Causes of red moles
The exact reason why red moles appear on the body is unknown; it may be a predisposition due to a genetic factor. But there are other reasons:
- pregnancy;
- exposure to chemicals;
- some diseases, including infectious ones;
- unsuitable climate (too hot or cold)
- mechanical damage to the skin, such as a bite or cuts, in which pieces of skin are not completely torn off.
Their manifestations are also possible at a more mature age, this is due to a gradual decrease in immunity. Neoplasms occur in 75% of the population over the age of 60 years.
It is impossible to somehow influence the appearance or non-appearance of red moles on the body, since they are inherent in us at the genetic level; if one of the parents had a lot of them, it means that the children will have a similar situation, and even identical maps of the location of nevi are possible.
Why do hemangiomas appear?
The exact causes of hemangiomas have not yet been identified; It is generally accepted that their appearance can provoke disruption of intrauterine development of the fetus due to a viral illness of the mother or oxygen starvation. Additional risk factors for the formation of congenital hemangioma:
- multiple and/or late pregnancy;
- increased amount of estrogen in the mother;
- her sedentary lifestyle;
- unbalanced diet;
- alcohol or nicotine intoxication of the fetus;
- his low birth weight.
In adults, the cause of neoplasm can be a hereditary predisposition, diseases of the cardiovascular system, excessive ultraviolet radiation, and increased levels of the female hormones estrogen.
Locations
An increase in the growth of moles is observed in people aged 0 to 20 years, and then from 45 years and older. The rest of the time they appear, but not as actively as in the first and last phases of life. Typically, red moles appear on the upper body, arms, legs and shoulders. Their favorite places are also the head, feet, and hands. They can be located throughout the body, and it is impossible to predict their subsequent locations. Their red color comes from the accumulation of small blood vessels at the base, which supply them with blood.
Stages of skin melanoma
There are four stages of melanoma development - 0, I, II, III, IV, of which I, II and III have substages A, B, C. The designations T is also used - the prevalence of the primary tumor, N - the absence, presence and prevalence of metastases in regional lymph nodes, M – absence or presence of metastasis to distant organs.
Staging is based on tumor size, thickness, rate of cell division, frequency and intensity of ulceration, and the absence or presence of metastases to lymph nodes and organs.
| Stage | Characteristic |
| 0 | Melanoma is only on the surface of the skin (in situ). Does not spread into underlying tissues. The lymph nodes are not affected, there are no distant metastases. |
| I (A, B) | At an early stage, the thickness of the tumor is up to 1 mm. There is no bleeding, ulcers or peeling. Low rate of cell division. There is no metastasis to lymph nodes and organs. |
| II (A, B, C) | Melanoma grows deep, its thickness is up to 2-4 mm. The surface of the tumor is hypertrophied, peels, ulcerated, and may bleed. There are no metastases in lymph nodes or distant organs. |
| III (A, B, C) | Melanoma of any thickness with growth deep into the tissue, with or without ulceration. Regional lymph nodes are affected and may be enlarged. There are no metastases in the organs. |
| IV | The tumor affects organs (brain, lungs, liver), distant areas of the skin and lymph nodes. |
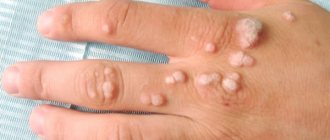
Types and classification
Moles have two main types:
- Pigmented. These include flat, often brown, nevi.
- Vascular, which are formed from changes in the structure of blood vessels.
They are also:
- Congenital - divided by size: small, medium and large.
- Acquired, divided into three types depending on the location of melanocytes in the layers of the epidermis.
- Hanging ones, they are also called papillomas.
There are invisible nevi that appear changing color over time. Also wandering, which change their location, appearing in one place or another. It is advisable to keep track of the location of your moles.
Folk recipes
If you do not like to use pharmaceutical drugs, but need to relieve redness, you can use traditional medicine recipes. By using them, you will be confident in the naturalness of the ingredients, and the cost will be significantly lower. You should use any of these recipes only after consulting with your doctor:
- Twice a day it is necessary to lubricate the red nevus with potassium permanganate until the problem is completely eliminated.
- A cucumber compress can help; for this you need to grate a small amount of the vegetable, wrap the resulting pulp in gauze and apply it to the tumor for 15-20 minutes.
- Fresh or sauerkraut applied to inflammation for 20 minutes can quickly get rid of the problem; the compress must be applied at least twice.
- If you boil juice from sour pomegranate and mix it in equal proportions with natural liquid honey, you will get another remedy for daily rubbing. The juice should be boiled for half an hour over low heat, and the redness should be lubricated with it several times a day.
- Grated raw or boiled potatoes can also help relieve redness and inflammation if applied as a compress for 20 minutes.
Are red moles dangerous?
Signs to pay attention to if small red moles appear:
- Color. If it is uneven and begins to change, this is a reason to visit a doctor.
- Inflammation around the formation, that is, redness in the form of a halo around the mole.
- An increase in the size of the mole or its thickening.
- The appearance of cracks and ulcers on the body of the mole.
- Hair loss if it grew from a mole.
- The appearance of itching, burning or tingling in the place where the mole is located.
- A change in the edges of the nevus also indicates that it is time to visit a specialist.
An accurate diagnosis can be made by a dermatologist or oncologist, and you can and should turn to them for help. Nevi are not dangerous as long as they are in a stable condition, in which case you can wait to see a doctor.
Halo around a mole and the reasons for its color change
The skin surrounding an ordinary nevus has a normal calm color. Such an element is melanoma-free and rarely becomes malignant. But not all pigmented nevi and birthmarks have a halo of healthy skin color. Sometimes a change in skin color occurs around the growths.
If a white, hyperemic, brown border appears around a mole, this is considered a reason to contact an oncologist. Such a sign may indicate that the element has begun to degenerate. To reduce the risk of developing melanoma, the changed formation is removed.
The color of the spot around the mole can be completely different, because the reason that caused it is also ambiguous.
Possible color options for the skin around the nevus:
- White spot around the mole.
- Red halo.
- Blue skin.
- Dark brown or black around the circumference.
Red moles in children
For most people, the bulk of moles appear in the first 20 years of life, then the formation of moles (nevi) subsides. They also tend to sometimes disappear on their own, and this happens due to the fact that the blood vessels supplying the mole dry out or become clogged. One in 100 newborns are already born with small red moles on their body, and they are considered more prone to change and develop into melanoma. This red neoplasm that rises slightly above the surface of the skin is called a Spitz nevus.
Children can also be born with large blue spots on their backs; they are called Mongolian spots and are most often found in children with Asian roots. Any moles are often injured, especially in childhood. This can cause complications, so it is advisable to sometimes see a doctor, and also try to protect children from such injuries.
Types of hemangiomas
There are 2 types of hemangiomas - congenital - formed during intrauterine development - and acquired; acquired in early childhood are often called infantile. By structure, single and multiple hemangiomas (hemangiomatosis) are distinguished; by structure - capillary, arterial and venous.
By education they are local and segmental. Local hemangiomas grow from one point, are distinguished by smooth edges and relatively small sizes. Segmental - large, with a “ragged” edge, often develop as part of combined pathologies of the chest, aorta, pelvis and sacrum, heart defects, etc.
Hemangiomas are classified according to their location:
- simple – formed on the surface of the skin;
- cavernous - grows under the skin;
- combined - the process involves the superficial and deep layers of the dermis;
- mixed - not only dermal, but also nervous and muscle tissues are involved in the process.
Do red moles need to be removed?
Not only is it possible, but it is also necessary. If the hemangioma increases in size, changes shape or color, this is, of course, a direct indication to see an oncologist as soon as possible for further examination, and removal if necessary. Of course, not using artisanal or folk methods, but with the help of modern specialists. If the mole behaves quite calmly and does not change shape or color, then most likely there is no need to be afraid and you can postpone removing the moles.
Signs of hemangioma and pathogenesis
Hemangioma is a red spot, in the center of which there is a point, and from it comes a network of small vessels. Usually the neoplasm is smooth and can protrude 1-2 cm above the skin. When pressed, it turns pale, but quickly returns to its normal appearance. A characteristic symptom is temperature unevenness: upon palpation, the hemangioma is noticeably warmer than the surrounding areas of the body. It may not manifest itself clinically and may be discovered by chance during examination.
The disease occurs in phases: growth, stabilization, and optionally spontaneous regression. Complications are possible during the growth and stabilization phases of hemangioma. If a neoplasm grows near a functional organ, its function may deteriorate - for example, in the periorbital zone it can contribute to decreased vision, and on the laryngeal mucosa - obstruction of breathing.
If the hemangioma is localized near the nerve ending, as it grows, weakness and numbness of the limbs, disruption of the bladder and gastrointestinal tract are possible. Large spinal hemangiomas can cause pain and increase the risk of compression fractures. New growths are easily injured, so they can cause bleeding.
Diagnostics
In medicine, there is a general method for diagnosing skin tumors. These include an initial examination and recording of all patient complaints (history). If a malignant tumor is suspected, an MRI or radiography is prescribed. All data obtained is analyzed and conclusions are drawn, on the basis of which a preliminary diagnosis is made. The main and final point in making a diagnosis is the histological method (biopsy). It is a microscopic sampling of tissue from the body of a mole, and is done to identify the pathology of cells in the neoplasm.
Causes and risk factors
Melanoma develops due to malignancy (malignant degeneration) of melanocytes. No reliable causes of cell degeneration have been identified; every person is at risk of the disease. Factors that increase the risk of tumor development:
- hereditary predisposition;
- Phototypes I and II – fair skin, hair and eyes, pink freckles;
- multiple moles, age spots;
- excessive ultraviolet radiation - both natural and in a solarium;
- age over 50 years;
- endocrine diseases;
- previous melanoma.
The combination of any three of these factors is a reason for regular preventive visits to a dermatologist.
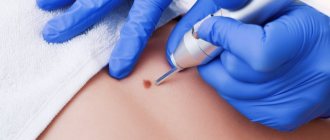
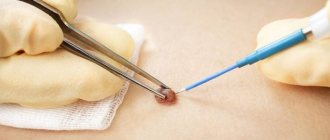
Methods for removing red moles
If the mole does not bother you in any way and is not located in high-risk areas, that is, on the arms, feet, or head and back, then it is quite possible not to remove it.
If the hemangioma bothers you, then it can only be removed by specialists, a dermatologist or oncologist. You should not take the risk of removing a nevus from a cosmetologist and exposing the incorrectly removed hemangioma to the risk of growth or the risk of infection.
There are several common procedures for removing them.
- Electrocautery. The nevus is burned with an electric current delivered using a small instrument. The grounding block will be placed somewhere so that the rest of the body is not exposed to electricity.
- Cryosurgery. The mole is frozen using liquid nitrogen. It is destroyed by extreme cold. Liquid nitrogen is sprayed for 10 seconds, the problem is solved in one session. This method is quick and relatively simple. The wound also does not require special care.
- Laser surgery. This procedure uses a concentrated yellow laser beam that emits enough heat to destroy the nevus from the inside. This method is quick and is used on an outpatient basis, meaning it does not require subsequent hospitalization. Depending on how many moles will be removed, one to three procedures may be required. There may be small scars that will disappear within 10 days.
- Surgical method. This is the process of removing a nevus from the upper part of the skin by cutting the lesion and then applying sutures. It is not a frequently used method, and after such an intervention there are scars.
In any case, if you have concerns and questions about why red moles appear, you need to see a doctor, if only to reassure yourself with good tests. Because unexplained questions create stress, which in turn contributes to a decrease in immunity. Be healthy.
How are hemangiomas treated?
The main method of treatment is surgical. In addition to cosmetic reasons, there are medical indications for this:
- rapid growth and threat of malignancy of the tumor;
- disruption of the normal functioning of organs - for example, if there is a tumor on the eyelid or tongue;
- impaired blood circulation – if the tumor is on a large vessel;
- infection and bleeding – for example, when on the genitals.
The priority is gentle, minimally invasive methods for removing hemangioma or vascular surgery methods to reduce blood flow in it. The excised tissue is sent for histological analysis.
If the neoplasm is small, it is possible to use electrocoagulation, radio wave or laser surgery, or cryodestruction with liquid nitrogen. For some forms of hemangiomas, sclerotherapy is effective - “gluing” damaged capillaries by injecting special solutions Source: Hemangiomas and vascular malformations. Modern theories and therapeutic tactics. Goncharova Y.A.: Child’s health, 2013.
For slow-growing tumors with a low risk of malignancy, conservative drug therapy with drugs from the group of beta-adrenergic receptor blockers is possible Source: Wong A., Hardy K., Kitajewsky A. Propranolol causes functional changes in hemangioma stem cells and hemangioma endothelial cells // Abstract book. ISSVA the 19th International Workshop on Vascular Anomalies. — 2012. – p. 245.. In some cases (if the tumor does not grow, does not bother, or there is a tendency towards its reverse development), they resort to wait-and-see tactics.
To ensure the effectiveness of treatment, after its completion, a control study is prescribed - ultrasound, tomography or dermatoscopy. To consult with a specialized specialist in St. Petersburg, fill out the online form.
Sources:
- What a pediatrician needs to know about infantile hemangiomas. Zakharova I.N., Kotlukova N.P., Roginsky V.V., Sokolov Yu.Yu., Zaitseva O.V., Maykova I.D., Idrisova G.R., Pshenichnikov I.I.: Medical Council , 2016
- Infantile hemangioma: classification, clinical picture and methods of correction. Sheptiy O.V., Kruglova L.S.: Russian Journal of Skin and Venereal Diseases, 2016.
- Hemangiomas and vascular malformations. Modern theories and therapeutic tactics. Goncharova Y.A.: Child’s health, 2013.
- Sires V. Systemic corticosteroid use in orbital lymphangioma /V. Sires, C. Goins, R. Anderson // Ophthal. Plast.Reconstr.Surg. — 2001. Mar. - Vol. 17(2). — P. 85 — 90.
- Wong A., Hardy K., Kitajewsky A. Propranolol causes functional changes in hemangioma stem cells and hemangioma endothelial cells // Abstract book. ISSVA the 19th International Workshop on Vascular Anomalies. — 2012. – p. 245.
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.