Men sometimes experience redness and itching of the scrotum.
Many factors contribute to this.
Itching is a symptom of many diseases.
In today's article we will talk about the causes and consequences that can lead to itching under the scrotum.
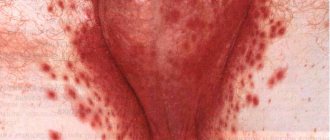
The mechanism for the occurrence of redness is that an abundant supply of blood enters the skin of the scrotum and testicles, as a result of which it turns red.
Blood flow, in addition to the scrotum and testicles, can also flow abundantly into the epididymis and spermatic cords.
In many cases, this is evidence that an inflammatory process has begun.
There are several reasons for the occurrence of such hyperemia.
Their elimination is aimed at destroying pathogenetic factors and reducing the inflammatory process:
- Infectious inflammation as a result of the activity of various pathogenic microorganisms. They can develop throughout the entire structure of the scrotum, testicles, epididymis, seminal canals, as a result of which the body begins a protective reaction to this process and the occurrence of severe itching of the scrotum and the occurrence of hyperemia.
- The causes of inflammation of the scrotum can also be non-infectious.
- Reduced blood flow from the testicles themselves, due to scrolling of the seminiferous ducts, which contain nerve fibers and small blood vessels.
If we talk about the infectious appearance of scrotal hyperemia, it is caused by several groups of bacteria.
They cause both itching of the scrotum itself and its hyperemia.
A nonspecific bacterial infection can be represented by the following pathogenic microorganisms:
- staphylococcus
- Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- streptococci
- even pathogens such as protea can connect
In addition to the fact that they can affect the scrotum itself and its tissues, they can also penetrate the testicles and their appendages.
They can be introduced simply through the bloodstream or through the flow of the lymph itself.
According to many doctors, these pathogens do not have a clear direction in choosing the damaged tissue and its cells.
This indicates promiscuity towards the cells they destroy.
When a man says that his scrotum itches and begins to itch, he is mostly to blame.
He immediately begins to get nervous and remembers what he did, who he slept with or didn’t sleep with.
Basically, the causes of such itching can be ordinary failure to observe personal genital hygiene.
And it’s enough just to take a shower or go to the bathroom and wash well with soap.
After this, the itching of the scrotum can be reduced or completely eliminated if this process is of a non-bacterial type, which affects much worse.
Despite all his shyness, a man should still visit the appropriate doctor.
Namely, a urologist or dermatovenerologist.
The doctor will examine the genitals for hyperemia and inflammation, both the testicles and the scrotum itself.
But many men are embarrassed by such an examination.
Despite the fact that severe itching of the scrotum begins, they remain their ground and endure what is fraught with danger for themselves.
The process can go into a chronic stage and affect much more and worse, affecting the entire body as a whole.
Moreover, any inflammatory processes can negatively affect the reproductive function of men.
Itching of the scrotum: manifestations and mechanism
Itching itself is a specific reaction of the body, which is manifested by an indefinable desire to scratch the area where pathogenic bacteria were involved.
In other words, this is an uncomfortable state that does not feel very pleasant.
Itching can appear not only on the scrotum, but also on almost any part of the body.
If we talk about the mechanism of the appearance of itching itself, then this is a specific innervation of epithelial cells.
Occurs as a result of various environmental influences or to create cell excitation (exogenous and endogenous factors).
The mechanism of itching is to produce an intense effect on the cells of the immune system and blood cells (leukocytes).
In addition to these cells, calcitonin or the main hormone produced in the thyroid gland may also be involved in the manifestation and occurrence of itching.
Itching of the penis also occurs, mainly during an infectious process (for sexually transmitted diseases, syphilis, gonorrhea, HIV infections, etc.).
The patient may notice itching in other areas, for example:
- Itching between the anus and scrotum
- Itching of the scrotum and anus
- Patients may also experience itching and burning in the scrotum itself.
- They notice itching around the scrotum itself
Men who came to see a doctor complain:
- for bloody calluses around or near the scrotum due to frequent and vigorous scratching
- on chafing from clothes that are too tight and not breathable
- for diaper rash
Diagnostics
Most pathologies manifested by itching of the scrotum are under the jurisdiction of a dermatologist. According to indications, patients are referred for consultation to an allergist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist and other specialists. The examination includes the following diagnostic procedures:
- Inspection.
The doctor identifies changes (swelling, hyperemia, rashes) that suggest the nature of the disease and determine a list of other studies. To identify scabies, it may be necessary to apply aniline dyes. - Luminescent diagnostics.
In the zone of fungal infections, a greenish glow is visible under a Wood's lamp. With erythrasma, the shade of the changed areas becomes reddish-brick. The fluorescence of nits in head lice is also visualized in the rays of the lamp. - Lab tests.
If an allergy is suspected, allergy tests are performed, immunoglobulin determinations, and a blood test for eosinophilia are prescribed. Scabies is confirmed by the results of a scraping examination. If mycoses and bacterial lesions are suspected, in doubtful cases, culture is performed on nutrient media.
The presence of pubic lice indicates promiscuity when choosing sexual partners and is an indication for testing for STIs. The examination plan for systemic diseases is drawn up taking into account the characteristics of the pathology, and may include laboratory tests, ultrasound, and MRI. If a mental disorder is suspected, consultation with a psychologist or psychiatrist is required.
Types of scrotal itching
Itching can be divided into several types:
Pruritoceptive - or itching, accompanied by inflammation, damage and dryness of the skin. It is with this type of scrotal itching that patients note severe itching and peeling of the scrotum itself.
Neuropathic – itching specific to various nervous disorders.
Neurogenic - itching is specific to various other types of disorders, but as a rule it is not of a nervous nature.
Psychogenic – itching characteristic of specific mental pathologies and disorders.
Thanks to the division into types, one can talk about pathogenic or non-pathogenic factors of itching.
If we talk about the non-pathogenic factor of itching of the scrotum, then the irritation itself that appears on the scrotum area is of a natural nature due to one or another effect.
For example, chemical, thermal, tactile, physical.
Usually goes away due to the elimination of the above reasons.
This reason is not serious and does not require a visit to a doctor's office.
A man just needs to take appropriate measures.
For example, go to the shower and do the appropriate hygiene procedures.
Stages of the disease
Stage 0 (hidden): lymphatic vessels are damaged, but this is not yet apparent. The transport capacity of the lymphatic system is still sufficient to remove lymph. No lymphedema.
Stage 1 (spontaneously reversible): When pressed with fingertips, a dimple appears on the skin, but it quickly returns to normal. Typically, when you wake up in the morning, the affected area is normal or nearly normal size.
Stage 2 (spontaneously irreversible): The scrotal tissue now has a spongy consistency and no dimple is left when pressing with your fingertips on the affected area. Fibrosis develops (overgrowth of connective tissue and scar formation). This marks the beginning of hardening of the skin and an increase in the size of the scrotum.
Stage 3 (elephantiasis or elephantiasis): At this stage, the swelling is irreversible and the affected area is usually very large. The skin is hard (fibrotic), warty.
Causes leading to severe itching of the scrotum and testicular area
There are many factors influencing such an unpleasant process.
Sometimes it is difficult to stop even with drugs with antihistamine effects.
Allergy
Touching the delicate skin of the genitals with poor-quality fabric of underwear, or contact with shampoo, gel, soap, little-known creams or ointments.
Sometimes behind the beautiful appearance there is hidden the treatment of linen with toxic dyes that contain large amounts of chromium.
If the underwear is made of synthetics, then this can also cause itching when worn for a long time, and leads to diaper rash in the genital area.
Many men note the occurrence of allergic itching due to the use of latex condoms.
Infections
A large number of both beneficial and pathogenic microorganisms constantly live on the surface of a man’s genitals.
If a man constantly follows the rules of personal hygiene, namely, changes his underwear daily and takes a shower, then beneficial and pathogenic microorganisms coexist peacefully.
But if a man does not follow these simple rules, then an inflammatory process may occur on the skin of the scrotum, leading to itching.
Due to damage to the delicate tissues of the skin.
Often the area where the testicles are located (the scrotum) is “attacked” by streptococcal bacteria.
Also, in addition to streptococcus, the scrotum can be “attacked” by mycoplasma and ureaplasma, and some types of fungi.
One of them is the Candida fungus (candidiasis).
It is with infectious dermatitis that a specific rash appears on the skin of the scrotum, somewhat reminiscent of a burn, the so-called urticarial rash.
If you look closely at it, it looks like a nettle burn.
Pediculosis
Despite all the observance of personal intimate hygiene, many men who are promiscuous can pick up a very unpleasant parasite.
These are pubic or body lice.
This parasitic disease is called pediculosis.
You can get infected almost anywhere:
- in public transport, when a large crowd of people is forced to come into contact with each other
- in a public bath, swimming pool, shower, sauna
- when visiting a public toilet
Itching is caused by parasite bites on the delicate skin of the genitals.
But with the bite itself, the patient does not feel pain.
The parasite's saliva contains an anesthetic substance, which it injects immediately after the bite.
Itching at the site of the bite begins only after 5 minutes.
Itching from head lice can be very painful and is accompanied by small bloody calluses after scratching.
Chlamydia
A disease of a sexually transmitted nature provokes severe itching in the area of the scrotum and testicles located in it.
Many men with chlamydia experience immediate itching in the scrotum area.
In fact, the itching is concentrated on the inner surface of the testicles, which indicates a large population of chlamydia parasites.
In addition to itching, the man also complains of pain and burning when urinating.
With timely treatment and taking appropriate medications, itching in the testicular area usually decreases or stops altogether.
Erythrasma
Occurs when the body’s immune properties decrease.
With this progression, the parasites begin to actively multiply and release their pathogenic waste into the human body.
The main characteristic symptom that appears with erythrasma is that the scrotum begins to take on the color of red brick.
Itching can move between the genital area to the anus and perineum.
The itching is not constant; it usually begins in the afternoon and intensifies in the evening.
With erythrasma, this process is specific only when the immune system is reduced, when the body is not able to resist a large number of pathogens.
Athlete's inguinal
The pathology is fungal type, the main causative agent is mycotic fungal spores.
Inguinal athlete's foot can become chronic, causing very serious consequences.
It may occur with periods of both decline and exacerbation.
Men aged 32 to 45 years are most often affected.
In addition to the itching of the testicles or scrotum, patients complain of the appearance of round spots on the genitals, somewhat reminiscent of lichen planus.
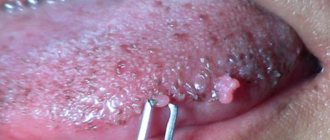
Herpetic genital infection
As you know, herpes is viral in nature.
This type of itching, known as herpetic itching, occurs due to the appearance of herpes on the genitals.
The cause of its appearance is unprotected sexual intercourse with a partner who already has such an infection.
To avoid infection, you must use a condom.
The main symptom of herpes on the genitals is the appearance of small blisters filled with a yellowish-whitish liquid.
Psoriasis
A specific autoimmune reaction of the body.
The pathogenesis of this condition has not been fully studied, and a means to completely cure this disease has not yet been found.
At the first signs of psoriasis in men, the testicles always begin to itch due to the appearance of psoriatic plaques on them.
The scrotum becomes covered with a whitish coating and peels off due to damage to the epithelial tissue.
Prevention
Measures to prevent scrotal peeling:
- Maintain intimate hygiene: wash your genitals twice a day with baby or intimate soap, if necessary, lubricate with moisturizers, use anti-sweat powders.
- Protected sex. A condom will not save you from fungus, so after questionable contact you need to wash your pubis and scrotum with soap.
- Comfortable underwear made from natural materials. Synthetic briefs and tight trousers are a direct path to dermatitis of the scrotal skin.
- Compliance with hygiene rules in the bathhouse, sauna, swimming pool. You cannot use other people's towels, washcloths, sheets, or soap. Do not allow the scrotum to come into contact with surfaces.
If you are prone to allergies, you should not overuse citrus fruits, cocoa, and chocolate.
Treatment for itchy scrotum
If we talk about such a symptom as itching of the scrotum rationally, then it can be reduced or completely eliminated.
For example, to reduce itching, you can wash the scrotum yourself with antiseptic solutions.
Every home has them (hydrogen peroxide, furatsilin tablets or solution, miramistin, chlorhexidine).
After washing, you can use Sinaflan ointment.
It is best to rinse before going to bed.
If we talk about folk methods, then various baths made from infusions of chamomile, oregano, and sweet clover have worked well.
If you nevertheless visit a doctor, then know that he will definitely prescribe hydrocortisone ointment.
This is the most famous and proven remedy for the treatment of itching of the scrotum.
Sometimes the doctor may also prescribe antihistamines to reduce itching and pain in the testicles.
Such drugs as triderm, panthenol, nezulin, gistane very well reduce itching in the scrotum.
Such ointments and tablets made on the basis of menthol cannot be used when the patient has deeply scratched the skin and there are ulcers and bloody cobwebs.
But basically, treatment will be effective only if the diagnosis is correctly determined.
With timely administration of appropriate medications and in order to avoid various complications.
But remember, every drug has side effects.
Therefore, before taking any medications, it is necessary to consult a specialist (urologist, infectious disease specialist).
Symptoms
They are obvious. If the skin on the scrotum peels off, then pieces of it fall off like dandruff. A man can notice them on his underwear and bed.
The skin also becomes red and rough. Often a man experiences unbearable itching. This is bad, because many people can’t stand it and start scratching their scrotum until it bleeds. When the skin heals, it becomes thin and therefore often cracks.
If the peeling is mild and there are no unpleasant sensations, then there is no need to worry - perhaps the skin is simply getting rid of dead epidermal cells.
Neurodermatitis
Another reason why the skin on the scrotum may peel off. Neurodermatitis is a chronic skin disease of a neurogenic-allergic nature that can affect a person at any age. Risk factors are:
- Atopy (unusual reaction to an allergen).
- Heredity.
- Skin hyperactivity.
- Autonomic nervous system disorder.
- Problems associated with the functions of higher nerve regulation centers.
The symptoms are as follows:
- Minor rashes.
- Local burning, tingling, desire to scratch the skin.
- Redness and swelling of the affected area.
- Impregnation of the skin with plasma or blood (infiltration).
- Severe peeling, which is fraught with the appearance of cracks, erosions and crusts.
Diagnosis is performed by a dermatologist, and treatment is prescribed by him. Enterosorbents, laxatives, diuretics, choleretic, vitamins, as well as histaglobulin, an antiallergen for subcutaneous administration, may be prescribed.
Corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, sedatives, antibiotics, antivirals, and mast cell membrane stabilizers are also often prescribed. Exactly what kind of therapy will depend on the individual case.
Fungus
Metabolic disorders, increased sweating, neglect of personal hygiene rules - all this can lead to the appearance of fungus.
It's easy to find out about its availability. In men, the fungus manifests itself as spots that differ in color from normal skin. The following symptoms are also possible:
- Pink spots that appear on the scrotum become yellow over time. Gradually there are more of them.
- Itching and pain occur.
- Peeling covers the entire area and may extend to the groin.
- Over time, the skin cracks.
- The areas become dry, and the protective properties of the dermis are impaired.
- Healthy skin in contact with the affected areas also peels off.
Treatment should be started even if minor rashes are noticed. It takes very little time for them to turn into a large spot that can “grow” right up to the buttocks.