Author:
- Galkin Alexey Vladimirovich
ENT pathology expert
5.00 (Votes: 1)
A furuncle in the nose occurs against the background of acute inflammation that has developed in the tissues surrounding the hair follicle and is characterized by the formation of purulent-necrotic masses. A favorable factor for the development of the pathological process is a decrease in the body’s resistance to the effects of staphylococcal flora (less often streptococcal).
How does a nasal boil develop?
The initial acute stage of the disease is characterized by a feeling of discomfort in the vestibule area. Pain appears, which can be of varying intensity - from not too strong to unbearable. Often the pain intensifies at night. If the boil turns black in the middle, this indicates that the root of the boil has formed. Characteristic symptoms:
- hyperemia of the affected area;
- swelling;
- pain at the site of the lesion;
- pain when pressed;
- increased body temperature (systemic symptom).
A laboratory blood test may reveal toxemia. In the next stage (purulent boil), if measures were taken at the wrong time or the treatment was not adequate, the symptoms become more complicated. Diagnosed:
- thrombus formation in the area of the angular vein (outwardly resembles the appearance of a thickened cord);
- increase in general body temperature to significant values;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- swelling of the eyelids, hyperemia of the mucous membrane of the eye, difficulty moving the eyeballs, pain;
- blurred vision;
- bulging eye.
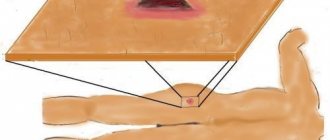
If you do not receive qualified help, swelling of the optic nerves may occur, which leads to complete or partial paralysis of the eye muscle.
Local treatment
Levomekol
A combined drug containing two active ingredients: chloramphenicol and methyluracil. Chloramphenicol is a powerful antibacterial drug that stops the growth of bacterial flora that causes the formation of boils. Methyluracil - promotes the activation of local immune defense, accelerates the restoration of damaged tissues.
The uniqueness of the drug is that microorganisms do not adapt well to it, so a stable flora is rarely formed. Levomekol is applied to the inflamed area 2-3 times a day for 7-10 days. This ointment can treat a boil in a child’s nose.
The only contraindication is an allergic reaction to the components of the drug.
Oxycort
An effective drug with a large number of therapeutic effects. It has an antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effect, reduces allergic reactions, and relieves itching.
The ointment is applied 2-3 times a day in a thin layer. Treatment is continued for 7-10 days.
The drug has few contraindications: hypersensitivity, herpetic infection, skin tuberculosis, various skin tumors. Oxycort should not be used during pregnancy or lactation.
Bactroban
The ointment appeared on the market relatively recently, but has already gained popularity. The unique structure protects against cross-resistance of microbes with other groups of antibiotics.
Apply to the skin of the nose or the inner surface of the wings of the nose 2-3 times a day. It practically does not penetrate through healthy skin into the bloodstream.
Contraindications: hypersensitivity of a person. Since the drug is new to the market, its effects on pregnant and lactating women have not been fully studied. In this regard, caution should be exercised when prescribing it during such important periods of a woman’s life.
Dioxidine ointment
It has bactericidal properties against the main microorganisms that cause boils. Active against bacteria resistant to other antibiotics. The ointment is applied to the skin 1-2 times a day in a thin layer.
Important! Strictly contraindicated in pregnant and lactating women. Animal experiments have shown that the drug can cause fetal death and mutations.
Also, the ointment is contraindicated in case of individual sensitivity and adrenal insufficiency.
Forms
The disease has two stages: in the first, the formation of an infiltrate (closed boil) occurs. In the second, pus appears, the pain intensifies and additional symptoms develop. Pus forms at the site of infiltration if you do not consult a doctor in time. In the first stage, the boil does not hurt much. The second stage is characterized by a deterioration in general condition and increased pain. Often in the second stage it is necessary to resort to surgical treatment of the boil. Complications after opening a boil usually develop if the opening was performed in violation of the rules of asepsis or by a non-specialist. The boil incision should not be wetted, as this promotes re-entry of infection and complicates the regeneration process. Is it possible to squeeze out a boil on your own? Attention! Under no circumstances should such attempts be made, as this can cause serious complications that threaten health and even life.
Stages of development
The first stage in the development of the disease is a traumatic injury to the skin and nasal mucosa (such as an abrasion, scratch or cut), through which the infection penetrates deep into the tissue. The causative agent of the disease is usually pathogenic staphylococci and streptococci. The infectious agent then spreads along the hair root into the follicle. This process is accompanied by local inflammation and the formation of a painful infiltrate. This stage of the boil is called the infiltration stage. After this, necrosis develops and a necrotic core is formed. The surrounding tissues undergo melting and transform into purulent masses, after which they begin to accumulate under the layer of epidermis surrounding the mouth of the follicle, which is why a subcutaneous abscess develops. This stage of the boil is called the abscess stage.
How does staphylococcus bacteria get into the nose and develop a boil?
A person can be a carrier of infections and not know it. Under suitable conditions (hypothermia, decreased general protective properties, exacerbation of any chronic pathology of the body, stress, increased physical activity, alcohol abuse), streptococci or staphylococci begin to manifest themselves. The formation of a boil is promoted by:
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- hazardous production;
- hypothermia or overheating of the body;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- unbalanced diet with insufficient amounts of vitamins, minerals, microelements;
- endocrine diseases;
- reduced immunity.
Treatment: is it always necessary to cut?
How a nasal boil will be treated depends on the stage of inflammation and the severity of the disease. Early treatment of the disease is the key to successful conservative treatment, without the help of a scalpel.
Important! Great care is required when handling an inflammatory focus. You cannot press, scratch, or pick at the boil. It is necessary to avoid facial stress on the facial muscles (smile less, eat semi-liquid food).
When the first signs of a nasal boil appear, powerful antibacterial therapy is prescribed. It can be local (ointments, alcohol solutions) and general (tablets, injections).
Diagnostics
Diagnosis should only be carried out by a doctor in a clinical setting. The doctor conducts an external examination, collects anamnesis and prescribes the necessary laboratory and diagnostic measures. Laboratory tests include: a general blood test, determining the number of neutrophils and ESR, a urine and blood test for carbohydrate content to exclude diabetes mellitus. In some cases, the material is examined to determine the pathogen (smear culture and antibiotic sensitivity determination). If necessary, consultation with doctors of related specialties (gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, dermatologist) is carried out.
Causes
Other reasons may be: hypothermia, vitamin deficiency, diabetes, skin injuries. Often several ulcers are observed at once, which are concentrated not only in the nose area, but also in other parts of the face and body. This spread of infection indicates the development of furunculosis.
Particularly severe forms of the disease are accompanied by the formation of carbuncles, when two (or more) boils merge into one lesion.
If left untreated, there is a risk of thrombosis of small veins, which opens the way to the vessels of the skull, which creates the risk of intracranial complications. Sepsis may develop.
General treatment
The following groups of drugs are actively used in treatment: broad-spectrum antibiotics, antihistamines (antiallergic) drugs and NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs).
Antibiotics for the treatment of boils in adults
| antibiotic | Frequency of reception |
| Clarithromycin | 2 rubles/day 5-7 days |
| Amoxiclav (can be taken during pregnancy and breastfeeding) | 2 days a week 7-10 days |
| Clindamycin | 3 times a day |
| Ceftriaxone | 2 times a day intramuscularly. |
Clarithromycin
A modern antibiotic from the macrolide group. Stops the growth of microorganisms by inhibiting the formation of microbial cell protein. There are many indications for use: various infections of the respiratory tract, inflammatory processes of the skin and soft tissues, treatment of gastric ulcer caused by H. pylori.
The most common side effects are associated with gastrointestinal motility disorders: severe nausea, heartburn, bitterness in the mouth, loose stools. Rarely, changes in the central nervous system occur: restlessness, anxiety, nightmares, hallucinations.
Contraindications for use are similar to many medications: intolerance to the components of the drug, severe problems with the liver and kidneys, pregnancy, lactation.
Amoxiclav
Contains two active components – amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. Amoxicillin is an antibacterial agent, however, it is quickly destroyed by the enzymes of some bacteria -