August 20, 2018
Averyanova Sveta
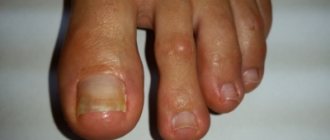
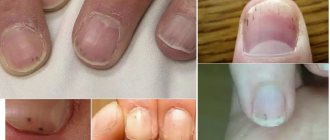
The child’s fingernails or toenails are peeling, and other unpleasant symptoms have appeared that are similar to manifestations of fungus: darkening, brittleness, fragility, even pus. In such a situation, parents ask questions: what to do and why this happens. Let's figure it out together.
Reasons why nails peel
Finding out the cause of peeling nails in children is quite simple. Analyze his diet, daily routine, remember whether there has been stress, illness or hand injuries in recent days. More often, destruction of the homogeneous nail structure occurs due to:
Injuries, mechanical damage
The nails of babies, especially infants, are very soft. Even a small blow with a hand or foot during play or crawling is enough for delamination. In this case, the plate dies and is independently replaced with a new one. The fingers turn blue and ache a little due to the bruise.
Wearing uncomfortable shoes
One-year-old babies begin to actively run outside, parents try to buy the most beautiful shoes, forgetting about convenience. They put on warm socks, not expecting that they take up a lot of free space inside the boots. As a result, the leg is cramped, the toes are injured, the soft nails are deformed, causing the plate to begin to peel.
Lack of vitamins
A strict diet, the need to exclude certain foods from the diet due to illness, and the spring period provoke a deficiency of a whole group of vitamins. For growth and the formation of the keratin layer, calcium, zinc, iron, gelatin, and vitamin E are needed.
It is easy to determine vitamin deficiency in a child: small white spots will appear on the nails, the plate will turn yellowish.
Simultaneously with the detachment on the fingers of a one-and-a-half-year-old baby, the hairs fall out, the skin turns pale, and jams appear in the corners of the lips (small weeping sores, itching).
Psychosis, nervousness
Detachment of the stratum corneum occurs after suffering stress or due to a bad habit - biting nails. Nervous children, who are under constant psycho-emotional stress, suck their fingers, damaging the plate with their teeth.
Babies often use their thumb for sucking; older children use everything, including their little finger. The nail breaks and may peel off entirely. Drug treatment, anti-inflammatory ointments and other external medications will not help in this case.
You need to see a doctor, preferably a neurologist or psychiatrist. It is imperative to establish a harmonious atmosphere at home and find out what is happening in kindergarten.
Fungal infection
You can catch the infection at the pool, in a store, trying on new shoes, in kindergarten, even at home or visiting. The fungus is not always infectious in nature. The cause of inflammation of the nail plate can be simple uncleanliness; if we are talking about a small child, then the parents are to blame for this.
Rarely changing socks, especially in summer, ignoring daily water procedures after walks, before bed, wearing wet shoes are the main provocateurs of fungus.
The nail will crack and gradually peel off if pus forms under the keratin layer. Sometimes parents note that the skin on their children’s feet is peeling and it is very itchy between the toes.
Important! Until the exact cause of the peeling of the nail plate in a small child is determined, do not give him a manicure, pedicure, especially with tools common to the whole family.
Delamination
Quite often, parents are faced with the fact that their child’s nails peel and break. Why is this happening?
This deviation causes:
- improper cutting of nails;
- lack of microelements, vitamins (vitamin A, E, B2, calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, zinc);
- mechanical damage. For example, nails on the hands peel if the child bites them or sucks fingers, on the feet - if he wears shoes that rub or squeeze the tips of the toes;
- health problems (iron deficiency anemia, adrenal dysfunction, onychomycosis).
In most cases, correction of nutrition, taking vitamin-mineral complexes, and rubbing vegetable oils rich in vitamins A and E into the nail plate helps to cope with delamination.
But if its cause is health problems, examination and tests will be needed.
Doctor Komarovsky's opinion
According to a well-known pediatrician, nails in newborns split for other reasons related to the functioning of internal organs and the peculiarities of the body’s development in the prenatal period:
Anemia
Nails do not have enough iron to mature keratin tissue. Nails grow slowly and constantly peel off if the anemia is chronic. Seasonal iron deficiency is easily eliminated by taking multivitamin complexes.
Disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract
Ulcers and gastritis, especially in young children, lead to improper absorption of minerals and vitamins. Calcium and iron are practically not absorbed during acute periods of illness, which immediately affects the condition of nails, hair, and skin.
Problems with the adrenal glands, thyroid gland
Thermodynamics are disrupted, resulting in a deficiency of nutrients supplied to the extremities. The baby's hands are cold, pale or even bluish. The nails peel and crumble. Such children are thin and weak, and often lag behind their peers in development.
Chronic illnesses, congenital pathologies
These are diabetes, malformations of internal organs, kidney and liver failure.
In the presence of serious diseases or malfunctions of the body, nail detachment will be an alarming symptom for parents. But it is not the fingers that need to be treated, but a chronic illness. After providing medical assistance to the heart, blood vessels, gastrointestinal tract, and taking a course of vitamins, the marigolds return to normal on their own.
Classification of fungal infections
In childhood, pathology is more common on the legs than on the hands. Depending on the clinical manifestation, the following forms of damage are distinguished:
- distal-lateral - the infection affects the nail bed and the lower part of the plate, which leads to thickening of the nail fold, sometimes leading to nail detachment;
- white superficial type - affects the upper layer of nail tissue, often observed on the 1st and 5th toes, which is associated with their high traumatization by shoes;
- proximal - the fungus penetrates under the nail fold, then into the matrix, so dystrophic changes affect the entire nail, cracks, irregularities and grooves appear on it, which can lead to its complete destruction;
- endonyx - a type of lesion in which there is no inflammatory reaction or hyperkeratosis, the nail plate becomes cloudy, turns white, and thickens slightly;
- total dystrophy - becomes a consequence of any of the forms described above, all elements are damaged, the nail disintegrates due to damage to the matrix, growth slows down.
Nail fungus in children may be accompanied by skin inflammation
The shape of the lesion is also determined by changes in the nail plate. The normotrophic type is characterized by maintaining normal thickness, transparency and color change, white stripes appear on the surface, and the plate becomes brittle. Sometimes yellowing of the nail is observed, and serous fluid is released from under it.
The hypertrophic type of lesion is rare in children; it is characteristic of the long-term course of onychomycosis. The nail plate thickens due to hyperkeratosis; this form can persist even several months after completion of therapy.
The onycholytic type is characterized by a gradual thinning of the nail and a change in color to dirty gray.
Symptoms
Signs of nail problems can be divided into two groups, based on the cause of peeling of the nail plate: infection (fungus) or other provocateurs.
Fungus
- Thickening of the plate.
- Pain in the toes.
- Cloudy, green tint of the keratin layer.
- Redness of the cuticle.
- Increased body temperature or locally in the area of inflammation.
- Peeling of the plate at the base of the nail.
- Changing the shape of the nail, thickening, softening the tissue.
- Uneven edges, grooves on the surface of the plate.
- Dark spots on the stock.
- In rare cases, the appearance of pus under the nail and cuticle. First of all, the root suffers, dark spots appear underneath it.
Eating disorders, injuries, habit of biting nails, tight shoes, etc.
- Deformation of the keratin tissue on the nails.
- Change in color - from yellow to bluish - in case of injury.
- The appearance of tiny white spots on the nail.
- Peeling of the top layer of the nail from the outer edge, the appearance of unevenness on the cut.
- Fragility.
The infection will always be accompanied by other symptoms of inflammation (redness of the cuticle, soreness, fluid under the nails), and everyday causes are less pronounced and can be treated much easier and faster.
Treating onycholysis (fungus) in children at home without doctor’s recommendations and examination is dangerous! You risk contracting the infection yourself and spreading it outside your home and work.
Prevention of onychomycosis
Prevention of fungal infection includes maintaining good personal hygiene. Children need to choose the right shoes and strive to use natural materials that are hygroscopic and can retain sweat. If injuries occur, they must be treated with antiseptics to prevent infection. Children visiting the pool should wear rubber flip flops to prevent contact with pathogens.
A fungal infection is an indicator of decreased immunity, therefore, with frequently recurrent mycoses, it is necessary to look for the cause. Pathology often develops against the background of increased blood glucose and can become a harbinger of diabetes. Parents need to provide proper nutrition to the child and avoid large amounts of sweets in the diet.
Diagnostics
A mycologist or dermatologist is involved in finding out the exact cause of splitting nails in children. If there is no specialized doctor in your city or region, contact a pediatrician. Diagnosis of the disease and treatment are carried out on the basis of an external examination.
If the clinic suspects a fungus or an infection of the tissues on the toes and hands, then laboratory and hardware tests are prescribed:
- scraping from the nail epidermis;
- microscopic examination of tissues.
Why do children get fungus?
Onychomycosis almost never affects children. The incidence increases with age and is highest in older people. But, according to statistics, pathology is diagnosed in an average of 17% of children of different ages. The lowest incidence is among newborns and children under 2 years old; in 7–10 year olds it is 1.8%, and in adolescents it reaches 18%. Fungi are resisted by nonspecific protective factors:
- integrity of the skin - resists the introduction of fungal cells;
- some lipids in the secretion of the sebaceous glands and the type of reaction of the sweat glands create conditions unsuitable for the existence of fungi;
- normal microflora of the skin prevents colonization and competes for nutrients;
- the accelerated process of keratinization of the upper layers of the skin, the rapid growth of nails allow you to get rid of the infection at an accelerated pace.
Immune mechanisms also protect against onychomycosis:
- transferrin protein;
- immunoglobulins;
- T lymphocytes;
- macrophages;
- complement system;
- dendrocytes and Langerhans cells.
The likelihood of the disease increases as you get older. This is due to the expansion of the social circle, visiting sports sections, the swimming pool, which increases the possibility of infection. Changes in skin acidity associated with puberty also act as an additional factor. The following conditions contribute to the development of onychomycosis:
- injuries to the fingers and nail plate;
- general decrease in immunity;
- pustular and inflammatory processes of the nail bed;
- wearing tight shoes, using artificial materials that limit shoe ventilation;
- violation of personal hygiene;
- contact with patients with fungal diseases.
The occurrence of the disease is associated with the introduction of fungal cells, often from close people. The risk increases in frequently ill children with congenital or acquired immune deficiency. Sometimes onychomycosis is the first sign of a pathology of the blood system, for example, leukemia, HIV infection.
Treatment of the disease
Therapy for sick and damaged nails is prescribed based on the doctor’s conclusion about the causes of the disease. If the cause of peeling is a fungus, then treatment will consist of the following steps:
- Eliminating the source of infection – fungus
Creams and ointments are used: Clotrimazole, Lamisil, Fluconazole, Ketoconazole. They are used daily for at least three months. You need to smear the sore nail, cuticle, skin on the feet, between the toes. To strengthen the keratin layer, Batrafen varnish is prescribed.
- Taking antiviral and immune-strengthening drugs
These are Anaferon, Immunal, multivitamins. They are used as a preventive measure to strengthen the resistance of an organism weakened by infection.
- Antibacterial therapy
It is necessary when a secondary infection has joined the affected area on the fingers.
- Removing the source of infection
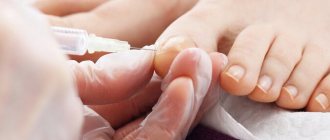
The affected nail is removed in a way that is painless for the baby - with a laser.
Treatment of fungal infection requires a systematic and responsible approach from parents. If you use ointments occasionally and stop keeping your baby’s feet and hands clean, the disease will subside for a while, only to resume the activity of dangerous microorganisms in a couple of weeks.
If the disease is provoked by other causes, then treatment is carried out as follows:
- Vitamin deficiency is treated with a course of multivitamins for at least 30 days.
- It is necessary to adhere to a proper, balanced diet - add fruits, milk, cottage cheese, and fish to the baby’s diet.
- Bruised nails are treated in the hospital or at home with healing ointments and pain relief. Sometimes it is better to remove a peeling nail so that it does not cause discomfort to the baby.
- If a small child bites his nails due to nervousness, consultation with a psychologist is required. Use a special varnish with a bitter taste (“Nekusayka”). Lubricate your nails every day: your baby will put his fingers in his mouth and understand that this is unpleasant. Gradually the bad habit will disappear.
- Problems of internal organs are treated according to a treatment regimen appropriate to the disease as prescribed by a doctor.
Forms and stages of the disease
With onychomycosis, the fungus invades the surface gradually.
At the initial stage, a tiny white or yellowish opaque spot appears on the nail plate. Over time, it grows throughout the nail, causing it to thicken and separate from the nail bed. This form of the disease is called distal subungual and is most often observed. With a white surface form, the nails peel off and a coating appears on their surface. In the initial stage, the fungus is easy to cure.
Pathological proximal subungual form occurs in patients with HIV infection. It affects the plate, which becomes white and opaque.
If the fungal infection is not treated, it turns into a total dystrophic form, in which the damaged nail must be removed.
Folk remedies
Grandmother's methods are suitable for the prevention of fungus and splitting of nails in children only as an auxiliary component to professional medical treatment. At home it is effective to use:
Foot and hand baths
Herbs, salt, and only natural ingredients are used.
- Sea salt and celandine decoction are added to warm water at the same time. The herb is brewed in boiling water and left for 2 hours. Mix with salt. The water is used warm, slightly salty to taste. Keep the arms and legs in the container for at least 15–20 minutes. Then wipe it off without rinsing.
Salt strengthens the plate, prevents brittle edges, but dries out the nails if you use the bath too often. Celandine fights fungi and infections, disinfecting the cuticle and the space under the root of the nail.
- Use milkweed baths for feet and hands at night for 1-2 weeks.
To do this, brew the herb with boiling water, let it brew for 2 hours, and add it to the container for the procedure.
Soak your fingers in water for 10-15 minutes every day.
Garlic lotions
You will need garlic - 1 clove (small), salt, water. Prepare a solution of salt and water in the following proportion: 1 tablespoon of salt, 1 liter of water. Finely grate the garlic, add 30 milliliters of saline solution to the bowl, stir, squeeze. It will turn out to be porridge.
Treat the affected nail from the cuticle to the edge every day, applying a swab or bandage for a few minutes. Don’t wipe your fingers afterwards, put on socks.
Important! Make sure that the baby does not put his hands in his mouth after baths with celandine. The grass is dangerous for the stomach and can cause an allergic reaction.
Therapeutic measures
First of all, it should be noted that the earlier the problem was addressed to a doctor, the greater the chances of eliminating it without unnecessary costs and negative consequences.
Therapeutic actions mainly concern cosmetic actions, which will be aimed at strengthening the baby’s nail plates:
If the reason lies in vitamin deficiency, then in this case multivitamin preparations should be prescribed: “Pikovit”, “Multitabs”, “Pregnavit”
Along with medications, it is recommended to pay attention to the child’s diet: increase the amount of foods that contain calcium and iron. The main emphasis should be on fresh cabbage, dairy products, cheeses, cereals, nuts (almonds), dried fruits (raisins, dried apricots).
External strengthening in the form of lubricating the nail plates with oils containing vitamins E and A.
The use of therapeutic warming baths
They should be based on vegetable oils, which can be supplemented with lemon juice or iodine. If the reason is the child’s nervous state, then it is necessary to try to wean him from a bad habit (smearing his nails with bitter substances) or to improve his mental balance. You can bring in a psychologist to help.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=CNg29avTghs
For fungal nail infections, it is better if treatment is prescribed by a highly specialized specialist, or rather, a mycologist. To determine the group affiliation of the fungus, he can give directions for the so-called “seeding”.
In case of fungal nail infections, various fungicides (ointments, varnishes, plasters) are used. The course of taking these forms of medication depends on the severity of the case: its duration, prevalence. The effect of the medications can occur within a period of two to four months. It is also necessary to carry out disinfection of all the child’s things and toys, underwear and bed linen.
Traditional treatment can be combined with treatment with folk remedies, however, only with the permission of the attending physician. Among “grandmother’s recipes,” warm baths using sea salt, as well as baths made from tinctures based on celandine leaves, are often used.
Parents must remember that no changes in the child’s condition are accidental or insignificant. Even split nails can be a signal that your baby has more serious diseases in the body.