05/24/2018 Many people who discover a spot under their nail begin to search on the Internet to find out what it could be? And it turns out that this can be a fatal disease - subungual melanoma.
In this article we will look at:
- concept of subungual melanoma;
- the chances of this type of tumor occurring;
- photos of symptoms with histological confirmation;
- ways to distinguish subungual melanoma from hematoma;
- procedures to clarify the diagnosis;
- prognosis and treatment.
Subungual melanoma – what is it?
The share of melanoma among skin tumors is only 4%. But it is from this malignant neoplasm that 80% of patients with skin tumors die [1]. In Russia, about 8,717 people a year currently develop skin melanoma (data for 2012) [2]. Subungual melanoma is located in the nail bed and usually appears as a stripe on the nail.
Sign up for the webinar “Carcinogens in cosmetics: truth, lies and... marketing”
Therapeutic methods for eliminating the defect
How to forget forever the black spots that are visible on the toenails is a pressing question that worries those who do not know how to treat a cosmetic defect. Therapy is prescribed depending on the factor that caused the aesthetic defect.
Options for eliminating fungal infection:
- Baths - surface wetting with a solution of chamomile, calendula, sage eliminates the fungus only at the initial stage of onychomycosis.
- Essential oils - tea tree or the combination drug Stop Active has a strong antimycotic effect.
- Varnishes - Loceryl, Domix Green help restore the nail on the big toe, but its use is effective only when no more than 70% of the nail bed is affected.
- Ointments - Exoderil, Clotrimazole and Terbizil are included in the treatment of superficial mycoses.
- Solutions - Exoderil - an antimycotic agent eliminates black spots on nails and any other color. Applying the solution to a cotton swab, a person lubricates the affected areas.
- Vitamins - zinc-based preparations help strengthen the legs, especially in the presence of onychodystrophy. Only when combined with other means can a brown spot or several visible defects under the nail disappear (usually combined with ointments).
If you managed to eliminate brown spots on your nails, but there is a fear of relapse, then it is rational to use protective varnishes (Demikten, Belvedere). Using the product, you can create a layer that will protect the nail on your big toe from the influence of external pathogenic microflora.
If the effect is systemic, that is, the nails have darkened on other parts of the foot, and not exclusively on the big toes, then treatment with ointments is supplemented by taking pills. Antimycotics accumulate in the stratum corneum and lead to the return of a healthy shade. It is also necessary to use medications from this group if the stratum corneum of the finger has also turned black in the lower part (affected the matrix).
Treatment of graphite lesions:
- onychomycosis (using antifungal agents);
- subcutaneous hematoma (resolves spontaneously);
- melanonychia (not corrected by medications).
The choice of therapeutic methods is wider if the defect appears on the body due to an ingrown plate. The surgeon removes black spots located and remaining on the toenails after a trimming procedure (which involves a roller), in which treatment involves the use of a scalpel, laser, or “radio knife.”
All these tools help restore proper growth of the protective membrane and eliminate pathological darkening. An alternative option is to cut off the rough edge with nail scissors in order to eliminate stains on the toenails (recovery begins after the pathological compression of the dermis is eliminated). Then take foot baths with salt, chamomile or oak bark to speed up healing and prevent increased inflammation.
Tip: The Fraser bracket is a device that helps alleviate the condition for patients who are looking for a way to treat an ingrown plate at home.
What are the chances of this type of tumor occurring in a resident of Russia?
Of the total number of melanomas, the share of this tumor is only 2% [3], i.e., in absolute values, in 170 people per year. Against the background of the country's total population of 146,000,000, this, in my opinion, is very small. At the same time, a low incidence rate does not eliminate the possibility of getting sick.
For representatives of other skin phototypes other than 2, the chances may be very different. Representatives of the Mongoloid and Negroid races have a higher (up to 40%) chance of developing melanoma of the nail bed [4, 5].
Where does subungual melanoma appear most often?
The tumor most often affects the big toes [3].
Causes of the disease
While other types of melanoma are often associated with excessive sun exposure, here the situation is radically different. Most often, this type of oncology develops on the toes, which are constantly protected from sunlight. Therefore, the causes of subungual melanoma do not include insolation, they look like this:
- mechanical injuries of the nail. This includes surgical and cosmetic intervention options in which the nail plate is damaged;
- physical injuries: burns, frostbite, etc.;
- chemical injuries. Usually we are talking about long-term exposure to aggressive chemicals, for example, in production;
- heredity. Up to 14% of all patients diagnosed with nail melanoma have mutations in certain genes4
- existing benign neoplasms, for example, dysplastic nevi, which are prone to transformation into malignant ones.
Most often, this disease occurs in people over 60 years of age. And there is another interesting fact: obviously, it depends on the race, because representatives of the Negroid, as well as Mongoloid races, suffer from the disease much more often - 40% more often than Caucasians. Among the latter, people at risk are fair-skinned, red-haired people, as well as people with a lot of freckles.
What does subungual melanoma look like? Photos and signs.
All pictures below are histologically confirmed and not taken from the Internet. The source is indicated in square brackets. There are 2 most common signs:
Sign I
Most often, subungual melanoma appears as a brown or black stripe. The strip starts from the nail fold and ends at the edge of the nail. This condition is called longitudinal melanonychia. Some medications can cause such bands to appear - retinoids and Docetaxel (Taxotere) [10]. This sign can also occur in conditions not associated with melanoma, for example, with fungal infection of the nail, pigmented nevus of the nail bed.
Subungual pigmented nevus in a 13-year-old boy [9]
Subungual melanoma stage I, 0.2 mm according to Breslow [10]
Sign II
The most common sign of this type of melanoma is Hutchinson's sign - a transition of pigmentation to the nail fold or fingertip. This feature is visible in 7 of the 8 images below. At the same time, it cannot be stated unequivocally that this symptom occurs only with melanoma. It can also be observed with a transparent cuticle [10].
8 cases of subungual melanomas in situ (initial stage) [6]
Subungual melanoma of the thumb with level 4 invasion according to Clark, thickness according to Breslow is not specified [8]
Subungual melanoma, Breslow thickness 1.5 mm [7]
Is it possible to remove an ingrown toenail at home?
If the nail has already grown into the periungual fold, then removing the part of the nail plate that has grown into the skin yourself at home will be difficult and dangerous.
Cutting off an ingrown toenail yourself will be very painful. In addition, a person without medical education can do something wrong with the nail, which will aggravate the situation or lead to a relapse in the future. In addition to surgical skills, during removal, sanitary and hygienic requirements must be observed, which are not always available at home.
It is very important to consult a podiatrist or surgeon at the first symptoms of an ingrown toenail so that the operation takes place correctly in a medical clinic. Correctly performed surgery and treatment will most likely allow you to quickly recover and avoid the recurrence of onychocryptosis.
How to distinguish subungual melanoma from everything else?
Here is a fairly simple algorithm.
Algorithm for the differential diagnosis of benign melanonychia and the same condition in melanoma [8]
ABCDEF rule for diagnosing nail bed melanoma
And (age) age - the peak incidence of subungual melanoma occurs between the ages of 50 and 70 years, and also denotes races with an increased risk: Asians, Africans - they account for 1/3 of all melanoma cases.
B (brown to black) – the color is brown and black, with a stripe width of more than 3 mm and blurry boundaries.
C (change) – change in the color of the nail plate or no change after treatment. D (digit) – finger as the most common site of injury.
E (extension) - spread of pigmentation to the nail fold or fingertip (Hutchinson's symptom).
F (Family) – relatives or the patient have a history of melanoma or dysplastic nevus syndrome. [eleven]
How to distinguish a hematoma from a subungual melanoma by dermatoscopy
Hematoma: [10]
- It moves under the nail along with its growth. You can track this by taking a photo of the formation against the background of a ruler located longitudinally. It is important to note that a hematoma does not always appear due to trauma.
- Color from red-blue to black-blue.
- Does not transfer to the cuticle, nail fold and fingertip.
- Does not involve the entire nail in the longitudinal direction.
- May change within a few weeks.
- The color intensity decreases from the center to the periphery.
- It may be preceded by trauma.
- Small blood spots oriented towards the edge of the nail on dermatoscopy
Subungual melanoma: [12]
- Heterogeneous color, irregular stripes with melanonychia.
- Triangular stripes.
- Spreads on the nail plate, free edge of the nail or fingertip.
- Destruction or dystrophy of the nail.
Treatment methods for hyperkeratosis of the nail plate
Hyperkeratosis is treated by a highly specialized specialist – a podiatrist. Therapy combines systemic and local methods and is prescribed after a comprehensive diagnosis. This approach allows you to accurately influence the cause of the pathology, reduce treatment time, and avoid complications and relapses. Since in most cases, subungual hyperkeratosis develops against the background of nail fungus, the patient is prescribed antifungal drugs - tablets, varnishes and ointments.
Local antifungal treatment and medical pedicure
Local treatment is aimed at suppressing fungal microflora and reducing keratinization. To do this, the clinic performs a medical pedicure - the surface layers of the thickened nail are removed with a cutter.
Baths
It is recommended to take warm salt foot baths every day - dissolve 100 grams of sea salt in 10 liters of water. After the procedure, the steamed tissues of the surface of the nail and the skin around it are removed with pumice and buffs. Then the local drug prescribed by the doctor is applied.
Removing the nail plate
In advanced cases, in order to ensure the delivery of drugs to the affected tissues, complete removal of the nail plate is indicated using mechanical cutters, special compounds and patches.
Diet
To get rid of the fungus, it is recommended to adjust your diet. Sweets and yeast baked goods are excluded from the menu. The diet is balanced in proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and microelements under the supervision of a nutritionist.
Immunotherapy
If immunodeficiency is detected during diagnosis, the immunologist prescribes immunomodulatory therapy.
Hygiene
Fungal infections actively multiply in a warm, humid environment, so the inner surface of shoes is treated daily with a pharmaceutical disinfectant solution, and socks, tights and stockings are washed daily. Shoes are changed if necessary - they should not stimulate foot sweating. Scissors and nail files must be strictly individual and treated with a disinfectant solution after use. You will also have to temporarily avoid going to saunas and swimming pools to prevent contact infection.
Traditional methods
Fungi are not sensitive or slightly sensitive to nonspecific agents, therefore traditional methods of treating nail hyperkeratosis are ineffective. Under their influence, the fungal flora develops immunity and infects new structures. The disease becomes severe. Podologists strongly recommend that if you suspect nail hyperkeratosis, you should immediately contact a specialist.
It is impossible to restore a nail plate affected by hyperkeratosis; you can cure the disease and wait until a healthy nail grows. The course of therapy is from 2 to 6 months. After 2 weeks and 2 months after complete elimination of symptoms, control tests are taken to determine the presence/absence of fungus.
Bibliography
- Miller AJ, Mihm MC. Melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2006; 355:51-65.
- Data from the Globocan 2012 study, International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC): https://gco.iarc.fr/today/online-analysis-multi-bars?mode=cancer&mode_population=hdi&population=643&sex=0&cancer=29&type=0&statistic=0&prevalence= 0&color_palette=default
- Kuchelmeister C, Schaumburg-Lever G, Garbe C. Acral cutaneous melanoma in caucasians: clinical features, histopathology and prognosis in 112 patients // J. Dermatol. – 2000
- Takematsu H, Obata M, Tomita Y. Subungual melanoma. A clinicopathologic study of 16 Japanese cases // Cancer. – 1985
- Wu XC, Eide MJ, King J. Racial and ethnic variations in incidence and survival of cutaneous melanoma in the United States, 1999–2006 // J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. – 2011.
- Jae Ho Lee, Ji-Hye Park, Jong Hee Lee, Dong-Youn Lee. Early Detection of Subungual Melanoma In Situ: Proposal of ABCD Strategy in Clinical Practice Based on Case Series Ann Dermatol. Feb 2022; 30(1): 36–40.
- Stephan Braun, MD and Peter Gerber, MD. Subungual malignant melanoma. CMAJ. 2015 Sep 8; 187(12): 909.
- Pierre Halteh, Richard Scher, MD, FACP, Amanda Artis, MS, MPH, and Shari R. Lipner, MD, PhD. A Survey Based Study of Management of Longitudinal Melanonychia Amongst Attending and Resident Dermatologists. J Am Acad Dermatol. May 2022; 76(5): 994–996.
- Kamran Khan and Arun A Mavanur. Longitudinal melanonychia. BMJ Case Rep. 2015; 2015: bcr2015213459.
- Holger A. Haenssle, Andreas Blum, Rainer Hofmann-Wellenhof, Juergen Kreusch, Wilhelm Stolz, Giuseppe Argenziano, Iris Zalaudek, and Franziska Brehmer. When all you have is a dermatoscope— start looking at the nails. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2014 Oct; 4(4): 11–20.
- Levit EK, Kagen MH, Scher RK, Grossman M, Altman E. The ABC rule for clinical detection of subungual melanoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000 Feb;42(2 Pt 1):269-74.
- Haenssle HA, Brehmer F, Zalaudek I, Hofmann-Wellenhof R, Kreusch J, Stolz W, Argenziano G, Blum A. Dermoscopy of nails. Hautarzt. 2014 Apr;65(4):301-11. doi: 10.1007/s00105-013-2707-x.
Treatment of a bunion on the big toe
The development of a treatment program is carried out by an orthopedic surgeon after examining the patient and establishing the stage of disease progression. At the initial stages, deformation of the metatarsophalangeal joint can be eliminated using conservative methods.
The following methods for eliminating bunions are effective:
- abductor bandage – ensures fixation of the big toe in an anatomically correct position using a special device, used during sleep, since it is difficult to move with it;
- corrective pads and interdigital partitions – intended for use throughout the day, they provide correction of the position of the phalanx and prevent pressure on the pathological area;
- orthopedic insoles - used at any stage of hallux valgus, necessary for proper distribution of the load on the foot and spine during walking; ideally, insoles should be made individually, taking into account the characteristics of the anatomical structure of the patient’s foot.
The following are used as auxiliary methods for treating a protruding thumb bone:
- massage;
- physiotherapeutic treatment;
- exercise therapy;
- hardware traction.
In advanced stages of pathology, when there is severe deformation of the joints, effective treatment is only possible through surgery. In modern medicine, closed operations performed through several punctures are widely used. During the intervention, the bone is removed and the phalanx of the finger is fixed in the correct position.
After surgical treatment, the patient must always wear comfortable shoes with arch support and orthopedic insoles to avoid relapse of the pathology.
Ringworm: Toenail Fungus
Ringworm: Toenail Fungus
A popular misconception is that ringworm occurs exclusively on the skin and hair. Unfortunately, doctors talk about an existing form of pathology that affects the toenails.
- Infection with this fungus is transmitted from contact with a patient or through his hygiene items.
- Presuming factors are decreased immunity, vitamin deficiency, and the presence of chronic forms of diseases.
External signs of the disease are similar to other fungal pathologies:
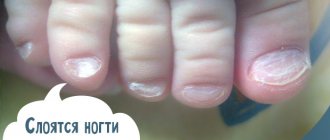
- Changing the appearance of nail plates
- Thickening, separation and crumbling of the nail bed
- The appearance of longitudinal grooves on the plate
When the form is advanced, the nail begins to separate from the bed. In most cases, the disease occurs in isolation, but sometimes doctors note simultaneous damage to the skin and hair.