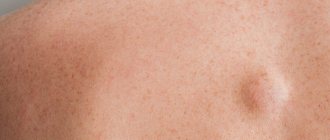
Lipoma is painless lumps or tubercles, called wen, since by their nature they are benign neoplasms from adipose tissue. Sometimes they are enclosed in a capsule of connective tissue.
Lipomatosis is multiple tumors on the body that require mandatory consultation with a surgeon.
The Miracle Doctor clinic uses a modern method of removing lipomatosis, which is much more effective than the laser and radio wave method.
Lipomatosis
Lipomatosis is a localized proliferation of adipose tissue between muscles, around nerve trunks, in subcutaneous fat, in the synovium of cartilage, tendons, and in the parenchyma of internal organs, including in the area of the vertebrae and the spinal canal.
In fact, a lipoma is a painless benign tumor, the structure of which resembles ordinary adipose tissue with the only difference - the fat of the lipoma is enclosed in a fibrous capsule.
The process of replacing healthy tissue with adipose tissue is irreversible. Therefore, lipoma atrophy (independent reduction of the wen) is an exception to the rule rather than a common occurrence.
Lipomatosis is not only a cosmetic defect (if it appears on the face, neck, hands), but also a direct threat to human life, since secondary changes can occur with the tumor, including fat necrosis, hyalinization and cancer.
In case of suspicious symptoms against the background of multiple body lipomas, you must urgently make an appointment with a dermatologist, surgeon or oncologist.
Today, the world's leading clinics offer the widest range of treatment for lipomatosis of any type, etiology and stage, using minimally invasive (gentle) methods. The most important thing is to seek help in time and not wait for the lipoma to resolve on its own. There are no such options here.
Which treatment method will be most effective?
Doctors begin to develop a treatment regimen only after making a final diagnosis based on the results of reliable diagnostic studies. Regardless of histological type, lipomas never regress on their own. Advanced medical institutions in leading countries around the world offer a wide range of traditional and invasive treatment methods.
Steroid use . Ointments and creams with topical corticosteroids reduce the size of lipomas due to their anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects. This sounds paradoxical, since long-term use of moderate and high doses of oral corticosteroids can lead to the development of steroid lipomatosis. Due to their mild effect, steroids are mainly recommended for patients with relatively small and asymptomatic lipomas.
Liposuction is a procedure for directly removing fat tissue from a lipoma using a needle and syringe. The intervention is similar to a simple injection and does not require anesthesia. Liposuction rarely develops complications, but it has a relatively high recurrence rate.
Collagenase injections (commercial name XIAFLEX) involve injecting the drug directly into the tumor. Collagenase dissolves its main structural component, that is, fat, and further breaks down collagen fibers. The fat inside a lipoma is similar in structure to normal adipose tissue, except that it is enclosed in a fibrous capsule. Thus, XIAFLEX affects the entire lipoma, significantly reducing the size of the tumor or completely eliminating it. Depending on the clinical situation, the doctor selects the required dosage of the drug. The dosage range varies from 0.058 mg to 0.44 mg per injection.
Deoxycholic acid injections (commercial name ATX-101) aim to emulsify (i.e. break down) fat and lipid compounds. Similar to XIAFLEX, deoxycholic acid injections are suitable for patients with large and giant lipomas, since surgical removal of such tumors is often associated with the development of bruises and scar formation. Currently, ATX-101 is primarily used in patients with fatty tumors in the neck, arms, legs, or torso. The dosage of the drug varies from 4.8 ml of a 4% solution to 4.8 ml of 1% per procedure.
Surgery . Surgical removal of lipomas is the most radical method of therapy, which leads to complete cure in 100% of patients. Surgery is indicated in cases where the fatty tumor is large or grows rapidly, causes pain, or causes functional impairment. Oncological suspicion and unclear histological type of tumor are absolute indications for surgery. The removed tissue is subject to examination with a mandatory final diagnosis. In addition, surgery may be performed for cosmetic reasons. Plastic surgery in Switzerland and other developed countries aims not only to remove tumors, but also to correct scars and soft tissue defects.
Send a request for treatment
Etiology of lipomatosis
The exact causes of lipomatosis are currently unknown. Bacteria, viruses and fungal infections are also not confirmed causes for the development of lipomas. However, there is proven medical observation that shows a predisposition to the appearance of lipomatosis in those people who suffer from obesity and diabetes.
Tentatively, lipomatosis may also be associated with lipid imbalance and hypertrophy of adipose tissue.
Secondary causes of lipomatosis:
- Age/gender (lipoma most often affects men over 45 years of age);
- Immune system disorders;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Presence of sexually transmitted diseases;
- Chronic diseases of internal organs;
- Abuse of bad habits;
- The use of certain drugs (antibiotics, protease inhibitors, etc.);
If we are talking about a hereditary factor, then lipomatosis is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner in 65% of cases, affecting more than one family member in the male line over several generations. This is due to mutations in mitochondrial DNA in men.
Types of lipomatosis
Most often, lipomas develop on visible parts of the body - neck, face, torso, armpits, hips, chest, shoulders. Less common in the parenchyma of internal organs and bones.
Visual lipomas, soft and mobile, small in size, cause practically no complaints from the patient, except for a cosmetic defect.
If a lipoma on the body begins to grow rapidly and increases to gigantic sizes, this situation cannot be left to chance.
Lipomatosis will begin to affect nerve endings, blood vessels, compression syndrome will occur and a sharp deterioration in the patient’s condition.
This situation can be quickly and favorably resolved with surgical treatment.
The situation is completely different with lipomatosis of internal organs: liver, pancreas, gall bladder, kidneys, lungs, etc.
Liver lipomatosis
This disease is characterized as fatty liver disease or NAFLD (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease), in which excessive amounts of fats - triglycerides - accumulate in the liver.
Fat, which is located in the liver at the level of the physiological norm, under the influence of negative factors, begins to be synthesized and utilized incorrectly, which leads to the development of pathology.
The normal level of triglycerides in the liver is 5% of the liver weight, with lipomatosis it is more than 40%.
Main causes of liver lipomatosis
- Metabolic disease.
- Sedentary lifestyle (hypodynamia).
- Diabetes.
- Abuse of junk food (excessive consumption of unhealthy fats).
- Uncontrolled use of medications (antibiotics, hormones, inhibitors, etc.).
- Genetic factor.
Including stress, nervous strain and additional chronic diseases of the digestive system with malabsorption syndrome (Cushing's syndrome).
Symptoms of NAFLD
Liver lipomatosis often occurs unnoticed and asymptomatic, especially in the early stages of development. Therefore, the patient may not pay attention to specific symptoms at all for a long time, and the disease itself becomes a “surprise” during a preventive examination.
It is vital not to neglect routine examinations. Even lipomatosis with timely diagnosis has a favorable outcome. It can be treated with medication and does not cause complications.
The main symptoms of liver lipomatosis:
- Severe chronic fatigue;
- Sudden weight loss, loss of appetite;
- Poor concentration;
- Heaviness in the right hypochondrium, dull pain;
- The appearance of dark spots on the neck and armpits;
- Enlarged liver (on palpation).
These symptoms should alert you and cause an urgent visit to the clinic.
Features of the course of liver lipomatosis
Liver lipomatosis has 3 stages of development:
- Fatty hepatosis (liver steatosis).
- Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
- Fibrous stage.
The first is characterized by a latent course, during which triglycerides begin to accumulate. This stage (liver steatosis) is reversible, so it is very important to identify the disease at the very beginning of the development of the pathology.
If the stage of liver steatosis is missed, the disease continues its progress until the activation of the inflammatory process (non-alcoholic steatohepatitis).
If you do not consult a doctor here, liver lipomatosis progresses to the stage of fibrosis, where hepatocytes die and are gradually replaced by connective tissue.
This stage is a point of no return, it is irreversible, and may be aggravated by the development of cancer or cirrhosis of the liver.
The liver has a huge reserve of strength and the ability to “suffer in silence,” so always pay attention to even minor symptoms and undergo timely diagnosis (at least an ultrasound of the liver and a blood test for liver function tests).
Diagnosis of fatty liver
The first diagnostic methods for fatty liver are:
- Ultrasound of the liver.
- CT and MRI.
- Biopsy.
Including laboratory blood tests (complete blood count, liver function tests, tumor markers).
With liver lipomatosis, ultrasound may show normal tissue echogenicity or slightly increased, so distinguishing, for example, liver cirrhosis from the fibrotic stage can be problematic.
- Therefore, if you have the slightest doubt, you need to undergo CT or MRI diagnostics, which will most accurately recognize the nature of focal fatty infiltration in the liver.
Treatment of liver lipomatosis
Treatment of fatty liver can be either conservative or surgical, depending on the stage and characteristics of the pathology.
Conservative treatment of liver lipomatosis includes:
- Taking hepatoprotectors (based on essential phospholipids);
- Medicines based on milk thistle;
- Vitamin preparations (alpha lipoic acid);
- Taking antioxidants, amino acids;
- Preparations based on urodeoxycholic acid.
Conservative therapy must be supplemented with diet and regular physical activity.
The goal of conservative treatment is to correct metabolic syndrome, reduce cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood, reduce the degree of liver damage, normalize intestinal flora (reduce wall permeability), normalize bilirubin, and increase tissue sensitivity to insulin.
Not all of these drugs are prescribed to patients at the same time. Their choice depends on the cause, stage and type of lipomatosis. Prescribed and monitored only by the attending physician.
Surgical treatment and blood transfusion are the last resort option for resolving the situation with fatty liver.
Prognosis for treatment of liver lipomatosis
If you do not ignore the symptoms, the outcome of treatment for liver lipomatosis is generally favorable. At the same time, we must not forget that this disease never goes away on its own, and with inaction it gets worse.
Timely examination and competent treatment significantly reduce the risk of complications, including malignancy.
How does cutaneous lipomatosis manifest?
Cutaneous lipomatosis is manifested by the appearance of palpable subcutaneous nodes. Typically, the size of such nodes does not exceed 2-3 centimeters, but they can also reach 8-10 centimeters and are called “giant lipomas”. Lipomas can develop in any part of the body where there are fat cells. However, they most often form on the neck, shoulders, chest and torso, armpits and thighs. Less commonly, lipomas occur in parenchymal internal organs or even in bones. Neoplasms in the oral and maxillofacial areas require special attention, since they often affect the parotid salivary glands, which makes diagnosis difficult.
Soft and mobile fatty formations of small size usually do not cause any complaints. However, with rapid growth or an unfavorable location, they can affect nerve endings, blood vessels and even joints, which leads to discomfort, pain, local sensitivity disorders and paresthesias, swelling and other signs of circulatory disorders (compression syndrome). It should be noted that all symptoms are local and can easily be associated with the presence of a lipoma. Another possible problem is an aesthetic defect, since skin lipomas often develop on the face and other visible parts of the body. This causes psychological discomfort, especially in women and children.
Most fatty tumors are benign and grow slowly, but secondary changes can occur. These are atrophy (the most favorable outcome when the volume of the tumor decreases without any external intervention), fat necrosis (accompanied by redness, pain and hyperthermia) and severe hyalinization. If suspicious symptoms appear, signs of malignant transformation, or in the presence of multiple recurrent lipomas, it is better to consult a dermatologist for examination and histological evaluation of the tumors.
Pancreatic lipomatosis
Pancreatic lipomatosis is quite rare. It is characterized by slow progression and scant symptoms. A patient who is faced with this pathology does not always understand the reason for his poor health and may misinterpret the symptoms.
The main types of pancreatic lipomatosis:
- Diffuse lipomatosis.
- Nodular lipomatosis.
- Mixed pancreatic lipomatosis.
The first type is characterized by the development of fatty formation over the entire surface of the gland. Diffuse lipomatosis does not have a clear localization and is often asymptomatic. Usually this pathology is determined by chance during a preventive examination or against the background of complaints and diseases of the digestive tract.
Diffuse lipomatosis is characterized by a specific “swing”. It can progress very slowly, then begin to develop sharply and intensively, and then stop its growth again.
Nodular lipomatosis is a more common pathology, which is characterized by the rapid development of nodular formations. These “nodules” are located in a capsule, so they have a denser structure and increased pain. They are usually located symmetrically on the gland.
Mixed lipomatosis is the rarest type of pancreatic obesity. It has features of both diffuse and nodular lipomatosis. This type of pathology usually provokes a metabolic disorder.
Causes of pancreatic lipomatosis
- Obesity 2-3 degrees;
- Diabetes mellitus type 2;
- Abuse of junk food, smoking and alcohol;
- Chronic diseases of the endocrine system;
- Oncopathology of the respiratory system;
- Age from 60 years;
- Hereditary factor;
- Metabolic and immune system disorders;
- Ecological unfavorable habitat.
Including a history of hepatitis of varying degrees of development.
Symptoms of pancreatic lipomatosis
The first stage of lipomatosis development is usually asymptomatic.
Further, as the pathology develops, the following may appear:
- Pain in the stomach area.
- Flatulence, bloating.
- Nausea after eating.
- Feeling of “fullness” in the abdomen.
- Fatty inclusions in stool.
- Constant dry mouth.
- Alternating constipation and diarrhea.
- Painful urination.
- The appearance of excessive appetite.
Including numbness of the limbs and dry skin.
If you have identified one or more of these symptoms, this is an important reason to contact a specialist and undergo a comprehensive examination.
- It is always wiser to prevent the development and complications of any pathology than to treat its consequences. And in this case, the forecast may not always be reassuring.
Often the development of lipomatosis is confused with the symptoms of pancreatitis, which makes it difficult to make a final diagnosis.
Stages of development of pancreatic lipomatosis
Pancreatic obesity has 3 stages of development:
- At the first stage, 30% of the pancreatic tissue is replaced by fat. It occurs without symptoms.
- Stage 2 pancreatic lipomatosis is characterized by the replacement of up to 60% of tissue, which is accompanied by various disorders of the digestive system, as well as severe pain (neoplasms can grow inside the organ).
- At the final stage of lipomatosis, more than 60% of the pancreas is replaced by adipose tissue, as a result of which it can no longer produce hormones and enzymes, which causes a number of pathological changes throughout the body.
Often patients with pancreatic lipomatosis experience the symptom of “drops of bloody dew” (Tuzhilin syndrome). These are round, small red bumps that appear on the upper part of the body and do not disappear when pressed.
This symptom is usually considered the main sign of chronic pancreatitis, but it is not specific.
The single factor that “triggers” the pathological process of pancreatic lipomatosis has not been determined. Therefore, according to statistics, we can only talk about hereditary predisposition, which doubles the occurrence of this pathology in patients.
In any case, modern medical capabilities make it possible to identify the disease in time and carry out effective treatment for lipomatosis.
Diagnosis of lipomatosis
Pathological obesity of the pancreas can be diagnosed using:
- Ultrasound of the pancreas;
- CT, MRI;
- Coprograms.
As well as general and biochemical blood tests.
The final fibrous degree of damage to the pancreas during ultrasound, as well as to the liver, is manifested by a slight increase in echogenicity, which excludes this research method as the only one for making a final diagnosis.
How to treat pancreatic lipomatosis
Treatment of this disease is aimed primarily at slowing down the replacement of healthy gland cells with adipose tissue.
Includes:
- Conservative therapy.
- Surgery.
Drug treatment of pancreatic lipomatosis is aimed at alleviating the symptoms of the pathology.
In this connection, the following may be prescribed:
- Antispasmodics (for pain in the abdominal area);
- Antidiarrheal medications;
- Antiemetics;
- Enzymes, vitamins and minerals;
- Drugs that normalize glucose levels (if necessary).
Complements conservative treatment - diet, proper alternation of rest and physical activity.
Surgery is a radical treatment that must be resorted to when a fatty tumor of the pancreas grows rapidly.
Surgical intervention at a late stage consists of complete excision of the gland and its ducts.
The type of drug, dosage and general scheme of surgical treatment are selected by the attending physician based on a number of diagnostic procedures and the patient’s condition.
Prognosis for pancreatic lipomatosis
Of course, you will not hear anything new if we tell you that timely examination is the key to a quick recovery. But, unfortunately, there is no “miracle” remedy that could return the patient to his previous standard of living at an advanced stage of the disease.
Therefore, in order not to deal with the negative consequences of lipomatosis: diabetes mellitus, functional pancreatic insufficiency and cancer, do not neglect preventive examinations.
After all, at the early stage of development of the pathology, the prognosis is most favorable, but advanced conditions have very disappointing statistics.
Treatment of dermatological diseases in the best clinics with Booking Health
To select the safest and most cost-effective treatment method, a patient with lipomatosis requires accurate diagnostic tests, as well as qualified doctors with extensive practical experience. Only a comprehensive examination can distinguish lipomatosis from more serious skin diseases. In some cases, it is more advisable for patients to turn to foreign specialists to make a correct diagnosis and carry out safe treatment.
People without experience of treatment abroad can contact ]Booking Health[/anchor], which is a certified international medical tourism operator. Along with a professional assessment of each case, Booking Health offers assistance in the following matters:
- Choosing a clinic based on specialization and treatment success rates
- Choosing a doctor and direct communication with him
- Development of a preliminary treatment program and estimation of its cost
- No surcharges or coefficients for foreign patients (save up to 50% of the initial cost of treatment)
- Make an appointment for the desired date
- Control of all stages of the medical program by our specialists
- Provision of health insurance in case of complications (coverage 200,000 euros, validity period 4 years)
- Assistance in purchasing and shipping necessary medications
- Receipt and translation of medical statements
- Control of final costing and return of unspent funds
- Organization of additional and control examinations, as well as remote consultations
- Booking hotels and air tickets, organizing transfers
- Translation services, assistance from a personal coordinator 24/7
Leave a request on our website, and a medical consultant or patient manager will contact you as soon as possible to discuss all the details in detail.
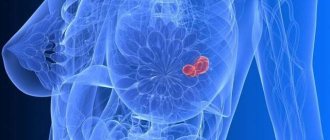
Lipomatosis of the mammary glands
Breast lipoma is also a benign tumor that consists of adipose and connective tissue. This pathology affects women after 45 years of age. The exact causes of breast lipomatosis are unknown.
Women at risk are:
- With a history of trauma to the mammary glands;
- Genetic predisposition (familial lipomatosis);
- In the age category from 40 years.
The disease is asymptomatic and usually breast lipomatosis is determined “by chance” during a routine examination by a doctor.
Sometimes women with breast lipoma may experience:
- Slight soreness in the mammary gland;
- Feeling of heaviness, discomfort;
- Breast deformity;
- Enlargement of regional lymph nodes.
Also, upon palpation, a small elastic seal may be felt in the chest.
Preventive examinations of a woman by a gynecologist or mammologist are mandatory!
You need to visit a doctor at least once a year without any complaints, and every 6 months, if you have a history of any disease of the breast or reproductive system.
Diagnosis of breast lipomatosis
The following will help confirm or refute the diagnosis:
- Consultation with an oncologist-mammologist.
- Ultrasound of the breast (before the birth of children).
- Digital mammogram (for women who have given birth).
- Tomosynthesis of mammary glands.
- Biopsy.
Including laboratory blood tests (biochemical blood test and tumor marker analysis).
Treatment and prognosis for mammary lipoma
Treatment of breast lipomatosis consists of a conservative approach and surgical intervention.
If a woman is not bothered by any symptoms of the disease, and the pathology is under the control of a doctor, drug therapy can be prescribed, aimed at generally strengthening the immune system and metabolism.
The decision on surgical intervention is made by the attending physician on an individual basis, based on the results of the study.
Direct indications for surgical treatment (sectoral resection):
- Intensive growth of the tumor;
- Discomfort, heaviness, chest pain;
- Elimination of a cosmetic defect (in case of deformation);
- High probability of degeneration into malignant pathology (due to genetic factor).
Unlike lipomatosis of the pancreas and liver, breast lipoma has no predisposition to malignancy, and therefore has the most favorable prognosis.
Causes of lipoma
The causes of lipomas on the head and body, as well as in internal organs and muscles, are not precisely known. There are several theories, each of which cannot definitively explain why this tumor occurs.
Genetic predisposition is the main theory. The gene responsible for the development of this benign neoplasm has not yet been identified, but it has been proven that children of parents suffering from lipoma very often inherit this feature. If one of the identical twins has it, then in almost 100% of cases it develops in the second one.
In case of lipid metabolism disorders (second theory), lipoproteins, clogging microscopic blood vessels, begin to accumulate, forming a clot of fat. Subsequently, it can grow capillaries and connective tissue, which will divide it into lobules, creating a lobular lipoma structure.
The theory of the appearance of a lipoma from clogged sebaceous glands is the third in a row. According to it, the fat secreted by the sebaceous gland cannot reach the surface of the skin due to blockage of the duct and begins to accumulate. The further process is similar to how it is described in the previous theory. Unfortunately, it is impossible to explain the appearance of a lipoma in the abdominal cavity by such a mechanism (there are no sebaceous glands in the abdomen).
Spinal epidural lipomatosis
Epidural lipomatosis is characterized by the accumulation of adipose tissue in the space of the spinal canal. This pathology usually occurs with obesity, Cushing's syndrome (malabsorption of the digestive system), prolactinoma.
Epidural lipomatosis is most often localized in the lumbar or thoracic region.
The main symptom that the patient presents with is pain. Since the growth of a fatty tumor causes compression and pinching of the spinal nerves .
Diagnosed using MRI. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, conservative or surgical treatment is prescribed, depending on the degree of development of the pathology.
The causes of spinal lipomatosis, as well as other types, are not fully understood.
Treatment
Treatment of lipoma without surgery is ineffective. Given its small size, doctors try a series of injections of the hormonal drug Diprospan directly into the tumor. Sometimes this allows you to get rid of the tumor, but the relapse rate is quite high.
Traditional methods are also ineffective. There are no traditional or non-traditional remedies that can resolve a lipoma, so if it causes discomfort, do not waste your time. Dobrobut.com recommends contacting a specialist to resolve the issue of surgery.
There are two types of indications for surgical intervention: relative and absolute.
Absolute situations are those when refusing surgery threatens the patient’s life or can lead to permanent disability and deterioration in quality of life. It can be:
- brain lipomas (located in the cranial cavity);
- intracardiac lipomas;
- threat of tumor rupture into the retroperitoneal space or abdominal cavity (you need to know about the symptoms of abdominal lipoma to prevent this situation).
Relative indications are situations in which the patient experiences discomfort, but there is no threat to life. A lipoma can grow and later cause more serious health problems:
- compression of the nerve, accompanied by pain;
- localization in a parenchymal organ (for example, surgical removal of a lipoma from a single kidney is the only way to prevent renal failure);
- permanent injury to the tumor (rare, but sometimes a lipoma can become malignant);
- poor circulation of a part of the body due to compression of blood vessels.
Even in the absence of serious symptoms, a lipoma can be removed at the request of the patient. For example, if the patient is not satisfied with how the lipoma on the neck looks.
Removal of a subcutaneous tumor is usually performed under local anesthesia after testing for allergies to the anesthetic. The surgeon makes an incision and excises the entire lipoma along with the capsule. The wound is sutured, and a rubber drain is left in it for several days, which is subsequently removed.
It is also possible to remove the tumor with a laser. There is no big difference between laser removal of a lipoma on the back (or anywhere under the skin) and traditional surgery, except that the blood loss with the first method is slightly lower, as is the risk of wound infection.
Surgery to remove breast lipoma
The tumor at this location is removed under anesthesia. They try to make the incision so that the scar after it is not visible. This is either the lateral surface of the organ or the fold under the gland. The surgical technique is approximately the same, however, if the lipoma is located deep within the gland, sectoral resection may be required. In any case, the question of the method and course of the operation is decided by the patient together with the doctor.
Surgical removal of kidney lipoma
The operation is also performed under anesthesia. The doctor, having reached the kidney, dissects it at the place where the lipoma is located, completely excises it along with the capsule, and then sutures it, leaving a tubular drainage. Subsequently, the drainage is also removed.
The operation can also be performed using the endoscopic method. This is a less traumatic intervention and has recently been preferred. Recovery after laparoscopic surgery takes much less time.
What to do if a brain lipoma is detected
If its symptoms appear, such as headaches, disturbances in motor functions and sensitivity in any part of the body, seizures, decreased vision or hearing, you should immediately consult a doctor. Such a lipoma can only be removed surgically using endoscopic or open access. It is carried out in specialized neurosurgery clinics. To clarify all questions, sign up for a consultation on the website of our clinic Dobrobut.com.
How to get rid of cardiodiaphragmatic lipoma
This pathology develops in the mediastinum - a special cavity of the chest where the heart, the vessels leaving it and the tracheobronchial tree are located. Most often it is asymptomatic, but as it grows, severe complications can occur, including sepsis or cancer. It is also possible to develop respiratory failure, as well as cardiac arrhythmias due to constant mechanical irritation of the heart. It is necessary to remove such a tumor immediately after its detection; the operation is performed by a thoracic surgeon or oncologist under anesthesia.
Since this type of lipoma is a special form of hernia, the operation after removing the hernial sac ends with plastic surgery of the hernial orifice. If this is not done, relapse is inevitable.
In most cases, lipoma does not pose a threat to life or health. However, if it bothers the patient, it is better to deal with it with the help of specialists.
Related services: Surgical operations Laparoscopy