Today you rarely meet a person with perfect skin without a single tumor. According to statistics, 70% of the population is infected to varying degrees with the human papillomavirus (HPV). Any growths on the skin cause unpleasant emotions, painful sensations or simply discomfort, both psychological and physical, which interferes with leading a full life.
Cost of services in our clinic
| Appointment with a dermatologist, candidate of medical sciences | 1500 rub. |
| Consultation with a dermatologist (KMS) when removing 2 tumors | 0 rub. |
| Removal of a neoplasm (wart, mole) using the radio wave method | 500 rub. |
| Make an appointment by phone: 8-800-707-15-60 (toll-free) |
| *The clinic is licensed to remove tumors |
Warts and papillomas are the most common manifestations of the human papillomavirus. Due to their common nature, they have many similarities, but there are also many differences between them. Initially, warts and papillomas appear on the body as benign formations, but some of them, under certain conditions, can degenerate into a malignant form. This necessitates their removal not only for aesthetic reasons.
What are warts
The content of the article
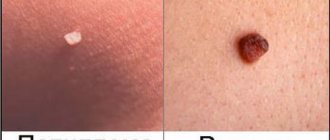
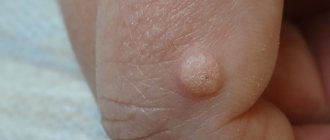
Warts are rounded elevations of the skin in the form of a papilla or nodule with clear contours and a dense structure, arising due to the active growth of the upper layers of the epithelium. They can appear in absolutely every person, at any age and on any part of the skin, from the head to the soles of the feet. The most common “targets” are exposed areas of the body that are often subject to injury: arms, elbows, knees, head. Warts can reach sizes from 1 mm to 15 mm: this directly depends on its type and location of formation. They are located on the body singly or in small groups, and their distribution depends on the functioning of the immune system. There is also a rapid increase in the number of growths when the integrity of the wart is damaged. Sometimes several warts merge, forming a large tumor with a wide base in the form of a cone or hemisphere. When they appear, the growths are flesh-colored, and over time they can acquire a brown or even black tint, sometimes gray or yellowish. Their surface can be smooth, slightly rough or pimply. Outwardly, they resemble acne or calluses, so they are quite easy to confuse. A feature of warts is the high probability of spontaneous remission, especially if they arose in childhood.
Are red moles dangerous?
In themselves, these formations are harmless and are not precancers.
If you have a lot of red moles on your body, the cause may be a serious liver or pancreas disease. Pay attention to this - this is a reason for examination.
Problems may arise in case of traumatization of hemangiomas. Even fairly small formations threaten heavy bleeding, which is not easy to stop.
Clinical case
Patient L, 26 years old, presented with a traumatized mass in the axillary region. According to her, she tore off a convex hemnagioma with the edge of a rigid corset of a wedding dress almost a few minutes before the start of the wedding ceremony. The hemangioma bled very heavily and a large blood stain appeared on her white dress. She had to wear the witness's jacket over her wedding dress. It was in such a strange outfit that the wedding took place.
What are papillomas
Papillomas are also benign formations. They come in a variety of shapes - leaf-shaped, spherical, filamentous or lobed, often resembling cauliflower in appearance. The growths have a soft, loose structure and are located on a thin stalk. Initially, their size is about 2 mm, but gradually they are able to grow up to 1-2 cm. The color of papillomas also varies from white to dark brown. The favorite location is areas of the body with thin and delicate skin, folds and mucous membranes, i.e. these are the neck, eyelids, nasolabial fold, armpits, area under the mammary glands, genitals, groin area, perianal fold, around the anus, in the rectum, urethra, bladder, etc. Quite rarely, papillomas can form in the oral cavity and on the vocal cords. The growth can be either single or multiple. Basically, there are 5-20 papillomas in one area. Their prevalence largely depends on the immune system and its ability to resist the virus. The main feature of this type of neoplasm is the increased threat of transition to a malignant form. This is especially true for papillomas that form on the mucous membranes of the female genital organs. If left untreated, they cause cancer.
Papillomas on the neck
We are accustomed to calling small nodules with a thin stalk on the neck warts, although in fact they are filiform papillomas. These formations are not life-threatening, but many people want to remove them.
Before removing a papilloma on the neck, you need to make sure that it is not a mole or other skin formation. Its characteristic features:
- The shape of a grain attached to the skin by thin threads, up to 2 mm long.
- Shade - from yellow to brown.
- They can be single (lower on the neck) or grouped up to ten pieces.
- In addition to the neck, papillomas appear on the face, eyelids, cheeks, and around the lips.
Papillomas on the neck appear due to a specific virus that penetrates in different ways - through contact with the skin, transfer to the fingertips.
Causes of warts and papillomas
The appearance of warts and papillomas is a consequence of the human papillomavirus (HPV) entering the body. And the well-known theory that warts appear from touching a frog is just a misconception. You can become infected with papillomavirus in several ways:
- sexually;
- during childbirth;
- contact and household.
- Speaking in more detail about the household contact method, we can highlight the following ways of infection entering the body:
- direct skin contact (handshake, kiss);
- through objects of common use (in the gym, in transport);
- when using personal items (razor, toothbrush);
- wearing someone else's shoes, walking barefoot in public places (baths, swimming pools, etc.);
- when carrying out cosmetic procedures with instruments that have not been disinfected (epilation, manicure).
The virus penetrates through microcracks, cuts or abrasions on the skin. After penetration, the pathogen goes into standby mode and is activated under certain conditions. That is why there is no exact definition of the incubation period of HPV. In people with a strong immune system, neoplasms do not form; the pathogen is destroyed and eliminated from the body within a year. The following factors can “activate” the virus and thereby cause the growth of warts and papillomas:
- infectious diseases that weaken the immune system;
- stressful situations and nervous overstrain;
- pregnancy;
- obesity;
- decreased immunity;
- undergoing chemotherapy;
- avitaminosis;
- diabetes;
- hormonal imbalance;
- heavy and prolonged physical activity;
- lack of hygiene;
- bad habits;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- long-term use of antibiotics that suppress the immune system.
Older people and children are most likely to become infected with the virus. This is due to the condition of the skin in this age category. Genetic predisposition also influences HPV susceptibility to some extent.
HPV prevention
The most effective method of preventing infections and complications caused by the human papillomavirus is vaccination. It is carried out before the onset of full puberty and before the start of sexual relations. The optimal age is from 9 to 11 years.
Other preventive measures are:
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle;
- balanced healthy diet;
- timely treatment of abrasions, scratches and other skin damage;
- informing children and adolescents about the dangers of smoking, since tobacco use increases the risk of oncogenic mutations of the virus;
- regular preventive examinations.
It is very important to monitor the child’s health and support immunity in accessible ways. Active physical activity, hardening, and outdoor games are encouraged, allowing the formation of an adequate immune response to environmental factors. It is advisable to abandon home self-medication and uncontrolled use of medications, since incorrect actions can reduce the natural defenses of the child’s body and lead to the activation of HPV.
Differences and similarities between warts and papillomas
It is often difficult to distinguish a wart from a papilloma, since they are very similar to each other. In some cases, it is difficult even for a dermatologist to do this during a visual examination. Warts and papillomas have the following common features:
- formation on the surface of the epithelium;
- the nature of the neoplasms is viral: they develop due to the entry of the human papillomavirus into the body;
- the initial character is benign;
- under certain conditions they can become malignant;
- may cause itching, irritation, swelling of nearby tissues;
- have blood vessels, so they bleed when injured;
- education and development are affected by the state of the immune system;
- After removal there is a risk of relapse.
Treatment results
The photo below shows the results of removal of neck papillomas using radio wave surgery
Rarely occur again. Reappearance of papillomas is possible with high virus activity in the body. In this situation, additional treatment with immunomodulators or consultation with an immunologist may be required.
Despite many similarities, neoplasms have an impressive list of differences
| Index | Warts | Papillomas |
| Form | Mostly round with clear contours | Mostly leaf-shaped or lobed with fuzzy, ragged contours, looks like cauliflower |
| Color | From flesh to light brown, sometimes pink, can even acquire a black tint due to the accumulation of dirt | White to dark brown |
| Localization | On open areas of the body: arms, legs, scalp, etc. | In folds and mucous membranes: armpits, genitals, neck, face, etc. |
| Structure | Dense | Soft |
| Fastening | Wide base | "Leg" |
| Size | Capable of shrinking and growing | Only increasing |
| Peculiarity | Capable of self-destruction without treatment | Do not disappear on their own, must be removed |
| Treatment | Removal, possibly drug treatment | Delete only |
| Tendency to malignancy | Almost never reborn | High probability of transition |
Papillomas on the eye
Papillomas can form on the upper and lower eyelids due to the penetration of the papillomavirus. For a long time, the disease may not manifest itself in any way, but its progression can even lead to deterioration of vision. Pathology can take two forms:
- Keratomas are elongated tuberous growths.
- Fibropapillomas are flat formations of various shapes.
Removal of eyelid papilloma is not carried out using a laser; a more preferable option is electrocoagulation.
Types of warts
Today there are over 100 types of HPV, each of which gives rise to a certain type of warts and papillomas. The incubation period is about 2-6 months, but it largely depends on the human immune system: a strong and healthy body easily fights the occurrence and proliferation of growths. The following types of warts are distinguished:
- ordinary (simple, vulgar);
- plantar (pinuses);
- flat (juvenile);
- senile (age-related keratomas).
Ordinary (simple, vulgar) - warts in the form of small dense dry nodules with an uneven and rough surface, variable sizes and a rounded shape. They do not cause itching, pain or discomfort. Simple warts reach from 3 to 10 mm in diameter. They are usually flesh-colored, sometimes pink, yellowish, or light brown. Due to the accumulation of contaminants in the porous surface, they can turn dirty gray. The favorite localization of simple warts is the back of the hands and fingers. Sometimes they are observed on the knees and elbows, rarely on the face and feet. After some time (it’s different for everyone), the tumor increases in size, and the skin in its place begins to peel off. The progression of the pathology is manifested by the formation of a large “mother” wart with a scattering of small ones around. When removed, small ones usually self-destruct over time. Plantar warts (spikes) are warts in the form of several fused nodules with a roll of keratinized skin around them. Inside the growths, many small black dots are visible - thrombosed capillaries. Plantar warts are round in shape, rise above the skin by 1-2 mm and can reach up to 2 cm in diameter. However, 75% of the tumor is located in the deep layers of the epithelium, so their main feature is inward growth. Outwardly, these warts resemble calluses, which is why they are often confused with each other. It's important to remember that, unlike a callus, a ring of dead skin forms around a wart. Spines are localized on the feet, rarely on the palms. Usually colored yellow or dark brown. This type of wart causes significant discomfort, itching and pain, aggravated by walking, and may even bleed. In 50% of cases it self-destructs without treatment, but this may take from 8 to 18 months. As the pathology progresses, the number and size of warts will increase, which may lead to the inability to walk due to unbearable pain. Flat (juvenile) - warts in the form of small flat papules with a smooth (sometimes scaly) surface, slightly raised above the surface of the skin. Traditionally it affects people aged 10 to 25 years. They are formed in multiple clusters or singly, which is quite rare. Usually the growths are flesh-colored, sometimes white, brown, yellowish or pink. They appear on the face, neck, knees, elbows, back, legs and arms (especially on the fingers and back of the hands), sometimes on the head of the penis. As a rule, they are painless and do not cause discomfort unless they are subjected to mechanical pressure or damage. Flat warts can suddenly disappear on their own just as they appeared, especially in childhood. But sometimes they are quite difficult to treat. Senile (seborrheic keratoses) are warts in the form of dark, flat, round or oval plaques that appear in old age. They reach a diameter of 0.2-3 cm, sometimes 4-6 cm. The pathogenesis is not clear, but their appearance is definitely not associated with HPV. Senile warts can affect any part of the body except the palms, soles of the feet, and mucous membranes. As a rule, they appear in multiple clusters (about 20 foci). Initially, they appear as small light brown spots or papules with clear contours. Over time, keratoses may retain their appearance and resemble freckles, or they may harden, forming a warty surface covered with easily removable thin crusts. In most cases, senile warts take on a mushroom shape and are dark brown or black in color. They develop very slowly, over decades, never degenerating into a malignant form. Typically, seborrheic keratoses are removed for aesthetic reasons or because they become itchy and irritating. If the growths, especially large and warty ones, are injured (rubbed against clothing, touched by something), they may bleed or become inflamed.
Causes of papillomas formation and risk factors
HPV can be transmitted sexually, as well as from an infected mother to a child during childbirth. The contact and household route of transmission of the virus cannot be ruled out, i.e. by sharing towels, clothes, etc. This explains the high prevalence of HPV in the world. Self-infection is also possible. In this case, if one papilloma is injured, the virus can be transferred to healthy areas of the skin and infect them.
The main causes of HPV infection are frequent changes of sexual partners and unprotected sexual contacts.
But infection with a virus does not always lead to the formation of papillomas, condylomas, etc. The likelihood of developing papillomatosis depends on various factors:
- immunodeficiency of any origin, including taking drugs that suppress the immune system (immunosuppressants, cytostatics, etc.), the presence of HIV infection, radiation injury;
- a decrease in the body’s defenses against the background of physiological changes during pregnancy;
- early onset of sexual activity, when the immune system is not yet fully formed and strengthened;
- microtraumas of the skin and mucous membranes;
- infection with highly oncogenic strains of HPV;
- the presence of several types of HPV in the body at the same time;
- the presence of other sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), in particular gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, herpes, cytomegalovirus infection, Epstein-Barr virus, hepatitis B and C, etc.;
- hormonal imbalances;
- exhaustion of the body, hypovitaminosis, chronic fatigue and severe stress;
- multiple births and abortions;
- the presence of severe chronic diseases, in particular diabetes;
- maintaining an unhealthy lifestyle, having bad habits;
- poor living conditions.
Older and overweight people are more prone to the formation of papillomas. At the same time, their tumors often form in the folds of the skin, which contributes to their injury and inflammation.
Types of papillomas
- The following types of papillomas are distinguished:
- filamentous (acrochords);
- anogenital.
Anogenital (genital condylomas) - papillomas in the form of flesh-colored or pale pink growths of an acute shape, prone to fusion. When rubbed, they become crimson and begin to bleed. Such growths reach 1-1.5 cm and in appearance they resemble cauliflower or cockscomb due to their lobed structure. They are usually transmitted sexually and have a specific localization: on the genitals, in the perineum, on the walls of the vagina, on the foreskin, scrotum and around the anus. Although with less frequency, even in the absence of anal sexual intercourse, they can even grow in the anus and urethra, causing bleeding and discomfort during bowel movements. If the virus enters the body through oral sex, then warts appear on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, in the pharynx, on the vocal cords or trachea. Sometimes they can form in the armpits, under the mammary glands, and in children - in the nasolabial folds. Anogenital papillomas are quite dangerous for humans for many reasons, the main one of which is the high probability of degeneration into a malignant form. Being inside a woman's vagina, they cause itching and burning, pain in the lower abdomen, pain and discomfort during sexual intercourse, and after it - spotting. Therefore, regardless of position, shape and size, genital warts should always be removed. Filiform - neoplasms in the form of thin, long, racemose shoots. They are also called facial because they are usually localized on the face, especially the eyelids and nasolabial folds, and neck. Rarely they can occur on the legs, in the groin folds, under the mammary glands and in the armpits. Those. they appear in areas of delicate and thin skin, in folds characterized by high humidity. It mainly affects older people. The process of formation of a growth begins with the appearance of a small nodule; over time, the formation acquires an elongated oval shape or remains round on a thin stalk. Traditionally, thread-like growths are flesh-colored, which is why they often go unnoticed for a long time, but sometimes they become yellow, brown or pink. They grow about 0.5-1 cm, exceeding that is extremely rare. The risk of acrochords degenerating into a malignant form is minimal, but if they are injured, an inflammatory process may develop. This type of neoplasm does not self-destruct and is prone to spreading to other parts of the body and increasing in size and number. For most people, this causes psychological discomfort, emotional stress and decreased self-esteem. Therefore, a cosmetic defect is the main reason for removing filamentous growths.
Types of acquired red moles on the body
- Simple (capillary). Proliferation of newly formed capillaries, small venous and arterial vessels. Looks like a red spot.
- Cavernous. A spongy cavity with blood - a red or bluish nodule. Often forms under the skin.
- Branched (racellose). A plexus of tortuous dilated capillary trunks. They pulsate, noise and trembling are detected. It is rare and occurs on the extremities or face. If injured, life-threatening bleeding may occur.
How to identify hemangioma? Press on top of it and it should fade or disappear.
Why are neoplasms dangerous?
The main danger that warts and papillomas pose is the threat of degeneration into a malignant form. The degree of their danger depends on the type of papillomavirus:
- high (oncogenic) – 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 52, 58, 59, 68;
- low (non-oncogenic) – 6, 11, 26, 41, 42, 50, 61, 73, 82, etc.;
- absent – 1, 2, 3, 4, 5.
There is a high probability of malignancy if warts and papillomas are constantly injured (rubbed against clothing, touched by something, etc.). In this case, infection with harmful bacteria may occur. To prevent the degeneration of a benign tumor into a malignant one, it is necessary to regularly visit a dermatologist and not hesitate to detect suspicious symptoms. Particularly dangerous are genital warts that affect the internal genital organs of a woman, since they can cause serious diseases: pseudo-erosion of the cervix, ectopia of the columnar epithelium, and cervical cancer. In addition, their presence is manifested by a number of unpleasant symptoms: burning and itching in the vagina, unpleasant odor, pain in the lower abdomen, pain and discharge of ichor during sexual intercourse. In men, the lack of treatment for papillomas leads to decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and infertility. It can also provoke dangerous diseases: adenocarcinoma, anal cancer, diseases of the penis, oral cavity or larynx.
Many varieties are not dangerous, but ignoring the treatment of warts and papillomas will provoke an increase in their number. And the constant attack of the body by viruses will ultimately lead to a deterioration in the overall health of a person.
What is HPV
The human papillomavirus affects only humans, and its main mode of transmission is sexual. Therefore, HPV is most common among sexually active people. This explains the fact that most often infection occurs at a young age at the beginning of sexual activity and at its peak, i.e. 15-25 years. Moreover, several strains (types) of HPV can be present in the human body at the same time, provoking the appearance of different types of tumor-like formations on the skin and mucous membranes.
The disease caused by HPV is called papillomatosis.
Infection with the virus occurs when it comes into contact with the skin or mucous membranes with particles of exfoliated skin or mucous membrane of an infected person. They attach to the membranes of immature epithelial cells, from where they penetrate into the cytoplasm of the cell, and subsequently into the nucleus. It is the cell nucleus that contains DNA, which is damaged by HPV. As a result, when the affected cell divides, the consequence will be the formation of not healthy new cells, but those that already have altered genetic information, which leads to failures in the mechanism of their reproduction and differentiation. This causes the appearance of tumors on the skin and mucous membranes.
HPV infection can lead not only to the formation of papillomas, but also warts, as well as flat and genital warts. However, it can also be asymptomatic. In this case, the patient will not show external signs of human papillomavirus infection, but he will act as a carrier and can infect others through unprotected sexual intercourse or at home.
Thus, HPV infection does not always lead to the formation of papillomas. This depends on the strength of the person’s immunity, but more often the first small papillomas appear 1-6 months after infection.
The human papillomavirus is intracellular. Therefore, with sufficient strength of the immune system, the body successfully suppresses its activity and does not allow it to provoke cell proliferation. But when the immune system is weakened as a result of certain factors, the body’s defenses fall, the virus becomes more active, which leads to the formation of papillomas.
All strains or types of HPV can be divided into 4 groups:
- non-oncogenic – strains 1-5, 63;
- low oncogenic risk – strains 6, 11, 40, 42-44, 54, 61, 70, 72, 81;
- medium oncogenic risk – strains 26, 31, 33, 35, 51-53, 58, 66;
- high oncogenic risk - strains 16, 18, 39, 45, 56, 59, 68, 73, 82 (types 16 and 18 are considered the most dangerous).
HPV strains of high oncogenic risk have special genes in their DNA that are responsible for the synthesis of specific oncoproteins (E6 and E7). Therefore, when it is integrated into the DNA of a human cell, its anticancer protection decreases. Oncoproteins destabilize the genome of skin cells, provoke their active reproduction and suppress the ability to differentiate. Therefore, this is fraught with a high risk of developing cancer when infected with strains of the human papillomavirus of high oncogenic risk.
The magnitude of the danger that papillomas pose directly depends on the type of HPV. Infection with strains with a high oncogenic risk is dangerous due to the development of:
- cervical cancer;
- malignant tumors of the anus, vulva, penis;
- oropharyngeal cancer, etc.
70% of cases of cervical cancer are caused by infection with types 16 and 18 of HPV.
But even when infected with strains of low oncogenic risk and the formation of papillomas, they should be treated carefully. Convex neoplasms are often injured by items of clothing, bleed and tend to become inflamed. At the same time, perhaps the greatest discomfort is caused by formations on the genital organs, which cause severe discomfort and complicate the conduct of an intimate life. In such cases, a secondary infection may occur, which can cause the development of purulent-septic complications. In addition, papillomas can form on the mucous membranes of almost any internal organ, which leads to disruption of their functioning. Thus, papillomatosis of the upper respiratory tract often occurs, which causes difficulty breathing.
Diagnostics
It is extremely important to correctly determine the type of tumor, taking into account oncogenicity and external similarity. Initially, the doctor conducts a clinical examination of the growth, if located on the genital organs - gynecological in women, proctological and urological in men. This is not enough to make an accurate diagnosis. To establish a reliable clinical picture, it is recommended to conduct research at the cellular level using special diagnostic methods, namely:
- cytological examination of cell morphology - to identify DNA mutations;
- colposcopy - examination of the vulva, vagina and cervix using a special microscope - colposcope;
- biopsy - sampling of cells and tissues for the purpose of diagnosing the pathogen;
- histology - a type of biopsy - to determine a precancerous condition;
- polymerase chain reaction (PCR) techniques - to identify all types of virus;
- Digene test. It is the most reliable and informative diagnostic method: it accurately determines the presence and type of HPV, the level of oncogenicity, and the degree of concentration of the pathogen in the body.
Most often, the diagnosis is made based on the results of using several methods, since individually each of them is erroneous to a certain extent.
Doctors to contact regarding this issue
Denezhkina Natalya Nikolaevna
Reshanova Lyudmila Mikhailovna
Varfolomeeva Oksana Igorevna
Chaplitsky Evgeniy Aleksandrovich, urologist-andrologist, specialist
Folk remedies for removing papillomas
There are several options for how to remove papillomas at home:
- Cauterize them with celandine juice.
- Apply tea tree oil to the formations every day.
- Make compresses with aloe vera gel. The substance is applied to gauze, which is then applied to the papilloma. Such compresses need to be changed every three hours.
- Constantly wipe the papilloma with a banana peel.
You can use folk remedies only if we are dealing with ordinary papilloma. If it bleeds, causes discomfort or other abnormalities, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Nowadays, there are many methods to remove papilloma. But this does not solve the problem of impaired immune system and metabolism. It is necessary to undergo a full examination to determine the causes of growths and undergo full therapy.
Methods for removing tumors
Treatment of warts and papillomas should only be performed under the guidance of a qualified specialist. There should be no self-medication, since the pathology will not only not be eliminated, but will also significantly worsen, and serious complications may arise. Under no circumstances should you resort to your grandmother’s methods of tying the growth with thread or sealing it with tape in order to deprive it of blood flow. This can only injure the neoplasm, which will inevitably lead to the appearance of new growths and increase the risk of malignancy. Treatment of warts can be carried out medicinally using the following drugs:
- Viferon;
- Salicylic and Oxolinic ointments;
- Clareol;
- Antipapillomas;
- Cryopharma;
- Panavir;
- Isoprinosine.
The main goal of therapy is to increase the patient’s immunity, so the doctor may prescribe Echinacea, Immunal, Eleutherococcus and Aloe extract, Ribomunil, Lykopid, Imudon, Anaferon, Actovegin, FiBSA, multivitamins and others.
However, the high infectivity and autoacculation of warts are arguments in favor of their removal. Papillomas can only be removed. Today, the most common methods for removing warts and papillomas are:
- cryodestruction - freezing with liquid nitrogen, after which after a while the growth disappears. It is characterized by the absence of pain and a small number of complications. Practically ineffective in the fight against genital warts;
- removal with a radio knife - cutting off not only the growth itself, but also the epithelium underneath it. The device does not come into contact with the tumor, but acts on it from a distance. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia and lasts no more than 30 minutes;
- laser removal - excision of the growth with a laser beam. During the procedure, healthy tissue is not affected, the blood vessels are sealed, which eliminates bleeding, inflammation and scarring. Removal is painless and quick;
- electrocoagulation – removal of tumors using alternating current. Rare relapses occur after this procedure;
- surgical method - indicated in the case of large and deep tumors. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. It has significant disadvantages: it causes relapses, leaves scars and scars.
Removal with a radio knife is one of the most popular procedures. It involves cutting off the growth using high-frequency radio waves. The procedure has many advantages:
- does not require special training;
- carried out quickly and painlessly;
- guarantees the absence of side effects in the future if all doctor’s recommendations are followed (relapses, scars, etc.);
- is particularly accurate and efficient;
- does not damage healthy tissue;
- bloodless and safe removal: the radio knife makes a cut, cauterizes blood vessels and disinfects;
- fast healing;
- affordable cost of the procedure.
As a rule, medical procedures are complemented by the use of measures to strengthen the immune system and destroy the human papilloma virus.
Treatment of HPV in children
Unfortunately, there are no effective medications for the treatment of papillomavirus in children, as well as in adults.
In most cases, the body copes on its own, and action is only necessary in situations where there is a risk of oncological processes or tumors interfere with the child’s daily life. What do they do if children develop papillomas?
- Do not panic. In the vast majority of cases, warts and other growths go away on their own within 2–3 years. The human papillomavirus is not only easily transmitted, but also quickly “leaves” the child’s body without any consequences or external help.
- Do not try to remove the growths at home, do not tear off or cut off under any circumstances. This is fraught with infection and the extensive appearance of new rashes.
- Contact a dermatologist if any suspicious elements appear on your child’s skin. During the consultation, the doctor will examine and give recommendations, and, if necessary, prescribe removal.
Medical care for manifestations of HPV is limited to the removal of formations that affect the quality of life or are located in places where they are often injured and cause discomfort (on the eyelid, in the genital area, in the larynx).
An extraordinary inspection is needed if:
- the color of the papilloma changes;
- the wart begins to grow or change shape;
- blood or other fluid is released from the formation;
- papilloma is subject to constant friction due to clothing;
- the rashes are on the face or mucous membranes.
It is advisable not to delay a visit to a dermatologist if the formation itches, hurts, causes other physical discomfort, or has been injured. In other cases, it is recommended to observe the “behavior” of the papilloma virus and control the elements on the child’s body.
Options for removing papillomas
There are 5 modern and proven methods, each of which has its own limitations, features and advantages.
- Electrocoagulation. The method is based on the influence of high-frequency electric current. It literally “burns out” the neoplasm, leaving in its place only a dry crust, which eventually falls off on its own.
- Radio wave surgery. This method allows you to remove warts and other elements without contact with the skin, which eliminates the risk of thermal damage to tissue.
- Laser therapy. It involves treating the affected area with light waves of a certain length.
- Cryodestruction. It involves “freezing” new growths with liquid nitrogen.
- Surgical excision. It is performed under local anesthesia using a scalpel.
It is strictly not recommended in childhood to resort to traditional methods of removing warts and to use medications from the pharmacy on your own without the supervision of a doctor. After removal of papillomas, children should not:
- tear off the crust;
- sunbathe;
- visit the baths;
- cover the treatment area with a plaster;
- scratch and rub the removal site.
You should not use creams and ointments without a dermatologist's prescription. In the first 1–4 days, it is advisable to refrain from walking in direct sunlight, swimming in public bodies of water and activities that can injure the treated area of skin.
Variety of papillomas: 7 main types
Scientists know more than 100 types of HPV, but the most common are 10 types of papillomas:
- Plantar papillomas
. Causes papilloma on the leg - papillomavirus types 1, 2, 4. Plantar papillomas look like growths on the soles of the feet. Plantar warts can be single or multiple. Over time, it becomes painful for a person affected by the disease to walk. Plantar papilloma is often confused with a callus and is not sought medical attention, while the infection affects new areas of the skin. - Vulgar papillomas
. These are oval, keratinized lumps with a yellowish tint, usually appearing on the hands of adults. In children, such tumors can be found on the knees. - Flat papillomas
. The result of activation of HPV types 3, 10. The growths look like flat, smooth bumps. - Lewandowski-Lutz papillomas . The second name is epidermodysplasia verruciformis. The infection results in the formation of many mottled, multi-colored warts on the arms and legs.
- Filiform papillomas. Formed in older people. Warts look like yellowish bumps. Placed on the eyelids, groins, armpits, and neck. Threaded papilloma injured by clothing or as a result of scratching requires urgent treatment, otherwise inflammation and complications cannot be avoided.
- Juvenile papillomas . Associated with infection with papillomavirus types 6, 11. Formed in the larynx. As a result, breathing becomes difficult and speech deteriorates. The virus spreads during childbirth, transmitted to the newborn from the mother.
- Genital warts . The occurrence of genital warts is the main manifestation of infection, the source of which was the human papillomavirus. Visually, genital warts look like ordinary warts, can be small in size (up to a centimeter), have a flesh-colored or pinkish color, a slightly bumpy or completely smooth surface. The most common place for the formation of genital warts is the external genitalia. In men, these formations appear on the scrotum and penis. In women - on the labia majora and minora, on the cervix, near the clitoris, in the vagina. If condylomas are irritated, itching and bleeding may occur during sexual intercourse. Such papillomas transform into cancerous tumors.