There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
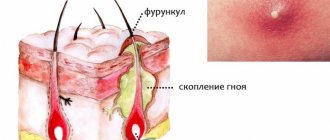
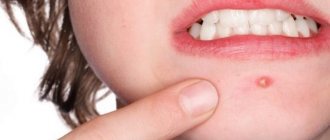
A furuncle is a purulent inflammation of the hair follicle. It develops due to staphylococcal infection entering the sebaceous glands due to microtraumas, non-compliance with hygiene rules, excessive sweating, allergies, and decreased immunity. By the nature of the rashes there are single and recurrent, in form single and multiple (furunculosis).
Stages of boil development and symptoms
As the boil matures, it sequentially goes through 3 stages of development. Each of them is characterized by a specific clinical picture.
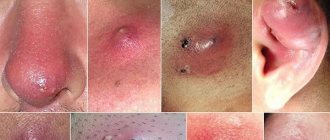
The first is the infiltration stage . After staphylococcus enters the hair follicle, inflammation gradually develops in a small limited area. The affected area turns red, hardens and swells.
At the second stage - suppuration and necrosis - the focus of inflammation increases to several centimeters in diameter. Pain in the affected tissue appears, increasing with palpation.
, the purulent-necrotic stage develops . A small, raised, cone-shaped pustule forms in the center of the infiltrate. A necrotic core of pus and dead cells forms inside the abscess. The process is often accompanied by intoxication fever, general weakness and severe pain.
After some time, the pustule bursts, pus flows out of it and the necrotic core comes off. Swelling subsides, pain subsides. The patient's condition is improving.
The last stage is healing . After cleansing the wound, a deep cavity remains at the site of the infiltration. Gradually it fills with granulation tissue. The skin is restored. Scars form in place of extensive boils.
Furuncles and carbuncles often develop on the face. Boils are common, and carbuncles are less common. The prolonged course of boils and the progression of inflammatory phenomena can lead to the development of a carbuncle.Etiology. The causative agents are streptococci and staphylococci, including Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus aureus.
Pathogenesis. The infection usually penetrates from the skin through the duct of the sebaceous gland or along the hair shaft into the subcutaneous base of the skin. A purulent follicular pustule forms in the pilosebaceous sac, followed by involvement of the dermis and surrounding tissue in the process. A boil often appears against the background of certain skin diseases. With pyoderma, sycosis, eczema, purulent acne, sensitization of the body is created, against the background of which a boil or carbuncle develops. Furuncles and carbuncles often occur in a number of common diseases, such as diabetes.
Pathological anatomy. With a boil, purulent inflammation occurs in the hair follicle, sebaceous gland and adjacent connective tissue. At the mouth of the follicle, a pustule is formed from neutrophilic leukocytes, which is surrounded by accumulations of microorganisms and their decay products. Further, inflammatory phenomena spread along the hair follicle to the papillary bodies and adjacent areas of connective tissue. In the center of the lesion, necrotic processes develop with the formation of a rod spreading to the epidermis. Breaking through it, the rod comes out, and the remaining cavity is filled with granulations, which, when mature, form a scar.
With carbuncle, such inflammatory changes appear in several hair follicles and sebaceous glands. Diffuse inflammation and extensive necrosis develop. In the circle of the affected tissues, purulent inflammation of the adjacent tissue and muscles adjacent to it occurs. Often veins are involved in the inflammatory process, the infection spreads along the vessel with the formation of phlebitis or thrombophlebitis. After the necrotic areas are rejected, the skin is perforated in many places and then the cavities are filled with granulation tissue and scarred.
Furuncle is a purulent-necrotic inflammation of the hair follicle (or follicles), sebaceous glands and surrounding connective tissue.
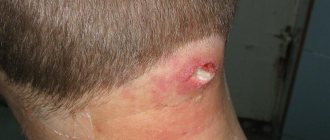
Clinical picture. Boils on the face are most often localized in the area of the upper or lower lip, less often on the nose, cheek, chin, forehead. With the development of a boil on the face, the general condition may be satisfactory; sometimes body temperature rises to 37.5-38 oC, chills. An area of reddened skin forms, on which a papule often appears. The pain in the affected tissues intensifies, they become denser, forming a painful, usually round infiltrate, covered with red or purplish-blue skin. The papule located in the center is filled with serous or purulent fluid. Subsequently, it empties and under it the area of necrosis - the rod - is torn off and pus is released. After the lesion is emptied, the inflammatory phenomena subside, and the infiltrate slowly resolves.
Complications. Boils on the face, located near and along the facial vein, can be complicated by phlebitis or thrombophlebitis.
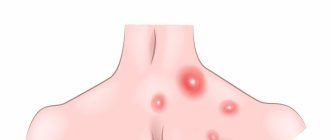
Carbuncle is an acute purulent-necrotic inflammation of several hair follicles and sebaceous glands with the formation of extensive necrosis of the skin and subcutaneous fat. Often, a carbuncle develops from a boil when it is not emptied and neighboring hair follicles and sebaceous glands are involved in the process.
Clinical picture. The course is moderate or severe, accompanied by an increase in body temperature above 38 ° C, chills, headache, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, insomnia, and sometimes delirium. In some patients, the disease occurs against the background of a satisfactory condition with moderate symptoms of intoxication. Patients complain of sharp pain at the site of the lesion, often spreading along the branches of the trigeminal nerve.
On external examination, the infiltrate is diffuse, painful, covered with bright red skin, adherent to the underlying tissues. Infiltration spreads to adjacent tissues, swelling in the surrounding tissues is significant. According to the location of the carbuncle, swelling and swelling of the adjacent tissues are located: when a carbuncle occurs on the upper lip, swelling of the buccal, infraorbital areas, wing and base of the nose; with carbuncle of the chin - buccal, submandibular and chin areas. With these localizations, the anterior facial vein is often involved in the process. In such cases, swelling and infiltration appear along its course to the inner corner of the eye. Regional lymph nodes on the affected side are painful, enlarged, and often fused into packets. Gradually, the infiltrate thickens in the center, the epidermis breaks through in several places. Thick pus is released from areas of skin perforation, and necrotic tissue is gradually rejected. This leads to subsidence of inflammatory phenomena, limitation of infiltration, reduction of swelling of surrounding tissues, cleansing of wounds and filling of cavities with granulations.
Complications. Facial carbuncle can be complicated by phlebitis, thrombophlebitis of the facial veins, which in turn can contribute to thrombosis of the dural sinuses, purulent meningitis, meningoencephalitis, brain abscess, and sepsis. A carbuncle of the chin and forehead can be complicated by the transition of inflammatory phenomena to the periosteum and bone, when secondary osteomyelitis of the body of the lower jaw and frontal bone develops.
Diagnosis and differential diagnosis of a boil or carbuncle are carried out on the basis of a characteristic clinical picture and blood tests (leukocytosis, shift of the leukocyte formula to the left, increase in ESR).
The future doctor must be able to diagnose boils and carbuncles. With a boil or carbuncle, differential diagnosis should be made with anthrax carbuncle. Anthrax carbuncle is characterized by low pain in the lesion, and a boil or carbuncle on the face is characterized by significant pain. Lesions on the face with anthrax are often combined with pustules on the oral mucosa, which is not typical for a boil or carbuncle. Bacteriological studies of the contents of the lesion (finding anthrax bacilli or isolating streptococcal and staphylococcal infections) allow a correct diagnosis.
Treatment. When diagnosing a boil, and especially a carbuncle, the doctor must ensure urgent hospitalization of the patient. In a hospital setting, general and local treatment is carried out. General treatment consists of antibacterial, desensitizing, detoxification therapy and restorative therapeutic measures, correction of homeostasis and metabolic processes. For carbuncle, the above treatment is carried out mainly by intravenous administration of drugs. When complications develop (phlebitis, thrombophlebitis, sepsis, etc.), intensive therapeutic measures and therapy are carried out to correct and provide life support systems.
Local treatment for a boil consists of 2-3 blockades around the lesion (tissue infiltrate with 0.25% amide anesthetics - lidocaine solution, antricaine - 30-60 ml with antibiotics, enzymes), UV irradiation of the boil area, bandages with a hypertonic solution , Vishnevsky ointment. With good outflow, phonophoresis of antibiotics, dimexide, and calcium chloride is indicated. For a carbuncle, a cross-shaped incision is made through the entire thickness of the affected tissue, necrotomy, and purulent leaks are opened.
When the infection spreads like phlebitis or thrombophlebitis, incisions are made in the central part of the lesion and along the course of the infiltrated vein.
With the development of boils and carbuncles, attention should be paid to the presence of concomitant diseases and appropriate examination, including endocryological examination, should be carried out.
"Surgical Dentistry" edited by Robustova T.G.
Fourth edition. Moscow "Medicine" 2010
Why are boils dangerous?
When boils are treated incorrectly, self-medication, attempts to squeeze out an abscess, or when it is injured (for example, by shaving), complications often develop. These include:
- phlegmon and soft tissue abscesses - extensive purulent lesions;
- thrombosis – blockage – of lymphatic and venous tracts;
- septic phlebitis, lymphangitis and lymphadenitis - inflammation of blood and lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes.
The entry of the pathogen into internal organs and the circulatory system sometimes results in a life-threatening condition - sepsis. When self-medicating boils on the face, the infection can enter the brain and cause meningitis.
The correct treatment for most boils is surgery.
Self-medication with ichthyol, Vishnevsky ointment, compresses can provoke uncontrolled spread and generalization of the purulent process, therefore only a doctor determines the treatment tactics for a boil. If the abscess is not properly opened and drained, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and other drugs cannot effectively act on the tissue affected by pus.
Opening and draining the boil
If the purulent process extends beyond the hair follicle, mandatory surgical intervention is required. It is performed using classical techniques or using a laser. Laser removal of a boil is accompanied by additional disinfection of the affected tissues of the boil. The most optimal intervention technique in each specific clinical case is determined by the doctor.
The surgeon also determines the time for opening in such a way that the rod is fully formed - otherwise a relapse of the disease is possible. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. After opening, pus and necrosis are removed. Drainage is removed according to indications. The tissues are treated with an antiseptic. An antibiotic ointment and a sterile dressing are applied to the wound.
Carbuncle
- purulent inflammation of several hair follicles, accompanied by necrosis (death) of the skin.
With a carbuncle, the purulent-necrotic process can involve large areas of the skin and subcutaneous tissue; in some cases, the treatment of a carbuncle requires quite extensive interventions - see the example above.
In the photo there is an infiltrate with skin necrosis in the center and severe inflammation around it - a carbuncle of the trunk.
Rehabilitation period
After 1-2 hours the patient is discharged from the clinic. If the drainage is removed, it must be removed by a surgeon after 1-2 days. It is recommended to limit physical activity for 2-3 days after the procedure. For 2 weeks, it is necessary to go for examinations and dressings at the frequency specified by the surgeon, as well as ensure a balanced diet and proper rest. The tissues heal completely within 10-14 days.
To consult, clarify prices and remove a boil in St. Petersburg, call SM-Clinic.