Types of psoriasis vary in severity, distribution and shape of the spots. The most common are vulgar (ordinary), guttate and seborrheic psoriasis. They can be cured if the disease is not started. More severe forms - pustular, erythrodermic psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis can lead to disability and death.
the following phenomena may or may not occur :
- stearin stain - when scraped, the scales peel off and look like a drop of ground stearin;
- terminal film - after complete removal of the scales, a thin, damp coating appears on top of the spots;
- pinpoint bleeding - after removing the film, drops of blood appear on the surface of the spots, which do not merge with each other.
The phenomenon is used to diagnose psoriasis and is called the psoriatic triad .
Ordinary (vulgar) psoriasis
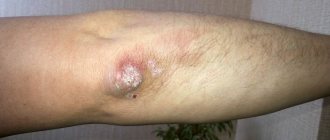
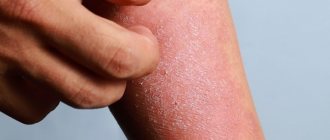
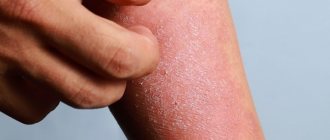
Vulgar psoriasis is the most common form, occurring in 80-90% of all patients with psoriasis. It begins with red spots that are raised above the surface of the skin. Then the spots grow and become covered with silvery, dry scales.
Manifestations
- papules are red-pink in color with clear boundaries, merge and form plaques with a silvery-white coating;
- itching;
- pronounced psoriatic triad.
Common sites of injury
- under the hair;
- on the bends of the elbows and knees;
- small of the back;
- sacrum.
Photo
Ordinary (vulgar) psoriasis
Initial stage of vulgar psoriasis
Ordinary (vulgar) psoriasis on the elbows
External treatment
Particular attention in the treatment of psoriasis is paid to the choice of external medications, since among patients there are predominantly people with mild and moderately severe disease, which are characterized mainly by skin manifestations.
These products are designed to cope with skin symptoms:
- reduce and eliminate itching;
- relieve inflammation;
- reduce the volume of lesions;
- promote regression of plaques;
- reduce skin peeling;
- moisturize dry areas.
Seborrheic psoriasis
Seborrheic psoriasis, due to its external manifestations, can easily be confused with dandruff (hence the name). It also begins with red spots, localized mainly under the hair.
Manifestations
- papules with yellowish scales;
- peeling and itching, especially pronounced on the scalp;
- rashes can move from the head to the forehead (“psoriatic crown”).
Common sites of injury
- scalp;
- forehead;
- chest and interscapular area;
- nasolabial folds and places behind the ears.
Photo
Seborrheic psoriasis under hair
“Psoriatic crown” with seborrheic psoriasis
Seborrheic psoriasis on the scalp
Guttate psoriasis
Guttate psoriasis often develops for the first time after streptococcal infections. Small spots spread over the entire body.
Manifestations
- dry papules of red, lilac, purple color, drop-shaped;
- slight peeling.
Common sites of injury
- usually spread over a large area of skin - often on the thighs;
- shins;
- forearms and shoulders;
- scalp;
- back and neck.
Photo
Guttate psoriasis on the thighs
Guttate psoriasis on the lower leg
Guttate psoriasis on the back
Pustular psoriasis
Pustular psoriasis is the most severe form of psoriasis. https://kinkyads.nz. Papules can spread to the entire body or to specific areas (such as the palms and soles).
Manifestations
- rashes in the form of pustular elements (pustules), which are filled with clear liquid. The skin above and below them is red, inflamed, thickened and comes off easily;
- fever, general malaise and joint damage.
Common sites of injury
- large areas of skin, including the oral mucosa;
- sometimes only the palms and soles of the feet are affected;
- shins and forearms.
Photo
Pustular psoriasis on the foot
Pustular psoriasis on the neck
Pustular psoriasis on the arm
General treatment regimen
Typically, patients with this pathology are prescribed the following treatments for psoriasis:
- Glucocorticosteroids - they give a good effect, help stop exacerbations, but have many contraindications. If used incorrectly, a decrease in the effectiveness of the drug, atrophy of the skin, and so-called “withdrawal dermatitis” may occur.
- Vitamin D3 analogues - such drugs are used to control psoriasis in the subsiding phase of exacerbation, however, they cannot be used for extensive lesions of the skin, they are contraindicated in children under 18 years of age and elderly people over 65 years of age, and they are not recommended for use in patients with calcium metabolism disorders .
- Products with salicylic acid provide exfoliating and anti-inflammatory effects; they are recommended for use in the stationary stage of the disease and for severe peeling. Particularly impressive treatment results can be obtained when combining salicylic acid and corticosteroids.
- Birch tar - despite the abundance of contraindications and side effects, drugs containing this substance are still prescribed to patients with psoriasis. Therefore, they must be used with caution, as coal tar can cause skin irritation.
- Products for the treatment of psoriasis containing activated zinc pyrithione. They are included in modern clinical recommendations for the treatment of psoriasis and are prescribed to accelerate the regression of rashes. Activated zinc pyrithione Skin-cap helps reduce inflammation and excess peeling and can be used on any area of the skin without restrictions.
As a rule, experts recommend course use of several drugs at once. This approach helps to achieve a pronounced effect and keep the disease under control. One of the common treatment regimens for limited forms of psoriasis is the prescription of an ointment or cream based on a glucocorticosteroid to relieve the severity of the process, and the second step is to prescribe the drug Skin-cap for further elimination of lesions and self-administration “as needed.”
Psoriatic arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis can be considered both a type of psoriasis and arthritis. There are 5 types of the disease, we will look at the common features.
Manifestations
- the skin becomes red, bluish, purple;
- joint damage, up to deformation;
- swelling of fingers and toes.
Common sites of injury
- small finger joints;
- knee and hip joints;
- joints on the shoulders and shoulder blades;
- vertebrae
Photo
Hand deformity due to psoriatic arthritis
Leg deformity due to psoriatic arthritis
Prevention
Considering your form of psoriasis and its type, you need to avoid anything that can cause complications.
If a patient suffers from psoriasis, he needs to follow a diet. All simple carbohydrates should be excluded from the diet. It is also better to avoid spicy and salty foods. To reduce the likelihood of exacerbations, you should not drink alcoholic beverages or coffee.
Proper nutrition will not completely cure the patient, but will reduce the likelihood of exacerbations and relapses. As a rule, nutrition is adjusted by the attending physician, taking into account the medical studies performed and the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. It is very important to organize the correct drinking regime and drink at least two liters of clean water per day.
In addition to alcohol and coffee, patients with psoriatic skin rashes should avoid smoked foods, canned fish, sweet carbonated drinks, and products with artificial additives and dyes.
One of the most dangerous products is herbs and spices, which contain aromatic substances and essential oils. They can lead to worsening of the skin condition and increase the symptoms of psoriasis.
All patients need to carefully care for both healthy and affected skin. It is better to avoid hot baths. It is not recommended to irritate the skin or use a hard washcloth. If the skin is itchy, do not scratch it. To relieve symptoms, it is better to use creams and ointments.
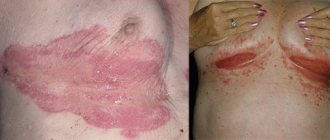
Erythrodermic psoriasis
Erythrodermic psoriasis (psoriatic erythroderma) is one of the severe forms of the disease, leading to disability and death. It often develops from vulgar psoriasis, especially with abrupt discontinuation of therapy and an unstable course of the disease. This form also appears as a result of alcohol abuse, severe stress, and a severe cold.
Manifestations
- inflammation spreads to 90% of the skin or more;
- the skin becomes bright red, hot to the touch, swollen;
- large and small dry white scales that are easily separated;
- itching, burning, tight skin, painful sensations;
- weakness, loss of appetite, increased sweating;
- elevated body temperature - 38-39°;
- lymph nodes enlarge;
- hair and nails fall out.
Common sites of injury
- the entire surface of the body.
Photo
Erythrodermic psoriasis on the body
Erythrodermic psoriasis
Risk factors that provoke the development of the disease
In the medical environment, there are usually several characteristic factors that can trigger the process. Moreover, the risk of developing the disease increases if there is a combination of several provoking factors. These include:
- Genetic predisposition. Scientists put forward the theory that the carriers of the disease are certain types of genes that affect the functioning of the immune system and immune cells of T-lymphocytes. For this reason, parents who suffer from psoriasis are highly likely to have a child who will also be susceptible to this disease.
- Dry, thin skin. Numerous studies have established a connection between skin characteristics and the risk of developing psoriasis. It turned out that people with thin and dry skin are more likely to suffer from this disease. The reason, as researchers believe, lies in the insufficient production of sebum, which acts as a natural moisturizer for the surface of the body, as well as in the structural features of epidermal cells.
- Impact of the external environment. A significant role in the increase in the number of people suffering from this disease can be played by the use of various cosmetic products and household chemicals, which often contain alcohols, solvents, surfactants and other aggressive components. These substances disrupt the natural functions of the skin, can cause irritation and lead to exacerbation of psoriasis.
- Excessive body hygiene. Pathological obsession with cleanliness also plays a cruel joke on people. The more active, intense and frequent you cleanse your skin, the more damage you can cause to it. Due to frequent use of soap when taking a bath or shower, the protective lipid layer of the skin is destroyed, this leads to the formation of microdamages on the surface, which can subsequently provoke an exacerbation or worsening of psoriasis.
- Unhealthy Lifestyle. Alcohol, smoking, constant stress, poor-quality and unbalanced nutrition, lack of normal rest and sleep - all this inevitably affects human health. It has been noted that certain foods, such as tomatoes and eggplants, as well as alcohol and smoking can worsen psoriasis.
- Immunodeficiencies. Decreased immunity, especially in HIV-positive patients, provokes skin problems and leads to exacerbation of psoriasis symptoms.
- Drug therapy. Taking certain medications can trigger the development of the disease. Beta-blockers, antidepressants, as well as drugs against malaria and seizures should be used with particular caution.
- Concomitant infections. In medical practice, many cases have been described in which signs of psoriasis develop in patients after skin damage by a fungus or as a result of a streptococcal infection.
- Changes in usual living conditions. Climate change, changes in time zones, and seasons have a negative impact on the general well-being of people. During periods of change in living conditions and environment, the body weakens, which opens the way for the development of various diseases.
- Impact of stress. Emotional and nervous tension, physical activity, disruption of work and rest schedules are some of the factors that provoke the appearance of the first symptoms of psoriasis.
- Injury to the skin. Prolonged scratching, friction, and pressure on the skin can cause microdamages and injuries. In certain situations, they can transform into characteristic psoriatic plaques.
Conclusion
Types of psoriasis vary in severity, size and distribution of patches. We looked at 6 main ones:
- psoriasis vulgaris is the most common form, in which the spots are more of a cosmetic defect. But, if left untreated, it can develop into other types;
- seborrheic psoriasis appears in areas of dandruff (hence the name) and resembles this disease in external manifestations;
- guttate psoriasis is small teardrop-shaped spots that spread throughout the body;
- pustular psoriasis is the most severe type of psoriasis, in which the papules are covered with blisters containing clear liquid;
- psoriatic arthritis is a disease that is accompanied by joint deformation. Severe form, leads to disability and death;
- erythrodermic psoriasis is a severe form of psoriasis, patches cover more than 90% of the body, and can be fatal.
The type of psoriasis determines its treatment. It is important to recognize the disease in time and make the correct diagnosis. Therefore, if you suspect psoriasis, immediately consult a dermatologist.
Recommendations for eliminating symptoms of the disease
Effective treatment of psoriasis is only possible with an integrated approach. It is important to take maximum precautions to reduce the risk of exacerbation of the disease. So, it is recommended:
- avoid injury to the skin;
- avoid hypothermia;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- avoid stressful situations;
- promptly treat infections and concomitant diseases;
- Avoid prolonged exposure to direct sunlight.
Patients with psoriasis need to be especially careful in observing personal hygiene requirements. If you take a shower or bath, then:
- use products without dyes and fragrances;
- choose a mild shampoo;
- avoid using rough sponges, creams, gels with abrasive particles;
- Avoid hard soap, as it dries the skin too much;
- adjust the water temperature to keep it warm;
- stay in the water for no longer than 10-15 minutes;
- use a soft towel, do not rub or scratch the skin.
After a shower and bath, it is recommended to use special body moisturizers. Try to comb your hair as little as possible so as not to irritate the surface of your scalp. The same applies to blow drying. If you cannot do without it, then choose a warm or cold stream.
Choose clothes that are light, made from natural fabrics, and have a loose fit so that they do not restrict movement and do not chafe.
In summer, you should not sunbathe for too long. To protect your skin from UV rays, apply sunscreen with a high SPF factor.
The best remedies for Psoriasis
Add to cart
Antipsoriasis cream 990 rub.
Add to cart
Magnipsor ointment RUB 1,490
Add to cart
Ultraviolet lamp Dermalight ® RUB 14,900.