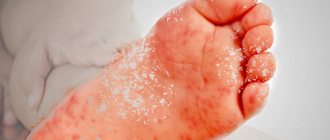
If the ulcer is localized in a place inaccessible to inspection (in women - in the vagina, on the cervix), primary syphilis may remain undiagnosed.
And if left untreated, it will progress to the next stage.
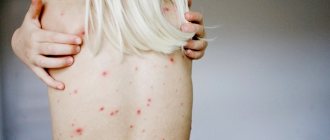
Secondary syphilis is characterized by the appearance of rashes on the skin, as well as spots localized in the neck area.
They are called the “necklace of Venus” or syphilitic leucoderma (pigment syphilide).
The appearance of characteristic spots on the neck, shoulders or torso is due to the lack of therapy at an early stage of the disease.
Or the use of ineffective drugs that could not cope with the infection.
When a Venus necklace appears on the neck, this is evidence that treponema pallidum has already spread throughout the body.
If at this stage the cerebrospinal fluid is examined for the presence of spirochetes, the result will be positive.
This means that the central nervous system has been damaged.
Depending on the state of the immune system, external signs of the disease will appear or be absent.
A little about syphilis
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection. The causative agent of this disease is Treponema pallidum, which is a bacterium that is capable of movement.
You can also read what kind of disease syphilism is in a similar article.
Upon contact with a person, it penetrates into the deep layers of the skin and destroys the wall of blood vessels. This leads to the formation of microthrombi and further necrosis of adjacent tissues. Penetrating into a blood vessel, treponema pallidum can be transported through the bloodstream to almost any organs and parts of the human body.
Thus, syphilis is a generalized infection, very resistant to various types of antibiotic therapy, so its treatment requires a professional approach.
Reasons for development
Venus's belt is a typical sign of secondary syphilis. By this time, severe damage to internal organs begins, and the nervous system is one of the first to be hit.
Atrophy of nerve endings leads to a decrease in the sensitivity of the epidermis, disruption of metabolic processes in it, and nutrient deficiency. This is a direct path to a change in the pigment composition of the skin layers, expressed in the appearance of white spots (pigment deficiency) in individual cells and its excessive accumulation in others.
This reason is also confirmed by laboratory studies: in the analyzes studying these spots, there is no causative agent Lewis - the bacterium itself, while papular eruptions, roseola and chancre contain Treponema pallidum in excess. The only mystery, even for modern scientists, remains the fundamental location of the Venus necklace on the neck.
Description of the disease
Ways of transmission of infection:
- The sexual tract occurs during any type of sexual intercourse (including anal, oral) due to the fact that the highest concentration of Treponema pallidum is determined in the discharge of syphilitic chancre, sperm, and vaginal secretions. When any of the listed liquids come into contact with the mucous membrane of the genital organs, oral cavity, or rectum, there is a high risk of transmission of infection from a person affected by syphilis to a healthy person.
- The contact-household route is implemented many times less frequently than the sexual route, but its role in the transmission of infection cannot be excluded. If there is a syphilitic chancre in the human oral cavity, treponemes can be transmitted through kissing, using shared utensils or cigarettes. If the chancre is on the surface of the body or genitals, then transmission through clothing, bedding, and towels is possible.
- Transfusion route – transmission of infection through blood transfusion. At the moment, this route is extremely rare, due to the fact that all blood at transfusion stations undergoes multiple, thorough testing for various sources of infection.
- The transplant route is the transmission of infection during organ transplantation. Also very rare due to the above reasons.
- The vertical route is transmission from mother to fetus both during the intrauterine development of the child and during childbirth.
- A professional path arises for people who work with blood, body secretions, whose profession is associated with injury to the surface of the skin (doctors, laboratory assistants, tattoo artists).
Syphilis occurs in stages and, in the absence of proper treatment, can last for decades. Each stage has a specific symptom complex.
Transmission routes
How is syphilis transmitted? Transmission of infection occurs in the following ways:
During sexual intercourse. Infection occurs during unprotected sexual intercourse. The causative agents of the disease can be present not only in the blood of the infected person, but also in a number of body fluids - semen or vaginal secretions. In this regard, the risk is so high that one sexual contact is enough.
The ability to transmit is present during any type of unprotected sexual intercourse: anal, oral and traditional. It is the most common method of transmission of the disease.
Household way. Treponema pallidums are not characterized by high viability, therefore, when outside a favorable environment, their life cycle is limited. This route is quite rare as a method of infection. The opportunity arises through direct close contact with a sick person if there is a hard chancre on his body.
In such cases, pathogens are found on the personal items of the sick person, and failure to take precautions leads to infection. A fairly frequently asked question is about the ability to transmit a virus in everyday life through a kiss or handshake. Infection through saliva is possible in the presence of syphilitic ulcers in the oral cavity.
Through bodily contact, infection occurs in the presence of microtraumas upon contact with infected surfaces.
Entry of the virus through the blood. When transfusing blood that has not been tested for the presence of a sexually transmitted disease, or using common medical instruments and non-disposable syringes during injections, blood transfusion transmission occurs from the virus carrier to a healthy person.
In everyday life, it is possible to share personal hygiene items that may contain contaminated blood, for example, shaving machines or toothbrushes, manicure accessories.
Transfer to the embryo from the mother. The baby receives congenital syphilis in the womb; of course, the natural placental barrier has the ability to protect against a number of infectious agents, but treponema is not one of them. Therefore, this type of disease in children is regarded as congenital.
Quite often, infection of the embryo leads to its death before birth. If this does not happen, then the risk of birth with damage to the vital functions of the body is 97%.
In addition to the intrauterine method of infection, transmission methods can be: during childbirth; when fed with mother's milk. Knowledge about the methods of transmission of infection helps to combat it successfully. For example, if the mother is infected just before birth, a caesarean section is performed and the baby is immediately transferred to artificial feeding.
Source: heal-skin.com
What does a syphilitic rash look like?
Syphilitic rash is extremely diverse in its manifestations.
So, manifestations of a syphilistic rash:
- In the primary stage, it is a single or multiple erosion with a dense bottom - chancre.
- With secondary syphilis , the process takes on a generalized form, the rash is characterized by a variety of morphological elements (roseola, papules, pustules, condylomas, etc.), which can be localized on any surface of the skin.
- Manifestations of tertiary syphilis, unlike the previous form, are localized. In certain areas of the skin, compactions (nodules, gummas) are detected, which undergo necrosis with the formation of a bright red ulcer with smooth edges. Subsequently, a rough scar is formed.
Syphilitic rash in women
The manifestations of the rash due to syphilis in women and men are practically no different. Only some difference in the localization of morphological elements is possible. In women, rashes are much more often localized in the chest area.
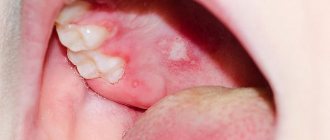
Hard chancroid, which forms at the site of infection, is more often than in men, found in the oral cavity (including in the form of syphilitic sore throat), in the anal area.
Syphilitic rash in men
In men, compared to women, a rash in the form of spots on the neck and palms of the hands is often detected.
What it is?
This is a skin reaction to the presence of the Lewis pathogen in the body - Treponema pallidum. It is expressed in small-sized pigment spots covering the upper part of the body, and in rare cases – its central part.
This symptom appears several months after the infection enters the body and in medicine has a less romantic name: syphilitic leukoderma. This name was given to it by the German infectious disease specialist A. Neisser at the end of the nineteenth century, but the first descriptions of this symptom are more ancient, and its Latin name is more familiar to the ears of even modern doctors - venereologists.
Leucoderma has two more literary names: “Venus’s crown” or “Venus’s belt”.
In addition to spots covering the body of men and women in the décolleté and neck area, signs of syphilis also include similar symptoms spreading throughout the body, baldness (focal or diffuse), and syphilitic ulcers.
All these symptoms are part of the legend about the curse of the goddess Venus on the earthly youth, who decided to take revenge on him for his betrayal with gifts: a red shirt, a hat and a pearl necklace, which turned out to be the main signs of the disease.
How does syphilis appear on the skin?
Syphilitic manifestations are very diverse and cause difficulties in the differential diagnosis of syphilis with other skin diseases. The morphological elements that appear on the skin during syphilis vary depending on the stage of the process.
During this period, the pathogen is in the human body, but its concentration is not enough to cause symptoms of the disease. There are no manifestations on the skin.
After the specified time period, when Treponema pallidum accumulates, the stage of primary syphilis develops. It is characterized by a single, but most contagious skin manifestation - chancre.
Chancre
It is formed, as a rule, at the site of penetration of Treponema pallidum (with genital contact - in the genital area, with oral-genital contact - in the oral cavity, in the lip area, etc.).
The formation of chancre occurs in several stages:
- formation of a small spot, pink-red color;
- formation of an erosive defect;
- compaction of the erosion bottom, color change to bright red. The erosion is covered with a transparent or brown film.
With timely treatment or, on the contrary, transition to the next stage of syphilis, the chancre again enters the spot stage and then completely disappears. As a rule, such a tumor does not cause discomfort in an infected person. Slight itching may occur in the area of erosion.
You might be interested! Hemorrhagic rash: photos, causes and principles of treatment
Chancre is classified according to the following criteria:
- by quantity (single, multiple);
- according to the depth of the skin lesion (erosive - affects only the superficial layers, ulcerative - the lesion affects the deep layers of the skin);
- by size (dwarf - less than 10 mm, medium - 10-20 mm, giant - more than 40 mm).
There are also atypical forms of chancre, which are extremely rare.
These include:
- chancre-amygdalid : a hard chancre located on the tonsil (in the ulcerative form of this process, a single tonsil is affected, it becomes compacted and a bright red ulceration with smooth edges is formed on the surface; in the angina-like form, a tissue defect does not form, the tonsil is dense, painless, pale treponema are found on its surface);
- chancre-felon (the clinical picture is similar to streptococcal felon, however, with a syphilitic nature, acute inflammation does not develop);
- indurative edema manifests itself in the genital area in the form of sharp swelling and changes in tissue turgor.
As a rule, diagnosing a typical chancre does not cause much difficulty. Its distinctive feature is the enlargement of regional lymph nodes, which remain dense and painless throughout the course of the primary stage.
Complications of chancroid:
- balanitis;
- balanoposthitis;
- phimosis;
- paraphimosis;
- phagedenism;
- gangrene.
Photo
The photograph shows the typical shape of chancre. There is a clear demarcation of this formation from healthy skin, a hyperemic surface of erosion, covered with a thin transparent film.
Diagnosis and treatment
This disease can be treated only after consultation with a specialist dermatovenerologist, who will prescribe all the necessary diagnostic measures and adequate appropriate treatment.
It is unacceptable to make independent decisions about taking medications, as well as the use of traditional medicine. Treatment of syphilitic lesions in the human body is a rather lengthy process, in which it is necessary to take medications continuously for several months. And in later stages of the disease, therapy can last several years.
Treponema pallidum is very sensitive to penicillin antibiotics, which is why they are prescribed to all syphilitics. If these drugs are ineffective, they are replaced with tetracyclines, fluoroquinolones or macrolides. Most often, treatment of syphilis occurs in a hospital setting, where the patient is administered penicillin every three hours for several weeks.
The patient is also prescribed vitamin substances that help strengthen and restore immunity, which suffers during long-term treatment with antibiotics. Among the medications prescribed to patients with syphilis are the following:
- Bicillin, Ampicillin, Retarpen, Azlocillin, Ticarcillin, Extensillin.
- Medicamycin, Clarithromycin, Ciprofloxacin, Ceftriaxone, Doxycycline.
- Miramistin, Doxilan, Biyoquinol, Bismoverol.
Treatment for syphilis can be considered successful only if the disease does not recur for five years. It is very important to follow all the doctor’s instructions, as well as completely avoid sexual intercourse during medication treatment.
It is very important to follow preventive measures, avoid casual sex, and do not neglect personal hygiene and barrier method of contraception. A patient with syphilis must have his own separate dishes, towel, razor and other supplies.
How to determine what causes skin changes? If a rash of unknown origin appears, you should consult a dermatologist. In many cases, the diagnosis becomes clear upon examination. To confirm the syphilitic cause of the disease, additional studies are carried out:
- detection of treponemas in discharge from chancre or erosions;
- non-treponemal tests (microprecipitation reaction or rapid reaction with plasma);
- treponemal tests (immunofluorescence reaction, treponemal immobilization reaction);
- enzyme immunoassay (passive hemagglutination reaction).
Laboratory diagnosis of syphilis is quite difficult. It is difficult to interpret the results yourself, so consultation with a doctor is necessary.
Source: furunkul.com; ginekolog-i-ya.ru
Drug treatment
Treatment of syphilis is carried out taking into account the clinical stages of the disease and the patient's susceptibility to drugs. Seronegative early syphilis is easier to treat; in late versions of the disease, even the most modern therapy is not able to eliminate the consequences of syphilis - scars, organ dysfunction, bone deformities and nervous system disorders.
There are two main methods of treating syphilis: continuous (permanent) and intermittent (course). During the process, control tests of urine and blood are required; the well-being of patients and the functioning of organ systems are monitored. Preference is given to complex therapy, which includes:
- Antibiotics (specific treatment for syphilis);
- General strengthening (immunomodulators, proteolytic enzymes, vitamin-mineral complexes);
- Symptomatic drugs (painkillers, anti-inflammatory, hepatoprotectors).
Prescribe a diet with an increased proportion of complete proteins and a limited amount of fat, and reduce physical activity. Sexual contact, smoking and alcohol are prohibited. Psychological trauma, stress and insomnia negatively affect the treatment of syphilis.
Patients with early latent and contagious syphilis undergo the first course of 14-25 days in the clinic, then are treated on an outpatient basis. Treatment of syphilis begins with penicillin antibiotics - sodium or potassium salt of benzylpenicillin, bicillins 1-5, phenoxymethylpenicillin are administered intramuscularly.
A single dose is calculated based on the patient’s weight; if there are inflammatory signs in the cerebrospinal fluid (spinal fluid), then the dosage is increased by 20%. The duration of the entire course is determined according to the stage and severity of the disease.
Permanent method: the starting course for seronegative primary syphilis will take 40-68 days; seropositive 76-125; secondary fresh syphilis 100-157.
Course treatment: tetracyclines (doxycycline) or macrolides (azithromycin), bismuth-based drugs - bismovrol, bijoquinol, and iodine - potassium or sodium iodide, calcium iodine are added to penicillins. Cyanocobalamin (Vit. B-12) and coamide solution enhance the effect of penicillin and help increase the concentration of the antibiotic in the blood.
Injections of pyrogenal or prodigiosan, autohemotherapy, and aloe are used as nonspecific therapy for syphilis, increasing resistance to infection. During pregnancy, syphilis is treated only with penicillin antibiotics, without drugs with bismuth salts.
Proactive (preventive) treatment: carried out as in the case of seronegative primary syphilis, if sexual contact with an infected person was 2-16 weeks ago. One course of penicillin is used for drug prevention of syphilis if contact occurred no more than 2 weeks ago.
Prevention of syphilis - identification of infected people and the circle of their sexual partners, preventive treatment and personal hygiene after sexual intercourse. Examinations for syphilis of people belonging to risk groups - doctors, teachers, staff of kindergartens and catering establishments.
Source: izppp.ru
ethnoscience
In addition to the main treatment of syphilis with the help of medications, this disease can be treated using traditional medicine.
For example, using wine and garlic. There are several ways to prepare this product. You need 100 ml of water, 200 ml of apple juice, 400 ml of red wine, 6-7 cloves of garlic, 200 mg of strawberry jam. Strawberry jam is poured with water and boiled, then juice and warm wine are added. Everything is mixed and cooled. Then crushed garlic is added to it, mixed again and left to brew for 3 hours. After this time, the product is filtered through gauze (double layer). Directions for use: take 100 ml every day.
You need cranberry juice (5 tablespoons), lemon juice (8 tablespoons), 200 ml of red wine, garlic (7-8 cloves). The wine is heated and mixed with lemon and cranberry juices, then heated again. Crushed garlic is added to the resulting mixture and infused for 4 hours. After which it is filtered. Directions for use: take 200 ml every day before bed.
You need garlic (7 cloves), hawthorn berries (200 g), Antonov apples (2 pcs.), rose hips (200 g) and water (2 liters). The apples are washed well and grated on a fine grater. The resulting gruel is mixed with hawthorn berries, garlic and rose hips.
The mixture is poured with boiling water (2 liters) and left to steep for 2 hours. After this, the resulting product is filtered through cheesecloth. Directions for use: take 0.5 cups every day 3 times after meals.
You need 0.5 teaspoons of ground cinnamon, 400 ml of red wine, 7-8 cloves of garlic, 70 ml of natural coffee, 6 tablespoons of honey. The wine is heated, cinnamon, coffee and honey are added to it, everything is mixed and heated to 40 degrees. Then it is removed from the heat and crushed garlic is added and filtered. Directions for use: Take 20 minutes after straining.
Treatment of syphilis with Yakut field grass and sedge. In the treatment of syphilis, a decoction prepared from the root of sandy sedge is very effective. It is necessary to thoroughly peel the root, chop it finely or grind it using a meat grinder, take 20 g and pour 600 ml of boiled water.
Place on low heat and cook until the amount of liquid is reduced by half. Then leave to brew for 2 hours. Strain and take 4 times a day, ¼ cup. Take 1.5 tablespoons of Yakut field herbs, pour 2 glasses of boiled water and leave for 4 hours. Then strain and take 1 teaspoon 5 times a day.
A folk remedy such as hops also helps in the treatment of syphilis. Method for preparing the decoction: 2 tablespoons of hops are poured into 500 ml of boiled water, then infused for 2 hours. After this, it is filtered and taken 4 times a day, 100 ml.
The shelf life of this decoction is short. It only needs to be stored in the refrigerator for 2 days. You can also prepare a decoction of burdock root. To do this, add 1 tablespoon of burdock root to 200 ml of water and heat over low heat for about 20 minutes. Then strain the broth and take 1 tablespoon 4 times a day.
Source: healthwill.ru
Secondary syphilis
In the absence of adequate treatment, primary syphilis progresses to the next stage. The period from the moment of infection to the onset of manifestations of secondary syphilis is 10 weeks . Secondary syphilis is characterized by the spread of treponemes through the hematogenous route, and therefore the process affects not only the area of direct infection, but the entire body as a whole.
The chancre disappears, general weakness develops, the temperature rises to 38C, headaches, pain in muscles and joints. There are no manifestations on the skin, so during this period it is extremely difficult to suspect a syphilitic infection.
When skin rashes appear, the general condition usually returns to normal. Secondary syphilis is characterized by true polymorphism. The main morphological elements are roseola and papules (roseola-papular rash), and the appearance of pustules and vesicles is also possible.
There is a wide variety of forms of skin lesions with secondary syphilis:
- spotted syphilide (the most common form, represented by roseola rash);
- papular syphilide;
- wide condylomas;
- pustular syphilide;
- acne pustular syphilide;
- smallpox syphilide;
- impetiginous syphilide;
- ectymatous pustular syphilide;
- rupioid pustular syphilide;
- syphilitic leukoderma;
- syphilitic alopecia.
Consequences of infection
It is important to understand that syphilitic roseola is a rash that appears when the disease has already become serious. If treatment is not started at this stage, it will lead to irreparable consequences, irreversible damage to the brain and spinal cord, circulatory system and other internal organs. Syphilis will smoothly and imperceptibly pass into the third stage, which is absolutely not amenable to therapy. With tertiary syphilis, which develops in 40% of patients, it is only possible to maintain vital body functions and stabilize the condition. Like many sexually transmitted diseases, syphilis often results in disability or death.
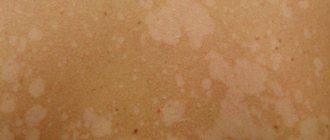
Necklace of Venus (syphilitic leucoderma)
It is a specific sign of syphilis. It forms in the neck area and appears as light, round lesions on the skin that look like a necklace.
Photo
The photograph shows a large number of light spots on the brown surface of the patient's skin, forming a characteristic Venus necklace .
Photo
The photograph shows a patient with a roseola rash , a characteristic manifestation of secondary syphilis.
Third stage of syphilis
Develops in the absence of adequate treatment 6-10 or more years after infection . The main morphological elements of this stage are syphilitic gumma, syphilitic tubercle. As a rule, at this stage, patients are concerned about severe aesthetic defects that form during the active course of syphilis.
Elements of the third stage of syphilis:
- Tuberous syphilide is a dense tubercle of a cyanotic hue, which can necrotize according to the coagulation type, resulting in the formation of an area of tissue atrophy. With liquefaction necrosis, an ulcerative defect is formed on the surface of the tubercle, in place of which, during the healing process, dense, receding scars are formed. Along the periphery of the resolving tubercles, new tubercles are formed that do not merge with each other.
- Gummous syphilide is a node that forms in the subcutaneous fat. In the center of the node, a center of tissue melting is determined, a hole is formed on the surface of the skin, through which exudate is released from the center of the gum. The size of the presented hole gradually increases, as necrotic processes are activated, and a gummous core is formed in the center of the lesion. After its rejection, the ulcer regenerates with the formation of a deep retracted scar.
Photo
The photograph shows a star-shaped scar in the nasal area, which forms after the healing of an ulcer in the tertiary period of syphilis.
Prevention
Disease prevention measures:
- Due to the fact that the main route of transmission of syphilis is sexual, the most important aspect of prevention is avoiding sexual contact with infected people.
- There is also preventive treatment that is given to pregnant women who have previously had syphilis; newborns whose mothers have not received a full course of treatment for syphilis.
- Also, special therapy is prescribed for people who have had sexual or personal contact with an infected person, if no more than 60 days have passed since the contact.