Transformation into a malignant tumor
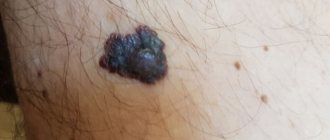
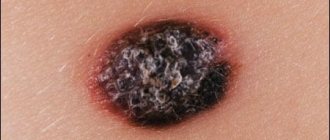
Under certain conditions, moles can degenerate into malignant formations - melanoma. Such factors include ultraviolet radiation, trauma to the mole, and genetic characteristics. During degeneration, the appearance of the mole changes - it increases in size, becomes ugly, multi-colored. The condition of the formation can be assessed using dermatoscopy and visual examination by a dermatovenerologist or oncologist.
You should constantly monitor moles and see a dermatologist at least once a year. This is especially true for those whose relatives had malignant skin diseases.
Types and characteristics of moles
A nevus (this is the scientific name of a mole) is a benign formation consisting of an accumulation of cells with excess melanin (so-called melanocytes) in different layers of the skin. Nevi can be congenital or acquired.
Let's look at the different types of nevi. In medicine, it is customary to distinguish epidermal, border and intradermal nevi. They all differ in localization in the thickness of the skin - the epidermal one is located in the uppermost layer, and the intradermal one, accordingly, in the deepest. Such moles are a cluster of melanocytes of small size (usually from a few millimeters to a centimeter), round in shape, smooth, with clear boundaries.
The following classification of moles has also become widespread:
- Complex nevus (also mixed) . This mole is located simultaneously in several layers of the skin. Otherwise, it is no more different from the above-mentioned formations.
- Pink and blue (blue) nevi . The first can most often be observed in blondes with very fair skin, since the melanin pigment in this case has a pinkish or reddish tint. The second type of nevus also differs only in the shade of the skin pigment, which in this version will be blue-violet.
- Halonevus (Setton's nevus) is a mole with a white halo around it.
- Papillomatous nevus . This mole is similar to a papilloma, which is why it got its name. It is characterized by a bumpy surface protruding above the skin level and may have a stalk (the so-called “hanging” mole).
- Congenital nevi . This is a large group that includes dysplastic nevus (Clark's nevus or atypical nevus), giant congenital nevus, nevus of Ita, nevus of Ota, vascular nevus, Jadassohn's nevus, etc. What they all have in common is that they develop in utero and the child is born with a spot on the skin. These spots can be of absolutely any shape, size, they can have a surface with a very different structure: from smooth to resembling brain convolutions and overgrown with hair, they can be localized on any part of the body, including the skin of the eyelids and genitals.
The last group, due to its size, can be classified as birthmarks rather than moles, however, if these nevi are small in size, then it will be difficult for a non-specialist to distinguish between these formations.
Other types of skin lesions
- Another formation is atheroma , which appears at the site of blockage of the sebaceous gland, most often on the scalp, neck, and back. The formation is painless and not dangerous; when pressed with a finger, it slips away.
- Hemangioma is a tumor that occurs on blood vessels. If the hemangioma has grown on capillaries (vessels located in the superficial layers of the skin), then it looks like a reddish spot. Benign.
- Lipoma or wen - grows in the fat layer. When it reaches a large size and causes discomfort, the wen is removed. However, in some cases, a lipoma can degenerate into a cancerous tumor.
- Papillomas or warts are formations of viral origin, often very similar to moles. Occurs with reduced immunity. They come in different colors and shapes. They can appear unnoticed and disappear without a trace. But sometimes they degenerate into cancerous formations.
There are many other types of neoplasms that cannot be distinguished from each other, much less understand their nature and danger to health. Without tormenting yourself with doubts, it is better to trust your doctor.
What is a mole?
Despite the fact that moles are something commonplace for us, not everything is currently known about moles. We know that moles are made up of nevus cells, which are very similar to ordinary melanocytes in that they also produce brown pigment. Nevus cells, just like melanocytes, can saturate the surrounding skin cells with pigment, i.e. make them brown.
Unfortunately, it is also known that nevus cells often become precursors to melanoma, one of the most malignant tumors. However, let’s not exaggerate out of the blue; on the Internet this is already done by everyone who is not too lazy.
What changes in education are alarming?
The following symptoms should not be ignored:
- The mole has increased to 6 or more millimeters in diameter.
- The color of education has changed. Light or dark spots appeared on its surface.
- The texture, texture, and density of the nevus have changed.
- The edges of the mole have become uneven.
- Both during palpation and at rest, the mole hurts and itches. The skin around the formation is red and swollen.
These changes are unfavorable signs. It is recommended that you seek professional advice immediately.
Surveillance for safety
For those who have many moles, we can advise, in addition to the rules of sun protection, constant monitoring.
“Only control of moles. If we are talking about hard-to-reach places, you need to ask help from loved ones - husband, wife, children, parents, friends. They should help fix moles in places where you yourself cannot. The optimal solution is photographic recording. If any mole bothers you, it must be recorded using a photo at the same time, under the same lighting, using the same camera. And it would be good to take additional centimeter measurements to better monitor the condition of the mole,” says the specialist.
Symptoms of degeneration
Doctors have identified the main signs that may indicate malignant degeneration of moles. These include:
- Rapid increase in size. One of the alarming symptoms is asymmetrical growth, which leads to a change in the shape of the nevus.
- Change in color, namely rapid and uneven darkening of the mole.
- The appearance of pain, burning at the site of localization of the formation.
- The appearance of ulcerations and cracks on the surface of the mole.
- Changes in surrounding tissues in the form of a swollen reddish corolla.
If you detect at least one of these signs, you should immediately consult a doctor. Within a short time, an ordinary mole can degenerate into a malignant skin tumor - melanoma. This tumor metastasizes quickly and has high mortality rates.
The location of a mole on areas of the skin that are constantly exposed to ultraviolet radiation (face, hands) is also a reason to consult a doctor. Intense exposure to sunlight is one of the main triggers for malignant degeneration.
How is the diagnosis done?
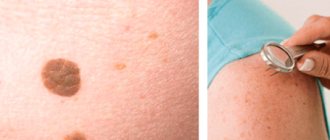
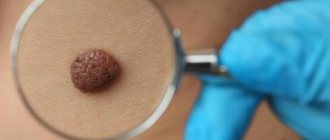
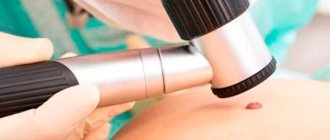
The most accurate method for diagnosing moles is dermatoscopy. The digital device dermatoscope allows you to “enlighten” the formation and enlarge its image. It becomes possible to study the texture and nature of skin pathology. Diagnosis is painless, safe and does not take much time.
Interesting: After dermatoscopy, all examined formations are recorded. At a subsequent visit to the doctor, you can monitor changes in nevi, their size, and shape.
During the examination, the dermatologist decides on the need for histological analysis. Most often, there are no contraindications for mole removal. It remains for the doctor to choose the optimal method.
Protection plan
If there are a lot of moles on the body, the expert says, and they appear again and again, you just need to observe. And, of course, spend less time in the open sun. “Be sure not to sunbathe in direct sunlight; you must use protective equipment with a filter of at least 50. Especially if we are talking about an insolation zone that is unusual for you. That is, for example, in those cases when we travel to the equator. In the zone of your usual mild insolation, you don’t have to use such products, since there is already little vitamin D supplied.
It is also necessary to strictly fulfill the standard requirements - go out into the sun only in the morning and evening hours, during the daytime solstice, that is, from 11 to 15 hours, it is better not to stay in the open sun at all,” says the dermatologist.
It is worth understanding that the sun is fraught not only with the development of moles, but also with photoaging, the specialist notes. After all, pigment spots will begin to appear from it. So you should pay special attention to yourself if there are risks of active development of moles.
Remove fear. How I said goodbye to moles Read more
Are they dangerous?
After the dermatologist explains to the patient why large moles appear and what is the reason for the specific formation, the doctor finds out the nature of the pigment spot and its type.
An increase in size and the appearance of new moles is usually observed after harmful exposure to UV rays and hormonal changes. Whether large moles are dangerous can be determined by the following factors:
- cessation of growth and loss of hairs on the surface of the spot;
- change in outline;
- the appearance of pronounced asymmetry;
- an increase in size of more than 5 mm in diameter;
- itching and burning in the area where the nevus is located;
- redness and swelling of the tissues around the spot;
- discharge;
- bleeding
For an experienced specialist, there is no problem in determining at first glance whether large moles can be removed and how dangerous they pose. But even the most expert dermatologist can evaluate a spot subjectively. Therefore, if there are more than three signs of danger, the doctor prescribes a test.
Reasons for appearance
The first stage of an education survey is to determine the source of its formation. There may be several reasons for the appearance of large moles:
- genetic predisposition;
- anomalies of intrauterine development of the fetus;
- Excessive tanning in the sun and solarium - negative effects of ultraviolet radiation;
- skin injuries;
- viruses, for example papillomavirus;
- frequent stress;
- diseases of internal organs - pancreas, liver;
- bowel dysfunction;
- exposure to radiation, toxins;
- taking certain oral contraceptives;
- after surgical interventions;
- pathologies associated with lipid metabolism.
Most often, patients complain that a large mole has grown due to hormonal changes. This can happen during pregnancy, during menopause, and during puberty.
Injury to nevi
Another factor that can trigger the onset of malignancy is trauma to the mole. Moreover, the formation can be injured either over a long period of time, for example, due to constant friction or squeezing by clothing, or as a result of a more serious external influence, for example, when a mole is cut.
If a mole is accidentally damaged, it must be thoroughly treated with a disinfectant solution. If bleeding occurs, it should be stopped using a sterile bandage or gauze. The injured formation should be examined by a doctor as soon as possible in order to determine a further course of action. The specialist may recommend removing the remaining part of the mole or undergoing routine examinations for malignancy over a period of time.
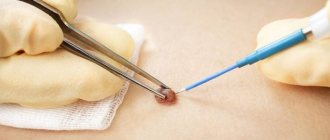
How to remove more moles?
There are several ways to get rid of large nevi:
- 1. Radio wave surgery. Using a special knife, the doctor excises the formation without affecting healthy tissue. There is no risk of bleeding, disinfection is ensured, and no scars are left. The technique is safe and painless.
- 2. Electrocoagulation. Heat treatment with electric current. There may be some slight discomfort. The healing process is fast.
- 3. Laser coagulation. Modern safe and painless technique. The equipment is equipped with cooling systems, so the patient feels only a slight tingling sensation. The formation of scars is excluded.
- 4. Cryodestruction. Exposure of nevus to liquid nitrogen at extremely low temperatures. Regeneration takes longer than with other methods.
All methods, except cryodestruction, allow you to save tissue particles for sending for histology. Surgical removal is indicated for very large moles and suspected cancer. The doctor excises the pigment spot with further sutures or tissue replacement with a deep incision.
Important features of congenital melanocytic nevi
- Small-sized UMNs are more common and may not appear until age two.
- Small and medium-sized nevi grow more slowly than the child himself and tend to darken and become hairy.
- Large and giant nevi usually occupy part of an anatomical area or all of it, for example an entire limb, neck, part of the back.
- Congenital giant melanocytic nevi transform into melanoma in 6–10% of cases.
Giant VN exceeds 20 cm in size, and such formations are sometimes compared to clothing, called “shirt” or “swimsuit” type. According to statistics, they are rare, affecting 1 in 500,000 newborns.
Giant VNs are only diagnosed at birth. Unfortunately, there is no prenatal screening to detect them, and they are not visualized on ultrasound.
The main medical problem with congenital giant melanocytic nevus is the high risk of developing melanoma, and the tumor can appear anywhere and anytime. What to do in this case? At the moment, the main method is staged excision.
If a mole grows, is it melanoma or cancer?
As we have already found out above, cell division in a mole is a normal phenomenon. Moreover, from my practice I have found out that almost all moles can increase during a person’s life. At the same time, it remains unclear - after all, cells of malignant tumors are also prone to rapid division and growth.
Unfortunately, without a microscope, we will not be able to determine by eye whether growth is associated with the degeneration of a mole. To find out this, a histological examination after removal of a mole is well suited. However, there is a less accurate, but simpler method - read on about it.