ICD-10 code for abscess of the gluteal region
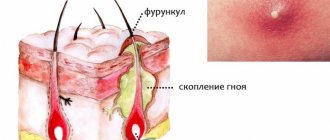
The pathological process can develop in any part of the body. Common locations are the face, neck, back, and butt. Inside the formation contains a purulent mass, which is formed by pathogenic microorganisms, dead cells or tissue detritus, metabolic products of bacteria, leukocytes, mononuclear cells, macrophages.
Abscess of the gluteal region (code L02.3 according to ICD-10) is an extensive area of purulent melting, protected from the tissue by a capsule. Its contents are a manifestation of the body's protective reaction. If the attribute is opened, phlegmon is formed.
Causes and causative agent of abscess
Pathology in the area of soft muscle tissue occurs due to a violation of the injection technique. An illness on the buttock is treated in a hospital or outpatient setting; two types of injections are prescribed: intramuscular and intravenous. It will be possible to protect the patient from the development of possible complications by following the rules of asepsis and antisepsis during the procedure by a medical professional.
The appearance of post-injection infiltrate is facilitated by factors that provoke abscess of the soft tissues of the buttock:
- Dirty hands are a common cause of the development of suppuration: staphylococci, streptococci, and pathogenic microorganisms enter through skin not treated with alcohol. Tissues are a favorable environment for the proliferation of bacteria, whose activity provokes an abscess.
- Repeated use of one syringe can result in a septic condition and death.
- Infiltration on the buttock occurs when the drug is administered multiple times in one place. This is typical for patients who are on a long-term injection course of medications.
- Antibiotics have an irritating effect on the body, drugs cause the formation of a purulent focus.
- Abscesses often occur in obese people on the buttock: a large layer of fat contributes to the formation of infiltrate.
- A high risk of abscesses is inherent in patients with diabetes mellitus and infectious skin diseases.
- An abscess is formed when scratching the injection site on the buttock with dirty hands.
- The group of factors predisposing to the development of an abscess includes pathologies associated with disruption of protective systems: immunodeficiency states, HIV status, tuberculosis.
Avoiding triggers reduces the risk of abscesses.
Furunculosis
Diabetes
Iron deficiency
Angina
22788 November 10
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Furunculosis: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition _
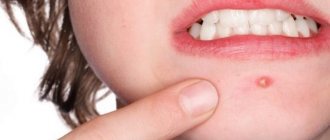
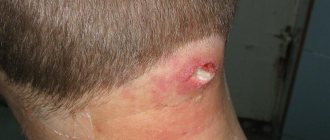
Furunculosis (furuncle) is an acute purulent-necrotic inflammation of the hair follicle, sebaceous gland and surrounding tissue. The disease is manifested by inflammatory elements, which open over time and pus is released from them.
Causes of boils
Furunculosis is characterized by the formation of multiple boils in limited areas of the skin, although the disease can be widespread. Relapses occur over several weeks and even years.
As a rule, furunculosis occurs in people with weakened immunity, with hypo- and vitamin deficiency, and poor skin hygiene. The causative agents of boils are usually staphylococci and streptococci ( S. aureus, S. haemolyticus, S. epidermidis
, β-hemolytic streptococcus). The disease can also be caused by other microorganisms (Proteus vulgaris, pneumococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa), which in most cases are detected in association with staphylococci and streptococci.
Furunculosis often occurs in adolescents and young people with severe sensitization (hypersensitivity) to the causative agents of the disease.
A number of factors contributing to the manifestation of boils have been described: violation of the integrity of the epidermis (microtraumas, maceration of the skin), hyperhidrosis (increased sweating), a shift in skin pH to the alkaline side, exposure to high and low temperatures, burns, ulcers. Endogenous risk factors for the development of furunculosis include impaired carbohydrate metabolism (diabetes mellitus), insufficient intake of proteins into the body, chronic intoxication, the presence of foci of staphylococcal infection in various organs and tissues, tuberculosis, anemia, sore throat, influenza, and gastrointestinal disorders.
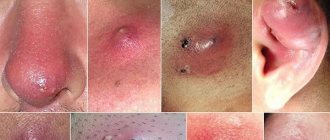
The boil can be localized on any part of the skin, with the exception of the palms and soles, where there are no hair follicles.
The most dangerous localization of a boil is considered to be on the face - in the area of the nose and upper lip. Here the inflammatory process tends to quickly move to the tissue where the branch of the anterior facial vein is located. The spread of infection can lead to thrombosis of the dural sinuses and purulent meningitis. The mortality rate for this complication reaches 80-100%.
Classification of furunculosis
Acute furunculosis is characterized by the formation of several boils at once.
Chronic furunculosis is a longer process (from several weeks to several months), when after the disappearance of one boil, new inflammatory elements appear.
Symptoms of furunculosis
The boil goes through three stages of development.
The first stage of infiltration is characterized by the formation of a painful inflammatory node with a diameter of 1-4 cm. The skin over the boil becomes purplish-red. In places with well-developed subcutaneous fatty tissue (buttocks, thighs, face), boils can reach even larger sizes. During the second, purulent-necrotic stage, suppuration and the formation of a necrotic core occur. A cone-shaped node protrudes above the surface of the skin, which softens in the center to form an abscess. Patients are bothered by burning and throbbing pain. Patients note significant pain when boils are localized on the scalp, the back of the fingers, the front surface of the leg, and in the external auditory canal. After opening the abscess and separating the pus mixed with blood, the purulent-necrotic rod is gradually rejected.
At the site of the opened boil, an ulcer with uneven edges forms.
During the third stage, a scar forms at the site of the boil. Depending on the depth of the inflammatory process, scars can be either barely noticeable or pronounced.
The evolution of one boil occurs within 7-10 days, but when some boils develop after others, the disease drags on for a long time.
With furunculosis, it is possible to increase body temperature to 37.2-39°C, weakness, and loss of appetite.
Diagnosis of furunculosis
The diagnosis is established based on complaints and examination of the patient. For all patients with furunculosis, the following questions are clarified:
- presence of concomitant diseases;
- medications currently taken;
- whether the patient is on a diet.
To exclude somatic pathology that contributes to the chronicity of the inflammatory process, additional research methods may be recommended:
- clinical blood test: general analysis, leukoformula, ESR (with microscopy of a blood smear in the presence of pathological changes);
Symptoms of appearance and what can be confused with
Purulent-inflammatory diseases of different nature have a similar clinical picture, localization, routes of infection, and treatment. The diagnosis can be determined based on the symptoms of pathological conditions with phlegmon and suppuration in the buttock area:
| Sign | Abscess | Phlegmon |
| Puffiness, swelling at the injection site | + | + |
| Redness of the skin on the buttock | + | + |
| Painful sensations during palpation of the abscess site | + | + |
| Intoxication | Accompanied by high fever | |
| A formation on the buttock can cause asthenovegetative syndrome (weakness, lethargy, decreased performance) | + | + |
| Fluctuation symptom is a distinctive feature of an abscess | + | – |
| Defining Clear Boundaries | + | There is a spread of the inflammatory reaction from the buttock to the surrounding tissues. |
| General blood analysis | Severe leukocytosis with a shift to the left |
The color, shape, and size of the pathologies on the buttock are the same; the abscess can be complicated by phlegmon, requiring surgical treatment. The doctor will conduct a differential diagnosis using additional studies.
Timely detection of the disease prevents the progression of the disease and simplifies treatment methods.
Publications in the media
Furuncle - acute purulent-necrotic inflammation of the hair follicle and surrounding soft tissues •
Furunculosis is multiple lesions with boils that appear simultaneously or sequentially one after another in different parts of the body. Most often, boils are localized in areas of the skin exposed to contamination (forearms, back of the hand) and friction (back of the neck, lower back, gluteal region, thighs).
Etiology . Golden, less often white staphylococcus.
Risk factors • Skin contamination and microtraumas • General exhaustion • Chronic diseases • Vitamin deficiencies • Diabetes.
Pathomorphology • Stage of serous infiltrate - cone-shaped infiltrate with regional hyperemia up to 1-1.5 cm in diameter • Purulent-necrotic stage - appearance of a purulent pustule at the apex • Stage of rejection of the necrotic core and healing.
Clinical picture
• During the formation of a pustule in the form of a nodule - slight itching and tingling • On days 1–2, an inflammatory infiltrate appears, protruding cone-shaped above the level of the skin, which turns red and becomes painful when touched • At the top of the infiltrate, a small accumulation of pus with a black dot appears (necrosis) in the center • The pustule usually breaks through and dries up, and on days 3–7 the infiltrate purulently melts and the necrotic tissue in the form of a rod, together with the remains of the hair, is excreted with pus • The resulting wound is cleaned, filled with granulation tissue and heals. The swelling around it gradually decreases, the pain disappears. A small, whitish, somewhat retracted scar remains at the site of inflammation.
• When the boil is localized in the external auditory canal, severe pain occurs in the nose • In the facial area (lips, forehead), as well as on the scrotum, boils are accompanied by significant swelling of the surrounding tissues
• A severe clinical course is typical for boils of the upper lip, nasolabial fold, nose, and periorbital region. Thrombophlebitis of the veins with a facial boil can spread through anastomoses to the venous sinuses of the dura mater, which leads to their thrombosis, creating a threat of the development of purulent basal meningitis. Facial swelling quickly increases, dense, painful veins are palpated, the patient’s general condition sharply worsens, body temperature reaches high values (40–41 °C), neck rigidity and blurred vision may be expressed.
Laboratory research . Leukocytosis with a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left, an increase in ESR.
TREATMENT
Management tactics • Patients with severe systemic inflammatory response syndrome, when boils are localized in the nasolabial triangle, and in the presence of severe concomitant diseases (DM, tumors) are subject to hospitalization.
Conservative treatment • Thorough cleansing of the skin around the source of inflammation •• 70% ethyl alcohol •• 2% salicylic alcohol •• 0.5–1% alcohol solution of brilliant green •• In the formative stage - 5% alcohol solution of iodine • Antibacterial therapy, first empirical, and then taking into account the data of bacteriological research •• oxacillin •• cefazolin • NSAIDs • Physiotherapeutic treatment: UHF, ultraviolet radiation • Detoxification therapy, immunomodulators (if necessary).
Surgery . _ Opening the boil with removal of the necrotic core.
Complications • Lymphangiitis • Regional lymphadenitis • Carbuncle • Acute thrombophlebitis • Sepsis, often develops with facial boils, due to attempts to squeeze out the contents, cutting it off while shaving.
Prevention • Compliance with personal hygiene requirements • Preventing clothing from rubbing areas of the skin where a boil may form.
Course and prognosis • With timely and correct treatment, the prognosis is favorable • In exhausted, weakened patients, if complications occur, the prognosis is serious.
ICD-10 • L02 Skin abscess, boil and carbuncle
What causes ulcers on a child’s bottom?
Abscesses in children occur due to the penetration of Staphylococcus aureus through injured skin into the body. Babies often get injured, damaged areas need to be treated with antiseptics. Against the background of decreased immunity, opportunistic microflora is activated, and as a result of the vital activity of microorganisms, an infiltrate of the gluteal region is formed.
The cause of an abscess is untreated infectious diseases that undermine the child’s immunity. Violation of the technique of drug administration can lead to the formation of an abscess.
Children have a high risk of pathology developing into phlegmon. Examination of the attribute, therapy at an early stage acts as a prevention of dangerous complications.
Ways of spread of purulent processes in the gluteal region
Ways of distribution of the substance in the interfascial spaces if the abscess breaks through with the formation of phlegmon:
- The surface of the thigh suffers when the tissue surrounding the sciatic nerve is involved in the pathological process.
- Purulent contents can flow into the pelvis and anus.
- As phlegmon develops, the underlying layers of tissue melt.
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
Good blood supply to the soft tissues and numerous ways of spreading pus into the internal organs cause the development of sepsis.
Treatment methods for buttock abscess
There are three ways to combat suppuration: physiotherapeutic, surgical, conservative methods of therapy. The tactics for eliminating the pathology depend on the prevalence, depth of the formation, stage, severity, and patient’s condition.
An abscess on the butt requires timely detection and treatment. Complicated cases of disease on the buttock can lead to disability of the patient.
Antibiotics and other drugs for conservative treatment
The initial stage of maturation of a purulent-inflammatory formation (furuncle, carbuncle) on the buttock is subject to conservative treatment. Pharmacies sell antibiotics aimed at suppressing the proliferation of parasitic microflora inside the body.
To eliminate the causative agent of the abscess, culture from the pathological area is required. It is carried out at the stage of surgical intervention; purulent contents are sent to the laboratory.
The infiltrate is treated with semisynthetic penicillins, macrolides, cephalosporins, and lincosamides. The course of antibacterial therapy lasts from 7 to 14 days, the dose of the drug is selected according to the body weight of an adult or child. Antibiotics for buttock abscess are a mandatory measure to reduce the risk of complications.
Inflammation on the butt is accompanied by severe discomfort; painkillers are used to relieve the unpleasant symptom. Substances are administered intramuscularly or orally; common drugs include Analgin and Ketorolac.
Infection with bacterial flora, which contributes to the development of an abscess, is accompanied by high body temperature. To combat intoxication syndrome, Ibuprofen and Paracetamol are used.
The buttock with a purulent infiltrate may itch. To reduce the patient's suffering, antihistamine products are prescribed: Tavegil, Suprastin, Loratadine, Erius.
Local treatment of an abscess includes the use of home remedies: honey cake, cabbage leaf, Vishnevsky liniment, Levomekol gel. They draw out pus, help restore skin integrity, and remove inflammation of the buttocks.
The treatment tactics for purulent-necrotic formations change as the patient’s condition worsens.
Causes of abscess, localization features and symptoms
The reasons are varied and are caused by exogenous and endogenous factors. Lead to the transition of a boil to an abscess form:
- weak immune system;
- concomitant acute pathology from other organs and systems or exacerbation of a chronic disease;
- hypovitaminosis;
- carbohydrate metabolism disorders - diabetes mellitus;
- violation of personal hygiene rules in combination with increased sweating or the influence of production factors;
- attempts to independently remove the core of an abscess-type boil before the end of its formation;
- incomplete removal of the purulent-necrotic core;
- secondary infection after self-removal or after surgical removal;
- the use of local heat in the first two stages of boil formation;
- accidental damage to an immature abscess, which creates a gateway for the addition of a new infection;
- general exhaustion of the body, stress due to lack of sleep, illness on the legs.
Most often, the cause of an abscess boil is irrational treatment.
The symptoms of the initial manifestations are characteristic of an ordinary boil. With an abscess boil, the patient's condition worsens. Pain, hyperemia, itching, a feeling of fullness increases, and symptoms of intoxication appear. There is an increase in temperature to subfebrile levels, chills, and weakness.
The danger of a boil depends on the location. In terms of complications, an abscess boil on the face poses the greatest danger. A boil on the upper lip, in front of the nose, in the nasolabial triangle can lead to the spread of infection through the veins of the head. It is fraught with the development of cavernous sinus thrombosis or inflammation of the membranes of the brain - meningitis.
Boils in this area occur as a result of frequent trauma to the skin during shaving or the habit of touching the face with unwashed hands or squeezing out pimples.
In the ear area, abscessing large boils have the following features:
- sharp pain radiating to the teeth and neck;
- when localized in the ear canal, the pain intensifies with any movements of the jaw, pulling the auricle back;
- due to the anatomical features of the external auditory canal, the inflammatory process can spread to the parotid salivary gland;
- The parotid lymph nodes become denser, increase in size, and their palpation causes pain.