Dark spots on the skin
Flawless, smooth skin is an almost unattainable ideal for a modern person, since almost everyone has small scars, moles, and spots of various colors. In general, spots are areas that differ in color (lighter or darker) from the surrounding skin. They are usually smooth to the touch, but in some cases there may be a slight protrusion or roughness. Most spots, although they can cause psychological discomfort, are not usually considered pathological. But some types of spots (both pink spots, white spots on the skin, and dark and even black spots on the skin) can be manifestations of diseases, signs of infection, an allergic reaction and other problems in the body, so if they are detected, it is best to consult a doctor - dermatologist. Only in this case will the treatment be adequate, safe and give the best effect. The doctor will correctly determine the causes of spots on the skin, and if the diagnosis is not clear, he will prescribe the necessary tests. In this section, we will look at the possible causes of dark spots on the skin.
Dark spots on the skin can be:
- Moles are collections of melanocytes (pigment cells) in the skin. They can be congenital (present from the moment of birth or appear in the first years of life), but more often they appear on the skin in adolescence, and then throughout life - acquired moles . Moles on each person’s body are completely individual, their size is quite different, as well as their color range - they can range from yellow to dark brown and even black. The structure of moles is also individual for each, they can be flat or convex, the surface of some is absolutely smooth, others are rough and covered with hairs. The size of moles can also vary - from one millimeter to several centimeters (such large moles are usually called birthmarks). Read more in the Moles section.
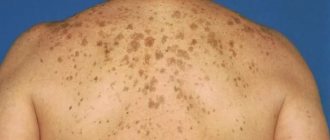
- Chloasma (melasma) are brownish-brown, dark spots on the skin, which generally have an uneven shape of varying sizes, with sharp boundaries and a smooth surface. They most often occur in women during pregnancy, and usually disappear after pregnancy. In most cases, such age spots form on the face, but they can also appear on the inner surfaces of the thighs and abdomen. But it is not uncommon for such age spots to occur in non-pregnant women, and even in men. Chloasma can also be caused by some gynecological diseases, liver diseases, the use of oral contraceptives, as well as prolonged exposure to the sun. Often, when the cause is eliminated, chloasma disappears. Read more in the Age spots section.
- Lentigines are dense pigment spots of brown or black-brown color, which most often rise slightly above the skin level. They have a shape with sharp outlines (most often it is round or elongated), and sizes can range from small dots to 2 centimeters in diameter. They can be either single or multiple, on any area of the skin. There may be senile lentigo (in older people, especially on exposed skin) and juvenile lentigo (usually genetic, in children under 10 years of age). Read more in the Age spots section.
Registration for consultation
- Melanoma is a malignant skin tumor that develops from melanocytes. Typically, skin melanoma looks like a pigment spot, sometimes in the form of a nodule. The color of the formation is usually brown, dark brown or black. According to statistics, melanoma makes up almost 1% of the total number of cancers, is much less common than basal cell or squamous cell carcinoma, but is a much more serious disease, since it is the most aggressive of all malignant tumors. Another characteristic feature of melanoma is that while older people suffer from skin cancer, young people can also suffer from melanoma. Melanoma is characterized by rapid and early metastasis. Melanoma quickly grows through several layers of skin, destroying it, and spreads through the lymphatic and blood vessels to other organs (lungs, brain, liver). New foci of melanoma appear there - metastases. The result of disruption of the activity of organs and tissues affected by the tumor can be fatal. Melanoma can occur at any age, starting in adolescence. Read more in the Melanoma section.
- Seborrheic keratoses, or senile warts , are brown or black raised lesions that appear anywhere on the skin. Their surface is loose, and the base is relatively small - it looks as if the wart is stuck to the skin. In the early stages of development, a wart can be confused with a mole, but over time it noticeably changes its color and size. The number of warts also increases with age. The causes of seborrheic keratosis are currently not well understood. The results of some scientific studies show that the development of this disease may be closely related to a person’s age and the effect of sunlight on his skin. From a medical point of view, seborrheic warts are absolutely harmless; they are benign skin tumors that can be removed for aesthetic reasons. But a consultation with a dermatologist is required, since in some cases, even experienced dermatologists cannot distinguish foci of seborrheic keratosis with the naked eye from other diseases (including dangerous tumors) and make a final diagnosis only after histological analysis.
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation is a common phenomenon that results in the formation of dark spots on the skin at the site of injury or inflammatory skin disease. It can develop as a result of any injury or inflammatory reaction of the skin. A dark spot on the skin may appear at the site of a scratch, burn, crack, or even an ordinary pimple. Sometimes pigmented spots are the result of traumatic cosmetic procedures - for example, laser skin resurfacing, chemical or mechanical peeling, dembrasion. The appearance of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation after cosmetic procedures can be explained by an individual skin reaction, non-compliance with recommendations (for example, if the patient does not avoid exposure to sunlight on the skin, does not use sunscreen, etc.), as well as an incorrectly performed procedure. Often the cause of the appearance of spots is various inflammatory skin diseases - acne, dermatitis, lichen, etc. Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation is manifested by the formation of dark spots on the skin in areas of inflammation or skin damage. The resulting dark spots on the body can last for several weeks, but in some patients - for years, and dark spots on the body can remain forever. In most cases, the degree of pigmentation weakens over time, and after a few months the spot disappears.
If black spots appear on the body or only one dark spot on the skin, also if another unusual spot or a combination of them appears, as well as if the old spot has visually changed, you need to contact a dermatologist to determine the cause of the incident and, if necessary, get timely treatment.
Ochronosis
Changes in skin color also occur in the case of so-called ochronosis. This disease is quite rare and is a specific lesion of cartilage, ligaments and tendons, expressed in slowly increasing immobility of the spine with deforming arthritis, otosclerosis, and damage to the cartilage of the larynx. The fabrics are painted in dark colors - ash-gray, brown or almost black. Such changes are also observed on the eyelids. In mild forms of ochronosis, the condition is limited to skin hyperpigmentation and the disease ends in recovery. In severe cases, a change in the color of the skin of the eyelids is accompanied by a spotty dark color of the mucous membrane of the eyes in the area of the palpebral fissure along the limbus. The disease is accompanied by alkaptonuria. The color of the skin during ochronosis is due to the deposition of ochronotic pigment in it. Ochronosis of an exogenous nature can also occur with phenol poisoning or long-term use of carbolic acid for medicinal purposes. The course is chronic.
Treatment: shock doses of vitamin C, measures aimed at reducing alcantonuria.
Hemochromatosis
This disease is accompanied by bronze coloration of the skin (one of the early symptoms), further development of liver cirrhosis, as well as bronze diabetes mellitus. Skin pigmentation is caused by the deposition of hematogenous pigment - hemosiderin, which is formed due to a violation of iron metabolism, with its accumulation in organs and tissues. Bronze coloration is predominantly localized on the neck and back of the hands. The eyelids turn gray-brown. Hemochromatosis is extremely rare and occurs exclusively in men aged 45-50 years. There are no more than 150 thousand patients in the world.
Treatment: diet including foods with limited iron content, drugs that remove iron from the body, repeated bloodletting in permissibly large doses.
Dyschromia
This change in skin color, including the skin of the eyelids, can occur with prolonged use of heavy metal salts for medicinal purposes, or with prolonged contact with them in the professional sphere. This kind of hyperpigmentation should be classified as excessive pigmentation of an exogenous order. Among the many varieties of this hyperpigmentation, cases of argyrosis and arsenomelanosis are especially common. With arsenomelanosis, the skin of the eyelids becomes covered with widespread and limited dark brown spots, hyperkeratosis occurs, and scales form. In some cases, the immediate cause of arsenomelanosis was long-term use of salvarsan and Fowler's tincture. The appearance of spots with arsenomelanosis is caused by the deposition of melanin.
Argyrosis is characterized by the appearance of a matte or gray-bluish color of the skin due to impregnation with silver salts, silver hydrochloride salt, in particular. On the eyelids, such impregnation occurs as a result of instillation of the drug into the conjunctival cavity or its introduction into the lacrimal sac. With argyrosis, silver particles are found in the papillary dermal layer, in the walls of the sweat and sebaceous glands, and in the hair follicles. Treatment: potassium iodide is prescribed orally.
The use of picric acid preparations can also lead to dyschromia - the appearance of a light yellow color of the skin of the eyelids. Finally, pigmentation of the skin of the eyelids of an exogenous nature can be caused by the so-called toxic melasma, the former name of which is Riehl melanosis, B-vitaminosis dermatosis. This dyschromia is based on intoxication with heavy hydrocarbons from coal and oil. Often their derivatives are added to cosmetics (vaseline, bergamot oil, etc.). In conditions of hypersensitivity of the body and with intense solar radiation, their use leads to the occurrence of erythema or follicular keratosis (atrophy with telangiectasia). The clinical picture reveals dark melanotic dotted or reticular pigmentation on the skin.
The phenomena of toxomelanoderma are also possible in some individuals when exposed to chlorine and bromine.
By contacting the Moscow Eye Clinic, each patient can be sure that some of the best Russian specialists will be responsible for the results of treatment. The high reputation of the clinic and thousands of grateful patients will certainly add to your confidence in the right choice. The most modern equipment for the diagnosis and treatment of eye diseases and an individual approach to the problems of each patient are a guarantee of high treatment results at the Moscow Eye Clinic. We provide diagnostics and treatment for children over 4 years of age and adults.