Any skin disease causes many unpleasant moments for those affected. This is not only disturbing redness, but also an unsightly appearance. Patients develop complexes and become constrained, fearing rejection from strangers. Coin eczema is no exception!
The second name for chronic skin dermatitis is nummular eczema. Patients suffer from rashes. They are bright, red, round in shape and have a clear visible edge. The affected area itches, provokes scratching, after which secondary infections occur and crusts form.
Plaques that resemble the shape of a coin make patients want to hide the affected area under clothing, although the disease is not contagious. If skin problems occur, you should definitely make an appointment with a dermatologist. If coin eczema is confirmed, treatment will be quite long and difficult. You need to be prepared for this.
Coin-shaped eczema photo with description 6 pieces
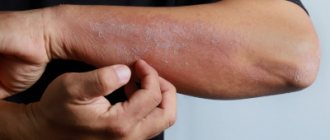
Coin-shaped eczema on the hands.
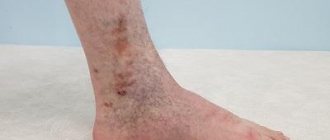
Photo 1. Coin-shaped eczema on the legs. Photo 2.
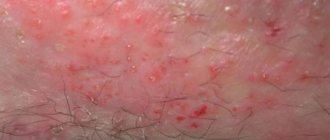
Coin-shaped eczema on the human body. Photo 3.
Coin-shaped eczema on the human body. Photo 4.
For greater clarity, you can view the visible symptoms of coin-shaped eczema in the photo; we will talk about treatment below. Looking at the rash, you can see features that indicate this particular disease. Sharply defined plaques are round in outline and approximately 1–3 cm in size. Larger spots are also possible. Redness rises above the skin. The disease got its name due to its appearance. The lesions are red with an admixture of blue, covered on top with small bubbles with a transparent light yellow liquid - vesicles.
They burst and release the substrate and the erosions become wet. The substrate dries out, forming crusts and scales. The locations of coin eczema are the surface of the palms on the back side, the places where the arms and legs bend, but they also occur on other parts of the body.
Etiology of microbial eczema
Microbial eczema appears during secondary inflammation of the skin affected by fungus or pathogenic bacteria. The causes of microbial eczema can be both pathogenic bacteria (for example, Neisser's gonococcus or fungi from the genus Candida) and an immune reaction to autoantigens.
Varieties
Based on the various causes of the rash, doctors divide microbial eczema into:
- varicose. It appears in connection with venous insufficiency and is usually localized in areas of ulceration;
- post-traumatic. These are rashes that appear in the area of healing wounds, abrasions and postoperative sutures;
- eczema of the nipples. Breastfeeding mothers most often suffer from these rashes. Eczema appears due to regular trauma to the skin of the nipples during feeding.
Causes of coin-shaped eczema
There is no complete understanding of the occurrence of this eczema. However, doctors consider its etiology to be one of the varieties of microbial. We can safely say that the risk of the disease is more frequent in people with chronic dysfunction of the epidermis and pathologies of internal organs. Since this is a microbial form, bacteria in the body are considered to be the culprit for skin problems. Factors that may impair the barrier functions of the epidermis are the following:
- Increased sweating - hyperhidrosis.
- Inflammation of the tonsils - tonsillitis.
- Sinus problems - sinusitis.
- Bronchitis.
- Everyone knows tuberculosis.
- Inflammation in the oral cavity and caries.
- Prostatitis.
- Diabetes mellitus, etc.
These are the most common possible ailments, leading to skin sensitization, and against the background of functional changes, coin-shaped eczema occurs, the photo of which is shown below.
Stressful situations also have a negative effect on the immune system. If there is a hereditary predisposition, the skin reaction process starts. Even errors in nutrition, improper use of medications and contact with antigens that activate allergy manifestations have an impact.
Find out more
How to distinguish psoriasis from dermatitis - similarities and differences
Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis are similar in the following:
- may be hereditary;
- develop in stages, periodically aggravate;
- the skin turns red and itches in the affected areas;
- microcracks and peeling appear.
In the first stages, the differences between psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis are almost invisible and a conclusion about the disease can only be drawn based on the results of examination and diagnosis. But over time, the clinical picture becomes more clear. For psoriasis:
- pale pink plaques;
- do not fade when pressed;
- do not swell;
- scales are large, whitish.
For dermatitis:
- the symptoms are acute with a transition to the chronic stage, while psoriasis is sluggish, chronic;
- no dry white plaques;
- blisters with suppuration may appear.
The difference between dermatitis and psoriasis can only be determined by a dermatologist - the sooner the nature of the lesion is determined, the faster and more successful the treatment.
How is seborrheic dermatitis different from psoriasis?
It is more difficult to distinguish between psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis. They look like lesions on the scalp with scales. The differences are as follows:
- psoriasis plaques are thicker and brighter in color;
- seborrheic scales are smaller and paler;
- seborrheic with a yellowish tint, removed without pain;
- psoriasis plaques are removed with a residual small drop of blood - blood dew syndrome.
Such subtle differences are only visible under special dermatological equipment.
Eczema or psoriasis
It is easier to distinguish eczema from psoriasis by the form of the disease. Eczema is cured faster, while chronic psoriasis is less treatable and can affect the nails and internal organs. Eczematous lesions are characterized by:
- severe itching, burning;
- lack of clear boundaries, blurriness;
- damage to the most delicate areas of the skin: folds, areas between the fingers;
- severe swelling of the affected area.
Do not try to diagnose yourself and determine whether it is eczema, psoriasis or dermatitis.
Dermatological specialists provide rapid diagnosis and effective treatment of psoriasis and dermatitis in adults and children. Modern equipment and proprietary treatment methods with 25 years of successful use are your opportunity to quickly identify and overcome skin diseases. September 9, 2021
Author of the article: dermatologist Mak Vladimir Fedorovich
Coin eczema. Medicinal causes
Symptoms of the disease sometimes appear due to self-administration of medications. Reactions are especially common when consuming a variety of nutritional supplements and medications sold without prescriptions. As a rule, such treatment is chosen independently, with frequent violations of rules and dosages. For example, using antifungal ointments to treat infections and fungi on the feet, the development of eczema is provoked.
The affected epidermis is ready at any moment to react with inflammation to the appearance of antigens. The predisposition is caused by a transition from a monovalent to a polyvalent reaction. In the first stages, an allergic effect of a substance is observed; over time, redness appears in response to various effects of different irritants.
Violation of membrane barriers, dyskinesia, fermentopathy of the digestive tract, contribute to the entry of foreign antigens. They penetrate like proteins that are not completely digested.
During the reaction, the protective properties of the skin are disrupted. It is much easier for infections to enter. Because of this, skin sensitization occurs, causing inflammation and damaging cells. Skin cells produce substances called cytokines and mediators. This accelerates inflammation. The exudation stage begins.
Swelling of the skin and blood vessels appears, we notice the appearance of red erythema with a polymorphic rash on the surface. Genetic predisposition greatly influences the course of the disease. It has been noted that if one of the parents is ill, the risk of developing the disease in children is 40%. In cases where both parents are affected, the risk is 60%.
Dermatitis and psoriasis - characteristics
Psoriasis is characterized by white scales on the surface of the skin. The affected area turns red within clear contours and is very flaky. Touching it is painful, a burning sensation is felt.
Frequent localizations of psoriasis areas:
- knees;
- hands;
- groin and genitals;
- face;
- scalp.
Among the causes of psoriasis:
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- liver diseases;
- severe stress;
- hormonal imbalances.
Dermatitis is the result of skin hypersensitivity. It manifests itself as an acute reaction to allergens. More common in childhood. A characteristic feature is long-term skin damage and redness, which is difficult to eliminate. Localized on the inner bends of the elbow and kneecaps.
Coin-shaped eczema - symptoms
Typical manifestations of the majority of patients with coin eczema, treatment of which should be carried out under the supervision of a competent dermatologist, are as follows:
- First, inflamed, round lesions appear. They are very itchy.
- After a short time, the spot becomes covered with serous bullae and papules. They itch a lot, so patients scratch them and the protruding exudate dries out, creating crusts. The erosive surface is exposed. Now it is easy for a secondary infection to penetrate.
- Papules grow, merging into a single mass and taking on the appearance of plaques with distinct boundaries.
- Starting as a rule on the extremities, weeping plaques can spread to the torso and buttocks area.
- The spots do not merge with each other, but attached infections, for example, staphylococcus, add their own symptoms. Pus forms under the crusts.
- Patients experience general weakness and nervousness.
The disease process periodically subsides and worsens again. Frequent changes in conditions can lead to a transition from coin eczema (see Photo) to true eczema. It has been noticed that males over 50 years of age often fall ill. Although women are also not uncommon. Children are very rarely affected.
Forecast
The coin form is considered the most severe type of eczema. It is difficult to treat, constantly recurs, and is quite variable. The disease cannot be completely cured, but it can be put into a state of long-term remission. To do this, you need to start treatment as early as possible and follow comprehensive approaches. You should not self-medicate, as the wrong approaches will only worsen the course of the disease. It is better to periodically see a doctor and supplement his recommendations with traditional methods agreed upon with him.
Diagnosis of coin-shaped eczema
It is not worthwhile to independently diagnose coin-shaped eczema of its causes and treat it at your own discretion. The disease can be confused with dermatitis, psoriasis, scabies, dermatomycosis, which are differentiated together.
The doctor will examine the lesions using a special device and collect anamnesis. Using a blood test, the degree of infection and the presence of viruses will be determined. Taking into account the condition of the skin, laboratory examinations will be prescribed: OAM, OAC and biochemistry. For complex forms, microbiological, allergological, and enzyme immunoassays are carried out. You will need consultations with a gastroenterologist, allergist, endocrinologist and neurologist.
Complications and consequences
If eczema is not treated, complications may occur. A secondary bacterial infection develops, which has the following symptoms.
Symptoms of secondary infection:
- weakness, poor health;
- fever;
- severe wetting;
- formation of purulent areas.
To prevent coin-shaped eczema from progressing and degenerating into a more severe form, it is necessary to promptly contact specialists and begin treatment. Doctors will be able to more accurately diagnose, understand the etiology of eczema and determine which drugs will be most effective in this case.
If you treat the disease yourself, there is a high probability of choosing the wrong path, which will only cause a deterioration in your well-being and the progression of an already severe form of eczema.
Treatment of coin-shaped eczema
Having noticed the described manifestations, experiencing itching and discomfort, each patient has a question - how to treat coin-shaped eczema? If you consult a doctor and carry out all the prescribed procedures correctly, the prognosis is quite favorable. It is impossible to completely get rid of the disease, but it is possible to achieve remission for a long time.
The fight against the disease must be comprehensive, combining medications, physiotherapeutic techniques and folk remedies. First, chronic lesions are sanitized and somatic corrections are made. It is important to stabilize the functions of various systems: endocrine, nervous, gastrointestinal tract.
Sedatives - used to relieve stress. First try lighter, herbal infusions. If the result is not satisfactory, antidepressants are prescribed. Tranquilizers and antipsychotics are also used. Sometimes desensitization of the body may be necessary. Using intravenous infusions, the body is saturated with calcium and sodium salts. If antihistamines are necessary, use: Suprastin, Diphenhydramine, Tavegil, etc. Complex cases are treated with topical steroids, detoxification, plasma replacement and antibacterial drugs. Moreover, the courses are purely individual.
Histaglobulin will help prevent exacerbations. For coin eczema, the causes of which are diagnosed as microbial, vitamin therapy and purified sulfur preparations work well. Medicines that improve digestion and eliminate dysbacteriosis are also prescribed.
Local exposure and care of the lesions help get rid of secondary viral or bacterial infections, due to which the course of the disease is delayed. Here, coin-shaped eczema is treated with folk remedies, along with medications. Weeping erosions, depending on the severity, are treated with hormonal aerosols, and antibacterial and astringent ointments based on zinc are used. Lotions with dimexide or boric acid dry well. Physiotherapeutic procedures are often prescribed.
During subsidence, substances containing topical steroids, antiseptic and antibacterial agents in the form of ointments are good. For extensive skin lesions, a dermatologist may prescribe corticosteroid hormones. This is usually prednisone, but sometimes corticosteroid injections are necessary. Particularly severe cases require plasmapheresis and hemosorption to cleanse the blood of substances that have a negative effect on the skin.
Bibliography
- Ado A.D. General allergology. M.; "Medicine", 1970.-543 p.
- Results of a study of the effectiveness of non-halogenated corticosteroids in the treatment of chronic eczema / I.M. Korsunskaya, N.A. Lukashova, Z.A. Nevozinskaya, E.E. Agafonova // Clinical. dermatology, venereology. 2008. - No. 4. — P. 101-105.
- Ryzhko, P.P. The use of antihistamines in the treatment of various dermatoses / P.P. Ryzhko // Ukr. magazine dermatology, venereology, cosmetology. 2002. - No. 1. — P. 39-41.
- Skripkin, Yu.K. Allergic dermatoses / Yu.K. Skripkin, B.A. Somov, Yu.S. Butov. M.: Medicine, 1975. - 245 p.
- Tishchenko, A.L. Optimal therapeutic doses of vitamin A in patients with eczema and psoriasis / A.L. Tishchenko // Vestn. dermatology and venereology. 1998. - No. 4. — P. 36-38.
- Turchina, I.P. Complex treatment of patients with eczema and neurodermatitis localized on the lower extremities / I.P. Turchin // Dermatovenerology, cosmetology, sexopathology. 2002. - No. 1-2 (5). - S. 98101.
- Yusupova, L.A. Treatment of patients with eczema / L.A. Yusupova, R.Kh. Kha-fizyanova // Ross. magazine skin diseases. 2005. - No. 6. — P. 20-22.
- Brazzini, B. New and established topical corticosteroids in dermatology: Clinical pharmacology and therapeutic use / B. Brazzini, N. Pimpinelli // Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2002. - N3. — P. 47-58.
- Buznikov, GA Serotonin and serotonin-like substances as regulators of early embryogenesis and / GA Buznikov, HW Lanbert, JM Lauder //Cell Tissue Res. 2001.-N 39.-P. 177-186.
- Catania, A. Inhibition of acute inflammation in the periphery by central action of salicylates / A. Catania, J. Arnold, A. Macaluso et al. //Proc. Natl Acad Sci USA. 1991. -Vol.88, N19. -P. 8544-85
Prevention of coin-shaped eczema
An important preventative stage is adherence to dietary nutrition. It should exclude any substances and allergens that can cause irritation:
- Alcohol.
- Seasonings.
- Pickles.
- Red berries and fruits and citrus fruits.
- Fish and seafood products.
- Nuts.
- Eggs.
If there is no intolerance to dairy products, then they are recommended. The basis of nutrition should be plant foods. Food is prepared by boiling, baking or steaming. Smoked and fried are contraindicated.
Regular hygiene procedures and timely treatment of infectious skin diseases, allergic dermatitis, varicose veins and others are prevention. After all, coin-shaped eczema is a disease that can be caused by previous diseases. If you are prone to skin manifestations, you need to be careful when contacting household chemicals. These are detergents, washing powders, soaps and cosmetics.
Features of the course of chronic eczema and differences from acute
We can talk about the process being chronic if the symptoms that first appeared did not go away within 2 months. Chronic eczema, unlike acute eczema, occurs in 2 stages, such as exacerbation and remission, which replace each other. Relapses usually occur in the cold season, but improvement can be noticed in the warm season. In addition to low temperature, exacerbation can be triggered by:
- increased sweating;
- contact with allergens, such as pollen;
- stress and anxiety;
- weakened immunity;
- taking certain medications;
- consumption of allergenic foods.
In the chronic stage of eczema, there is always a rash and itching. Moreover, itching usually precedes the appearance of rashes and can be used to determine that an exacerbation will soon occur. With chronic eczema, there are more dry crusts on the skin than weeping rashes, which is why this form of the disease is sometimes called dry. The crusts crack and itch very much, causing discomfort and even insomnia.
With exacerbation, the signs of chronic eczema intensify. New weeping rashes appear next to the dry crusts, but less exudate comes out of them than in the acute form. Other characteristic symptoms include:
- severe peeling of the skin;
- violation of skin pigmentation, development of pigment spots;
- pronounced linear pattern on the skin;
- excessive compaction and hardening of the rash;
- scratches and cracks in areas of thickening.
Chronic eczema in remission is manifested by constant peeling of the lesions. The skin in these places scars, so it becomes dense, and can acquire a blue-red tint in dark-skinned people and pale pink or beige in light-skinned people.