces of the oral cavity. There are not only single papillomas, but also multiple growths. Some are soft and mobile to the touch, others have a keratinized surface.
Before removing growths with such characteristic signs, cytological and histological studies of the material obtained from the mouth must be carried out. Laboratory tests can distinguish papilloma from genital warts or epithelioma and determine the degree of oncogenicity of HPV.
Complex therapy of papilloma in the mouth
Specialists need to clearly limit the growth, identify hidden foci of papilloma in the mouth, the treatment of which is not started without consultation with an oncologist, dentist, or ENT doctor. The choice of therapeutic technique affects the final results, but it is difficult to achieve 100% results.
To increase the effectiveness of treatment, it is carried out comprehensively. According to medical research and patient reviews, this approach reduces the number of relapses, that is, the appearance of new tumors in the oral cavity.
Removal of papillomas in the oral cavity
Treatment of small growths of the mucosal epithelium is fairly quick and almost painless. It is easier to get rid of small round formations on a thin stalk. Typically, oral papilloma has an uneven edge in the shape of a cockscomb or cauliflower. Its color is close to the tone of the mucous membranes, sometimes it is darker or lighter. Removal of such tumors is carried out by deep coagulation with radio waves, evaporation with a laser beam, or traditional surgical excision.
Oral fibroma is a benign neoplasm consisting of fibers of mature connective tissue. It is a clearly demarcated rounded nodule on a stalk or broad base, covered with unchanged mucosa. Characterized by slow exophytic growth. Oral fibroma can be located on the inner surface of the cheeks, mucous membrane of the lips, soft palate, gums, and tongue. Diagnosis of oral fibroma is made by inspection, palpation, ultrasound and histological examination. An orthopantomogram, radiography and periodontogram are used to identify inflammatory processes that provoke the formation of fibroids. Treatment of oral fibroma boils down to its excision. Along with papilloma, lipoma, myoma, nevus and myxoma, fibroma is a benign tumor of the oral cavity. It most often occurs in children aged 6 to 15 years. Clinical dentistry considers traumatic and inflammatory factors to be the causes of the formation of oral fibroma, and a hereditary predisposition can also be traced. Quite often, the history of patients with oral fibroma reveals regular biting of the same area of soft tissue of the oral cavity, which precedes its appearance. Factors that provoke the appearance of fibroma also include trauma to the mucous membrane with a sharp tooth edge, a poorly fixed prosthesis or crown; chronic inflammatory processes of the oral cavity (gingivitis, stomatitis, periodontitis, glossitis, etc.) Signs of oral fibroma Oral fibroma has the appearance of a formation rising above the general surface of the mucous membrane with a wide base or stalk. It is painless, has a hemispherical shape and is covered with a mucous membrane of the usual pink color. The surface of oral fibroma is smooth and, unlike papilloma, has no outgrowths. No changes in the mucous membrane in the area of fibroma are usually observed. In rare cases, ulceration is observed over the tumor. In this case, an infection may occur with the development of inflammatory manifestations: redness, swelling, pain in the area of the fibroma. Oral fibroids typically exhibit a slow increase in size. If the fibroma is not traumatized, its size can remain stable for a long time. With constant trauma, malignant degeneration of the tumor is possible. Diagnosis of oral fibroma The characteristic clinical picture of oral fibroma in most cases allows the dentist to make a diagnosis based on examination and palpation of the formation. To determine the depth of growth of the base of the fibroma into the underlying tissue, ultrasound can be performed. In rare cases, usually when there is ulceration or inflammatory changes in the area of the fibroma, a biopsy of the formation is indicated. More often, histological examination of oral fibroma is carried out after its removal. An important point is the diagnosis of the causative factor in the formation of oral fibroma. For this purpose, a thorough dental examination is carried out aimed at identifying inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, radiography or radiovisiography, an orthopantomogram and a periodontogram are performed. Patients with dentures need to consult an orthopedic dentist to avoid the traumatic effect of the existing denture on the tissues of the oral cavity. Treatment of oral fibroids The most effective treatment for oral fibroids is surgical excision. Pedicled oral fibroids are removed along with the stem using two bordering incisions. The fibroma at the base is excised together with the base using a bordering or arcuate incision. Removal of fibroma on the red border of the lip is made with an incision perpendicular to the passage of the fibers of the orbicularis oris muscle. For large oral fibroids, to prevent deformation of the mucosa, patch closure of the defect remaining after tumor removal is performed. The flap is cut out using a V-shaped incision from adjacent tissues.
Epulis, popularly called supragingival, refers to benign tumors of the maxillofacial region. Epulis is a tumor-like neoplasm with a diameter of 0.5 to 6-7 centimeters, which is located on the alveolar process of the jaw. The predominant localization of the supragingival is the area of small molars, although in some cases it can occur at the level of any teeth of the upper or lower jaws.
The cause of the occurrence has not been definitively established, but in the vast majority of cases it occurs as a result of prolonged irritation of the mucous membrane of the alveolar process, for example, by the sharp edge of a decayed tooth or from irritation of the mucous membrane by dentures. It occurs quite often in pregnant women; they are often diagnosed with hypertrophic gingivitis. Epulis grows slowly, although pregnant women often experience accelerated growth, apparently caused by hormonal changes in the body. As a rule, patients do not experience any pain, except in cases of injury to the teeth of the opposite jaw. The supragingival partly or completely covers the coronal part of one tooth, and more often than not several teeth at once from the vestibular and sometimes from the lingual surface.
Most often, the tumor has a wide stalk and is covered with ordinary mucosa, without any pathological changes; if the epulis is injured, then areas of erosion and hemorrhage appear. It differs from malignant tumors in that there are no areas of tumor decay. Prolonged growth of the supragingival can lead to destruction of the alveolar process and its spongy substance. In this case, osteoporosis of the bone will be visible on the x-ray.
The color of epulid is slightly different from the color of the oral mucosa - sometimes it has a red-brown or even bluish tint.
Treatment for epulide is only surgical. Considering that epulis has a growth zone in the periosteum and in the bone, after removing the tumor within the visible healthy mucosa, you need to do a thorough curettage around the tumor and remove the softened bone. Sometimes the tooth itself is also removed if it is located in the area of tumor growth and the alveolar process is destroyed by the tumor process. After removal, in some cases, the supragingival tissue may reappear in the same or other areas of the jaws.
Causes
The most common causes of bumps on the gums are:
- illiterate and irregular dental care;
- n injuries in the oral cavity;
- n consequences of wearing dentures.
Lack of regular dental care causes plaque to appear on them, which becomes a suitable habitat for pathogenic bacteria. As a result of their reproduction, a lump with pus often appears on the gum.
Often the tumor appears after injury or unprofessional installation of dentures. This occurs after the use of low quality materials and insufficient antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity.
Lumps on the gums in most cases indicate the presence of dental diseases. Most of them can cause significant discomfort, which necessitates immediate contact with a specialist.
Where does the abscess come from and what is its danger?
In the vast majority of cases, an abscess on the gum is associated with a tooth, often with a milk tooth. The most amazing thing is that the tooth may appear healthy from the outside, it may have a beautiful filling, and the tooth may not hurt. Why does pus still appear?
Baby teeth are less resistant to infection than permanent teeth; they are designed for a short service life, although they, like permanent teeth, have a nerve and roots. However, the roots of baby teeth begin to dissolve after five years. Caries in such teeth spreads much faster. Within three months, a cavity can form in the tooth, reaching the nerve. If caries is not treated, all pathogenic bacteria enter the dental nerve, and then, through the nerve, the microbes enter the bone. Bone is quite comfortable for microbes. They multiply there, dissolve the bone, which is accompanied by the formation of pus. If the tooth is open, there is a hole in it, pus comes out into the oral cavity. If food particles, fragments of destroyed enamel get into the tooth, or the tooth is covered with a filling without adequate treatment, pus can no longer flow freely. If the pus cannot flow out through the tooth cavity, it begins to look for another way out. The pus melts the bone and comes out under the gum. The outer covering of the gum, under which the pus has come out, swells and takes the form of a lump. Over time, the lump may burst and pus leaks out.
Once the pus is released, the lump may disappear and the gums may heal until the pus collects in large quantities again. The danger of such “bumps” is as follows:
- there is always an infection in the body (you should never forget that the abscess is not just on the gum, but in the head);
- the pus that is in the jaw dissolves the bone and can damage the growing permanent tooth.
The disappearance of an abscess next to a tooth never means recovery.
Symptoms that appear along with an abscess
- redness on the gum;
- tooth pain (optional);
- There is a hole in the tooth or there may be a filling on it;
- enlarged lymph nodes (dense “balls” appear under the lower jaw).
Sometimes a lump is discovered by chance, and the child may not be bothered by anything at all. The parent should periodically examine the child's mouth independently.
Diseases leading to the appearance of lumps
Gum bumps can form in parallel with dental diseases occurring in the oral cavity. They are not painful if they are formed as a result of:
- hematomas after removal of tooth roots;
- fistula;
- epulis;
- periodontitis.
A hematoma in the form of a watery tumor occurs as a consequence of an incorrectly extracted tooth. Such a neoplasm is not dangerous and is prone to spontaneous resorption.
The fistula (in the form of a white lump on the gum) is often chronic. It is a neoplasm with a hole for draining pus, located on the gum above or below the tooth and appears as a result of advanced pulpitis.
Epulis
- a formation that has a natural color or red color. This type of cone is distinguished by the presence of a stalk, and mainly affects the lower jaw. The reasons for its appearance are everyday mechanical stress, poor quality dentures, malocclusion and hormonal imbalance in women.
Periodontitis appears as a hard lump on the surface of the gums. An abscess forms at the base of the tooth root, transforming over time into a cystic formation.
Painful bumps occur as a result of periostitis (flux) or gingivitis. Flux is known as inflammation of bone tissue, accompanied by severe pain, increased body temperature, swelling of the mucous membranes, and enlarged lymph nodes. With gingivitis, small red spherical formations appear, and bleeding from the soft gum tissue often develops.
Bumps on a child’s gums form for the same reasons as in adults. To the factors already listed is added the period of teething, during which tumor-like formations appear in the oral cavity.
Most types of bumps on the gums require mandatory treatment. In the absence of proper therapy, the patient may develop dangerous irreversible complications.
Dentists' recommendations
Epulis is a gum tumor that poses a great danger to the health of teeth and the entire body. Treatment of the pathology is complex and lengthy, but even with high-quality treatment, the risk of relapse cannot be ruled out.
It is not always possible to prevent the occurrence of epulis on the gums of a child or an adult, but with timely consultation with a specialist, complications, complex treatment, long recovery and aesthetic defects that remain after surgery can be avoided.
The best prevention is to visit the dentist every 6 months. If you are concerned about discomfort and a feeling of rubbing of the mucous membranes or gums, you should immediately consult a dentist, without waiting for a tumor or other pathologies to occur.
Diagnosis and treatment of gum formations
A gingival lump can be easily identified during a visual examination and instrumental examination. To clarify the diagnosis, an x-ray or biopsy may be indicated.
Treatment methods are determined by the root cause of the formation on the gums. First of all, you will need to limit the further development of the infection and eliminate pain.
Traditional treatment is as follows:
- fistula
– elimination of pus by rinsing (using Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, decoctions of medicinal herbs, saline solution);
- epulis
– surgical treatment (removal with a scalpel, cryodestruction or diathermocoagulation);
- periodontitis
– unsealing and cleaning of root canals, removal of accumulated pus, mouth baths made of soda solution or herbal decoctions;
- periostitis
– opening the tooth and placing special medications under a temporary filling (if there is no positive result, the diseased tooth must be removed);
- gingivitis
– cleaning of periodontal pockets, antibacterial and antiseptic treatment, removal of pathological formations.
Traditional medicine offers treatment with freshly squeezed juice of Kalanchoe leaves, used in the form of lotions. Another option is to chew the leaves, having previously cleared them of the film. A popular remedy for bumps in the mouth is rinsing with regular vodka.
If the formation on the gum causes discomfort
If a bubble near a molar causes pain, this indicates an infectious inflammatory process. Discomfort is also typical with gum injuries and hematomas. Painful formations can be caused by a cyst, cancer, fibroma, periostitis, periodontitis.
Gingivitis - the disease affects only one gum, and the periodontium near the molar remains uninjured. The main symptoms of the pathology are swelling, bleeding, and peeling of the epithelium. Gingivitis often occurs against the background of halitosis. Sometimes pathology develops as a result of endocrine and metabolic disorders.
When treating, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of gingivitis. Professional oral hygiene, diagnosis and treatment of metabolic disorders are performed. To eliminate inflammation and prevent further spread of bacteria, antibiotic therapy is administered. For pain and severe discomfort, analgesics are prescribed.
Periodontitis - purulent bumps on the gums appear as a result of degeneration of the alveolar process, through which the tooth root is held in the alveolus. Tissues can be destroyed due to poor oral hygiene and internal pathologies.
In the initial stages, periodontitis is treated by teeth cleaning at the dental clinic and further proper care. An advanced form of the disease, in which the teeth become loose, pus accumulates, requires surgical intervention - restoration of the alveolar processes or removal of molars.
Periostitis or flux is a dense formation near a problematic molar with carious lesions. Patients complain of pain radiating to the temple, chest, neck, ear. The condition gradually worsens and the temperature can rise to 38 degrees. In the oral cavity, lesions due to periostitis are hyperemic. A purulent fistula forms. When the discharge is removed, the discomfort decreases.
Causes of periostitis: trauma, periodontitis, osteomyelitis, weak immune system, infectious pathologies occurring in the body and vitamin deficiency.