What is pemphigus? Symptoms, causes and treatment
Pemphigus is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by the appearance of a special type of blisters on the surface of previously healthy skin and mucous membranes. Among the types of pemphigus can be distinguished: vulgar, vegetative, erythematous and foliate.
Pemphigus can be diagnosed if acantholytic cells are detected, which are detected in a smear taken or as part of blisters in the epidermis itself (during histological examination). To treat pemphigus, glucocorticosteroids are first used (a whole course of treatment is prescribed). The latter always goes well with extracorporeal hemocorrection (plasmophoresis, cryoapherosis, hemosorption).
general information
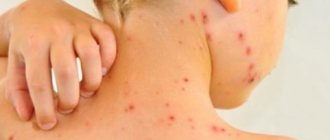
Streptodermia refers to a pathology caused by streptococci. If we talk about the external manifestations of the disease, blisters and purulent rashes that itch appear on the skin.
Streptoderma in children can occur in two different forms: acute and chronic. Acute is characterized by pronounced symptoms, and chronic - by periodicity.
According to the degree of damage, the disease is classified into superficial, deep and intertriginous. Each form has a specific feature.
Symptoms
If streptoderma occurs, what is the treatment? Before we know the treatment options, let's find out the symptoms. The disease in children occurs in extremely severe forms:
- temperature up to 39C,
- poisoning,
- large lymph nodes.
The texture of the skin may vary depending on the form of the pathology:
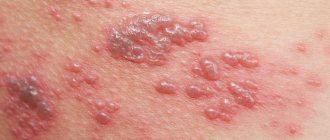
- Superficial. Initially, red spots form on the skin. After a couple of days they turn into blisters with a certain liquid inside. The blisters grow up to two cm in diameter, after which they rupture. Yellow crusts form in this area. After this, the skin in this area heals, and the pathology develops further.
- Dry streptoderma . This form usually occurs in boys. Light and pink spots up to 5 cm in diameter form on the skin. They are found everywhere on the body. After they disappear, scars may remain.
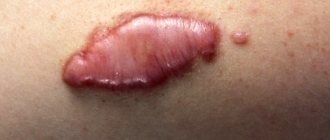
- Streptococcal infection. The pathology extends specifically to the corners of the lips; it is encountered when there is a deficiency of vitamin B. Small cracks form on the skin, causing discomfort. After some time, they form into pustules that become crusty. The child has difficulty consuming food, as it causes pain.
- Felon. In a situation where streptococcus spreads to the area around the nails, panaritium develops. Oddly enough, this disease is more often encountered by children at an early age who bite their nails.
- Streptococcal diaper rash. This form of pathology is typical for breastfed children. Blisters form in the folds of the skin.
Understanding how streptoderma begins to develop in children, treatment which requires timely contact with a dermatologist and the implementation of therapeutic actions, not a minute can be lost. If you constantly put off going to the doctor, the pathology can develop into a chronic form, and it will be almost impossible to achieve a final cure.
streptoderma, treatment
Types of pemphigus
People distinguish between true pemphigus (pemphigus) and other blisters on the skin. The true one is of the following types:
- ordinary, or vulgar - occurs most often. Externally intact and undamaged skin becomes covered with blisters with serous fluid inside, which burst easily and quickly and heal. Localization - the mouth area and the mucous membrane of the lips, as well as the nasolabial triangle. At first glance, harmless bubbles appear more and more often, each time occupying a larger area throughout the body. When they burst, they leave pink eczema in this place. The child should begin receiving adequate therapy between 6 months and 2 years. Otherwise, there is a danger of death;
- vegetative - the course of the disease differs from the usual type only in the consequences on the skin. In this case, instead of eczema, vegetation papillomas of a grayish tint remain. These papillomas are growing;
- leaf-shaped - got its name due to the visual appearance of the crusts formed after the bursting of bubbles. A distinctive feature of this species is the rapid development of pathology. In this case, the count is not in months, but in days. In this case, the skin peels off in whole pieces shaped like leaves;
- erythematous - is a complication after leaf-shaped and has no striking differences from the previous form of pathology;
- seborrheic - originates in the hair on the head and face. Small bubbles quickly become a yellowish crust. The progression of the pathology is slow, affecting the back, abdomen and limbs. After peeling off the crust, weeping eczema remains.
There are other types of pemphigus that are not related to pemphigus:
- infectious viral pemphigus in children - develops under the influence of viruses: Coxsackie, enterovirus 71. In this case, the latter option may have the nature of an epidemic. It has specific localization sites - feet and palms, butt and genitals;
- congenital syphilis - occurs when there is intrauterine infection with syphilis. It appears within a couple of days after birth. The blisters burst quickly and leave behind weeping pink eczema.
Untrue types of pathology in medicine refer to the symptoms of pemphigus in children. This course of the disease allows for faster and more correct treatment of pemphigus in children, aimed at eliminating the root cause. The most difficult thing in this pathology is establishing the true cause of the disease.
A rare but severe type of true pemphigus is the paratumor type. It has the most striking symptoms. It occurs against the background of leukemia and lymphoma, and also appears as a harbinger of the development of a malignant tumor.
Causes
The causative agent of streptoderma, the photo of which you will find below, is group A streptococcus. However, it is worth noting that infection can only develop in a situation where certain factors are present:
- skin damage,
- lack of following basic hygiene rules,
- weak immune system,
- disruption of the endocrine system,
- dermatological diseases,
- depressive mood
- vitamin deficiency,
- constant washing of the skin, which leads to damage to the protective layer,
- strong influence of different temperature ranges,
- poisoning,
- circulatory disorders.
Therapy
Streptoderma has occurred ? Even in cases where the initial examination was carried out by a pediatrician, only a dermatologist can select therapy. Doctors in this field have an understanding of drugs with a narrow scope of action.
The first step is to limit the child’s diet. The course of treatment also involves avoiding water procedures, which can cause the spread of the disease. Healthy areas of the skin should be washed with a solution of chamomile, and damaged areas should not be touched at all.
The sick person needs to choose the right wardrobe, from which items of clothing made from synthetics and wool must be removed.
Doctors advise popping blisters that form on the skin with a disinfected needle, after which the abscess should be drained twice a day. Healthy areas of the skin are washed with a boron solution.
If crusts appear on the skin, they should be treated with antibacterial gels or ointments.
In more complex situations, many other medications may be prescribed:
- antibiotics for streptoderma of the tetracycline or chloramphenicol series,
- means that prevent the occurrence of an allergic reaction,
- means aimed at improving the body's immune system,
- vitamin preparations,
- antipyretic.
The set of medications must be discussed with the doctor. With the right treatment, the symptoms disappear within a week, but after the severe form is eliminated, scars may remain. This is what streptoderma looks like .
what does streptoderma look like?
Diagnostics
Experts say that a correct diagnosis can be made based on a comprehensive examination of the patient, which includes several important stages:
- Examination of the patient for the presence of a clinical picture. At this point, the doctor establishes the nature of the lesions, their localization, the degree of development of the disease, etc.
- Cytological analysis necessary to establish the presence of acantholic cells in smears of biomaterial.
- Carrying out the Nikolsky test, which allows to differentiate pemphigus from similar pathological processes.
- Method of direct immunofluorescence. This study allows us to detect the presence of immunoglobulin in the intercellular substance of the epidermis.
- A histological study, which is based on a technique for detecting crevices and other damage within the epidermis.
Only the totality of all the results makes it possible to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe an effective course of treatment, leading to the patient’s recovery.
Causes of complications and re-infection
The reason for re-infection may be incorrect therapy when, for example, if you have primary criteria for improvement, you decide to stop therapy. The most important thing is to remember that you need to unquestioningly follow the advice and instructions of your doctor.
streptoderma complications
What can streptoderma be confused with?
Pyoderma
With pyoderma, the sebaceous and sweat glands are damaged. The rash appears in certain areas of the skin - parts of the body, scalp.
Herpetic rash
Herpes is characterized by the presence of blisters with constant inflammatory processes. They burst and provoke development.
Thrush or candidiasis
Candidiasis is characterized by erythematous papules or reddened, wet plaques. In the pathology under consideration, the lesion, as a rule, occurs in the mucous membranes or fold areas.
Manifestations of allergies
An allergic rash continues to occur as long as the influence is the causative agent of the allergy.
Types of disease
- Streptococcal impetigo. The most common standard form of the disease. A characteristic rash forms on the face, arms and legs. This form is also the most limited, since the pathogen does not move beyond the upper layer of the skin, which has certain protective mechanisms. The appearance of the integument does not change, only individual blisters with liquid appear on the reddened areas. Initially, the patient will experience itching, after which the blisters become darker, which helps the blister to crust over. The duration of this process reaches one week. However, it is worth remembering that if the rash resolves, bacteria are further transferred to healthy areas of the integument, which has its negative consequences for the sick person.
- Bullous impetigo. The rashes are located on the arms and legs and had a fairly impressive diameter. Once the blisters open, these areas of skin develop ulcers that can spread quickly.
- Streptococcal diaper rash. Most of the patients are young children and overweight people. The location of the rash is under the mammary glands, in the axillary folds, intergluteal or inguinal-femoral folds. If you are overweight, the abdominal area is affected.
- Ringworm common. Appears in the form of bright pink rashes. The place of appearance is the face. The rash may become smaller due to exposure to direct sunlight. Those areas of the skin that are affected will not take on a tan like before.
- Streptococcal infection is characterized by the formation of blisters in the corners of the mouth. After the blisters disappear, a crack appears in their place, which in a matter of minutes becomes covered with a yellow crust. It also happens that children tear off the crust, but it forms again.
- Streptococcal ecthyma is the most complex form of the disease. The disease is accompanied by the appearance of characteristic lesions and scars on the arms and legs. In case of development of ecthyma, as a rule, there is a deterioration in health.
Mechanism of bubble formation
Human skin can be figuratively described as a water-spring “mattress” covered with a kind of “wall”. The “mattress” does not participate in the formation of bubbles - only the top layer, the epidermis, suffers.
The epidermal layer consists of 10-20 cell layers, which look like bricks under a microscope. The “bricks” of the second layer of the epidermis are connected to each other by peculiar “bridges”. On top of the “wall” there are layers of cells that are no longer quite similar to cells, reminiscent of applied cream. These are scales, corneocytes, necessary for protection from mechanical, chemical and physical damage.
If, under the influence of internal or external causes, antibodies are formed that destroy the “bridges” - desmosomes between the cells of the basal layer (this is called acantholysis and can be seen under a microscope), this is true pemphigus. If tissue fluid penetrates between the basal and upper layers of the epidermis without destroying the “bridges,” it is pemphigoid. Viral pemphigus also occurs without destruction of desmosomes.
Therapy and drugs
Throughout the spread of the disease, basic hygiene rules should be observed: in the first days, it is forbidden to take baths and wet impetigo, and it is forbidden to comb the affected areas.
Therapy for this disease is aimed at destroying the pathogen and strengthening the protective functions of the immune system. As a complex treatment, antibacterial drugs of the category of cephalosporins, macrolides and penicillins are prescribed. If you have bullous streptoderma, you should stop taking medications. As an immunocorrective treatment, the drugs “Likopida”, “Amiksin” and their analogues are effective. Treatment with drugs for . Restoration of microflora in the intestines occurs with the help of probiotics and prebiotics. Appropriate antihistamines will help get rid of scabies.
Means that increase the body’s resistance to infections in the form of solutions - “Eleutherococcus”, “Echinacea”, “Leuzea”, etc.
Sets of vitamin nutrients should also be taken in accordance with the instructions.
Local treatment includes antiseptic drugs that prevent the spread of putrefactive bacteria. Such medications include various alcohols, brilliant green, as well as their analogues - “Fukartsin”, “Chlorhexidine”, “Miramistin”, “Rivanol” or the cauterizing agent “Resorcinol”.
The use of a huge number of zinc-based pastes, preparations and ointments for streptoderma in children with intense scabies.
Coping at home
Non-medicinal products include available substances that can be purchased at home. You can use creams based on the active element panthenol, which is good for burns.
Burgundy skin is immediately lubricated with sour cream, kefir or ointment after sunbathing. The procedure is repeated every half hour, waiting for complete absorption.
It is better to open large blisters in the surgeon's office. He will immediately apply a bandage with a medicinal agent, which will have to be rewound daily. The released bacterial environment can infect others; antiseptic treatment is required before applying the medicine and after opening the compress. Levomekol or Syntomycin will help reduce the development of inflammation.
In case of fungal infection of the feet, treat the skin with camphor or alcohol solutions. Pruritic disorders are relieved by Fenistil gel and other painkillers. If chemicals come into contact with human tissue, you cannot use a specific type of drug.
It is better to select a remedy together with a dermatologist.
Preventive measures and prognosis
Due to the high risk of infection, sick children should keep their distance for some time and not contact other people. Quarantine is provided for up to 10 days. For the entire period of therapy, it is necessary to follow the rules of hygiene.
To prevent the development of the disease, it is necessary to disinfect the child’s personal belongings. Sick children should have a proper diet rich in nutrients. To improve the quality of the immune system, certain measures should be taken.
streptoderma treatment
As a rule, streptoderma ICD 10 in children is cured without any problems. Exacerbation of the disease and re-infection are observed mainly in children from disadvantaged families or in children with weak immunity. With timely treatment, symptoms disappear within one week. If you do not attach any importance to this, the disease can develop into a more severe form. In the worst case, the disease can lead to blood poisoning. For streptoderma, treatment with ointments and antibacterial agents is mandatory.
Treatment methods for urticaria in children
This disease should be treated depending on its form. The pseudoallergic variety requires examination for the underlying disease. Allergic – allergen exclusion and immunotherapy.
In the acute period:
- eliminate contact with the allergen;
- the child is prescribed a hypoallergenic diet for several days;
- remove the allergen from the body, prescribe plenty of fluids;
- use sorbents and antihistamines (types and dosage regimen are determined only with a doctor);
- for severe swelling, a specialist may prescribe a diuretic;
- Prescribe antipruritic ointments for the arms, legs, or other areas of the child’s body that are prone to hives.
Parents should carefully monitor the cleanliness of the house and promptly wash clothes and bedding with hypoallergenic products.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of infection, you should follow the following rules:
- follow the rules of hygiene,
- disinfect damage to the skin,
- strengthen the name system with useful substances,
- do not carry out frequent water procedures, as this may pose a certain danger for the child,
- In case of primary symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Streptoderma on the face can be treated, but only if you consult a doctor in a timely manner. The earlier therapy was carried out, the easier it is to exclude complications and transition to the chronic stage. You can undergo a full examination in a clinical clinic.