There are many pathogens that cause damage to human skin. A special place among such diseases is occupied by lichen. There are various types of them, including pityriasis versicolor.
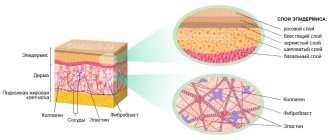
Pityriasis versicolor is a disease that occurs over a long period of time and is caused by a fungus. During it, the epidermis is damaged, as a result of which pigmented spots appear on the skin, the shade of which can be different: yellow, pink, brown or brown. This deprivation is characterized by pityriasis-like peeling, hence the name. The main and easiest way to diagnose it is to perform the Balzer test.
Causes
Pityriasis versicolor is caused by infection with the fungus Pityrosporum orbiculare. Even in a healthy person, it can normally be present in the stratum corneum of the epidermis and hair follicles. It is quite difficult to become infected from contact with a sick person. Most often, the activation of the fungus is caused by certain provoking factors. These include:
- Decreased immunity level.
- Development of seborrhea.
- Excessive sweating.
- Features of the chemical composition of sweat.
- Impaired exfoliation of the epidermis.
- Individual predisposition to the disease.
- Presence of diabetes mellitus.
- A person has tuberculosis.
- Changes in the body during puberty.
- Chronic pathologies in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Use of clothing made from synthetic fabrics.
Symptoms of pityriasis versicolor
When infected with pityriasis versicolor, the following symptoms appear:
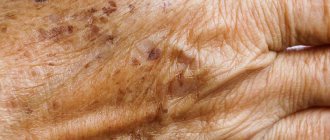
- Pigmented spots appear on the skin, the color of which can vary from yellow to brown.
- The surface of these spots is covered with very fine peeling.
- Localization of spots is mainly on the skin of the back, chest, abdomen, shoulders and sides of the body.
- After scraping off the peeling spots, it only intensifies.
- After recovery, white spots remain at the sites of lichen lesions, which gradually become the same color as healthy skin.
Ringworm can bother a person for a very long time - from several months to several years.
Target
Figure 1 - When glucose chains are long enough, they accumulate and can incorporate a triiodide ion, resulting in a color reaction between iodine and starch or long dextrins
The color reaction between iodine and glucose chains (dextrins and starch) is used to determine their presence in the wort. In addition to producing a wort of desired fermentability, the goal of mashing is to reduce the maximum length of dextrins in the sweet wort to less than 9 glucose molecules for straight chains and less than 60 for branched chains. In this case, they no longer react with iodine, and the wort or mash is called iodine negative. If this is not done and these long chains of glucose are transferred into the beer, it can develop what is called "starch haze". Despite its name, in most cases this haze is not caused by the starch itself, but by long dextrins that become less soluble and precipitate in the presence of alcohol. These dextrins give a color reaction with iodine ranging from red to violet.
Diagnosis of versicolor versicolor
In order to confidently say that a person is sick with pityriasis versicolor or versicolor versicolor, he needs to undergo a number of the following studies:
- Consultation with a dermatologist.
- Examine the skin using a Wood's lamp.
- Make a microscopic analysis of skin flakes.
- Perform a Balzer test.
For the disease multicolored or pityriasis versicolor, a characteristic feature is a skin rash that is spotty in nature. However, a similar picture can be seen in the presence of other diseases associated with dermatology. That is why, to diagnose this type of lichen, it is necessary to carry out differential diagnosis. The Balzer test helps doctors with this. It is a simple and accessible technique that is widely used in medical practice.
Precautionary measures
It is strictly prohibited to treat some forms of lichen with iodine. It dries out the skin and irritates inflamed areas, which can lead to eczema.
In addition, you cannot use highly concentrated iodine; 5% is used for the test , otherwise you can cause a burn.
It is also necessary to use iodine very carefully when mucous membranes are close to each other - delicate mucous membranes are very susceptible to aggressive substances, and even 5% iodine can leave behind quite severe burns.
What kind of test is this?
The Balzer test is an accessible, effective and inexpensive method used in the process of diagnosing pityriasis versicolor or pityriasis versicolor.
Since the symptoms of some skin diseases are similar to each other, it is this test that makes it possible to conduct comparative diagnostics. Balzer's test is capable of identifying lichen versicolor or pityriasis versicolor among many different lichens. It will help to distinguish it from vitiligo, pink zoster or syphilitic roseola.
The essence of the test
Many people know that iodine solution, depending on the amount, turns the skin orange or brown. In places where lichen versicolor is localized, the epithelium loosens. It is due to this that the Balzer test with iodine is very effective.
When an iodine solution is applied to the source of lichen, the loosened epithelium absorbs and retains a large amount of the solution, as a result of which the lichen becomes much darker. The patch of pityriasis versicolor stands out in color on healthy skin lightly stained yellow with iodine, since it has a dark brown tint. This result becomes possible due to the loosened upper layer of the skin - the epidermis, which, during the disease with such lichen, differs from healthy skin by the increased conductivity of the iodine solution, and as a result, becomes more colored.
The Balzer iodine test is an additional diagnostic method for lichen versicolor, which makes it possible to make a diagnosis even in cases where, after clinical examinations, doctors still have any doubts.
Since this test is absolutely harmless, it can be performed by everyone. Even pregnant and breastfeeding women are no exception.
How to do everything yourself?
Before performing the Balzer test at home, you need to determine the type of skin rash (not all types of lichen can be safely treated with iodine):
- Pityriasis rosea is a seasonal disease, at risk are women 20-40 years old. Spots appear on the stomach, back, chest and sides of the body. The formations are large (3cm), flaky.
- Ringworm is diagnosed mainly in children; it is transmitted to them from sick animals. Plaques in this case are up to 4 cm, pink, most often localized on the face, neck, head, and shoulders.
- Shingles is a disease of older people, especially those who did not have chickenpox in childhood. It is caused by herpes. The affected area becomes covered with blisters that itch and hurt. After the bubbles burst, a crust forms in their place.
- Lichen versicolor is most often diagnosed in young people. The spots are located on the back, neck, and shoulders. Large areas of the lesion may be yellow, pink or brown.
Once the type of suspected lichen has been established, a test can be carried out. The affected areas are lubricated with iodine, and after 20 minutes the result is assessed.
Healthy skin lubricated with iodine will remain shiny and acquire a golden hue. Skin affected by ringworm will be dull and dark brown.
A positive reaction to iodine is a good reason not only to start antifungal therapy, but also to improve immunity.
Ringworm is a disease that is not very treatable, and even with a slight decrease in the body's immune forces, it can appear again.
Procedure
The Balzer iodine test technique is very simple and accessible. For the procedure, you need to use a 5% alcohol solution of iodine. Using a cotton swab or just cotton wool, you need to lubricate the area of peeling with an iodine solution. In cases where a person is sick with pityriasis versicolor or pityriasis versicolor, the result will be noticeable immediately, since the pityriasis patches will become darker in color compared to healthy skin.
The Balzer test can also be performed by replacing iodine with aniline dyes: brilliant green or methylene blue. The results will not be different. However, the classic Balzer test involves the use of iodine solution.
How to do an iodine test for starch
As already mentioned, the procedure is not particularly complicated. It does not involve the use of special equipment and does not require any special skills. All you need to make an iodine test of wort for starch is a pipette, a cotton swab, iodine and a saucer.
The procedure will be as follows:
- After completing the temperature pause in the range of 69-720, take a small amount of wort (a teaspoon).
- Pour the wort onto a saucer (it is advisable to use white dishes for the most accurate determination of color changes).
- Using a pipette, add 2-3 drops of iodine to the wort. This volume should not be exceeded. If there is more iodine, its color will not change, even if starch is present.
- Mix the resulting substance with a cotton swab.
- After 20-30 seconds, check the color of the sample.
If the color has not changed, you can safely continue cooking. If the test gives a positive result, the pause should be extended for another 10 minutes, and then the procedure should be repeated.
Follow us on VKontakte
Read us in Zen
Read us on Telegram
Tell friends:
Return to articles feed
Carrying out at home
Looking at the simplicity of performing the Balzer test, it seems that every person can perform it independently at home. However, it should be borne in mind that this test is only part of the entire range of examinations that the patient undergoes. In addition to the iodine test, this complex provides a number of additional examinations. Among them are the following: conducting a microscopic analysis of skin flakes, inoculating the fungus on specific nutrient media, etc.
Only conducting a full-fledged study and studying the results of examinations allows a dermatologist to make the correct diagnosis and draw up an appropriate treatment regimen. Even the presence of a positive Balzer test does not become a final indicator for a specialist in the field of dermatology that a person has lichen versicolor.
Pros and contraindications of diagnostics
The iodine test is prescribed for adults and children; it is safe at any age. also has some advantages over other diagnostic methods - cost-effectiveness, efficiency, and ease of testing.
No special equipment is required, and the result can be seen in just 20 minutes.
However, the Balzer test has contraindications:
- scaly form of pathology;
- pityriasis rosea;
- lichen of viral etiology - red flat and shingles;
- damage to the scalp;
- large lesion diameter - more than 2 cm;
- the patient is allergic to iodine.