Eczema is a chronic skin pathology that manifests itself in the form of foci of inflammation on the body, arms, legs and head. Rashes that form on the skin go through several stages of development: primary redness, dense nodules that transform into blisters, then weeping erosions form, which during the healing process are covered with a scab (the so-called “crust”). The last stage is peeling. Against the background of eczema, secondary purulent infections often develop. If left untreated for a long time, cosmetic defects of the skin may appear in patients of all ages.
Causes and symptoms of the disease
Doctors cannot give a definite answer to the question of what are the basic conditions for the development of pathology. Among the causes of eczema in patients, the following factors are considered:
- genetic conditioning;
- chronic allergies;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- psycho-emotional triggers.
Dermatologists distinguish several types of eczema: true, microbial, occupational and seborrheic. The clinical picture in each case turns out to be unique, as are the factors that provoke the inflammatory process on the surface of the skin.
| Types of eczema | Symptoms | Diagnosis of eczema |
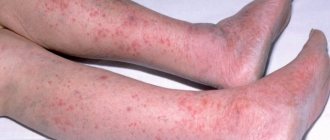
| True | Symmetrical foci of inflammation in open areas of the skin, hyperpigmentation, weeping surface. Later, numerous vesicles form, in place of which microscopic erosions gradually develop. Exudate accumulates on them. Patients experience attacks of itching, and as the vesicles heal, peeling of the skin occurs | Diagnosis is carried out by a dermatologist during an examination of the patient. Symmetrical rashes on the arms, legs or face indicate that a child or adult is experiencing true eczema. |
| Microbial | Develops against the background of traumatic skin injuries, fungal, bacterial or viral infections. The lesions are asymmetrical and concentrated on the patient’s lower extremities. Varicose veins become a risk factor. Failure to comply with the rules of personal hygiene leads to the accelerated development of pathology. Under the skin adjacent to the pathological focus, accumulations of infiltrate are formed | The diagnosis is established by taking a history and visual examination of the patient. The doctor pays attention to traumatic injuries to the skin of the lower extremities, mycoses, and varicose veins. Bacteriological studies of scrapings are performed to identify the resistance of the eczema pathogen to antibiotics |
| Professional | It develops against the background of the patient’s professional activity due to regular contact of the skin with allergens: chemicals, dust, cleaning products, air with atypical humidity. The size of the rash varies. Foci of inflammation can be located on any part of the patient’s body. A characteristic symptom of eczema is an abundance of small vesicles | The main diagnostic technique is to exclude the factor that provokes inflammatory processes. If the professional nature of the rash is confirmed, the dermatologist can prescribe the appropriate course of treatment to the patient. |
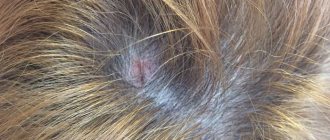
| Seborrheic | Affects the skin of the scalp. The affected areas are dry and profusely peeling. Itching intensifies after performing hygiene procedures. Zones of inflammation have distinct boundaries. In some cases, the course of the disease is complicated by the formation of swelling and weeping cracks in the surface layers of the skin | Some dermatologists do not agree that seborrheic eczema can be considered an independent type of pathology (changes in the skin are considered a special case of the true type of disease). The main diagnostic technique is histological examination of cells to exclude microbial eczema from the diagnostic report |
Are you experiencing symptoms of eczema?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Types of eczema
Eczema is manifested by skin rashes and a number of other general symptoms, but according to the origin and characteristics of the course, several types of this disease can be distinguished:
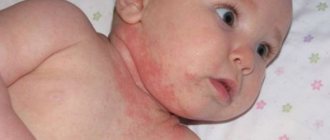
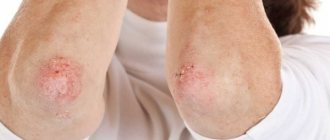
- Atopic dermatitis affects adults and children, and is associated with dehydration of the skin, which cannot withstand the harmful effects of the environment and allergens entering the body. In young children, symptoms occur on the cheeks, in older children - in the bends of the elbows and knees, on the neck, but in general the location can be anywhere.
- Contact dermatitis is a reaction to local exposure to an allergen or irritant. It occurs precisely at the point of contact. Contact allergens include some metals (nickel, cobalt), latex, the juice of certain plants, as well as many components of household chemicals and cosmetics.
- Seborrheic dermatitis is also associated with dysregulation of the sebaceous glands, and affects the scalp, less often the forehead, the area behind the ears, the wings of the nose and the upper back. Appears as fatty, dense crusts or scales, and in infants the condition is known as gneiss.
Treatment and prevention
The above classification of eczema and description of the symptoms of the disease indicate the impossibility of self-treatment. Consultation with a dermatologist and consistent adherence to his recommendations remain the only way to relieve seasonal exacerbations. The key task of the doctor is to identify provoking factors. After this, a treatment strategy is formed - medications are prescribed to treat eczema. It may include systemic and local therapy. Physiotherapeutic procedures are an additional option.
Systemic therapy
The basis of drug treatment is antihistamines, which are designed to reduce the risk of developing acute allergic reactions of the patient to various internal and external factors. Sedatives are prescribed against the background of high psycho-emotional stress experienced by adults and children. Plasmapheresis and other types of hemocorrection are used in severe cases of the disease complicated by systemic pathologies.
If the effectiveness of the treatment is low, the doctor may prescribe the patient oral glucocorticosteroids. As the condition of the child or adult improves, the dose of hormonal drugs is reduced.
Local therapy
Retinol ointment is applied to local areas of inflammation. An alternative can be applications of pastes with keratolytic properties. Anti-inflammatory and antiseptic components contribute to the successful elimination of bacteria, viruses or fungal infections. If there are a significant number of vesicles, the patient is prescribed drugs with individually selected components. Their combination is based on the clinical picture of the pathology and the cause of inflammatory processes on the skin identified during diagnosis.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic complexes include:
- ozone therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- laser stimulation.
In difficult cases, a dermatologist may insist on treating eczema-affected skin areas using cryotherapy. After overcoming the acute phase of the disease, therapeutic and mud baths are recommended for children and adults. In some cases, irradiation of damaged skin areas with ultraviolet rays is prescribed. To determine the correct treatment, the dermatologist may refer the patient to a physical therapist.
Preventive measures
If signs of eczema are detected, patients should seek advice from a dermatologist. After confirming the diagnosis, you should follow a diet - you must exclude foods that can provoke allergic reactions from your diet. It is recommended to refrain from drinking alcohol and smoking cigarettes.
Personal hygiene rules when treating eczema of the feet, hands, arms, legs or face include avoiding scented soaps. To moisturize the skin, it is permissible to use water-based creams.
Is eczema contagious?
Eczema has skin symptoms such as rashes and peeling that are noticeable to others, which is why people often wonder if the condition is transferable to others.
This question of whether eczema is contagious is very important, since the appearance of the skin is unpleasant to contemplate and often repels others, which leads to stigmatization, social isolation and various psychological problems, from neurosis to depression. In many countries, the psychological aspects of this disease are studied very deeply because it greatly affects the quality of life. Both the patient himself and loved ones must have a good understanding of the nature of the disease, be confident in their own safety, and that eczema can be cured.
Questions and answers
Are there differences in the causes of eczema on the hands and eczema on the feet?
The appearance of foci of inflammation on the extremities is in most cases associated with traumatic factors or exposure to aggressive chemicals. The formation of vesicles or weeping on the body is often the result of allergic reactions and systemic pathologies identified in patients.
What are the main clinical recommendations for diagnosed eczema?
A patient with a confirmed diagnosis of eczema should discuss with a dermatologist the advisability of consultations with other doctors: endocrinologist, allergist, gastroenterologist. Their use can reduce the frequency of exacerbations of the disease and reduce the intensity of reactions to factors that provoke the inflammatory process.
Do patients with chronic eczema need to take any medications regularly?
Drug and hardware treatment along with courses of physiotherapy are prescribed during periods of exacerbations. After relief of acute symptoms of the disease, the patient does not need to systematically take medications. A significant role during this period is played by the child or adult’s compliance with the recommendations of the attending physician and preventive measures.
Bibliography
- Akhtyamov, S.N. Practical dermatocosmetology / S.N. Akhtyamov, Yu.S. Butov. M.: Medicine, 2003. - 391 p.
- Arkhangelskaya, E.I. Materials on the clinic, etiology and pathogenesis of diffuse streptoderma and microbial eczema: abstract. dis. Dr. med. Sciences / E.I. Arkhangelskaya. L., 1973. - 38 p.
- Aizikovich, JI.A. Abstracts of scientific works of the VIII All-Russian Congress of Dermatovenerologists / JI.A. Aizikovich, T.V. Sokolova. 4.1. // Dermatology. - 2001.- P. 205.
- Buxton, P.K. Dermatology / P.K. Buxton. M.: Publishing house BINOM, 2005, - 175 p.
- Belousova, T.A. Neurogenic factors in the pathogenesis of eczema: abstract. dis. . Ph.D. honey. Sciences/T.A. Belousova. M., 1984. - 18 p.
- Demidova, M.A. Epidemiological and pharmacoeconomic aspects of the use of antihistamines in the treatment of patients with eczema / M.A. Demidova, E.V. Bogdanova // Ross. magazine skin and venereal diseases. 2009. - No. 2. — P. 46-49.
- Kudryavtseva, E.V. Lokoid and modern approaches to external therapy of atopic dermatitis / E.V. Kudryavtseva, AB Karaulov // Immunopathology, allergology, infectology. 2003. - No. 4. — P. 57-62.
- Mikhailenko, A.A. Allergy and allergic diseases /AA Mikhailepko, G.A. Bazanov. M.: Med. information agency, 2009. - 304 p. thirty.
- Prokhorenkov, V.I. Eczema / V.I. Prokhorenkov, T.A. Yakovlev 3rd ed. - Krasnoyarsk: PIK "Offset", 1994. - 255 p.
Undesirable manifestations
When using an external remedy, undesirable manifestations are possible, but they are mild.
Undesirable manifestations in all forms:
- local reactions: itching, burning, dry skin, folliculitis, hypertrichosis, steroid acne, allergic skin manifestations;
- when applying bandages: stretch marks, prickly heat, attachment of secondary flora, weeping;
- systemic manifestations: increased blood pressure, leaching of calcium from bones, weight gain, edema, ulcerative defects of the digestive tract mucosa, exacerbation of focal infections, menstrual irregularities, poor sleep, agitation.
The list is supplemented by the following undesirable manifestations of individual forms:
| Akriderm | Akriderm genta |
|
|
Working with a psychologist
To suppress the clinical manifestations of nervous eczema, diet, folk and drug treatment are usually not enough. The specialist must necessarily assess the psychological atmosphere in which his patient lives, and if he is regularly exposed to stress, the help of a psychologist is indicated.
Constant conflict situations in the family and at work affect the functioning of the nervous system, aggravating the course of the disease. Psychotherapy techniques help break the connection between emotional stress and eczema, promoting recovery. Such techniques include:
- breathing exercises;
- relaxing music;
- auto-training;
- visualization.
Initially, the patient, together with a psychotherapist, masters these relaxation methods, after which he can practice them independently at home.
HOW TO MAKE AN APPOINTMENT at the PsorMak Institute for Healthy Skin
1. Click the button you see below -
Make an appointment
2. Fill in the fields in the form that appears. Be sure to check the correct phone number so that our specialist can reach you. After filling out, click on the “Submit” button.
3. Wait for our specialist to call. He will answer any of your questions and agree on the date and time of your visit to PsorMak.
The initial appointment includes:
- Visual examination , which will allow the specialist to get a general understanding of the condition of your skin and the pathology itself.
- Collecting anamnesis - finding out information about the development of the disease, living conditions, previous diseases, operations, injuries, chronic pathologies, allergic reactions, heredity, etc. Together with a general examination, this allows you to make a fairly accurate diagnosis and choose a method of treatment and/or prevention.