Dry skin care steps
1. Washing should be done in the morning and evening, using hydrophilic soap, milk or foam for dry skin. After washing, wipe the skin with an alcohol-free tonic.
2. Creams for dry skin are divided into:
- to a moisturizing and nourishing cream containing hyaluronic acid oils. This cream is applied to the skin after washing your face in the morning;
- night nourishing cream;
- eye cream. It is applied after each wash;
- anti-aging cream. They begin to use it after 25 years;
- cream with UV protection.
- serum containing hyaluronic acid and having a moisturizing effect. Cleanse the face with the serum before applying the cream.
3.Masks for dry skin:
- yolk-oil-honey mask. Mix the yolk with a teaspoon of honey and a spoonful of almond or olive oil. Apply with a brush to clean skin in layers. After the third layer, give the mask 25 minutes and rinse with warm water. This mask can be used 1-2 times a week. A tangible result will appear in a month and a half;
- yolk-oil mask. The yolk is mixed with a teaspoon of peach, almond or olive oil. Apply the mask to the face in 2-3 layers. After 25 minutes, remove the mask with a damp cotton swab. Wash your face with warm water and apply moisturizer;
- mayonnaise for skin. Gradually add 15 g of olive oil to the yolk. The resulting mayonnaise is applied to the skin and removed after 20 minutes with a damp cotton swab;
- hot mask made from flaxseed flour. Boil in 2000 ml of water with 3 tbsp. spoons of flaxseed until you get a viscous paste. Add a spoonful of honey and olive oil to the cooled mass. Apply the mask to the face and décolleté, cover the face and neck with a warm towel. After 20 minutes, wash off the mask with warm water and rinse your face and neck with cold water.
Skin hydration
There are several ways to get rid of flaking on your face. Initially, it is necessary to determine the causes of the problem. In the case of an allergic reaction, exposure to allergens should be eliminated by purifying the air or replacing cosmetic products. In winter, switch to using products with a high fat content that can withstand low temperatures. Optimize your diet based on the amount of water you consume. You need to drink at least 1.5 liters of purified drinking water per day to maintain your water balance.
Pay attention to cleansing and moisturizing your face, especially after a day of work. Sweat, dust and other impurities that come into contact with the face negatively affect the overall condition of the skin. Use specialized gels and lotions to cleanse your face. This kind of procedure is carried out twice a day. Don’t forget about vitamins, vitamin D3, regulates calcium-phosphorus metabolism, and vitamin complexes, as a rule, contain B vitamins, vitamins A, C, folic acid and Omega-3, they will help compensate for the lack of vitamins in the body. Take care of your own skin, take care of it, and you will look great for many years.
What is not recommended to do
If you have dry skin, you should not use:
- scrubs;
- cosmetics containing alcohol;
- soap;
- acid cosmetics;
- You can't sunbathe.
Cosmetics beneficial for dry skin:
- creams containing aloe vera;
- glycerol;
- hyaluronic and lactic acid;
- antioxidants;
- hazelnut, jojoba, jasmine and almond oils.
We must remember that only regular care for dry skin, using recommended products, will give a positive result.
Skin xerosis. Solving the problem externally
Xerosis is caused by impaired sebum and sweating, a deficiency of amino acids contained in the stratum corneum of the skin, and dehydration. Most often, xerosis appears on the skin of the feet due to an initially small number of sebaceous glands, slow turnover of epithelial cells and a pronounced violation of the protective functions of the skin.
The main cause of dryness is a lack of moisture in the stratum corneum of the skin; with a long-term process, peeling, a feeling of tightness, irritation, microcracks and itching appear.
Dryness occurs due to insufficient care, poor circulation, which is facilitated by constitutional features, wearing tight clothes and tights, tight shoes, insufficient moisture intake, and also due to alkalization of the skin with hygiene products and the use of harsh abrasive products. The problem with dryness most often manifests itself in the autumn-winter period due to the fact that with the onset of cold weather, the feet are constantly in contact with warmer and coarser woolen fabrics and synthetics, and this prevents sufficient air penetration; In addition, seasonal vitamin deficiency affects it. At the same time, problems can also arise in the summer, which is associated with prolonged exposure to the sun and walking barefoot. With proper and regular care, an aesthetically pleasing appearance is achieved. The main causes of skin xerosis and options for their correction are presented in Table 1.
The main pathogenetic mechanisms of increased skin dryness are:
1) a decrease in barrier function due to the failure of the lipids of the stratum corneum, a violation of their structure and location, which causes defects in the intercellular lipid layers, which leads to an increase in transepidermal moisture loss;
2) a decrease in the ability to retain moisture due to a lack of hygroscopic substances inside corneocytes, the so-called natural moisturizing factor (NMF), which consists of free amino acids and their derivatives, lactic acid, urea and other components that create the hydrolipid mantle of the skin [5];
3) disruption of moisture transport from the dermis to the epidermis and stratum corneum.
All this leads to dehydration of the epidermis and the development of a clinical picture of xerosis [1–3].
The group of chronic dermatoses, accompanied by dryness, hyperkeratosis and peeling, includes a large number of skin diseases. These include such common diseases as psoriasis, eczema, atopic dermatitis with lichenification, squamous-hyperkeratotic forms of mycoses, and rare nosological forms - ichthyosis, keratoderma, etc. Xerosis is also characteristic of age-related changes or can be caused by concomitant somatic pathologies - diseases thyroid gland, diabetes mellitus (DM), vitamin deficiency, metabolic disorders.
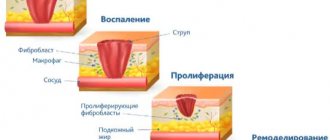
The process of development of dehydration at the cellular level is presented in Figure 1, and the stages of clinical manifestations during the development of skin xerosis with possible correction methods are shown in Figure 2. It should be noted that these phases can be traced for all manifestations of dry skin, both in chronic dermatoses and for somatic diseases.
Xerosis of the skin of the feet in diabetes is one of the provoking factors of diabetic foot syndrome. Statistics show that the appearance of diabetic foot signs is associated with the stage of decompensation in individuals suffering from type 2 diabetes; manifests itself in 90% of patients [4]. This condition occurs due to angio- and neuropathy of the feet, i.e. destruction of nerves and blood vessels, while tissue nutrition deteriorates, their protective function decreases, and this leads to trophic changes and thereby increases the risk of developing gangrene or ulcers even with minimal injuries. Such patients complain of discomfort in the legs, stabbing and burning pain when the legs are at rest, at night, as well as severe pain when walking. Over time, the sensitivity of the feet noticeably decreases, the color of the skin of the lower extremities changes - it becomes pale or with a slight brownish pigmentation, at the same time dryness, peeling of the skin, cracks, microvesicles with serous contents, as well as thickening of the stratum corneum of the skin of the feet appear. All this shows that xerosis of the skin in diabetes, both due to general dehydration and autonomic diabetic neuropathy with impaired innervation and regulation of the sweat glands, is not only a cosmetic problem, but also one of the links in the development of diabetic foot syndrome.
Dry skin to one degree or another occurs in 85% of patients at the appointment. Therefore, practicing doctors encounter such patients every day, sometimes they make up the majority of adult dermatological appointments. Advances in pharmacology, in particular combined anti-inflammatory drugs with exfoliating components, have significantly improved the quality of life of patients, and their availability and variety in pharmacy chains make it possible to make choices and experiment with treatment methods. Over time, new issues have arisen in the treatment of dermatoses accompanied by hyperkeratoses, namely, the duration of use of combined and monosteroids, anti-relapse and preventive therapy, care for hyperkeratotic conditions and peeling, the correction of which is initially difficult due to genetic “breakage” or due to concomitant diseases.
Currently, there is a reassessment of the importance of cosmeceuticals in the therapy and care of the skin of patients with xerosis, chronic dermatoses, and diabetes. There are a number of modern lines of medical cosmetics for skin care for hyperkeratosis, which have proven themselves, are widely available for everyday use and often have a pronounced softening, exfoliating and moisturizing effect. Basic drugs, most often based on topical steroids, have high expectations in terms of their antiproliferative, resolving, antipruritic, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and healing effects. But such properties, while maintaining a softening, moisturizing and exfoliating effect, are also inherent in classic dermatropic components with metabolic, hydrating and softening effects: urea, various acids, panthenol, complexes of oils, alkaloids and flavonoids.
To successfully combat dry feet, you first need to find out the cause of its occurrence. Diagnosis of dry skin involves excluding fungal infections, various endocrinopathies, skin diseases, and identifying the causes of xerosis. If the cause is any disease, then it is necessary to first cure it or correct the condition, and then deal with the manifestations. In some cases, with a severe inflammatory reaction, the prescription of glucocorticosteroid or combination creams with the parallel use of care products is required. But sometimes the use of moisturizers, which have pronounced effectiveness in treating dryness of various origins, high organoleptic properties, a high safety profile and good tolerability, leads to the desired result. At the same time, it has been clinically proven that anti-inflammatory drugs in combination with emollients are more effective than monotherapy with glucocorticosteroids. Thus, one of the main tasks when the skin barrier function is impaired is protection and hydration. Examples of products that effectively solve these problems are foot balms Balzamed and Balzamed intensive (Esparma GmbH, Germany), which are recommended for daily care of dry and sensitive skin of the feet, prone to redness, irritation, the formation of chafing and calluses, especially in patients with diabetes. .
Balzamed balms provide the skin of the feet with sufficient hydration and nutrition, preventing the formation of chafing and calluses, the appearance of peeling, redness and irritation on the skin of the feet. Balzamed balms contain a balanced composition of vital vitamins, moisturizing components and softening vegetable oils.
Balzamed and Balzamed intensive balms contain the following components:
Vitamin A, which protects against excessive keratinization and increases the skin's resistance to infections, protects it from the formation of microcracks, slows down the aging process, improves its elasticity and general condition.
Vitamin E (tocopherol acetate) is an antioxidant, binds free radicals, protects skin cells from metabolic damage caused by metabolic disorders, as well as from external environmental influences, helps reduce skin itching.
Vitamin F increases skin elasticity, regulates moisture content, and promotes rapid healing of microcracks.
Provitamin B5 (panthenol) accelerates the healing of small wounds, maintains water balance and skin resistance to external environmental influences, stimulates the regeneration of skin and mucous membranes, normalizes cellular metabolism, accelerates mitosis and increases the strength of collagen fibers, has a regenerating and anti-inflammatory effect.
Lactic acid promotes exfoliation and hydration, faster cell renewal.
Urea increases the absorption of water by keratinized areas of the skin, actively moisturizes dry skin and increases its permeability to vitamins, and also protects against external environmental influences; easily penetrates into the deep layers of the epidermis and serves as a conductor for other active components; has keratolytic, wound healing and bacteriostatic effects.
Avocado and jojoba oils contain vitamins A, B, D, E and K, soften, moisturize and nourish the skin, have a protective effect, restore skin elasticity, and prevent premature aging.
Zinc stearate, which is part of Balzamed intensive, stabilizes the skin of the feet and promotes healing.
Thus, the components included in the balms Balzamed and Balzamed intensive have a pronounced anti-inflammatory, antipruritic, exfoliating and antimicrobial effect, help restore damaged skin, increase the regenerative and barrier functions of the skin, prevent the feeling of dryness and irritation, relieve itching, promote hydration and restoration of affected areas of the epidermis. These drugs can be used both in complex therapy with anti-inflammatory glucocorticosteroid drugs, and independently, as a means of daily skin care.
In order to achieve maximum positive results, it is recommended to apply the foot balm daily to the damp skin of the feet, especially to areas subject to pressure and friction, rubbing in with light massaging movements.
Regular care of the skin of the feet using Balzamed will prevent the appearance of peeling, redness and irritation on the feet, the formation of corns and calluses, give elasticity and firmness to the skin, and prevent premature aging.
Skin xerosis is, as a rule, cyclical in nature with periods of deterioration, especially in the autumn-winter period, and therefore foot balms Balzamed and Balzamed intensive are the main links in both therapeutic and preventive care for the skin of the feet and allow you to completely cope with the problem of dry skin , including with such serious concomitant diseases as diabetes.
Ointments and creams for dermatitis
Creams or ointments for dermatitis have slightly different compositions. Thus, the ointment is made on a fat basis, which can be used as vegetable or mineral oils or animal fats. Such products have a dense, slightly viscous structure. They are not immediately absorbed into the skin, but penetrate into its deeper layers. Ointments are not recommended for treating wet surfaces. They are much more effective against dry rashes and chronic inflammation.
Creams have a different base - hydrophilic. Thanks to this, they have a lighter structure, are well absorbed and do not leave greasy marks on the skin. The creams are suitable for the treatment of moderately weeping rashes; they are used for acute inflammation, for lesions of the facial skin and areas with a large number of sebaceous glands, where the use of oily products is undesirable.
Let's consider several options for dermatitis remedies used in medical practice:
- hormonal ointments with pronounced antiallergic and anti-inflammatory effects, which include topical corticosteroids;
- non-hormonal topical agents that have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects, relieve itching and promote wound healing.
Non-hormonal drugs
Non-hormonal creams do not contain corticosteroids. The composition may be based primarily on plant components, or not contain them at all. These medications do not act quickly. Their main advantage is the possibility of using them for a long time, including in children. Among non-hormonal creams and ointments there are products with antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, moisturizing, and regenerating effects.
Hormonal drugs
Hormonal ointments and creams in the treatment of dermatitis are considered more effective than non-hormonal ones. The drugs can contain either one active component (topical glucocorticosteroid) or have a complex effect due to the presence of an antibiotic and an antifungal agent in the composition. The use of combined drugs is advisable in case of a complicated course of the disease, when a secondary bacterial or fungal infection is added to the inflammation.
Treatment of atopic dermatitis
To achieve maximum effectiveness from therapy, it is recommended to follow an integrated approach:
- identify and, if possible, eliminate the factors causing atopic dermatitis;
- drug therapy with local agents, selected depending on the severity and form of inflammation;
- proper skin care using moisturizers and softening agents (emollients).[4]
Akriderm preparations are products for the local treatment of manifestations of atopic dermatitis with a wide spectrum of action, produced in the form of cream and ointment of 15 g and 30 g. Depending on the severity, localization, form and course of the disease, the drug is selected:
- with one active ingredient – Akriderm® ointment and cream;
- combined preparations “hormone + antibiotic” - ointments and creams Akriderm GENTA;
- combined preparations “hormone + antibiotic + antimicrobial component” - ointments and creams Akriderm GK.
The modern drug Akriderm GK is a potent drug[5] and has 4 effects at once:
- anti-inflammatory;
- antiallergic;
- antibacterial;
- antifungal. [6]
Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis
The cause of seborrheic dermatitis is infection of the skin by the yeast-like fungus Malassezia. For its treatment, external antimycotics or antifungal drugs are prescribed. Akriderm SK ointment contains betamethasone and salicylic acid. The drug has anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, anti-exudative, anti-edematous and antipruritic effects, inhibits the accumulation of leukocytes, inhibits phagocytosis, reduces vascular tissue permeability, and prevents the formation of inflammatory edema. As a result of use, the microflora of the skin is restored, scales are exfoliated and sebum production is normalized.[7]
Treatment of allergic dermatitis
To successfully treat allergic dermatitis, it is first necessary to determine the allergen that provoked the disease and partially or even completely eliminate the provoking substance. In the acute period, a specialist may prescribe the use of compresses with cold water and tanning decoctions, which are applied every 3-4 hours for 15 minutes. This helps reduce skin weeping. Drug treatment involves the use of topical glucocorticosteroids in the form of ointments and creams, which are selected depending on the form and severity of inflammation.[8]
If allergic dermatitis is complicated by a microbial infection, it is recommended to use combined external medications, such as Akriderm GK, which, in addition to GCS, contain an antibiotic (gentamicin) and an antifungal component (clotrimazole).
Remember that treatment of dermatitis and selection of medications is carried out only by a specialist dermatologist after a preliminary consultation and examination of the patient.
How to choose pharmacy cosmetics?
Depending on the activity of the sebaceous glands, four skin types can be distinguished: normal, dry, oily, combination. In normal condition, the skin has a natural protective mechanism, which is a dense barrier of a layer of epidermis and sebaceous glands that create a stable lipid film. Such a barrier does not release water and protects against the penetration of microbes and allergens. Based on this, in order for the product to really provide what is needed, it should be selected based not only on the specifics of the problem, but also in accordance with the skin type.
Dry skin
If there is insufficient activity of the sebaceous glands, the risk of both infectious and allergic reactions increases. Aggressive environmental factors can cause dry skin: wind, frost, sun rays and dry home air. The problem may also arise due to internal factors: poor diet, vitamin deficiency, insufficient water intake or skin diseases (allergies, inflammatory and infectious diseases).
Main signs of dry skin:
- feeling of tightness;
- increased sensitivity;
- cracks;
- irritation;
- narrowed pores;
- peeling;
- early appearance of signs of aging.
Oily skin
This skin is characterized by excessive activity of the sebaceous glands. Often, this condition is caused by hereditary factors and endocrine disorders. However, at the same time, poor nutrition and improper skin care make a significant contribution.
Main signs of oily skin:
- greasy shine;
- clogged pores;
- black dots;
- acne;
- comedones;
- milia.
Combination skin
The most problematic type, in which there is a combination of several skin types. For example, oily skin in the T-zone (forehead, nose and chin) and dry or normal skin in the rest of the face. The difficulty of caring for such skin lies in the need to combine different skin care products. The causes of this condition of the skin can be: hormonal changes, local increased activity of the sebaceous glands, genetic predisposition, poor nutrition and improper care.
Before purchasing cosmetics, pay attention to your skin and, if you have serious problems, consult a dermatologist.