Atheroma is a common benign neoplasm, which is most often localized on the face, neck or torso. It does not pose a serious threat to health, but if left untreated, it can cause inconvenience and aesthetic discomfort. By origin it refers to retention (residual) cysts. There are two main types of neoplasm - true and false.
When the disease occurs, the full functioning of the sebaceous glands is disrupted, which leads to difficulty in the outflow of secretions. Most often, atheromas appear in young people aged 20-30 years. According to statistics, women get sick twice as often as men. Let's take a closer look at the clinical picture, the causes of atheroma and methods of its treatment.
Symptoms of atheroma
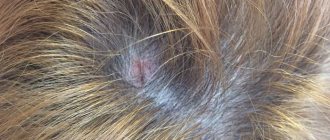
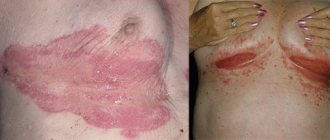
Atheroma appears in areas rich in sebaceous glands (in particular, on the back, scalp, face, neck, shoulders). Visually, it is a soft, round growth that protrudes slightly under the skin. Sometimes the contents are liquid, so fluctuation (oscillating movement) is felt. At the top, a clogged duct in the form of a black dot is often noticeable. If the tumor is localized in an area of close contact with clothing, signs of inflammation may be present. If it is on the scalp, the hair above it thins. Against the background of constant trauma, necrosis often occurs, ulcers and bleeding appear.
Small atheroma (up to 2 cm) is characterized by painlessness and elasticity upon palpation. In the case of an inflammatory process, the clinical picture can vary greatly. In such a situation, a person feels strong discomfort when pressing. The neoplasm increases in size, and a local increase in temperature is noted.
Symptoms of the disease
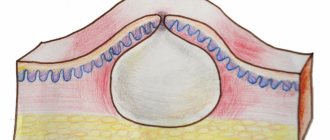
Atheromas look like rounded neoplasms of regular shape and are elastic to the touch. The contents of the tumor are mainly represented by the protein keratin, which is synthesized by its internal walls.
This condition is more common in women aged 40-50 years. Atheromas can appear on any part of the body. However, favorite places are the shoulders, back, head and neck.
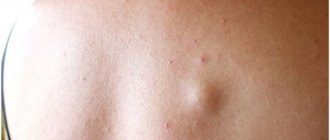
The classic patient complaint is the presence of an elastic tumor, which is located in a certain area of the skin. The formation is mobile and painless (in the absence of an inflammatory process). The skin over the neoplasm has an unchanged color and does not fold.
Sometimes the atheroma has a connection (a small hole) with the outer part of the skin, through which white or yellow masses can be released, often with an unpleasant odor. The growth rate of atheroma depends on the individual characteristics of the individual patient. Sometimes the size of the clogged gland does not change for years, and in some patients it increases significantly in a few months.
- Develops on the hairy areas of the body, most often the head, face, back, external genitalia
- The size of the atheroma ranges from a few millimeters to the size of a hazelnut
- The formation is located superficially, it has a dense elastic consistency, with clear boundaries, and is mobile
- The skin does not gather into a fold over the atheroma
- The color of the skin over the formation is unchanged or slightly lighter
- A blocked duct can be seen in the middle of the formation
- On palpation the formation is painless.
Reasons for the appearance of the tumor
Atheromas can arise for various reasons (the mechanism of development is similar to cysts). Often there are congenital causes, for example, abnormalities in the structure and function of the sebaceous glands, genetic pathologies. In most cases, such neoplasms are multiple. Sometimes the reason lies in acquired pathologies and conditions leading to the appearance of atheromas. They occur against the background of blockage of the ducts of the sebaceous glands. At the same time, there are a number of factors that can lead to the appearance of a neoplasm. Among them:
- minor damage to the skin (scratches);
- deviations from the endocrine system (hormonal changes);
- inflammatory skin damage (for example, acne);
- metabolic disorders leading to changes in sebum secretion;
- swelling of the hair follicle;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- use of low-quality cosmetics.
Getting rid of atheroma
Atheroma is a benign neoplasm, which is colloquially called a wen . Officially, its second name is sebaceous cyst. The size of the atheroma can be different - from a tiny tubercle to a large plum. Dense, mobile tumors protrude from under the skin, stretching it. They usually occur in areas where there are hair follicles - primarily on the head (particularly on the face).
In a calm state, atheromas do not cause obvious physical discomfort. However, they can become inflamed, which leads to a general deterioration of a person’s condition – fever, swelling, and pain. In exceptional cases, festering “wen” can break through the skin and come out - and deep ulcers form.
Causes
It is believed that atheromas can be either congenital or acquired . In the first case, the child is already born with a specific pathology - his sebaceous glands are located too deep, not allowing normal outflow through the pores. The gland works, but the fat cannot come out - an enclosed pouch forms under the skin, which increases over time.
In the second case, the initially “working” sebaceous gland is clogged. This may be due to improperly selected hygiene products, genetically determined excessive sweating, hormonal disorders (including those caused by taking specific medications), and concomitant diseases (oily seborrhea, acne).
Possible inconvenience and risk
Network specialists warn that self-removal, “squeezing out” atheroma (especially festering) is unacceptable ! Even in a medical office, this manipulation is performed with extreme caution so as not to damage the fat capsule.
It is still necessary to remove the atheroma, but this should only be done by professionals. You should get rid of such a tumor for several reasons:
- so as not to wait for inflammation and the subsequent appearance of an ulcer;
- to get rid of an obvious cosmetic defect;
- to prevent degeneration - in some cases, atheroma can transform into a malignant tumor.
Methods of treatment and removal of atheroma
It is most often proposed to remove atheroma using the usual surgical method, radio wave method or laser. The network of Hi-Tech Cosmetology clinics uses the laser method - the most convenient, safe and less traumatic. Bleeding is minimal, no scars are left on the skin, the patient does not require a rehabilitation period, and the procedure itself takes place very quickly, under light local anesthesia. It is important that there is no need to shave off the hair if the tumor is on the scalp.
The only limitation concerns the condition of the atheroma - in case of suppuration, it will be necessary to resort to surgery followed by drug treatment of inflammation. That is why you should not delay your visit to the doctor.
If you have any questions, you can contact a specialist.
Prices for procedures to get rid of atheroma
Laser removal of skin tumors
Read more about the procedure
Prices
Per unit (fixed prices)
| Removal of neoplasms with laser Up to 10 mm (nevi (moles), fibromas, seborrheic keratomas, atheromas, angiomas, flat warts, hemangiomas, cutaneous horns, basal cell carcinomas, curatoacanths, botryomics, telangiectasia, xanthelasma, dermatofibromas, epidermoid cysts) | ||
| On the body (torso) | Cost: 1190 rubles | |
| On the face, scalp | Cost: 1490 rubles | |
| In the orbital area (except for the mucous membrane of the eye) | Cost: 1990 rubles | |
| Removal of neoplasms with laser More than 10 mm (nevi (moles), fibromas, seborrheic keratomas, atheromas, angiomas, flat warts, hemangiomas, cutaneous horns, basal cell carcinomas, curatoacanthomas, botryomics, telangiectasia, xanthelasma, dermatofibromas, epidermoid cysts) | ||
| On the body (torso) | Cost: 1590 rubles | |
| On the face, scalp | Cost: 1990 rubles | |
| In the orbital area (except for the mucous membrane of the eye) | Cost: 2690 rubles | |
| Removal of skin papillomas on the body (torso) | ||
| from 1 to 5 pcs | Cost: 300 rubles | |
| from 6 to 15 pcs | Cost: 200 rubles | |
| from 15 to 30 pcs | Cost: 150 rubles | |
| over 30 pcs | Cost: 90 rubles | |
| Removal of skin papillomas on the face (except for the mucous membrane of the eye) | ||
| from 1 to 5 pcs | Cost: 990 rubles | |
| Over 5 pcs | Cost: 690 rubles | |
| Removal of molluscum contagiosum, milia | ||
| On the body (torso) | Cost: 300 rubles | |
| On the face | Cost: 690 rubles | |
| In the orbital area (except for the mucous membrane of the eye) | Cost: 990 rubles | |
| Anesthesia | ||
| Infiltration needle 30G/32G lidocaine | Cost: 100 rubles | |
| Infiltration needle 30G/32G ultracaine | Cost: 390 rubles | |
| Superficial anesthesia Emla 2.5 g, fixed price | Cost: 490 rubles | |
| Scar correction injection (Kenalog or Diprospan) ampoule | Cost: 2500 rubles | |
| Examination BEFORE/AFTER removal of skin tumors (consultation with a dermatologist) | Cost: Free | |
| Consultation with a dermatologist | Cost: 1000 rubles | |
| Primary consultation with a dermatologist-oncologist | Cost: 1000 rubles | |
| Repeated consultation with a dermatologist-oncologist with issuance of a conclusion based on histology results | Cost: 500 rubles | |
| Dermatoscopy | Cost: 490 rubles | |
| Histology of one neoplasm | Cost: 2690 rubles | |
Promotion
| Consultation + dermatoscopy + laser removal of tumor 3 in 1 + 25% discount on additional removals | Cost: 1790 rubles |
All prices: Laser tumor removal
Laser removal of atheroma
More about the procedure
Prices
Per unit (fixed prices)
| Removal of atheroma with laser up to 10 mm | ||
| On the body (torso) | Cost: 1190 rubles | |
| On the face, scalp | Cost: 1490 rubles | |
| In the orbital area (except for the mucous membrane of the eye) | Cost: 1990 rubles | |
| Removal of atheroma with laser more than 10 mm | ||
| On the body (torso) | Cost: 1590 rubles | |
| On the face, scalp | Cost: 1990 rubles | |
| In the orbital area (except for the mucous membrane of the eye) | Cost: 2690 rubles | |
| Histology of one neoplasm | Cost: 2690 rubles | |
| Dermatoscopy | Cost: 490 rubles | |
| Infiltration needle 30G/32G lidocaine | Cost: 100 rubles | |
| Infiltration needle 30G/32G ultracaine | Cost: 390 rubles | |
| Consultation with a dermatologist | Cost: 1000 rubles | |
| Primary consultation with a dermatologist-oncologist | Cost: 1000 rubles | |
| Repeated consultation with a dermatologist-oncologist with issuance of a conclusion based on histology results | Cost: 500 rubles | |
| Examination BEFORE/AFTER removal of skin tumors (consultation with a dermatologist) | Cost: Free | |
Promotion
| Consultation + dermatoscopy + laser removal of tumor 3 in 1 + 25% discount on additional removals | Cost: 1790 rubles |
All prices: Laser removal of atheroma
Diagnosis and treatment of atheroma
Diagnosing atheroma is not difficult. As a rule, examination and palpation are sufficient for a specialist. Sometimes it is necessary to additionally perform an ultrasound of soft tissues to determine the exact size of the tumor. To exclude a malignant tumor, a puncture biopsy may be prescribed.
The treatment of atheroma is carried out by a surgeon. After diagnosis, he will prescribe appropriate therapy. The main indications for removal of atheroma are cosmetic defects and complaints of frequent inflammation. Removal is carried out under sterile operating room conditions. It is prohibited to try to open the wen on your own, since the risk of infectious complications is high. There are three main methods of removal; the most suitable method is chosen individually (according to localization). Let's take a closer look at each one separately:
- Surgical intervention. The capsule is opened, the contents are cleaned and removed. At the end, stitches are applied (for about 7-10 days). Thanks to local anesthesia, the patient does not experience discomfort.
- Radio wave method. High frequency waves heat and vaporize damaged tissue. As a result, a small wound surface remains, which heals over time. No stitches are required.
- Laser method. This is the most modern and safe technique. In the case of a small wen, a beam is directed at it and burned out. For a tumor larger than 10 mm, the procedure begins with opening the capsule with further laser treatment of the cavity. As in the previous method, no stitches are required. The laser leaves no scars.
Removal of atheroma on the head
Patient review, Igor, 32 years old
“To be honest, I was tormented by atheromas on my head: they began to appear in adolescence and appeared again and again. I began to find out whether it was possible to remove atheroma on the head: it turned out that it was not only possible, but also necessary.
I was happy with everything about Platinental: the doctor, the location of the clinic, the cost of the procedure, and the preparation. Before the operation, they did tests, told all the details, including whether it was possible to wash your hair during rehabilitation - it turns out you CAN! You didn't even need to shave your head!
Now a year has passed, I don’t remember about atheromas.”
Surgical removal of scalp atheroma is performed under local anesthesia. Since the main task is to remove the atheroma completely, it is impossible to do without an incision. Another thing is how it is made. At Platinental we use a variety of techniques from the arsenal of plastic surgery. They allow you to make the incision almost invisible.
Scar after removal of scalp atheroma. Surgeon: Vasiliev Maxim.
Depending on the situation, either classical surgery using the thinnest nanoscalpel, or laser treatment of atheroma, or radiosurgery is used. The correctly chosen method will help not only to get rid of atheroma forever, but also to get rid of scars, thanks to a unique multi-stage technology for working with sutures.
Preventive actions
Prevention of atheroma will prevent its reappearance. It is necessary to eliminate the root causes that may lead to its development. It is important to observe the rules of personal hygiene and regularly care for your skin (taking into account its type). It is forbidden to squeeze out pimples and other formations on the skin yourself. It is necessary to monitor hormonal levels, controlling metabolism.
Diet plays an important role in prevention. It is necessary to maintain a balanced diet, since a lack of vitamins and microelements, as well as an excess of fried, spicy and fatty foods, lead to malfunction of the sebaceous glands. If atheromatosis is diagnosed, all unwanted foods and alcohol-containing drinks should be excluded from the daily diet.
Possible complications
A very common complication of atheroma is its suppuration. After the addition of a bacterial infection, the tumor increases in size with the appearance of:
- Secondary inflammation of atheroma
- Development of suppurative processes in the skin and subcutaneous tissue
- Re-formation of atheroma after its spontaneous opening or poor-quality removal (relapse)
- Scars after elimination of a neoplasm
- In very rare cases, it is possible to transform an atheroma (epidermoid) into a malignant tumor; retention atheromas never become malignant.
If left untreated, the atheroma membrane may rupture on its own, which is accompanied by the release of thick pus with the sebaceous contents of the tumor. Further spread of infection to nearby tissues threatens the development of phlegmon. In such a case, the patient requires immediate surgical intervention with drainage of the affected tissue area.
Specialists at the Shifa clinic recommend removing atheroma in Moscow even before complications develop. Elimination of a blocked sebaceous gland at an early stage of development prevents deterioration of the patient's condition and guarantees a good cosmetic effect.
How to sign up for the procedure
If you decide to remove the tumor, you can contact an experienced surgeon, Kirill Viktorovich Listratenkov. He has been specializing in surgical interventions using the latest technologies for many years. At the initial appointment, the doctor will conduct an examination, collect anamnesis to identify possible contraindications, and tell you in detail about the procedure. Complete confidentiality and security are guaranteed.
The pricing policy is loyal. Accurate information about the cost can be obtained by contacting the administrator at the specified number. To make an appointment for a consultation, simply leave a request online, indicating the desired date and time. In addition to atheromas, Kirill Viktorovich can remove nevus and a number of other neoplasms.
Treatment
Treatment of skin atheroma is not required if it is small in size and not inflamed. In this case, it is enough to observe the neoplasm. As the size of the tumor increases, if it causes discomfort and is a cosmetic defect, it is removed surgically. Surgery is performed under local anesthesia. There is no conservative treatment for the disease.
The intervention is performed in a clinic and does not require hospitalization if the skin atheroma is small and located in a place convenient for the intervention. The tumor is excised along with the capsule, as this gives a better effect and reduces the risk of relapse in the same place. An uncomplicated tumor is operated on in one of the following ways:
- an incision is made at the site of the neoplasm in its center, the contents are removed, and then the capsule is excised;
- an incision is made along the edge, the cyst is moved along with the intact capsule and removed with a surgical spoon;
- enucleation using two incisions and jaws, which remove the neoplasm along with the capsule.
The latter method of surgical intervention is the most effective. After removal, self-absorbing internal sutures and atraumatic thread sutures are applied, which must be removed after a week.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out on the basis of an individual examination, according to the clinical picture:
- localization;
- appearance;
- symptoms;
- visual observation, the presence of a (black dot) excretory duct;
- the presence of clear boundaries of the tumor;
- no pain.
A more accurate diagnosis is obtained using morphological and histological studies. In order to exclude lipoma and malignant tumors.
Removal of atheromas on the face
Self-treatment by squeezing is unacceptable. You can get infected and have serious complications. Neoplasms in the form of atheromas are localized in areas where many sebaceous glands are located. There are many such zones on the face. Most often it can form on the forehead, eyebrows, nasolabial triangle and cheeks. Inflammation, pain, suppuration, signs of fluctuation (formation of liquid masses under the skin) provide an indication for removing the cause of discomfort - the cyst. It can only be removed through surgery. Traditionally, using laser surgery and using radio wave excision. During the operation, using traditional surgery, an incision is made in the skin over the cyst, the contents are removed and the capsule is peeled out. When using the laser method of surgery, a laser scalpel is used, and when using the radio wave method, a surgical electrode is used that emits a high-frequency current. When using alternative methods, secondary formations of cysts in the same place are excluded.