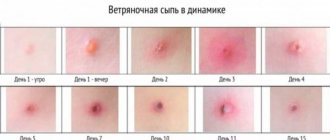
In recent years, the incidence of human papillomavirus infection has been increasing. According to WHO, every year around the world, about 250,000 women with HPV infection die from cervical cancer. Against this background, the search for effective treatments for this infection becomes extremely important. The problem of its diagnosis and treatment attracts the attention of doctors of various specialties: dermatologists, gynecologists, urologists, oncologists, immunologists, virologists, pathomorphologists. At the moment, most scientists have come to a consensus - the manifestations of the human papillomavirus can be combated using immunomodulators with antiviral activity.
- What are immunomodulators
- List of drugs
- Antiviral for HPV
- Is it possible to use VIFERON Suppositories vaginally?
- Treatment of mucous membranes in men
- Alternative Treatments
What are immunomodulators
Immunomodulatory agents include drugs of a chemical and biological nature that can modulate (inhibit or stimulate) immune responses. At the same time, the immunological effect of immunomodulators depends on the initial state of a person’s immunity: these drugs reduce high and increase low levels of immunity. This postulate especially applies to interferon preparations. Immunotherapy also includes treatment methods based on the use of immunotropic agents for diseases in the pathogenesis of which there are disorders affecting the immune system.
The main criterion for prescribing immunomodulators is the clinical picture of the disease (acute or chronic infectious-inflammatory process), which is accompanied by a decrease in immune parameters and is difficult to treat. In this case, immunomodulators play the role of the main assistant, which promotes effective therapy and relieves the manifestations of many diseases.
Since HPV infection is also a disease that is quite difficult to combat, and the outcome of treatment depends on the state of the immune system, various immunomodulators are widely used in the treatment of this infection.
VISION: effectiveness + naturalness
Vision has managed to combine high efficiency with a 100% natural composition. She has created a number of dietary supplements with immunomodulatory properties: they actively stimulate the immune system, strengthen and cleanse the body, without causing any harm and without causing side effects.
What is special about Vision products:
- in a completely natural composition, which includes plant materials grown in environmentally friendly areas of our planet;
- in a unique technology of drying and cryogenic crushing of plant materials, thanks to which all valuable substances, vitamins and minerals are preserved to the maximum;
- high degree of absorption (about 98%);
- in the absence of contraindications and side effects;
- in gentle and correct stimulation of the immune system, due to which after therapy the immune system continues to work independently;
- in high quality products that meet GMP and ISO22000 standards.
All Vision drugs are certified by the Ministry of Health and studied during clinical trials conducted at the Institute of the Russian Federation: Research Institute of Nutrition of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences.
You can view all certificates, research results and other documentation confirming the quality and safety of dietary supplements on the company’s official website.
Treatment of papillomas (6, 11 and many other strains, of which there are 180 in total) with Vision immunomodulators occurs easily, without disrupting the functioning of the body and without severely affecting the functioning of the main systems, as happens when treating with synthetic drugs.
Remember that even the highest quality immunomodulator for papillomas is not a panacea, but only a good addition to the main treatment, if required. They should be used only in combination.
Immunomodulators for HPV: list of drugs
Drugs that are synthetic complex purine derivatives
This group of immunomodulators, used in the treatment of manifestations of the human papillomavirus, have immunostimulating activity and a nonspecific antiviral effect. They restore the activity of lymphocytes, which are the main cells of the immune system. It has been clinically proven that low lymphocyte activity is a predisposing factor to the pronounced development of clinical manifestations of HPV. Also, this type of drug increases the functioning of natural killer cells and the so-called T-helpers - T-lymphocytes, the main function of which is to coordinate the immune response.
Some of the drugs in this group have an extensive list of side effects, including problems with the gastrointestinal tract, liver and biliary tract. Adverse reactions such as headache, drowsiness, insomnia, itching and joint pain are also possible. Contraindications include children under 3 years of age, pregnancy, kidney disease and hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
Preparations with the active ingredient glucosaminylmuramyl dipeptide (GMDP)
GMDP is a fragment of the shell of pathogenic bacteria that cause infectious and inflammatory diseases of various organs and systems. When this fragment enters the body, the immune system perceives it as a foreign pathogenic agent and immediately begins producing antibodies. Thanks to this, there is a general activation of the entire immune system, which promotes recovery or reduces the frequency of relapses of viral infections, including HPV.
Side effects include an increase in body temperature to subfebrile and febrile levels, and diarrhea is also possible. Drugs in this group are contraindicated for metabolic disorders and for women during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Preparations containing natural plant materials as active ingredients
This group of drugs was created based on the discovery of Nobel Prize laureate N.N. Semenov about the powerful immunostimulating properties of biologically active substances contained in plant cells. Plant extracts and auxiliary components strengthen the nonspecific part of the immune system, which increases the human body’s resistance to various viral and some bacterial infections. The immunomodulatory effect activates leukocytes, which is especially important in the fight against chronic and protracted inflammatory processes.
Allergic reactions are possible when using these drugs. Contraindications for use include diseases of the excretory system, pregnancy, lactation and children under 18 years of age.
What foods to include in your diet to strengthen your immune system?
In addition to standard pharmaceutical drugs, you can strengthen your immune system with natural foods.
Diversify your menu with products that contain:
- vitamin A (fruits and vegetables of red, yellow and orange colors, eggs, liver, medium-fat dairy products);
- vitamin B (nuts, seeds, mushrooms, buckwheat, hard cheese);
- vitamin C (citrus fruits, kiwi, rose hips, currants, sea buckthorn);
- vitamin E (cabbage, salads, bran, cold-pressed vegetable oils, sprouted wheat).
Also, do not forget about microelements such as zinc, iodine, selenium, calcium, iron: they are contained in sufficient quantities in greens, which should be supplemented with almost every meal, especially lunch and dinner (dinner can consist of greens - this is light, well digestible and healthy meal).
Water is another important factor influencing the effectiveness of HPV treatment. The more clean water enters your body, the more intensely it will cleanse itself and get rid of toxic substances. This way, the body’s forces will be directed specifically at protecting against infections, and not at fighting constantly incoming toxins.
Natural and natural immunomodulator products that are worth supplementing your diet include:
- honey (for a visible effect - at least 100 g per day, but not more than 200 g, so as not to overload the pancreas);
- ginger root (medicinal teas made from it);
- garlic (at least 1 clove of garlic every day for 3-5 months);
- propolis is a substance produced by bees from raw materials from tree buds (the preventive course lasts about 45 days);
- rose hips (contains 40 more vitamin C than lemons);
- chamomile, viburnum, cranberry tea;
- juices from carrots, rowan;
- berries: raspberries, currants, strawberries, blueberries, dogwood.
Antiviral drugs against HPV
After infecting a cell, the virus can remain free or penetrate the cell’s genome. In either case, the virus alters normal cellular processes. And instead of producing everything necessary for its life, the cell provides mechanisms for the synthesis of viral DNA molecules, which will later be used to create new viral particles. But viruses are not always capable of causing disease. With an adequate immune response, the body gets rid of the virus on its own. If the body's immune response is ineffective, long-term carriage of the virus is possible, which can lead to benign or malignant, depending on the type of virus, manifestations of the disease.
In order to break the chain of endless reproduction of the virus and subsequent development of the disease, the need to treat HPV infection with immunomodulators with antiviral activity has been recognized, because To date, not a single antiviral drug against HPV has been developed that specifically targets the human papillomavirus.
VIFERON for HPV
Are there drugs that fight viruses and at the same time help restore the immune system? Of course, such drugs exist. One of these drugs that helps restore the immune system and has a wide spectrum of antiviral activity is the drug VIFERON.
Recombinant interferon alpha-2b, which is part of this drug, prevents the synthesis of viral DNA and blocks the reproduction of the virus, helps restore the immune system, and also has antiproliferative properties. It is identical to human interferon alpha-2b, but is produced using modern technology without the use of donor blood.
The drug, which is available in the form of suppositories, gel and ointment, was developed as a result of fundamental research in the field of immunology, which has proven that in the presence of antioxidants (vitamins C, E), the antiviral effect of interferon is enhanced.
Method of use and dosage of VIFERON suppositories for HPV
VIFERON Suppositories are produced in the form of bullet-shaped rectal suppositories of white-yellow or yellow color. During the treatment process, the drug suppresses the activity of viruses and increases the effectiveness of the body's own immune response to pathogenic microorganisms.
The drug in the form of suppositories can be used during pregnancy (from the 14th week), as well as during breastfeeding and when treating children.
The recommended dose for adults is VIFERON 500,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day after 12 hours every day for 5-10 days. According to clinical indications, therapy can be continued.
Pregnant women from the second trimester of pregnancy (starting from the 14th week of gestation) are prescribed VIFERON 500,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day every 12 hours daily for 10 days, then for 9 days 3 times with an interval of 3 days (on the fourth day) 1 suppository 2 times a day after 12 hours. Then every 4 weeks until delivery - the drug in a dosage of 150,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day every 12 hours every day for 5 days. If necessary, the drug is prescribed before delivery (from the 38th week of gestation) at a dosage of 500,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day after 12 hours every day for 10 days.
Why are immunomodulators prescribed for papillomavirus infection?
Weak immunity is the main reason for the “awakening” of HPV. Therefore, during antiviral therapy, doctors place greater emphasis on those drugs that stimulate the activity of the immune system and strengthen it. These drugs include various forms of immunomodulators: both chemical and natural.
Naturally, with the help of these drugs it is impossible to cure the disease completely and clear the blood of the virus, so immunomodulators should be taken in combination with:
- surgical removal of benign formations, if they manifest themselves;
- preventive measures to prevent relapses;
- post-treatment observation of the patient.
Is it possible to use VIFERON Suppositories for HPV vaginally?
Antiviral suppositories VIFERON are produced only for rectal use. Vaginal use is not provided for in the instructions for the medicine. The use of the drug in complex therapy is aimed at increasing the level of immune defense of the body as a whole. Therefore, inserting suppositories directly into the site of infection is not required.
There are many blood vessels in the rectum that absorb the medicine directly injected into the rectal cavity. Blood from the rectum, bypassing the liver, directly enters the systemic circulation. This ensures the systemic effect of the drug. Moreover, the liver does not undergo additional stress, which is an undeniable advantage of drugs with rectal administration.
Treatment of mucous membranes with HPV in men
When treating manifestations of the papilloma virus on the mucous membrane in men, rectal suppositories VIFERON are also used, which will help get rid of the unpleasant manifestations of the virus and will help strengthen the immune system.
Without consulting a urologist, it is not recommended to use any medicinal creams and ointments, self-medicate, or even refuse therapy prescribed by a doctor. If left untreated, condylomas can grow, covering more and more territories and affecting the urethra and other internal organs. The development of complications can be prevented by timely consultation with a specialist and the use of antiviral drugs.
Alternative treatments for HPV on the skin
Drug therapy for manifestations of the human papillomavirus is perfectly combined with the removal of neoplasms in the form of warts, papillomas on the body and condylomas, which are located in men and women in the anogenital area (including the skin of the genitals, anus and the mucous membrane of the vagina, cervix, glans penis, rectum ).
Today, there are several productive methods of getting rid of these tumors, which are mostly painless, safe and do not leave scars.
Methods for removing papillomas and condylomas
Surgical excision
Currently, such an intervention is used infrequently; it is mainly used in the treatment of malignant neoplasms, when wide excision is necessary.
Medical removal (cauterization) for HPV
This is the removal of growths on the skin using medications - solutions of acids, alkalis, salts. New growths on the skin are removed with the help of these drugs by cauterization. As a rule, a crust forms at the site of removal, which disappears within 5-7 days. Complete tissue healing occurs within 10-14 days. For multiple tumors, additional procedures may be required.
Laser removal of papilloma
With this method of removal, papillomas and condylomas are burned using a laser beam. When removed, neighboring areas are not damaged. After the procedure, a microscopic wound usually remains, which heals within 2-3 weeks. You can use a laser to remove both single and multiple formations located on the face and body, including in delicate places (on the eyelids, armpits, perineum).
Radio wave removal for HPV
This method uses the Surgitron device. The main working part of the device is the electrode, which is a thin tungsten filament. High frequency radio waves are concentrated at the end of the electrode. By acting on organic tissue, a beam of waves sets in motion the water molecules in the cell, as a result of which the cell ruptures and it evaporates, resulting in a “cold” tissue cut in the desired area of the skin or mucous membrane. At the same time, the surrounding tissues and blood vessels remain intact, which in some cases allows one to avoid heavy bleeding. After an incision with a radio knife, a fibrin film forms on the surgical wound, and then a crust, which gradually disappears and leaves an invisible scar.
Cryodestruction of papillomas
Cryodestruction of papillomas consists of a targeted effect on the formation with a very low temperature (about -196° C). For this, liquid nitrogen and a special metal point attachment, which acts as a conductor, are usually used. During this procedure, papilloma cells die. Healthy tissue in the area of its formation is covered with a small crust, which falls off after a short period of time.
Electrocoagulation of papillomas with HPV
This method involves the removal of pathological tissues by exposing them to electric current. The procedure is carried out using special devices equipped with an electrode or loop, which are heated under the influence of electric current to high temperatures. A crust also forms at the site of the removed wart, which falls off over time.
All methods of removing papillomas and condylomas have their pros and cons, which can only be assessed with your attending physician, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient. The use of any traditional medicine recipes found on the Internet is also allowed only after consultation with a specialist.
There are no pills or procedures that will get rid of the human papillomavirus once and for all. However, today there are drugs and treatment methods that will help reduce recurrences of infection or even forget about them.
Reference and information material
Author of the article
Belyaev Dmitry Alexandrovich
General doctor
Loading...
Take other surveys
Finding ways to solve the problem of widespread HPV infection is the most important medical and social problem of modern healthcare. Low sexual culture of the population, frequent changes of sexual partners, unprotected sex increase the risk of developing HPV infection, contributing to an increase in the number of inflammatory diseases of the genital tract, reproductive dysfunction, as well as the formation of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia of the cervix [1, 2].
A number of human papillomavirus strains are highly oncogenic: in 70% of cases, strains 16 and 18 are associated with cervical cancer (CC), in 10% - strains 31 and 45 [1]. In an International Agency for Research on Cancer study of 3085 cases of invasive cervical cancer, HPV-16 was detected in 54% of squamous cell carcinomas and 42% of adenocarcinomas, and HPV-18 was detected in 11 and 37% of cases, respectively [2–4] .
Most men and women who are sexually active are infected with HPV, and the main feature of this infection is considered to be its widespread prevalence among adolescents and young women, mainly under 25 years of age. More than 80% of women are diagnosed with HPV within 2 years after the start of sexual activity, while up to 20% become infected with the virus if they have one sexual partner [2]. HPV is detected in 99.7% of women with a histologically confirmed diagnosis of cervical cancer. The risk of infection with one strain of HPV does not reduce the risk of infection with a phylogenetically related type of virus [3].
According to modern studies, 85% of women with typical condylomas of the vulva and perineum have additional foci of papillomavirus infection in the vagina or cervix, in 10–25% of cases associated with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN - Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia) of varying degrees of severity [5] .
Often, human papillomavirus infection is detected together with other sexually transmitted diseases: urogenital chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus and herpetic infections, which has a significant impact on clinical manifestations, course characteristics and prognosis.
HPV is associated with diseases of the urogenital tract such as chronic endocervicitis and vaginitis, condylomas of the cervix and external genitalia, CIN, breast cancer, intraepithelial neoplasia of the vulva (VIN - Vulvar Intraepithelial Neoplasia) and vagina (VaIN - Vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia), prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia ( PIN – Prostate intraepithelial neoplasia) and anal intraepithelial neoplasia (AIN – Anal intraepithelial neoplasia) [6].
Long-term persistence of HPV is accompanied by the development of secondary immunodeficiency states caused by exhaustion and, as a consequence, insufficient functioning of the immune system. To date, it has been established that HPV does not infect antigen-presenting cells, and is the reason for the absence of a direct pathway for activating the immune system in this pathology. Early HPV viral proteins are localized predominantly in the nuclei of infected cells, without leading to the formation of a full-fledged immune response [2]. At the same time, early HPV proteins are actively synthesized and initiate the processes of malignancy in infected epithelial cells. Late HPV genes contain codons that are rarely used by mammals, which is why the synthesis of viral capsid proteins proceeds slowly and in small quantities, inhibiting the development of antiviral immunity. Thus, in the process of evolution, a mechanism has developed by which a viral infection is protected from the systemic effects of the host immunity.
Activation of cytotoxic lymphocytes is the leading mechanism of defense in the human body against the introduction of HPV infection. The cytotoxic immune response in CIN involves four steps: phagocytosis and presentation of HPV antigens by cervical macrophages, activation of Th1 helper cells, activation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes, and destruction of virus-infected cells. Evidence of the relevance of cellular immunity in case of HPV is the fact of a combination of spontaneous regression, for example, warts with infiltration of surrounding tissues by lymphocytes and macrophages. However, when the cellular component of immunity is suppressed and the number of Langerhans cells decreases, papillomavirus infection is activated. The long-term persistence of HPV is facilitated by the ability of the virus to “escape” systemic immune surveillance, established in a number of studies [6, 7]. Although HPV, as noted, primarily infects basal cells, viral replication and assembly of viral particles occur in differentiated cells of the superficial layer of epithelial cells. After replication, the virus exits the cells, which undergo subsequent apoptosis, and this process is not accompanied by signs of inflammation. Effector cells of the immune system produce a number of cytokines, incl. interferons-α, -β and -γ, which reduce the transcription of the E6 and E7 genes in HPV types 16, 18 and 33 in virus-transformed cells [7].
Currently, there is no single etiotropic therapy and there is practically no systemic treatment for patients with HPV-associated infection. Nevertheless, several principles for the treatment of this group of diseases have been formulated, following which allows one to achieve the best results.
The first principle of treatment of HPV-associated diseases is an integrated approach, including the use of various methods of destruction of hyper- and neoplastic formations. These methods include the use of cytotoxic drugs (podophyllin, podophyllotoxin, etc.); chemical (trichloroacetic acid, Solcoderm, etc.) and physical destruction (cryodestruction, laser destruction, diathermocoagulation, electrosurgical method, photodynamic therapy).
The proven involvement of immune mechanisms in the development of HPV infection, manifested by secondary immunodeficiency, serves as a rationale for the use of immunomodulatory drugs in its therapy [7]. In this regard, the second principle of therapy for HPV-associated diseases is the inclusion in the treatment plan of immunotropic drugs of different groups and mechanisms of action, which can significantly increase the effectiveness of therapy, reduce the frequency of relapses and promote the elimination/eradication of the virus. It should be noted that among the immunomodulatory agents used to prevent cervical cancer, the HPV vaccine has also been used in recent years.
The modern classification of immunomodulatory agents includes immunomodulators of microbial origin, natural and synthetic immunomodulators, and cytokine-based immunomodulators. To date, the only immunomodulatory agent recommended by the European guidelines for the treatment of dermatological diseases is inosine pranobex, which indicates not only the peculiarities of its mechanism of action, but also the clinical significance of this drug [16].
Possibilities of using the drug inosine pranobex
Inosine pranobex (Isoprinosine), a drug combining distinct immunomodulatory properties with antiviral activity, has been developed.
According to the chemical structure, inosine pranobex is a complex synthetic drug, which is a molecular complex including inosine (hypoxanthine riboside): para-acetylaminobenzoic acid (acidoben): N,N-dimethylamino-2-propanol (dimepranol) = 1:3:3 complex .
Isoprinosine belongs to the class of immunopharmacological (immunotropic) drugs, to the group of immunomodulators. Its main effect is immunomodulatory, manifested in the restoration of the reduced function of the most important cells of the immune system - T-lymphocytes and peripheral blood monocytes. It should be noted that the physicochemical properties of the drug differ from the individual components that form its structure, which determines the differences in their pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics. It is more soluble than inosine, which improves its absorption in the gastrointestinal tract and has significantly higher biological activity [8].
In clinical studies, the drug normalizes the deficiency or dysfunction of cellular immunity by increasing the activity of Th1-cell type reactions that trigger the maturation and differentiation of T lymphocytes and potentiate lymphoproliferative reactions in response to the action of mitogens or cells activated by antigens [7]. In addition, Isoprinosine has a modulating effect on the cytotoxic effects of T-lymphocytes and natural killer cells (NK-cells), the functions of subpopulations of T8 suppressors and T4 helpers, increases the formation of surface markers of immunoglobulin G and complement on their plasma membranes, and normalizes the ratio between subpopulations of T-helpers and T-suppressors, which is considered as restoration of the CD4/CD8 immunoregulatory index. The effect of the drug is accompanied by an increase in the production of cytokines by immunocompetent cells, in particular, the formation of interleukin-1 (IL-1) and IL-2, and the formation of receptors for IL-2 increases. Its important properties are an increase in the secretion of endogenous interferon-γ, as well as a decrease in the biosynthesis of IL-4. There is evidence that Isoprinosine potentiates the chemotaxis and phagocytic activity of neutrophils, monocytes and macrophage cells [9].
Molecular mechanisms of action of Isoprinosine, incl. Defining antiviral properties include increased suppressed/reduced synthesis of mRNA in lymphocytes and the implementation of translation processes in these cells. In addition, Isoprinosine in high concentrations can inhibit the activity of cGMP phosphodiesterase. These mechanisms determine the antiviral activity of the drug, which is nonspecific and has been established against a significant number of viruses - herpes simplex types I and II, herpes Zoster, Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, etc. [10].
Isoprinosine is a low-toxic substance and in this regard has advantages over other synthetic immunomodulatory agents with antiviral activity. The pharmacokinetics of Isoprinosine is determined by the structure and properties of the components that form its molecule [11].
The drug does not have allergenic, mutagenic, carcinogenic or embryotoxic properties. Approved for use by children and adults [12].
In medical practice, Isoprinosine began to be used in 1973 in the USA, and since 1978 in the countries of the European Union. Under various trade names, the drug is registered in 73 countries as a medicinal product for the treatment of a number of viral and immunodeficiency diseases, for a total of 22 indications.
In the Russian Federation, Isoprinosine (Teva Pharmaceutical Enterprises Ltd.) was registered in 1997.
Clinical studies have demonstrated good tolerability of Isoprinosine. Side effects with its use are rare and are represented mainly by headaches, heaviness in the stomach, and hot flashes. In some cases, a slight increase in the level of uric acid in the blood has been reported. Side effects are eliminated when the drug is stopped [13].
According to the instructions for the medical use of Isoprinosine, approved by the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation, indications for its use in our country are the treatment of influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections; infections caused by herpes virus types 1, 2 and 3 and 4: genital and labial herpes, herpetic keratitis, herpes zoster, chicken pox, infectious mononucleosis caused by the Epstein-Barr virus; cytomegalovirus infection; severe measles; papillomavirus infection: papillomas of the larynx/vocal cords (fibrous type), papillomavirus infection of the genitals in men and women, warts; molluscum contagiosum. Contraindications to the use of Isoprinosine: hypersensitivity to the components of the drug; gout; urolithiasis disease; arrhythmias, chronic renal failure; children under 3 years of age (body weight up to 15–20 kg) [10, 19].
A number of randomized placebo-controlled clinical studies have established the high effectiveness of the use of Isoprinosine in the treatment of infections caused by the herpes simplex virus. Monotherapy in doses of 3–4 g/day in short courses (5–10 days) until the symptoms of the disease disappear, in the asymptomatic period – 1 tablet 2 times a day for 30 days to reduce the number of relapses [19]. Long-term use for 6 months in a continuous mode leads to a reduction in the duration of the acute period and prevents repeated exacerbations within 12–24 months [14]. At the same time, the effect of Isoprinosine significantly differs from placebo and is comparable in effectiveness to the effect of the antiviral drug acyclovir. It was also found that the drug has therapeutic and preventive effects on a number of patients with herpes infection resistant to treatment with traditional antiviral drugs [8].
Clinical studies on mono- and combined therapy with Isoprinosine for condylomas of the external genital organs in men and women (genital, vulvovaginal and endocervical condylomas associated with HPV) indicate its 100% effectiveness, which is associated with the effect of the drug on HPV not only in areas of condyloma localization that are difficult to reach for surgical or laser treatment, but also in the nerve ganglia.
In the acute phase, Isoprinosine is prescribed at 50 mg/kg of the patient’s body weight (6–8 tablets per day, divided into 3–4 doses) for 14–28 days, then repeating this course three times at intervals of 1 month [11, 15 , 19].
Isoprinosine has been studied clinically and for common warts on the hands and face, and flat warts of the feet. It was found that when using the drug at a dose of 50 mg/kg/day for 7 to 60 days (before clearing the skin of warts), its use was accompanied by a decrease or disappearance of warts of these types and cleansing of the skin. Research also found an increase in the number of T helper cells—CD4 lymphocytes—in the peripheral blood and an increase in the ratio of CD4/CD8 helper cells, which suppress cytotoxic cells of the immune system [16].
A clinical study was conducted of the effectiveness of Isoprinosine (50 mg/kg/day) for papillomas of the larynx/vocal cords (fibrous type) in combination with surgical removal (laser surgery) of the latter. It was found that taking the drug for 2 days before surgery and for the next 8 days is accompanied by a significant decrease in the frequency of complications of laser therapy, absence of bleeding during surgery, absence or slightly pronounced swelling of the laryngeal tissue, elimination of the need for tracheotomy and improvement of the voice and speech of patients after surgery, as well as reducing the frequency of disease relapses. Additional results of the use of Isoprinosine in combination with surgical treatment are simplification and greater efficiency of surgical removal of laryngeal papillomas [16]. There is evidence of the effective use of the drug by children and adults in the treatment of a sexually and domestically transmitted infectious disease - molluscum contagiosum. The use of Isoprinosine at a dose of 50 mg/kg/day for 10 days, both in monotherapy and in combination with standard methods of external therapy, leads to the resolution of skin rashes in both acute and chronic cases of the disease. The effectiveness of therapy reaches more than 75% [17].
Conclusion
Thus, HPV-associated genital diseases are a widespread type of pathology that has great medical and social significance due to the high risk of developing neoplastic processes, primarily cervical cancer. Experimental and clinical studies indicate that immune mechanisms play an important role in the pathogenesis of HPV-associated diseases and secondary immunodeficiencies caused by them, which made it possible to include immunomodulatory drugs in the arsenal of therapeutic measures for these diseases [18]. The results of numerous clinical studies indicate that Isoprinosine is a drug with immunomodulatory activity and nonspecific antiviral properties, the indications for use of which are a number of viral and immunodeficiency diseases, incl. HPV-associated, and in gynecological practice.