Trophic venous eczema - what is it?
Trophic venous eczema is a pathological condition that occurs in the form of autoimmune dermatitis, that is, serous non-infectious inflammation of the skin (mostly the papillary layer of the dermis and epidermis), accompanied by symptoms of swelling, redness, itching and pain.
Trophic venous eczema
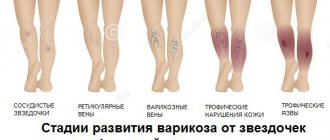
Venous eczema is a type and common form of eczema, which is caused by congestion in the skin due to impaired venous outflow. Venous eczema is also called varicose, congestive or gravitational. It most often has a chronic (recurrent) course. The pathology affects one or both lower extremities in combination with venous insufficiency. In the modern European, and most popular among leading experts, classification of chronic venous diseases - CEAP, this pathology is designated as C4a. This means quite severe tissue damage due to chronic venous edema.
Why does trophic venous eczema occur?
Venous eczema is most often observed in middle-aged and elderly patients - according to leading European dermatologists, it affects up to 20% of patients over 70 years of age. This is due to the following reasons:
- Phlebeurysm.
- Previous deep vein thrombosis of the affected limb.
- The presence of venous trophic ulcers.
- Previous cellulitis on the affected limb.
- Chronic swelling of the lower leg, aggravated by hot weather and prolonged static position (standing).
The main cause of the pathology is varicose veins, which is why you can sometimes come across the term “Varicose eczema”.
Venous eczema of atypical localization
Quite often, signs of eczema can be found in young patients with a long history of varicose veins. There is no doctor, both in public and private clinics, who would not observe venous eczema in patients under 40 years of age.
Causes of the disease
Until now, doctors cannot unequivocally answer the question about the causes of the development of eczema in adults and children. Most experts agree that the disease develops as a result of the complex influence of endogenous factors (for example, genetic predisposition) and exogenous factors (occupational, etc.). Simply put, external factors most often include various allergens that affect the body constantly or for a long time. To internal, endogenous – genetic predisposition. It has been proven that if there is a person with eczema in the family, the risk of the disease in relatives increases significantly. If one of the parents (mainly the mother) is ill, the risk of developing eczema in a child is approximately 40%; if both parents are ill, it is almost 60%
The most common factors that provoke eczema:
- chronic allergies;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- psycho-emotional triggers.
They also additionally identify factors that can weaken the body’s immunity and thereby provoke the development of eczema. This:
- chronic inflammatory processes;
- secondary immunodeficiencies;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- foci of chronic infection in the body.
Among the possible causes of eczema are psychosomatics: constant stress, various disorders of the autonomic system, anxiety and depression. Patients often exhibit functional changes in the activity of the central nervous system, a predominance of the activity of unconditioned reflexes over the activity of conditioned ones, as well as an imbalance between the activity of the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts of the autonomic nervous system.
Trophic venous eczema is very bad
Varicose eczema has a chronic, relapsing course and a tendency to progress. Quite often you can encounter a situation, especially in public hospitals, when only dermatologists treat venous eczema. Considering the main etiological component of the pathology, impaired venous outflow, treatment of such patients takes years.
Chronic recurrent eczema on the right lower limb
The disease slowly recedes, but invariably appears again. Moreover, trophic changes in the lower extremities progress, lipodermatosclerosis occurs, and then an ulcer appears.
Prevention of facial rashes
To prevent relapse of the disease, as well as in the case of a genetic predisposition (one or both parents suffer from eczema), the following rules should be followed:
- adhere to a diet: exclude spicy, fried foods, sweets, baked goods, strong broths, chicken, citrus fruits from the diet;
- lead a healthy lifestyle, play sports, walk in the fresh air, get enough sleep;
- use only hypoallergenic creams, shampoos and other hygiene cosmetics;
- if there are rashes on the skin, you need to protect your face from direct sunlight (wear a hat with a brim in the summer, use sunscreen); During the period of remission you can sunbathe.
Treatment of eczema on the face is a problem, so you need to contact a dermatologist at the initial stage of the disease, and then regularly carry out maintenance treatment.
Why does trophic venous eczema almost always appear on the lower extremities?
The answer to this question lies in the pathogenesis of varicose veins, the dominant cause of venous eczema. Varicose veins affect exclusively the lower extremities, where, according to the gravity gradient, it is in their distal parts that trophic disorders occur. One of which is venous eczema.
Trophic eczema of the lower extremities
Pathological eczematous changes in the skin of the lower extremities are most often caused by varicose veins, since they are the cause of impaired venous outflow (up to 90% according to leading experts in the region).
Trophic venous eczema - diagnosis
Diagnosis of venous eczema in public and private urban medical institutions often begins in a dermatologist’s office, where a specialist evaluates local changes in the skin. It is very important here that the patient is referred to a good phlebologist in a timely manner. If eczematous changes are associated with venous pathology, then treatment of skin manifestations only is likely to be ineffective. Even a visual examination by a phlebologist using all kinds of functional tests often does not reveal the true cause of the pathology. At this stage, the best solution would be a good ultrasound examination of the veins of the lower extremities.
Ultrasound diagnosis of trophic venous eczema
Only competent modern diagnostics of the venous system will help determine the correct treatment tactics.
Seek help from a dermatologist
It is important to confirm the diagnosis before prescribing either treatment or diet.
If you find suspicious rashes on your skin, be sure to consult a dermatologist. The effectiveness of treatment directly depends on the correctness of the diagnosis. Therefore, it is important not to delay or self-medicate. We invite you to a consultation at the PsorMak Institute for Healthy Skin. We have extensive experience in successfully treating various types of dermatitis, and we guarantee the achievement of long-term remission. April 28, 2021
Author of the article: dermatologist Mak Vladimir Fedorovich
Trophic eczema, treatment in Moscow
Good treatment of venous eczema in Moscow can be divided into local (topical effect on skin inflammation) and treatment of the venous system. In the first, a dermatologist is often actively involved. Local treatment includes:
- Ointments and creams, steroid drugs, both as part of the latter and as part of systemic treatment.
- The use of antibiotics and antiseptics when an infection occurs.
Often, in the conditions of public medicine, patient care ends at the stage of the above topical treatment. This is not the best solution, since the disease is based on completely different reasons and a relapse of the disease will not take long to occur. Namely, venous stasis, which requires a slightly different approach. It is very important that a patient in Moscow has a timely appointment and diagnosis with a good phlebologist who can determine the correct tactics for managing the patient. The treatment of venous eczema is based on eliminating stasis and improving venous blood flow. Correction of the latter most often involves removing pathologically altered varicose veins. The presence of innovative technologies in modern Moscow centers makes it possible to effectively treat even complicated forms of varicose veins, moreover, on an outpatient basis.
Treatment of trophic eczema in our phlebology center
Leading medical centers in Moscow for the treatment of venous pathology use thermoobliteration techniques for these purposes. In a good city medical phlebology center you can count on safe, effective treatment. Modern vein removal procedures are performed under local anesthesia through skin punctures with minimal surgical trauma.
How is coin-shaped eczema diagnosed?
A dermatologist may suspect coin-shaped eczema based on external signs. To confirm, standard tests are prescribed, including a general analysis of urine and blood, and a biochemical blood test. The patient may need to consult a neurologist, gastroenterologist, allergist and endocrinologist.
Coin-shaped eczema must be distinguished from other types of dermatitis, psoriasis, scabies and dermatomycosis. For this purpose, an enzyme immunoassay test of blood for antibodies is performed. To identify an infection, a microbiological examination of a smear from the site of inflammation is carried out. It also helps determine antibiotic sensitivity and prescribe the correct treatment.
Trophic varicose eczema - treatment without surgery
The main factor in the development of congestive eczema is the pathology of the venous system. Therefore, there is no need to talk about any effective treatment without radical intervention. The best solution would be to stop the inflammation and carry out a procedure to remove varicose veins. But is surgery really that scary?
Trophic eczema - laser treatment in our center
Modern European technologies for vein removal are not inferior to advanced manipulations in dentistry in terms of minimal surgical trauma and possible side effects. But today it would not even occur to anyone to refuse caries treatment due to fear of intervention.
Trophic venous eczema - laser treatment (EVLO, EVLT), radiofrequency treatment (RFA, RFO)
Considering that radical treatment of varicose eczema is the treatment of venous pathology, it is modern methods of removing varicose veins that will be the main way to combat eczema itself. Today, the undisputed leaders at the forefront of innovative treatment of varicose veins are thermal obliteration techniques, laser and radiofrequency. If we compare both technologies, there are simply no fundamental differences for the patient.
Treatment of trophic eczema with radiofrequency
What are the advantages of thermoobliteration technologies:
- Radicality and effectiveness (when used by experienced specialists, the result is practically 100%).
- Low invasiveness, the procedure is carried out through skin punctures.
- Highest cosmetic value.
- Full outpatient, no need for anesthesia or hospitalization.
- Safety and comfort of the procedure for the patient.
The result of laser treatment of trophic eczema after 1 month
After endovascular treatment, the symptoms of eczema quickly resolve on their own.
Results of treatment of trophic venous eczema. Photos before and after treatment
The result of treatment of trophic eczema using endovenous laser coagulation (EVLC) using German Biolitec technology in our center
Photos before and after treatment of trophic eczema on the left lower limb
The result of treatment of trophic venous eczema using radiofrequency ablation (RFA) in our patient
Photos before and after treatment of trophic venous eczema on the left lower limb
Frequently asked questions from patients on the Internet about trophic venous eczema
How to treat venous eczema of the legs in Moscow?
For good treatment of venous eczema of the lower extremities in Moscow, you need to contact a competent specialist, a phlebologist. The doctor will conduct a detailed diagnosis, including an ultrasound examination. Only after this can we talk about modern treatment. The best solution would be to find a good city phlebological center, where the ultrasound will be performed by the phlebologist himself.
What is the modern treatment for venous eczema of the legs in Moscow?
In Moscow, good modern treatment of venous eczema that meets European standards includes innovative technologies for both diagnosis and treatment. Leading city phlebological centers, including our Moscow Innovative Phlebological Center, successfully treat venous eczema. First, a detailed duplex angioscanning of the venous system of the lower extremities is performed. Only then is treatment prescribed, including the fight against local inflammation and modern treatment of the true cause of eczema, varicose veins.
How to treat venous eczema with folk remedies?
Specialists of the Moscow City Phlebological Center have good experience in working with various trophic disorders in venous diseases, including venous eczema. Leading phlebologists at our center do not recommend treating venous eczema with folk remedies. The disease responds well to treatment using modern technologies, but we often encountered serious complications after treatment with folk remedies.
My mother has venous eczema on her legs, which doctor is best to see?
If you suspect that your mother has venous eczema, it is better to first contact a good phlebologist, a doctor specializing in the diagnosis and treatment of venous pathology. First you need to understand the cause of inflammation in the lower extremities. You may need the help of a dermatologist. If eczema is of venous origin, then now there are modern European technologies with the help of which curing your mother will not present any special problems.
Eczema: symptoms and types
The main symptom of the disease is redness of the skin, which is also accompanied by:
- skin rashes in the form of “bubbles”, which open quite quickly, creating a “wet” effect, for which the disease is called “wetting eczema”;
- itching and peeling of reddened areas of infection (itching can have varying degrees of intensity);
- the appearance of cracks at the affected sites;
- cosmetic defects;
- thickening of the skin at the site of redness;
- increased body temperature during periods of exacerbation of eczema.
Sometimes the symptoms of eczema are similar to signs of other types of diseases (allergies, fungus, psoriasis, scabies, etc.). This suggests that self-medication in this case is impossible, because only a doctor can determine and prescribe what to treat and how. Otherwise, you will only harm your health.
If skin eczema occurs in a mild form, that is, with a small number of rashes and mild itching, then it can be confused with an allergy, that is, you miss the opportunity to quickly cure the disease and reduce the risks of unpleasant consequences and complications.
Types of eczema and their features
The classification of eczema is based mainly on the causes of infection, but the signs and pattern of development of the disease are almost the same.
- True (idiopathic) eczema: can last for several years with varying intensity of manifestations of the main symptoms; Most often it is localized on the face and back of the hands, and without treatment it spreads to other parts of the body.
- Microbial eczema: occurs as a result of bacterial infection, most often on the legs, sometimes on the face, or at wounds, burns, or ulcers on the body; often appears at the site of chronic lesions under the influence of any infections.
- Mycotic eczema: affects the skin as a result of a fungal infection, resulting in a characteristic allergic inflammation that occurs on the limbs and body, less often on the face.
- Seborrheic eczema: occurs in patients diagnosed with seborrhea; characteristic locations are places on the body where there are many sebaceous glands, for example, on the face (eyelids, eyebrows, nasolabial folds), as well as on the scalp, on the chest and in the area of the interscapular triangle.
- Varicose eczema: most often “located” asymmetrically on the legs and has a blue or purple color, caused by trophic disorders.
- Sycosiform eczema: It is caused by the bacterium Staphylococcus. The most common sites of occurrence are areas on the face with hair follicles, such as the beard and upper lip.
- Coin-shaped eczema: has a blue-pink color, appears in the form of papules and vesicles; the rashes are located in a circle, the diameter of which varies from 1.5 cm to 3 cm.
- Dyshidrotic eczema: localized on the palms, feet, fingers and toes; manifests itself as blistering rashes with swelling and nodules.
- Callous eczema: the main places of localization are the palms and soles of the feet with thickening of the upper layer of skin at the affected sites and the appearance of blisters, which then begin to resemble calluses (this form of eczema is similar in its symptoms to dyshidrotic).
In especially severe cases, a bacterial infection is “attached” to eczema, which causes purulent inflammation and a more severe spread of the disease.
There is also occupational eczema, which appears on the back of the hands and open areas of the body under working conditions that “contribute” to the development of infection. Eczema also has two forms: acute and chronic, differing in the degree and intensity of symptoms. It is necessary to treat one form or another in different ways using different approaches.
Childhood eczema occurs quite often. The appearance of eczema in children is often associated with dysbiosis, a reaction to certain foods and various abnormalities in the gastrointestinal tract. The danger of childhood eczema is that it most provokes the development of complications and unpleasant consequences.