Testicles are male reproductive glands located in the scrotum (lat. Scrotum). Their task is to produce male sex hormones and male gametes. Inside the scrotum, in addition to the testicles, there are blood and lymphatic vessels and nerves.
The scrotum and testicles are located outside the body to keep them at a lower temperature than inside the body. It is very important for fertility and sperm function. After the 28th week of pregnancy, the testicles of a male fetus begin to descend from the abdominal wall into the scrotum.
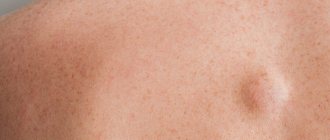
Due to external influences and complex anatomy, a man may develop a lump or nodule in a small area of the testicle. The reason for the formation of a lump on the testicle can be different.
Spermatocele: definition
A spermatocele (seminal cyst) is a cavity filled with a clear or yellowish fluid. Most often, this pathology is detected in boys during the period of growing up and puberty, as well as in men over 40. In both cases, this is due to age-related changes occurring in the body. A congenital cyst may form. This is a minor malformation that can result from pregnancy complications in the mother.
Classification. Types of testicular tumors
Testicular tumors are very diverse in their cellular structure, but 90–95% of them belong to the group of germ cell tumors:
- intratubular neoplasia;
- yolk sac tumor;
- seminoma;
- teratoma;
- trophoblastic tumor (choriocarcinoma);
- embryonal cancer;
- mixed tumors
The remaining 5–10% are benign and malignant Leydig or Sertoli cell tumors, adult and juvenile granulosa cell tumors, theca fibromas and mixed ones.
Giving rise to cancerous invasion - the penetration of cells through the restrictive basement membrane - intratubular neoplasia (TIN) or carcinoma in situ is often found in the surroundings of a testicular tumor, and in 2-5% of patients it is found even in a healthy testicle, so its treatment is very serious. Since four out of 10 germ cell tumors are seminomas, and the rest are all other histological types with the same response to treatment, all testicular germ cell tumors (GCTs) are clinically divided into two groups: seminomas and non-seminomas, which are treated differently.
Treatment methods
In the early stages, doctors use a wait-and-see approach. It is possible that the pathology will disappear over time. This is especially true for congenital seminal cysts. If the ball in the scrotum enlarges, swelling forms on the testicle, pain or severe discomfort appears, then urgent treatment is indicated. Drug therapy or surgical removal of the cyst is possible.
Conservative therapy includes painkillers, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs. Often, the doctor recommends surgical removal of the cyst - this is the most effective method of treatment. In some cases, a microsurgical method is used, that is, scraping tissue from the cyst.
Causes of nodules in the testicles
Lumps in the testicles are a very common symptom due to a number of reasons leading to this condition. Most do not require medical intervention and are not serious illnesses. But there are also certain conditions that require urgent treatment.
On the other hand, in the case of testicular cancer, early detection of symptoms leads to a significantly better prognosis.
Regular self-examination is recommended (at least once every three months).
Causes of nodules on the testicles:
- Injury – blows to the testicles cause edema (swelling) and may contribute to the formation of lumps. If the injury is too severe, more serious problems may arise, so a visit to the doctor is recommended.
- A special type of injury is testicular torsion (testicular rotational injury), which damages the blood and lymph vessels, nerves and vas deferens, leading to the formation of a tumor (requiring medical intervention).
- A hydrocele is an accumulation of fluid in the scrotum and enlargement of the testicles (often does not require medical intervention).
- Varicocele is an enlargement of the veins that drain blood from the testicles. As a result, superficially visible nodules or edema (swelling) are formed. It is not always visible and can only be felt. It is one of the most common causes of testicular tumors, with an estimated one in six men suffering from varicocele. Medical intervention is required in both symptomatic and acute forms.
- Cysts are accumulations of fluid in the testicles that form a growth. Treatment may or may not be required.
- Epididymitis is inflammation of the epididymis. Causes redness, pain, heat, thickening of the epididymis, testicular orchitis - pain and swelling. Antibacterial therapy is prescribed or symptomatic treatment is carried out.
- An inguinal hernia is the passage of abdominal structures through the same passage through which the testicles and related structures passed during the prenatal period. An inguinal hernia can descend into the scrotum and lead to their enlargement. The hernia should only be treated surgically.
- Testicular tumors are the most severe case. It can cause lumps on the testicles. Early detection can provide a better prognosis. Often the lump is felt when swimming or showering. The tumor grows quickly, causing pain, possible bleeding, erythema (redness of the skin), and fever.
Wen: what is it?
A fatty tissue is a neoplasm that consists of adipose and connective tissue, can have different sizes and can be easily felt through the skin. A ball on the skin of the scrotum can be detected during the development of the inflammatory process. Then education becomes painful. When pressed, the fatty tissues roll freely under the skin. These are usually white balls that can reach a size of five to thirty millimeters. If there is no inflammation, then the biggest problem from wen is a cosmetic defect.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of a lump on the scrotum should begin with a trip to the doctor. During the examination, the doctor will feel the scrotum and determine the presence of balls on the man’s testicle, their number, location, shape and size. An experienced doctor will be able to understand by the appearance of the formation what type of tumor the patient has.
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe a number of tests, such as:
- blood test for tumor markers;
- general blood analysis;
- blood chemistry;
- spermogram.
These tests will help find signs of an inflammatory or tumor process, as well as traces of the proliferation of viruses or bacteria.
Next, the doctor will prescribe a number of instrumental studies, such as:
- diaphanoscopy – transillumination method;
- Ultrasound of the scrotum;
- MRI;
- biopsy.
Diaphanoscopy of the testicle
Causes of pathology
A ball on the skin of the scrotum can form due to active secretion of the sebaceous glands and metabolic disorders. Sometimes such neoplasms develop as a result of slag deposits due to pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract or endocrine system. Equally important are various hormonal imbalances or excessive sweating. Fatty skin can occur after injury, mechanical damage to the skin, as a consequence of acne, with a sedentary lifestyle or poor diet.
External manifestation
It is not difficult to notice a wen on the scrotum. Such neoplasms are easily palpable and diagnosed during a standard examination. A characteristic sign of the accumulation of sebaceous gland secretions under the skin is the appearance of a wen, resembling a small pea that easily rolls under the skin. Wen are rarely painful, but if an inflammatory or purulent process occurs, they begin to cause discomfort. Sometimes discomfort can occur due to friction with clothing or as a result of injury.
If a ball is found in the scrotum, you should consult a specialist to determine that the neoplasm is truly a safe wen. Alarming symptoms are pain, rapid increase in the size of the formation, sudden disturbances in the genital area or difficulty urinating, discomfort when walking due to friction with clothing. Any of these signs should alert a man.
Tumors of the scrotum
Neoplasms of epidermal origin are more often diagnosed. Less common are liposarcoma, neurofibrosarcoma, liyomyosarcoma and rhabdomyosarcoma of the scrotum. Scrotal cancer can be squamous cell or basal cell. Squamous cell tumors of the scrotum are more common, usually developing against the background of long-term ulcers and fistulas. With prolonged professional contact with tar, soot, fuel oil and some other carcinogenic substances, they can occur on intact skin. It has been established that scrotal tumors are more often diagnosed 10-15 years after contact with a carcinogen. The average age of patients is 40-60 years.
In the early stages, squamous cell carcinoma of the scrotum appears as a firm, painless nodule. Subsequently, ulceration and infiltration of surrounding tissues are observed. A tumor of the scrotum quickly metastasizes to the inguinal-femoral lymph nodes. Due to the scant clinical symptoms, patients often first consult a doctor only after the appearance of ulcers or the development of pain caused by the spread of the process to nearby anatomical formations.
Basal cell tumors of the scrotum are diagnosed very rarely; only about 30 cases of this cancer are described in the literature. The causes of development and risk factors have not been established. Scrotal tumors grow slowly and have a low tendency to metastasize. The diagnosis of squamous cell and basal cell cancer of the scrotum is made on the basis of anamnesis, external examination data, results of ultrasound of the scrotum, ultrasound of the penis, ultrasound of the prostate, MRI of the prostate and other studies.
The purpose of these studies is to determine the size and extent of the scrotal tumor, assess the involvement of regional lymph nodes and nearby organs, as well as differential diagnosis of primary and secondary malignant lesions of the scrotum. The final diagnosis is made after an aspiration biopsy or surgical removal of a scrotal tumor followed by histological examination.
Treatment tactics are determined depending on the extent of the cancer process. For local nodes, excision of the scrotal tumor is performed with 2-3 cm of healthy tissue along the periphery and the underlying fleshy layer. For large defects, plastic surgery is performed. If there are metastases in regional lymph nodes, lymphadenectomy is performed. Indications for prophylactic removal of lymph nodes have not yet been determined due to the small number of cases of malignant tumors of the scrotum.
Most oncologists, in the absence of obvious signs of metastasis of a scrotal tumor, perform an open or aspiration biopsy of the lymph nodes, followed by histological examination, and remove the lymph nodes only if malignant cells are detected in the resulting material. The prognosis is determined by the type and stage of the scrotal tumor. The five-year survival rate for local processes is 75%, for damage to lymph nodes and nearby organs – 8%.
Treatment of wen
You can get rid of the tumor surgically. Today, this is the most effective treatment method that helps quickly eliminate cosmetic defects. The doctor may suggest several methods of performing the operation: traditional excision or liposuction.
Liposuction involves preliminary suction of the contents of the wen with a special instrument. The use of this method does not guarantee that over time a new formation will not appear in the same place. During liposuction, only the fat filling is removed, while the capsule itself remains. Practice shows that after such a procedure the relapse rate is very high.
Traditional surgical removal of the wen involves removing both the contents and the capsule completely. The procedure is painful and is therefore performed under local anesthesia. Today, this is the most effective technique that helps get rid of wen without relapse. After the operation, the contents of the formation are necessarily sent for histology to exclude malignancy.
Prices for treatment at Euroonco
- Consultation with an oncologist— RUB 5,100.
- Consultation with a chemotherapist— RUB 6,900.
- Consultation with a urologist, doctor of medical sciences/professor - 10,500 rubles.
- Immunotherapy (without the cost of medications) - RUB 19,000.
- Intrathecal chemotherapy - RUB 26,600.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Make an appointment with an oncologist
Traditional methods
In some cases, the formation of a wen is associated with the formation of atypical fat cells. In this case, treatment can be carried out using traditional methods, and surgical intervention is usually not required. Before starting treatment at home, consultation with a specialist is mandatory.
You can remove the wen using a fresh Kalanchoe leaf. You need to cut the plant and apply it to the damaged area, securing it with a bandage. The bandage needs to be changed approximately once a day. The course of treatment is usually not too long. It takes about one to two weeks for the fat to disappear on its own.
You can use coltsfoot dressings for ten days. The sheet should be applied to the sore spot and changed as needed. Lamb fat is quite effective. A tablespoon of the product is melted in a water bath and then cooled to room temperature. Then a small amount of fat is applied to the wen area and massaged a little. After just a couple of procedures, you can notice that the tumor becomes smaller.
Judging by the reviews, cosmetic red clay, which is mixed with sour milk and salt to enhance the effect, helps a lot. The mixture is applied to the wen, after which you need to protect the damaged area with a piece of polyethylene. The procedures must be repeated until the wen completely disappears.
You can take burdock root internally. First you need to pass the plant through a meat grinder (500 g is enough) to get a paste. Next, the slurry is poured with 700 ml of vodka, and then left to infuse for about a month. When the infusion is ready, you need to take one tablespoon twice a day.
Prognosis for testicular cancer
First of all, the prognosis depends on how far the cancer has spread in the body. All malignant testicular tumors are conventionally divided into three types:
- Localized - within the testicle.
- Regional - have managed to grow into neighboring organs and spread to nearby lymph nodes.
- Common - in the presence of distant metastases.
The main prognostic indicator is five-year survival rate - the percentage of patients alive within five years from the date of diagnosis of the disease. For different stages of testicular cancer, the five-year survival rate is:
- For localized ones - 99%.
- For regional ones - 96%.
- With common ones - 73%.
In addition to stage, other factors are also important, such as the type of tumor and levels of tumor markers in the blood after testicular removal.
Other causes of balls
If a ball appears in the scrotum, this may indicate not only a benign neoplasm. The causes may be various pathologies, for example, oncology, dropsy, hernia, inflammation of the lymphatic ducts, varicocele, hematocele. A red or white subcutaneous ball, single or multiple boils, and lumps can be caused by sexually transmitted diseases, allergic reactions or infections. In some cases, the reason for the appearance of white balls on the scrotum is a banal failure to comply with the rules of personal hygiene.
With sexually transmitted diseases, neoplasms on the genitals resemble a rash or pimples with watery contents, small purulent ulcers, and cone-like growths. Most likely, these are signs of syphilis, herpes or HPV. Multiple red pimples may appear due to the activation of a fungal infection. This pathology is accompanied by discomfort when urinating and a strong burning sensation in the perineum.
A ball in the scrotum can appear when wearing synthetic underwear, using harsh detergents or due to the use of latex condoms. In this case, the appearance of red blisters or pimples that are very itchy and flaky is typical. These are symptoms of contact allergies, which can be eliminated by eliminating allergens from everyday life.
White balls on the scrotum may indicate cancer. The tumor can be benign or malignant. The pathological process is accompanied by heaviness and swelling in the damaged area, severe pain.