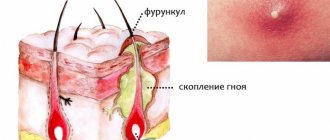
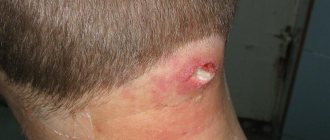
A furuncle is an inflammatory process that affects the hair follicles and surrounding tissues, characterized by a purulent-necrotic reaction and intoxication of the entire body. The main pathogens are ingested pyogenic bacteria, mainly Staphylococcus aureus. The main reasons for the occurrence of such a pathology can be: microscopic injuries to the skin (from shaving, depilation, ingrown hairs, dry skin, scratching, etc.), disruption of the metabolic response and immune defense of the surface layers, skin contamination and blockage of the ducts of the glands located next to the follicle , impaired sweating and sebum secretion, hypo- and avitaminosis, endocrine disorders.
A boil, as a skin disease, is characterized by a staged process:
- Development of infiltrate within 1-2 days (hyperemia of the skin, thickening, the skin stretches and becomes flattened, shiny over the area of formation of the pathological process, extremely painful);
- On the 3-4th day, suppuration of the follicular pustule occurs, with a necrotic center;
- Rejection of the necrotic core of the boil;
- The healing process with scarring lasts up to 10 days.
In addition to a local reaction, a boil is characterized by intoxication of the body. Often there is a temperature reaction to the infectious agent and pus, as well as general weakness.
A boil can be treated either conservatively or surgically. In the first stages, local anti-inflammatory drugs and antiseptics may be prescribed. The skin at the site of hyperemia is thoroughly cleaned (disinfected with iodine or alcohol solution), applications with ichthyol ointment are applied, dry heat and UHF are applied. After opening the boil during the process of discharge of purulent-necrotic masses, a wet-dry bandage and applications with a hypertonic solution are applied, this promotes better discharge of pus. After complete cleansing of the ulcer, antibacterial ointments are applied to the wound; levomekol is excellent. When the process is localized to the face, severe complications (purulent meningitis or sepsis) may occur, so systemic antibacterial drugs must be prescribed. In general terms, the medical impact for this pathology is the same for any location, although there are minor differences in the clinic and treatment methods. The surgical method is used when it is impossible to remove the purulent-necrotic rod on its own.
Furuncle in the ear
A boil in the ear receives therapeutic treatment with minor differences. The opening and rejection of necrotic masses may be accompanied by their flow into the middle ear, which is very unfavorable and dangerous for the hearing organ, therefore the use of dry heat, which can also contribute to the occurrence of sepsis, is not recommended. It is recommended that the patient sleep on the affected side to prevent swelling. Be sure to contact an otolaryngologist. The specialist manages the patient conservatively throughout the entire period and only if necessary can perform minor surgery. Under no circumstances should you attempt to clean your ears at this time, squeeze out the boil, or carry out any other activities. The vascular network on the head is very well developed, so in this location it is necessary to approach treatment methods very carefully so as not to cause life-threatening complications. In addition to the local reaction, severe headache, loss of appetite, fever, and irritability often occur. When such a clinic develops, symptomatic additional treatment is prescribed: antipyretic, anti-inflammatory, analgesics.
Why does a boil burst?
The boil opens as it matures. Under the influence of the negative activity of staphylococci, the hair root and the sebaceous gland located next to it melt, and the affected area increases. The human immune system never stops fighting foreign microorganisms and attacks it with white blood cells. From this moment on, the boil can open at any time.
The boil begins to burst when the amount of pus reaches its maximum. In the speedy breakthrough of the abscess, the body’s defenses are of great importance.
After the boil has burst, it is necessary to free the wound from pus and treat the abscess with disinfectants and anti-inflammatory agents. When the boil has already burst, the patient's condition improves significantly.
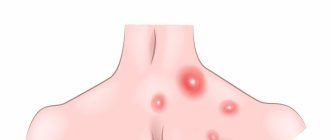
Furuncle on the back
If you find a boil on your back, you should consult a doctor. This pathology can manifest itself either in a local clinic or in intense muscle pain. In case of complications and development of phlegmon (spread abscess), surgical intervention is necessary. The doctor carefully opens the cavity, cleans it of necrotic masses, and bluntly breaks off adhesions if they are present. The lesion is drained and a bandage with a hypertonic solution is applied (for better drainage of pus). A boil on the back is treated with local and systemic antibacterial therapy. If there is a fever and general weakness, antipyretic drugs are prescribed. Muscle pain is relieved with local and systemic analgesics. You should not try to remove a back boil yourself, comb it, or rip it off. Such actions can only lead to aggravation of the pathological process and the development of complications. Often with such localization there are not single, but multiple boils. A formation containing several necrotic rods is called a carbuncle. In case of multiple position of hair follicles, immunotherapy is recommended, and vitamin B complexes are also prescribed.
Brief information
A furuncle is a purulent inflammation around the hair root. The reason for the development of the pathology lies in pathogenic bacteria that penetrate the hair follicle and, through their vital activity, cause inflammation. Its unpleasant feature is the ability to spread to neighboring follicular sacs.
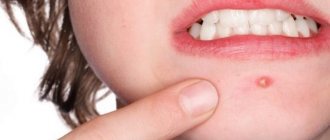
The abscess looks like a large red pimple, accompanied by pain when touched. Its body consists of a pustule and a rod. A pustule is a bulb filled with pus. Those who encounter an abscess for the first time do not know the main thing - what the core of a boil looks like: a purulent compaction of a yellow or green hue, located along the length of the boil.
To remove the contents, you must wait until it is fully ripe. The degree of readiness of the boil is determined by the “cap” - the top becomes white, because the pus has moved as close as possible to the upper layers of the skin, the swelling around the boil goes away, and the pain intensifies.
Important! Under no circumstances should you puncture an abscess or try to squeeze it out before it has matured.
Furunculosis occurs equally among adults and children. If a child develops a disease, it is recommended that treatment be carried out under the supervision of a pediatrician.
Furuncle under armpit
When the boil is localized in the armpit, movements of the upper limb are significantly hampered due to the sharp pain of the formation. It is difficult to adduct or abduct the arm. This condition worsens the patient’s life and makes it impossible to perform usual actions. A developed vascular network can contribute to the spread of infection throughout the body. Regional lymph nodes often become inflamed in response to local inflammation, making movement even more difficult. Fever is typical. A boil under the armpit is treated mainly conservatively. During the period of illness, shaving the armpit and using deodorants are prohibited. It is recommended to thoroughly wash the skin and disinfect the skin with alcohol or iodine solution. In general, conservative measures are carried out, as with boils of other locations. After opening the formation, applications with saline solution and antibacterial ointments are applied. Antibiotics and, if necessary, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. With proper conservative treatment and avoidance of trauma to the pathological focus, surgical treatment is extremely rarely resorted to.
Means for the treatment of furunculosis
You can speed up the maturation of a boil with the help of ointments. They relieve inflammation and swelling of soft tissues, thereby reducing pain, draw out pus and provoke an independent breakthrough of the boil. Adherents of traditional medicine can prepare compresses according to the recipes below. Modern medicine offers a list of ointments that draw out pus, which can be purchased at any pharmacy at an affordable price.
Folk remedies
Simple remedies such as:
- Aloe. Fresh aloe pulp, cleared of the thick crust, is applied to the abscess and secured with a bandage or plaster. Change the compress every 3-4 hours.
- Golden mustache. The leaves of the plant are finely chopped and applied as a paste to the abscess. The top is covered with a gauze bandage. The compress should be changed at the same frequency as aloe leaves.
- Garlic and onion mixture. A clove of garlic and a couple of layers of onion are crushed to a mushy state, diluted with 10-15 drops of vegetable oil. The resulting mixture is applied as a compress to the formation.
When using these products, the maturation of chiria lasts from 4 to 7 days. There are cases when, when using pulling agents, the boil opened on its own, all that remained was to remove the contents. After ripening, the pus is removed and the wound needs periodic disinfection with peroxide, without using the above-mentioned agents.
Modern drugs
The following drugs can be purchased at the pharmacy to draw out pus:
- Vishnevsky balm.
- Ichthyol ointment.
- Syntomycin ointment.
- Streptocide.
The medications are applied in the form of a compress: a little medication is squeezed out onto a cotton swab and applied to the wound using bandages or adhesive tape.
In case the abscess breaks out on its own, you need to constantly apply gauze bandages. This way, the wound will be closed from infection, and the pus will be released onto the dressing material without staining clothing or other surfaces.
It is not always possible to open an abscess on its own, but it is possible to remove the core and pus manually only at a mature stage.
Furuncle on the leg
A boil on the leg or buttock often causes trouble when walking or sitting. Sometimes pain and inflammation significantly complicate the movement of the patient, who tries to spare the affected leg. Boils of the buttock are often complicated by the formation of phlegmon. This often leads to the formation of extensive necrosis, resulting in a scarring process. For this reason, a boil on the buttock is most often treated surgically with opening and drainage of the abscess. With this localization, the patient is recommended to spare the affected area, try to sit on the healthy side, and thoroughly disinfect the site of the pathological process. After rejection of the boil core, bandages with antibacterial ointments should be constantly changed to prevent infection of surrounding tissues with the formation of purulent streaks. After the formation of such ulcers, scars are formed that have an extremely negative cosmetic effect. A boil on the leg is treated conservatively, similar to that for other locations. In case of complications, minor operations are used to open the abscesses. In addition to local treatment, systemic antibacterial drugs are prescribed. With a single boil on the leg and careful handling of it, and with a favorable course of the disease, you can carry out conservative measures yourself. If the boil on the leg does not go away for a long time (more than two weeks) or is complicated by the appearance of a temperature reaction, then you should definitely consult a doctor.
Useful video
See more about removing the boil stem in the video below:
At the second stage of the disease, a purulent-necrotic boil core forms. After this stage is completed, a white abscess is visible on the surface of the boil, which rises significantly above the surface of the skin. There is a red inflammatory halo around it.
After the abscess matures, it breaks through and all the contents come out. The core of the boil is also removed independently, after which the wound begins to gradually heal. However, there may be cases when pus comes out of the boil, but the rod does not.
Furuncle during pregnancy
Treatment for boils during pregnancy is the most gentle. Everything is carried out within the framework of conservative therapy; if possible, it is recommended to use only local antibacterial agents. Any pathological process, as well as excessive use of medications, can significantly disrupt the development of the fetus. Systemic antibacterial drugs are prescribed only in extremely severe cases: multiple furunculosis, often recurrent, severe condition of the mother (fever, diffuse cellulitis, sepsis). In extremely severe cases, there may be a question of termination of pregnancy and appropriate therapy. To prevent such life-threatening conditions from arising, you should not touch the developing boil or try to cut or squeeze it out yourself. During pregnancy, if a woman experiences even a single boil, it is imperative to consult a doctor for advice and periodic monitoring of the development of the pathological process. A pregnant woman must follow a diet. If a boil occurs, it is worth reducing the proportion of carbohydrates. B vitamins have a beneficial effect on the skin and its immune processes. Complex vitamin complexes are prescribed. Biological food additives with vitamins, yeast. The diet should be varied, balanced and regular. Walking in the fresh air and doing gymnastics are very useful for stimulating the immune system.
Treatment of a boil of any location is aimed at preventing the development of complications. With a favorable course of the process, the necrotic core is independently rejected and a small ulcer is formed at the site of the boil, which often heals without leaving a trace.